多模态融合的高分遥感图像语义分割方法
多模态融合的高分遥感图像语义分割方法(python)
论文地址:http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-ZNZK202004012.htm
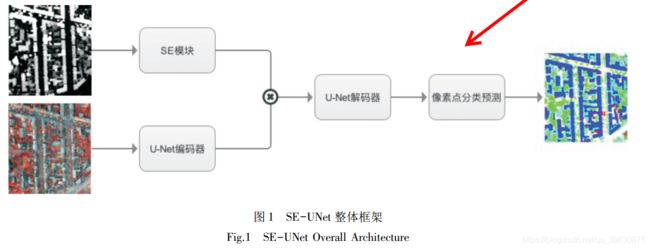
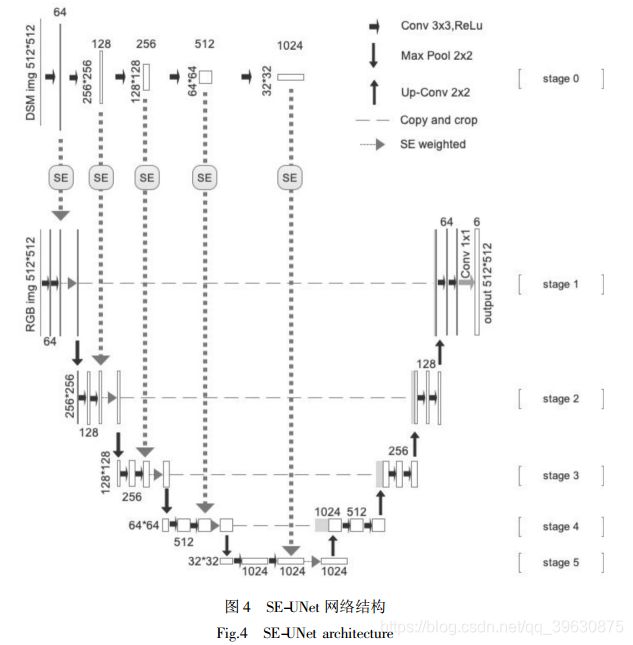
1、SE-UNet 网络模型
2、SE-UNet的具体设计方案
3、SE-UNet的pytorch复现
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.utils.model_zoo as model_zoo
from torch.nn import functional as F
import torch
class SEBlock(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,ch_in):
super(SEBlock, self).__init__()
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=False)
self.global_pool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d((1, 1)) # N * 32 * 1 * 1
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(in_features = int(ch_in), out_features = int(ch_in//2))
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(in_features = int(ch_in//2), out_features = int(ch_in))
self.sigmoid = nn.Sigmoid()
def forward(self, x):
# sequeeze
out = self.global_pool(x)
out = out.view(out.size(0), -1)
# Excitation
out = self.fc1(out)
out = self.relu(out)
out = self.fc2(out)
out = self.sigmoid(out)
out = out.view(out.size(0), out.size(1), 1, 1)
# Scale
# out = out * x
# out += x
# out = self.relu(out)
return out
class DoubleConv(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_ch, out_ch):
super(DoubleConv, self).__init__()
self.conv = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_ch, out_ch, 3, padding=1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(out_ch), #添加了BN层
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(out_ch, out_ch, 3, padding=1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(out_ch),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
)
def forward(self, input):
return self.conv(input)
class Unet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_ch, out_ch):
super(Unet, self).__init__()
self.pool = nn.MaxPool2d(2)
self.conv1 = DoubleConv(in_ch, 64)
self.pool1 = nn.MaxPool2d(2)
self.conv2 = DoubleConv(64, 128)
self.pool2 = nn.MaxPool2d(2)
self.conv3 = DoubleConv(128, 256)
self.pool3 = nn.MaxPool2d(2)
self.conv4 = DoubleConv(256, 512)
self.pool4 = nn.MaxPool2d(2)
self.conv5 = DoubleConv(512, 1024)
# 逆卷积,也可以使用上采样(保证k=stride,stride即上采样倍数)
self.up6 = nn.ConvTranspose2d(1024, 512, 2, stride=2)
self.conv6 = DoubleConv(1024, 512)
self.up7 = nn.ConvTranspose2d(512, 256, 2, stride=2)
self.conv7 = DoubleConv(512, 256)
self.up8 = nn.ConvTranspose2d(256, 128, 2, stride=2)
self.conv8 = DoubleConv(256, 128)
self.up9 = nn.ConvTranspose2d(128, 64, 2, stride=2)
self.conv9 = DoubleConv(128, 64)
self.conv10 = nn.Conv2d(64, out_ch, 1)
self.conv1_dilation = nn.Conv2d(2048, 256, 1, stride=1, padding=0, bias=False, dilation=1) # dilation就是空洞率,即间隔
self.conv2_dilation = nn.Conv2d(2048, 256, 2, stride=1, padding=2, bias=False, dilation=2) # dilation就是空洞率,即间隔
self.conv4_dilation = nn.Conv2d(2048, 256, 4, stride=1, padding=4, bias=False, dilation=4) # dilation就是空洞率,即间隔
self.global_pool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d((1, 1))
self.upsample = nn.Upsample(scale_factor=7, mode='bicubic', align_corners=True)
self.conv_c = nn.Conv2d(2816, 1024, 1, stride=1, padding=0, bias=False, dilation=1) # dilation就是空洞率,即间隔
self.upsample1 = nn.Upsample(scale_factor=2, mode='bicubic', align_corners=True)
self.R1 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(1, 64, 3, 1, 1, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(64),
nn.ReLU(inplace=False)
) # N * 16 * 16 * 16
self.RP2 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(64, 128, 3, 1, 1, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(128),
nn.ReLU(inplace=False),
nn.MaxPool2d(2, 2),
nn.ReLU(inplace=False)
) # N * 16 * 16 * 16
self.RP3 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(128, 256, 3, 1, 1, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(256),
nn.ReLU(inplace=False),
nn.MaxPool2d(2, 2),
nn.ReLU(inplace=False)
)
self.RP4 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(256, 512, 3, 1, 1, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(512),
nn.ReLU(inplace=False),
nn.MaxPool2d(2, 2),
nn.ReLU(inplace=False)
)
self.RP5 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(512, 1024, 3, 1, 1, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(1024),
nn.ReLU(inplace=False),
nn.MaxPool2d(2, 2),
nn.ReLU(inplace=False)
)
self.SE1 = SEBlock(64)
self.SE2 = SEBlock(128)
self.SE3 = SEBlock(256)
self.SE4 = SEBlock(512)
self.SE5 = SEBlock(1024)
def forward(self, DSM, RGB):
c1_DSM = self.R1(DSM) # [2, 64, 512, 512]
c1_SE_DSM = self.SE1(c1_DSM) # [2, 64, 1, 1]
c1_RGB = self.conv1(RGB) # [2, 64, 512, 512]
c1_RGB = c1_SE_DSM * c1_RGB # [2, 64, 512, 512]
p1_RGB = self.pool1(c1_RGB) # [2, 64, 256, 256]
c2_DSM = self.RP2(c1_DSM) # [2, 128, 256, 256]
c2_SE_DSM = self.SE2(c2_DSM) # [2, 128, 1, 1]
c2_RGB = self.conv2(p1_RGB) # [2, 128, 256, 256]
c2_RGB = c2_SE_DSM * c2_RGB # [2, 128, 256, 256]
p2_RGB = self.pool2(c2_RGB) # [2, 128, 128, 128]
c3_DSM = self.RP3(c2_DSM) # [2, 256, 128, 128]
c3_SE_DSM = self.SE3(c3_DSM) # [2, 256, 1, 1]
c3_RGB = self.conv3(p2_RGB) # [2, 256, 128, 128]
c3_RGB = c3_SE_DSM * c3_RGB # [2, 256, 128, 128]
p3_RGB = self.pool3(c3_RGB) # [2, 256, 64, 64]
c4_DSM = self.RP4(c3_DSM) # [2, 512, 64, 64]
c4_SE_DSM = self.SE4(c4_DSM) # [2, 512, 1, 1]
c4_RGB = self.conv4(p3_RGB) # [2, 512, 64, 64]
c4_RGB = c4_SE_DSM * c4_RGB # [2, 512, 64, 64]
p4_RGB = self.pool4(c4_RGB) # [2, 512, 32, 32]
c5_DSM = self.RP5(c4_DSM) # [2, 1024, 32, 32]
c5_SE_DSM = self.SE5(c5_DSM) # [2, 1024, 1, 1]
c5_RGB = self.conv5(p4_RGB) # [2, 1024, 32, 32]
c5_RGB = c5_SE_DSM * c5_RGB # [2, 1024, 32, 32]
up_6 = self.up6(c5_RGB) # [2, 512, 64, 64]
merge6 = torch.cat([up_6, c4_RGB], dim=1) # [2, 1024, 64, 64]
c6 = self.conv6(merge6) # [2, 512, 64, 64]
up_7 = self.up7(c6) # [2, 256, 128, 128]
merge7 = torch.cat([up_7, c3_RGB], dim=1) # [2, 512, 128, 128]
c7 = self.conv7(merge7) # [2, 256, 128, 128]
up_8 = self.up8(c7) # [2, 128, 256, 256]
merge8 = torch.cat([up_8, c2_RGB], dim=1) # [2, 256, 256, 256]
c8 = self.conv8(merge8) # [2, 128, 256, 256]
up_9 = self.up9(c8) # [2, 64, 512, 512]
merge9 = torch.cat([up_9, c1_RGB], dim=1) # [2, 128, 512, 512]
c9 = self.conv9(merge9) # [2, 64, 512, 512]
c10 = self.conv10(c9) # [2, 3, 512, 512]
out = nn.Sigmoid()(c10) # [2, 3, 512, 512]
return out
if __name__ == "__main__":
DSM = torch.randn(2, 1, 512, 512)
RGB = torch.randn(2, 3, 512, 512)
UNet = Unet(3,3)
out_result = UNet(DSM,RGB)
print(out_result)
print(out_result.shape)