CGAL例程:点云数据三维重建
作者:西蒙·吉罗多
链接:CGAL 5.4 - Manual: Surface Reconstruction from Point Clouds https://doc.cgal.org/latest/Manual/tuto_reconstruction.html
https://doc.cgal.org/latest/Manual/tuto_reconstruction.html
目录
2 我应该使用哪种算法?
3 管道概览
4 读取点云数据
5 点云预处理
5.1 异常值去除
5.2 简化
5.3 平滑
5.4 正态估计和定向
6 三维重建
6.1 泊松算法
6.2 前进算法
6.3 尺度空间
7 输出和后处理
8 完整代码示例
9 完整的管道图像
1 概述
使用点云重建三维表面是计算几何处理中的一个核心主题。它是一个病态的问题:有无数个表面近似于单个点云,而点云本身并不能定义一个表面。因此,用户必须定义额外的假设和约束,并且可以通过许多不同的方式来实现重建。本教程提供了不同的CGAL 算法实现表面重建。
2 我应该使用哪种算法?
- 泊松曲面重建
- 前进曲面重建
- 尺度空间曲面重建
由于表面重建是一个病态问题,因此必须使用先验知识对其进行正则化。先验知识的不同,使用的算法也是不同的。例如,泊松总是生成封闭的形状(包络体),并且需要法线但不插入输入点(输出表面不完全通过输入点)。下表列出了输入、输出的不同属性,以帮助用户选择最适合每个问题的方法:
| 选项 | 泊松 | 前进 | 尺度空间 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 需要法线吗? | 是 | 否 | 否 |
| 处理噪音吗? | 是 | 预处理 | 是 |
| 是否处理可变的抽样? | 是 | 是 | 预处理 |
| 输入点是否正好在表面上? | 否 | 是 | 是 |
| 输出是否始终关闭? | 是 | 否 | 否 |
| 输出总是平滑的吗? | 是 | 否 | 否 |
| 输出总是多方面的吗? | 是 | 是 | 可选 |
| 输出总是可定向的吗? | 是的 | 是 | 可选 |
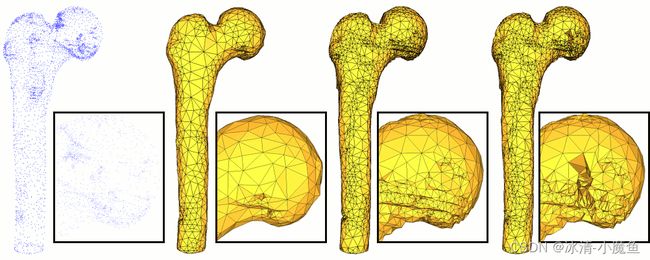
图 0.1应用于相同输入的重建方法比较(全图和特写)。从左到右:原始点云;泊松; 前进;尺度空间。
有关这些不同方法的更多信息,请参见它们各自的手册页和重建部分章节。
3 管道概览
本教程旨在更全面地了解 CGAL 为处理点云重建的可能性,下图显示了使用 CGAL 工具重建表面的步骤。
我们现在更详细地阐述其中的一些步骤。
4 读取点云数据
CGAL 中重建算法使用容器迭代器作为输入数据,并使用属性映射来访问点(以及需要时的法线)。点通常以纯文本格式(表示为“XYZ”格式)存储,其中每个点由换行符分隔,每个坐标由空格分隔。其他可用格式为“OFF”、“PLY”和“LAS”。CGAL 提供了读取这些格式的函数:
read_XYZ()read_OFF()read_PLY()read_PLY_with_properties()read_LAS()read_LAS_with_properties()
CGAL 还提供了一个专用容器CGAL::Point_set_3来处理具有附加属性(例如法线向量)的点集。在这种情况下,属性映射很容易处理,如以下部分所示。此结构使用流运算符以读取前面描述的任何格式的点集。使用这种方法会产生更短的代码,如以下示例所示:
Point_set points;
std::string fname = argc==1?CGAL::data_file_path("points_3/kitten.xyz") : argv[1];
if (argc < 2)
{
std::cerr << "Usage: " << argv[0] << " [input.xyz/off/ply/las]" << std::endl;
std::cerr <<"Running " << argv[0] << " data/kitten.xyz -1\n";
}
std::ifstream stream (fname, std::ios_base::binary);
if (!stream)
{
std::cerr << "Error: cannot read file " << fname << std::endl;
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
stream >> points;
std::cout << "Read " << points.size () << " point(s)" << std::endl;
if (points.empty())
return EXIT_FAILURE;
5 点云预处理
因为重建算法一些点云数据并不总是能满足特定要求,所以可能需要一些预处理步骤来产生最佳结果。请注意,此预处理步骤是可选的:当输入点云没有缺陷时,可以对其应用重建而无需任何预处理。
图 0.3是不同预处理算法生产的重建效果图。第一组没有使用预处理算法;第二组使用平滑预处理;第三组使用网格预处理。
5.1 异常值去除
一些采集技术会生成远离表面的点。这些点,通常称为“异常值”,与重建无关。在带有异常值的点云数据上,使用 CGAL 重建算法会产生过度失真的输出,因此、在执行重建之前,需要过滤掉这些异常值。
typename Point_set::iterator rout_it = CGAL::remove_outliers
(points,
24, // Number of neighbors considered for evaluation
points.parameters().threshold_percent (5.0)); // Percentage of points to remove
points.remove(rout_it, points.end());
std::cout << points.number_of_removed_points()
<< " point(s) are outliers." << std::endl;
// Applying point set processing algorithm to a CGAL::Point_set_3
// object does not erase the points from memory but place them in
// the garbage of the object: memory can be freeed by the user.
points.collect_garbage(); 5.2 简化
一些激光扫描仪生成具有广泛可变采样的点。通常,扫描线的采样非常密集,但两条扫描线之间的间隙要大得多,从而导致点云数据的采集密度过大。这种类型的输入点云可能会使用算法生成不完美的输出。CGAL 提供了几种简化算法。除了减少输入点云的大小并因此减少计算时间之外,其中一些可以帮助使输入更加均匀。grid_simplify_point_set()定义用户指定大小的网格,每个网格保留一个点云数据。
// Compute average spacing using neighborhood of 6 points
double spacing = CGAL::compute_average_spacing (points, 6);
// Simplify using a grid of size 2 * average spacing
typename Point_set::iterator gsim_it = CGAL::grid_simplify_point_set (points, 2. * spacing);
points.remove(gsim_it, points.end());
std::cout << points.number_of_removed_points()
<< " point(s) removed after simplification." << std::endl;
points.collect_garbage(); 5.3 平滑
尽管通过“泊松”或“尺度空间”算法重建表面,可以在内部处理噪声,但人们可能希望更严格地控制平滑步骤。例如,噪声较少的点云数据可以从一些可靠的平滑算法中受益,并通过提供相关属性(带边界的定向网格)的“前进前沿”进行重建。CGAL提供了两个函数来平滑噪声点云,使其具有良好的近似性(例如,曲率不降低):
jet_smooth_point_set()bilateral_smooth_point_set()
这些函数可以直接修改容器:
CGAL::jet_smooth_point_set(点,24); 5.4 正态估计和定向
泊松曲面重建需要具有定向法向量的点。要将算法应用于原始点云,必须首先估计法线,例如使用以下两个函数之一:
pca_estimate_normals()jet_estimate_normals()
PCA 速度更快,但在存在高曲率的情况下JET更准确。这些函数只估计法线的方向,而不是它们的方向(向量的方向可能不是局部一致的)。要正确定位法线,可以使用以下函数:
mst_orient_normals()scanline_orient_normals()
第一个使用最小生成树在越来越大的邻域中持续传播法线的方向。对于具有许多尖锐特征和遮挡的数据(例如,在机载 LIDAR 数据中很常见),第二种算法可能会产生更好的结果:它利用排列成扫描线的点云来估计视线每个点,从而相应地定向法线。
请注意,如果它们的方向不一致,它们也可以直接用于输入法线。
CGAL::jet_estimate_normals
(points, 24); // Use 24 neighbors
// Orientation of normals, returns iterator to first unoriented point
typename Point_set::iterator unoriented_points_begin =
CGAL::mst_orient_normals(points, 24); // Use 24 neighbors
points.remove (unoriented_points_begin, points.end()); 6 三维重建
6.1 泊松算法
泊松算法包括计算一个隐函数,其梯度与输入法向量场匹配:该指示函数在推断形状的内部和外部具有相反的符号(因此需要闭合形状)。因此,此方法需要法线并产生平滑的闭合曲面。如果期望表面对输入点进行插值,则不合适。相反,如果目标是用光滑的表面逼近噪声数据多的点云,它表现得很好。
CGAL::Surface_mesh output_mesh;
CGAL::poisson_surface_reconstruction_delaunay
(points.begin(), points.end(),
points.point_map(), points.normal_map(),
output_mesh, spacing); 6.2 前进算法
前进算法是一种基于 Delaunay 的方法,它对输入点的子集进行插值。它生成描述重建三角面的点索引的三元组:它使用优先级队列根据大小标准(有利于小面)和角度标准(有利于平滑)。它的主要优点是生成带边界的定向流形表面:与泊松相反,它不需要法线,也不必重建封闭形状。但是,如果点云有噪声,则需要进行预处理。
前进算法包提供了几种构造函数的方法。这是一个简单的例子:
typedef std::array Facet; // Triple of indices
std::vector facets;
// The function is called using directly the points raw iterators
CGAL::advancing_front_surface_reconstruction(points.points().begin(),
points.points().end(),
std::back_inserter(facets));
std::cout << facets.size ()
<< " facet(s) generated by reconstruction." << std::endl;
6.3 尺度空间
尺度空间算法旨在产生一个对输入点(插值)进行插值的表面,同时对噪声的有鲁棒性。更具体地说,它首先对输入点集应用几次平滑滤波器(如Jet 平滑),以产生一个尺度空间;然后,对最平滑的比例进行网格划分(例如使用前进算法 网格划分器);最后,平滑点之间产生的连通性被传播到原始的原始输入点集。如果输入点云有噪声,但用户仍希望表面准确地通过这些点,则此方法是正确的选择。
CGAL::Scale_space_surface_reconstruction_3 reconstruct
(points.points().begin(), points.points().end());
// Smooth using 4 iterations of Jet Smoothing
reconstruct.increase_scale (4, CGAL::Scale_space_reconstruction_3::Jet_smoother());
// Mesh with the Advancing Front mesher with a maximum facet length of 0.5
reconstruct.reconstruct_surface (CGAL::Scale_space_reconstruction_3::Advancing_front_mesher(0.5));
7 输出和后处理
这些方法中的每一种都会产生以不同方式存储的三角形网格。如果此输出网格受到孔或自相交等缺陷的阻碍,CGAL 会在Polygon Mesh Processing包中提供多种算法对其进行后处理(孔填充、重新划分网格等) 。我们在这里不讨论这些函数,因为有许多后处理可能性,其相关性很大程度上取决于用户对输出网格的期望。网格(无论是否经过后处理)可以很容易地以 PLY 格式保存(此处使用二进制变体):
std::ofstream f ("out_poisson.ply", std::ios_base::binary);
CGAL::IO::set_binary_mode (f);
CGAL::IO::write_PLY(f, output_mesh);
f.close ();
多边形也可以通过迭代点和面以 OFF 格式保存:
std::ofstream f ("out_sp.off");
f << "OFF" << std::endl << points.size () << " "
<< reconstruct.number_of_facets() << " 0" << std::endl;
for (Point_set::Index idx : points)
f << points.point (idx) << std::endl;
for (const auto& facet : CGAL::make_range (reconstruct.facets_begin(), reconstruct.facets_end()))
f << "3 "<< facet << std::endl;
f.close ();最后,如果多边形可以转换成多边形网格,也可以使用流算子直接保存为OFF格式:
// copy points for random access
std::vector vertices;
vertices.reserve (points.size());
std::copy (points.points().begin(), points.points().end(), std::back_inserter (vertices));
CGAL::Surface_mesh output_mesh;
CGAL::Polygon_mesh_processing::polygon_soup_to_polygon_mesh (vertices, facets, output_mesh);
std::ofstream f ("out_af.off");
f << output_mesh;
f.close (); 8 完整代码示例
本教程中使用的所有代码片段都可以组装成一个完整的算法管道(前提是使用了正确的包含文件)。我们给出了一个完整的代码示例,它实现了本教程中描述的所有步骤。用户可以在运行时使用第二个参数选择重建方法。
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
// types
typedef CGAL::Exact_predicates_inexact_constructions_kernel Kernel;
typedef Kernel::FT FT;
typedef Kernel::Point_3 Point_3;
typedef Kernel::Vector_3 Vector_3;
typedef Kernel::Sphere_3 Sphere_3;
typedef CGAL::Point_set_3 Point_set;
int main(int argc, char*argv[])
{
Point_set points;
std::string fname = argc==1?CGAL::data_file_path("points_3/kitten.xyz") : argv[1];
if (argc < 2)
{
std::cerr << "Usage: " << argv[0] << " [input.xyz/off/ply/las]" << std::endl;
std::cerr <<"Running " << argv[0] << " data/kitten.xyz -1\n";
}
std::ifstream stream (fname, std::ios_base::binary);
if (!stream)
{
std::cerr << "Error: cannot read file " << fname << std::endl;
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
stream >> points;
std::cout << "Read " << points.size () << " point(s)" << std::endl;
if (points.empty())
return EXIT_FAILURE;
typename Point_set::iterator rout_it = CGAL::remove_outliers
(points,
24, // Number of neighbors considered for evaluation
points.parameters().threshold_percent (5.0)); // Percentage of points to remove
points.remove(rout_it, points.end());
std::cout << points.number_of_removed_points()
<< " point(s) are outliers." << std::endl;
// Applying point set processing algorithm to a CGAL::Point_set_3
// object does not erase the points from memory but place them in
// the garbage of the object: memory can be freeed by the user.
points.collect_garbage();
// Compute average spacing using neighborhood of 6 points
double spacing = CGAL::compute_average_spacing (points, 6);
// Simplify using a grid of size 2 * average spacing
typename Point_set::iterator gsim_it = CGAL::grid_simplify_point_set (points, 2. * spacing);
points.remove(gsim_it, points.end());
std::cout << points.number_of_removed_points()
<< " point(s) removed after simplification." << std::endl;
points.collect_garbage();
CGAL::jet_smooth_point_set (points, 24);
int reconstruction_choice
= argc==1? -1 : (argc < 3 ? 0 : atoi(argv[2]));
if (reconstruction_choice == 0 || reconstruction_choice==-1) // Poisson
{
CGAL::jet_estimate_normals
(points, 24); // Use 24 neighbors
// Orientation of normals, returns iterator to first unoriented point
typename Point_set::iterator unoriented_points_begin =
CGAL::mst_orient_normals(points, 24); // Use 24 neighbors
points.remove (unoriented_points_begin, points.end());
CGAL::Surface_mesh output_mesh;
CGAL::poisson_surface_reconstruction_delaunay
(points.begin(), points.end(),
points.point_map(), points.normal_map(),
output_mesh, spacing);
std::ofstream f ("out_poisson.ply", std::ios_base::binary);
CGAL::IO::set_binary_mode (f);
CGAL::IO::write_PLY(f, output_mesh);
f.close ();
}
if (reconstruction_choice == 1 || reconstruction_choice==-1) // Advancing front
{
typedef std::array Facet; // Triple of indices
std::vector facets;
// The function is called using directly the points raw iterators
CGAL::advancing_front_surface_reconstruction(points.points().begin(),
points.points().end(),
std::back_inserter(facets));
std::cout << facets.size ()
<< " facet(s) generated by reconstruction." << std::endl;
// copy points for random access
std::vector vertices;
vertices.reserve (points.size());
std::copy (points.points().begin(), points.points().end(), std::back_inserter (vertices));
CGAL::Surface_mesh output_mesh;
CGAL::Polygon_mesh_processing::polygon_soup_to_polygon_mesh (vertices, facets, output_mesh);
std::ofstream f ("out_af.off");
f << output_mesh;
f.close ();
}
if (reconstruction_choice == 2 || reconstruction_choice==-1) // Scale space
{
CGAL::Scale_space_surface_reconstruction_3 reconstruct
(points.points().begin(), points.points().end());
// Smooth using 4 iterations of Jet Smoothing
reconstruct.increase_scale (4, CGAL::Scale_space_reconstruction_3::Jet_smoother());
// Mesh with the Advancing Front mesher with a maximum facet length of 0.5
reconstruct.reconstruct_surface (CGAL::Scale_space_reconstruction_3::Advancing_front_mesher(0.5));
std::ofstream f ("out_sp.off");
f << "OFF" << std::endl << points.size () << " "
<< reconstruct.number_of_facets() << " 0" << std::endl;
for (Point_set::Index idx : points)
f << points.point (idx) << std::endl;
for (const auto& facet : CGAL::make_range (reconstruct.facets_begin(), reconstruct.facets_end()))
f << "3 "<< facet << std::endl;
f.close ();
}
else // Handle error
{
std::cerr << "Error: invalid reconstruction id: " << reconstruction_choice << std::endl;
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
} 9 完整的管道图像
下图是应用于熊雕像完整重建管道的示例(由EPFL 计算机图形和几何实验室 [5]提供)。还应用了两种网格处理算法(孔填充和各向同性重新划分网格)(有关详细信息,请参阅多边形网格处理一章)。