opencv c++ 霍夫圆检测
1、原理
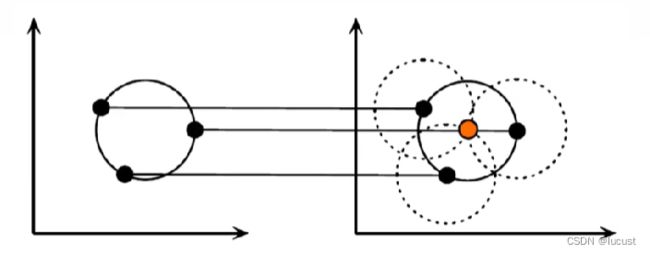
a)对某点![]() ,以其为圆心的圆为无数(一圈圈的圆),将其从x-y平面坐标系上转换到r-θ极坐标系上后,则变成了以r、θ为自变量,
,以其为圆心的圆为无数(一圈圈的圆),将其从x-y平面坐标系上转换到r-θ极坐标系上后,则变成了以r、θ为自变量,![]() 为固定值,x、y为因变量的式子:
为固定值,x、y为因变量的式子:
![]()
b)其余点作同样操作,可以得到,当半径r为某值![]() 时,使得三个圆同时交于1点,从而获取这些点构成的圆的圆心,半径
时,使得三个圆同时交于1点,从而获取这些点构成的圆的圆心,半径![]() 。
。
圆的参数方程:
![]()
![]()
注:在实际实现时,会设定一个固定的半径r来进行检测(因为r的范围太大了)。
2、API
void cv::HoughCircles ( InputArray image,
OutputArray circles,
int method,
double dp,
double minDist,
double param1 = 100,
double param2 = 100,
int minRadius = 0,
int maxRadius = 0
) image ——输入的灰度图像。
circles——输出,数据类型为vector (x,y,radius) or (x,y,radius,votes) .
method ——检测方法
dp ——累加器分辨率与图像分辨率的反比. For example, if dp=1 , the accumulator has the same resolution as the input image. If dp=2 , the accumulator has half as big width and height. For HOUGH_GRADIENT_ALT the recommended value is dp=1.5, unless some small very circles need to be detected.
minDist ——两个被检测圆的圆心的最小距离,即在这个距离范围内,不会出现第二个被检测出的圆。 If the parameter is too small, multiple neighbor circles may be falsely detected in addition to a true one. If it is too large, some circles may be missed.
param1 ——Canny边缘检测的高阈值。
param2 ——累计阈值,当相交于同一点的圆的个数大于它时,才记录这个被识别到的圆。
minRadius——圆的最小半径
maxRadius ——圆的最大半径。If <= 0, uses the maximum image dimension. If < 0, HOUGH_GRADIENT returns centers without finding the radius. HOUGH_GRADIENT_ALT always computes circle radiuses.
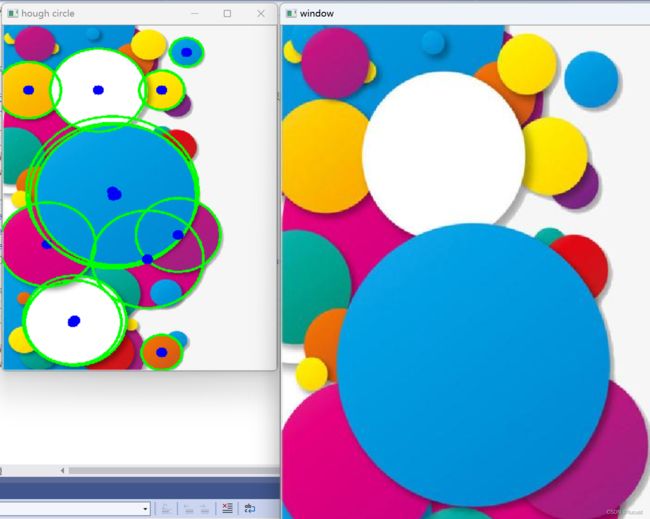
3、代码:
说明:HoughCircles 会基于canny自动二值化图,因此输入灰度图即可,但由于该算法对图像噪点敏感,必须在调用前对灰度图进行降噪处理。
void QuickDemo::hough_circle(Mat& image)
{
//霍夫圆检测会基于canny自动二值化图,因此输入灰度图即可,但在传入之前,需要对图像进行降噪。
Mat gray, binary;
cvtColor(image, gray, COLOR_BGR2GRAY);
GaussianBlur(gray, gray, Size(9, 9), 2, 2);
namedWindow("hough gray", WINDOW_FREERATIO);
imshow("hough gray", gray);
vector circles;
double mindist = 2;
double min_r = 10;
double max_r = 200;
HoughCircles(gray, circles, HOUGH_GRADIENT, 1.5, mindist, 100, 100, min_r, max_r);
for (size_t i = 0; i < circles.size(); ++i) {
circle(image, Point(circles[i][0], circles[i][1]), circles[i][2], Scalar(0, 255, 0), 3, 8);
circle(image, Point(circles[i][0], circles[i][1]), 10, Scalar(250, 0, 0), -1, 8);
}
namedWindow("hough circle", WINDOW_FREERATIO);
imshow("hough circle", image);
}