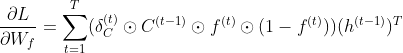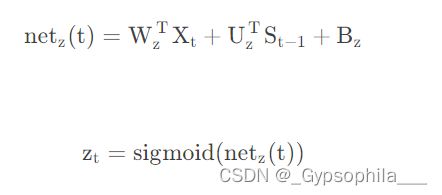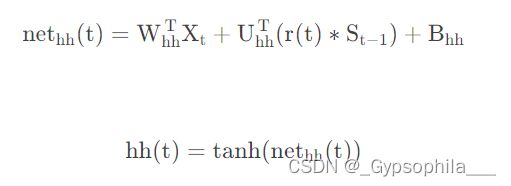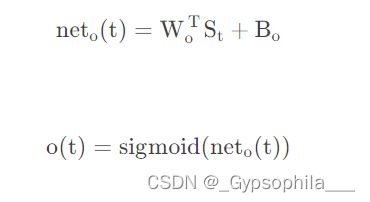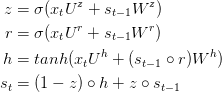NNDL 作业10:第六章课后题(LSTM | GRU)
习题6-3 当使用公式(6.50)作为循环神经网络得状态更新公式时,分析其可能存在梯度爆炸的原因并给出解决办法.
令![]() 为在第k时刻函数
为在第k时刻函数![]() 的输入,在计算误差项
的输入,在计算误差项![]() 时,梯度有可能过大,从而导致梯度爆炸
时,梯度有可能过大,从而导致梯度爆炸
解决:增加门控机制,使用长短期记忆神经网络
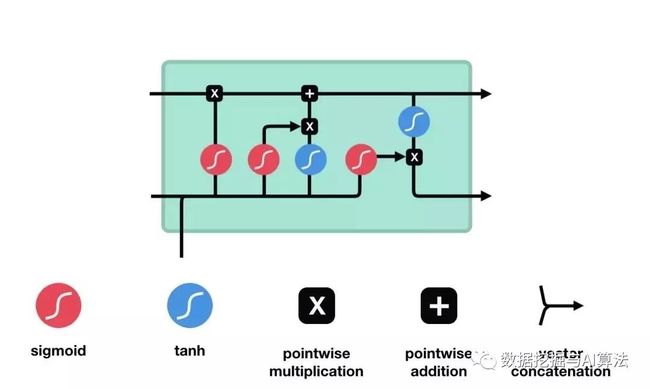
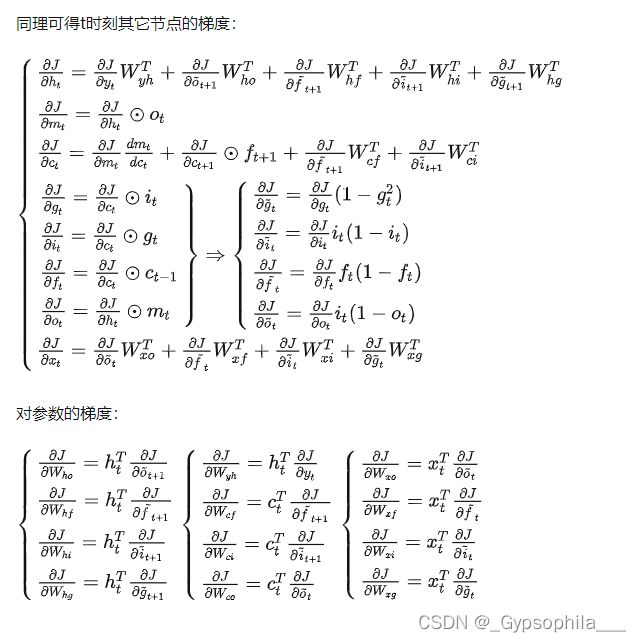
习题6-4 推导LSTM网络中参数的梯度,并分析其避免梯度消失的效果编辑
LSTM通过门控机制解决梯度问题,forget input output门非0即1 门为1时 梯度能很好地在LSTM传递,减轻了梯度消失发生的概率 门为0时 上一时刻信息对当前无影响 没必要传递更新参数
习题6-5 推导GRU网络中参数的梯度,并分析其避免梯度消失的效果编辑
在获得前一个时刻神经单元的输入![]() 和当前时刻的输入
和当前时刻的输入![]() 之后,首先是将两者进行合并输入到r(t)中去。计算过程为:
之后,首先是将两者进行合并输入到r(t)中去。计算过程为: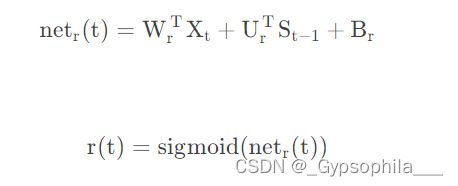
在获得前一个时刻神经单元的输入![]() 和当前时刻的输入
和当前时刻的输入![]() 输入到z(t)中去,具体计算过程为:
输入到z(t)中去,具体计算过程为:
再然后是产生hht的部分,这一部分相对于其他两个部分复杂一点,其输入包括当前时刻的输入![]()
和计算出来的r(t), 首先是计算出来的r(t)和![]() 进行对位相乘,再将计算结果与
进行对位相乘,再将计算结果与![]() 进行加法合并。
进行加法合并。
在计算完成r(t),z(t),hh(t)之后,我们要计算的就是该单元的输出值以及向输出层传递的值。先计算该单元的输出值: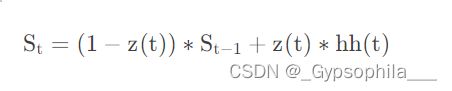
最后计算输出值(如果该单元有输出值):
GRU具有调节信息流动的门单元,但没有一个单独的记忆单元,GRU将输入门和遗忘门整合成一个升级门,通过门控制梯度
附加题 6-1P 什么时候应该用GRU? 什么时候用LSTM?
GRUS
GRU 背后的原理与 LSTM 非常相似,即用门控机制控制输入、记忆等信息而在当前时间步做出预测,表达式由以下给出:
GRU 有两个有两个门,即一个重置门(reset gate)和一个更新门(update gate)。从直观上来说,重置门决定了如何将新的输入信息与前面的记忆相结合,更新门定义了前面记忆保存到当前时间步的量。如果我们将重置门设置为 1,更新门设置为 0,那么我们将再次获得标准 RNN 模型。使用门控机制学习长期依赖关系的基本思想和 LSTM 一致,但还是有一些关键区别:
- GRU 有两个门(重置门与更新门),而 LSTM 有三个门(输入门、遗忘门和输出门)。
- GRU 并不会控制并保留内部记忆(c_t),且没有 LSTM 中的输出门。
- LSTM 中的输入与遗忘门对应于 GRU 的更新门,重置门直接作用于前面的隐藏状态。
-
在计算输出时并不应用二阶非线性。
GRU 是标准循环神经网络的改进版,GRU 使用了更新门(update gate)与重置门(reset gate)。基本上,这两个门控向量决定了哪些信息最终能作为门控循环单元的输出。这两个门控机制的特殊之处在于,它们能够保存长期序列中的信息,且不会随时间而清除或因为与预测不相关而移除。
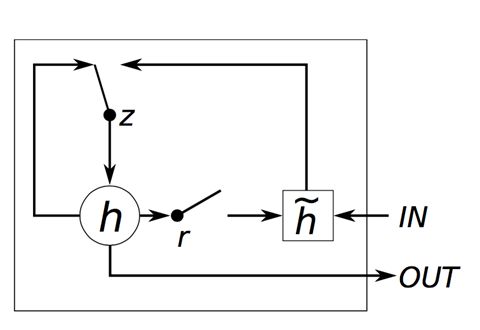
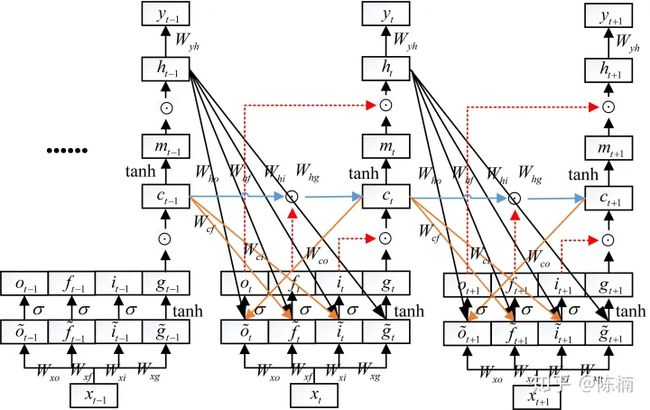
【LSTM】LSTM 的控制流程与 RNN 相似,都是在前向传播过程中处理流过节点的信息,不同之处在于 LSTM内部具有“门”结构,而各个“门”之间分工配合,更好地处理长时间的序列信息。其具体内部结构如下图所示。
与 LSTM 相比,GRU 内部少了一个”门控“,参数比LSTM 少,但是却也能够达到与 LSTM 相当的功能。因而很多时候我们也就会选择更加“实用的 ”GRU 。
附加题 6-2P LSTM BP推导,并用Numpy实现
import numpy as np
import torch
def sigmoid(x):
return 1 / (1 + np.exp(-x))
class LSTMCell:
def __init__(self, weight_ih, weight_hh, bias_ih, bias_hh):
self.weight_ih = weight_ih
self.weight_hh = weight_hh
self.bias_ih = bias_ih
self.bias_hh = bias_hh
self.dc_prev = None
self.dh_prev = None
self.weight_ih_grad_stack = []
self.weight_hh_grad_stack = []
self.bias_ih_grad_stack = []
self.bias_hh_grad_stack = []
self.x_stack = []
self.dx_list = []
self.dh_prev_stack = []
self.h_prev_stack = []
self.c_prev_stack = []
self.h_next_stack = []
self.c_next_stack = []
self.input_gate_stack = []
self.forget_gate_stack = []
self.output_gate_stack = []
self.cell_memory_stack = []
def __call__(self, x, h_prev, c_prev):
a_vector = np.dot(x, self.weight_ih.T) + np.dot(h_prev, self.weight_hh.T)
a_vector += self.bias_ih + self.bias_hh
h_size = np.shape(h_prev)[1]
a_i = a_vector[:, h_size * 0:h_size * 1]
a_f = a_vector[:, h_size * 1:h_size * 2]
a_c = a_vector[:, h_size * 2:h_size * 3]
a_o = a_vector[:, h_size * 3:]
input_gate = sigmoid(a_i)
forget_gate = sigmoid(a_f)
cell_memory = np.tanh(a_c)
output_gate = sigmoid(a_o)
c_next = (forget_gate * c_prev) + (input_gate * cell_memory)
h_next = output_gate * np.tanh(c_next)
self.x_stack.append(x)
self.h_prev_stack.append(h_prev)
self.c_prev_stack.append(c_prev)
self.c_next_stack.append(c_next)
self.h_next_stack.append(h_next)
self.input_gate_stack.append(input_gate)
self.forget_gate_stack.append(forget_gate)
self.output_gate_stack.append(output_gate)
self.cell_memory_stack.append(cell_memory)
self.dc_prev = np.zeros_like(c_next)
self.dh_prev = np.zeros_like(h_next)
return h_next, c_next
def backward(self, dh_next):
x_stack = self.x_stack.pop()
h_prev = self.h_prev_stack.pop()
c_prev = self.c_prev_stack.pop()
c_next = self.c_next_stack.pop()
input_gate = self.input_gate_stack.pop()
forget_gate = self.forget_gate_stack.pop()
output_gate = self.output_gate_stack.pop()
cell_memory = self.cell_memory_stack.pop()
dh = dh_next + self.dh_prev
d_tanh_c = dh * output_gate * (1 - np.square(np.tanh(c_next)))
dc = d_tanh_c + self.dc_prev
dc_prev = dc * forget_gate
self.dc_prev = dc_prev
d_input_gate = dc * cell_memory
d_forget_gate = dc * c_prev
d_cell_memory = dc * input_gate
d_output_gate = dh * np.tanh(c_next)
d_ai = d_input_gate * input_gate * (1 - input_gate)
d_af = d_forget_gate * forget_gate * (1 - forget_gate)
d_ao = d_output_gate * output_gate * (1 - output_gate)
d_ac = d_cell_memory * (1 - np.square(cell_memory))
da = np.concatenate((d_ai, d_af, d_ac, d_ao), axis=1)
dx = np.dot(da, self.weight_ih)
dh_prev = np.dot(da, self.weight_hh)
self.dh_prev = dh_prev
self.dx_list.insert(0, dx)
self.dh_prev_stack.append(dh_prev)
self.weight_ih_grad_stack.append(np.dot(da.T, x_stack))
self.weight_hh_grad_stack.append(np.dot(da.T, h_prev))
db = np.sum(da, axis=0)
self.bias_ih_grad_stack.append(db)
self.bias_hh_grad_stack.append(db)
return dh_prev
np.random.seed(123)
torch.random.manual_seed(123)
np.set_printoptions(precision=6, suppress=True)
lstm_torch = torch.nn.LSTMCell(2, 3).double()
lstm_numpy = LSTMCell(lstm_torch.weight_ih.data.numpy(),
lstm_torch.weight_hh.data.numpy(),
lstm_torch.bias_ih.data.numpy(),
lstm_torch.bias_hh.data.numpy())
x_numpy = np.random.random((4, 2))
x_torch = torch.tensor(x_numpy, requires_grad=True)
h_numpy = np.random.random((4, 3))
h_torch = torch.tensor(h_numpy, requires_grad=True)
c_numpy = np.random.random((4, 3))
c_torch = torch.tensor(c_numpy, requires_grad=True)
dh_numpy = np.random.random((4, 3))
dh_torch = torch.tensor(dh_numpy, requires_grad=True)
h_numpy, c_numpy = lstm_numpy(x_numpy, h_numpy, c_numpy)
h_torch, c_torch = lstm_torch(x_torch, (h_torch, c_torch))
h_torch.backward(dh_torch)
dh_numpy = lstm_numpy.backward(dh_numpy)
print("h_numpy :\n", h_numpy)
print("h_torch :\n", h_torch.data.numpy())
print("c_numpy :\n", c_numpy)
print("c_torch :\n", c_torch.data.numpy())
print("dx_numpy :\n", np.sum(lstm_numpy.dx_list, axis=0))
print("dx_torch :\n", x_torch.grad.data.numpy())
print("w_ih_grad_numpy :\n",
np.sum(lstm_numpy.weight_ih_grad_stack, axis=0))
print("w_ih_grad_torch :\n",
lstm_torch.weight_ih.grad.data.numpy())
print("w_hh_grad_numpy :\n",
np.sum(lstm_numpy.weight_hh_grad_stack, axis=0))
print("w_hh_grad_torch :\n",
lstm_torch.weight_hh.grad.data.numpy())
print("b_ih_grad_numpy :\n",
np.sum(lstm_numpy.bias_ih_grad_stack, axis=0))
print("b_ih_grad_torch :\n",
lstm_torch.bias_ih.grad.data.numpy())
print("b_hh_grad_numpy :\n",
np.sum(lstm_numpy.bias_hh_grad_stack, axis=0))
print("b_hh_grad_torch :\n",
lstm_torch.bias_hh.grad.data.numpy())
h_numpy :
[[ 0.055856 0.234159 0.138457]
[ 0.094461 0.245843 0.224411]
[ 0.020396 0.086745 0.082545]
[-0.003794 0.040677 0.063094]]
h_torch :
[[ 0.055856 0.234159 0.138457]
[ 0.094461 0.245843 0.224411]
[ 0.020396 0.086745 0.082545]
[-0.003794 0.040677 0.063094]]
c_numpy :
[[ 0.092093 0.384992 0.213364]
[ 0.151362 0.424671 0.318313]
[ 0.033245 0.141979 0.120822]
[-0.0061 0.062946 0.094999]]
c_torch :
[[ 0.092093 0.384992 0.213364]
[ 0.151362 0.424671 0.318313]
[ 0.033245 0.141979 0.120822]
[-0.0061 0.062946 0.094999]]
dx_numpy :
[[-0.144016 0.029775]
[-0.229789 0.140921]
[-0.246041 -0.009354]
[-0.088844 0.036652]]
dx_torch :
[[-0.144016 0.029775]
[-0.229789 0.140921]
[-0.246041 -0.009354]
[-0.088844 0.036652]]
w_ih_grad_numpy :
[[-0.056788 -0.036448]
[ 0.018742 0.014428]
[ 0.007827 0.024828]
[ 0.07856 0.05437 ]
[ 0.061267 0.045952]
[ 0.083886 0.0655 ]
[ 0.229755 0.156008]
[ 0.345218 0.251984]
[ 0.430385 0.376664]
[ 0.014239 0.011767]
[ 0.054866 0.044531]
[ 0.04654 0.048565]]
w_ih_grad_torch :
[[-0.056788 -0.036448]
[ 0.018742 0.014428]
[ 0.007827 0.024828]
[ 0.07856 0.05437 ]
[ 0.061267 0.045952]
[ 0.083886 0.0655 ]
[ 0.229755 0.156008]
[ 0.345218 0.251984]
[ 0.430385 0.376664]
[ 0.014239 0.011767]
[ 0.054866 0.044531]
[ 0.04654 0.048565]]
w_hh_grad_numpy :
[[-0.037698 -0.048568 -0.021069]
[ 0.016749 0.016277 0.007556]
[ 0.035743 0.02156 0.000111]
[ 0.060824 0.069505 0.029101]
[ 0.060402 0.051634 0.025643]
[ 0.068116 0.06966 0.035544]
[ 0.168965 0.217076 0.075904]
[ 0.248277 0.290927 0.138279]
[ 0.384974 0.401949 0.167006]
[ 0.015448 0.0139 0.005158]
[ 0.057147 0.048975 0.022261]
[ 0.057297 0.048308 0.017745]]
w_hh_grad_torch :
[[-0.037698 -0.048568 -0.021069]
[ 0.016749 0.016277 0.007556]
[ 0.035743 0.02156 0.000111]
[ 0.060824 0.069505 0.029101]
[ 0.060402 0.051634 0.025643]
[ 0.068116 0.06966 0.035544]
[ 0.168965 0.217076 0.075904]
[ 0.248277 0.290927 0.138279]
[ 0.384974 0.401949 0.167006]
[ 0.015448 0.0139 0.005158]
[ 0.057147 0.048975 0.022261]
[ 0.057297 0.048308 0.017745]]
b_ih_grad_numpy :
[-0.084682 0.032588 0.046412 0.126449 0.111421 0.139337 0.361956
0.539519 0.761838 0.027649 0.103695 0.099405]
b_ih_grad_torch :
[-0.084682 0.032588 0.046412 0.126449 0.111421 0.139337 0.361956
0.539519 0.761838 0.027649 0.103695 0.099405]
b_hh_grad_numpy :
[-0.084682 0.032588 0.046412 0.126449 0.111421 0.139337 0.361956
0.539519 0.761838 0.027649 0.103695 0.099405]
b_hh_grad_torch :
[-0.084682 0.032588 0.046412 0.126449 0.111421 0.139337 0.361956
0.539519 0.761838 0.027649 0.103695 0.099405]
ref:
GRU和LSTM在各种使用场景应该如何选择? - 知乎 (zhihu.com)
LSTM与GRU简单介绍 - 知乎 (zhihu.com)
人人都能看懂的LSTM介绍及反向传播算法推导(非常详细) - 知乎 (zhihu.com)
https://blog.csdn.net/hei653779919/article/details/104153065