HM机器学习-numpy(数值型运算)
基础介绍
-
为什么学习?
快速 、方便、科学计算的基础库 -
什么是numpy
多用于大型、多维数组上执行数值运算;重在数值计算,是大部分python科学计算库的基础库 -
创建数组(矩阵)np,array命令
-
np.arrange命令和range类似,但生成的是ndarray类型的数组
-
查看数组类型np.dtype print(t3.dtype)结果是int64(64位的数据类型)

当数据量太大时,可以考虑指定数据类型降低内存 -
如何指定数据类型t4=np.array(range(1,4),dtype=float)
-
修改数据类型
t5=t5,astype(“int8”) -
取小数
t7=np.round(b,2)#2是位数
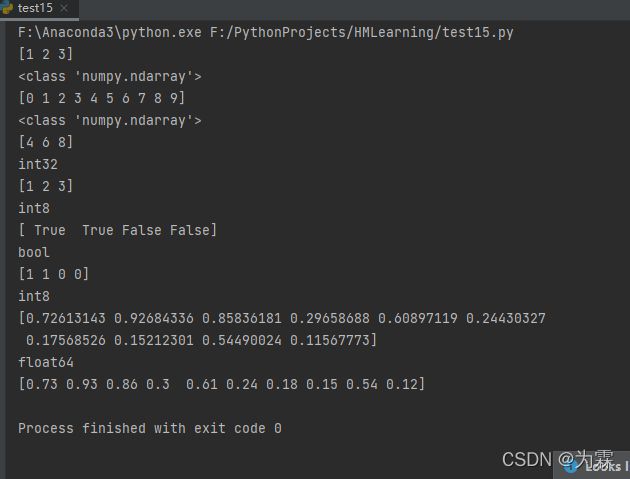
import numpy as np
import random
#使用numpy生成数组,得到ndarray的数据类型
t1=np.array([1,2,3])
print(t1)
print(type(t1))
t2=np.array(range(10))
print(t2)
print(type(t2))
t3=np.arange(4,10,2)#生成起点为4,终点为10,步长为2的数组
print(t3)
print(t3.dtype)
#numpy中的数据类型
t4=np.array(range(1,4),dtype="i1")
t5=np.array([1,1,0,0],dtype=bool)
print(t4)
print(t4.dtype)
print(t5)
print(t5.dtype)
#调整数据类型
t6=t5.astype("int8")
print(t6)
print(t6.dtype)
#numpy中的小数
t7=np.array([random.random() for i in range(10)])
print(t7)
print(t7.dtype)
#取小数
t8 = np.round(t7,2)
print(t8)
数组的形状
- anacond里调用ipython
- 查看数组的形状 t2.shape
运行结果(a,b,c),a是块数,b是行数,c是列数 - 改变数组形状t3.reshape(a,b)
代码如下:
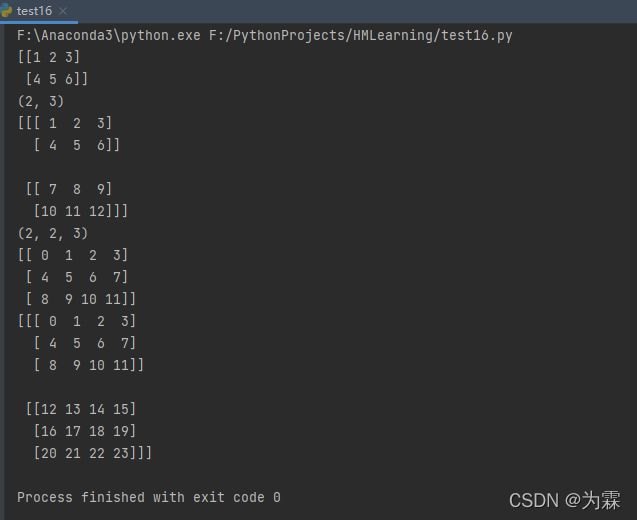
import numpy as np
t2=np.array([[1,2,3],[4,5,6]])
print(t2)
print(t2.shape)
t3=np.array([[[1,2,3],[4,5,6]],[[7,8,9],[10,11,12]]])
print(t3)
print(t3.shape)
t4=np.arange(12)
t4_1=t4.reshape(3,4)
print(t4_1)
t5=np.arange(24)
t5_1=t5.reshape(2,3,4)
print(t5_1)
注意有return方法的时候,一般原值不会发生改变,也就是说t5本身不改变。除了extend方法
运行结果
注意t5.reshape(24,)是一维数组,而(1,24)是二维的
- 如何把数组转化为1维数据?
b.reshape(num_b,) 如何知道总num呢?用 b.shape[0]*b.shape[1]
或者用b.flatten()命令
(base) PS C:\Users\admin> ipython
Python 3.7.6 (default, Jan 8 2020, 20:23:39) [MSC v.1916 64 bit (AMD64)]
Type 'copyright', 'credits' or 'license' for more information
IPython 7.12.0 -- An enhanced Interactive Python. Type '?' for help.
In [1]: import numpy as np
In [2]: t1=np.arange(24)
In [3]: t1.reshape(4,6)
Out[3]:
array([[ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5],
[ 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11],
[12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17],
[18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23]])
In [4]: t2=t1.reshape(4,6)
In [5]: t2.flatten()
Out[5]:
array([ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16,
17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23])
数组的计算
- **数组和数计算:**数组+2就是每个元素加2,乘除都是一样的
In [9]: t3+2
Out[9]:
array([[ 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7],
[ 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13],
[14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19],
[20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 25]])
In [10]:
数组和数组计算:
In [15]: t6
Out[15]:
array([[100, 101, 102, 103, 104, 105],
[106, 107, 108, 109, 110, 111],
[112, 113, 114, 115, 116, 117],
[118, 119, 120, 121, 122, 123]])
In [16]: t3+t6
Out[16]:
array([[100, 102, 104, 106, 108, 110],
[112, 114, 116, 118, 120, 122],
[124, 126, 128, 130, 132, 134],
[136, 138, 140, 142, 144, 146]])
In [17]: t3*t6
Out[17]:
array([[ 0, 101, 204, 309, 416, 525],
[ 636, 749, 864, 981, 1100, 1221],
[1344, 1469, 1596, 1725, 1856, 1989],
[2124, 2261, 2400, 2541, 2684, 2829]])
In [18]: t7=np.arange(0,6)
In [19]: t7
Out[19]: array([0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5])
In [20]: t3-t7
Out[20]:
array([[ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[ 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6],
[12, 12, 12, 12, 12, 12],
[18, 18, 18, 18, 18, 18]])
In [21]: t8=np.arange(4).reshape((4,1))
In [22]: t8
Out[22]:
array([[0],
[1],
[2],
[3]])
In [23]: t5-t8
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
NameError Traceback (most recent call last)
<ipython-input-23-bb7457655934> in <module>
----> 1 t5-t8
NameError: name 't5' is not defined
In [24]: t3-t8
Out[24]:
array([[ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5],
[ 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10],
[10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15],
[15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20]])
- 二维数组计算:行或者列某一维度一样时,把对应的维度进行计算,如果每个维度都不同,则无法计算
2.三维数组计算-广播原则(通用原则) 如果两个数组的后援维度,即从末尾开始算的维度轴长度相符或其中一方长度为1,则认为广播兼容。广播会在缺失或者长度为1的维度上进行。如何理解?参照t3和t8 t7的计算。
那么问题来了:
shape(3,3,3)和(3,2)无法计算
shape(3,3,2)的数组和(3,2)可以计算,也可以和**(3,3)**计算
有哪些好处:比如每列的数据减去列的平均值结果
3. 轴
- 在numpy中,轴可以理解为方向,用0,1,2表示;对于一维数组,只有一个0轴,对于2维数组,有0和1轴,对于三维数组,有0,1,2轴。此时0轴表示块方向,1表示行方向,2表示列方向。
- 有了轴概念,计算会更方便,计算一个2维数组的值,必须指定方向。回顾np.arange(0,10).reshape(2,5)时,2表示行数(0轴长度,包含数据的条数),5表示列数,表示1轴长度为5
_第4张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/77fdf67a18774094bb8263823e7ce735.jpg)
numpy读取数据
- pandas有很强大的数据读取能力。
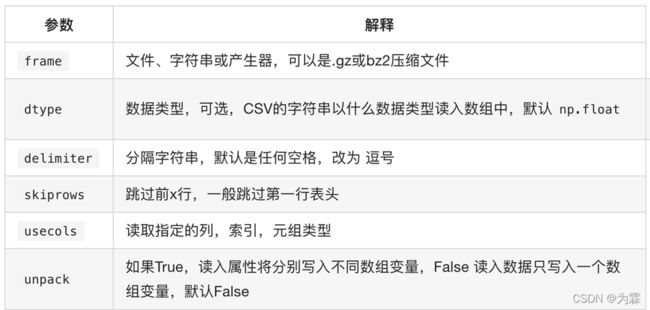
- np.loadtxt(frame(放路径).dtype(指定类型)=np.float, dellimiter(分隔)=None,skiprows(跳过那几行)=0, usecols(用那几行)=None,unpack(转至)=False)
- 现在这里有一个英国和美国各自youtube1000多个视频的点击,喜欢,不喜欢,评论数量([“views”,“likes”,“dislikes”,“comment_total”])的csv,运用刚刚所学习的只是,我们尝试来对其进行操作
(1)先复制:在powershell中选用Copy-Item <源文件夹> <目标文件夹>
(2)`import numpy as np
us_file_path="./youtube_video_data/US_video_data_numbers.csv"
uk_file_path="./youtube_video_data/GB_video_data_numbers.csv"
t1=np.loadtxt(us_file_path,delimiter=",",dtype=“int”,unpack=True)#unpack是是否转置
t2=np.loadtxt(us_file_path,delimiter=",",dtype=“int”)
print(t1)
print("****************************")
print(t2)`
4. numpy转置
转置是一种变换,对于numpy中的数组来说,就是在对角线方向交换数据,目的也是为了更方便的去处理数据。三个命令:t2.transpose(), t2.T, t2.swapaxes(1,0)
In [2]: import numpy as np
In [3]: t2=np.arange(24).reshape(4,6)
In [4]: t2.transpose
Out[4]: <function ndarray.transpose>
In [5]: t2.transpose()
Out[5]:
array([[ 0, 6, 12, 18],
[ 1, 7, 13, 19],
[ 2, 8, 14, 20],
[ 3, 9, 15, 21],
[ 4, 10, 16, 22],
[ 5, 11, 17, 23]])
In [6]: t2.T
Out[6]:
array([[ 0, 6, 12, 18],
[ 1, 7, 13, 19],
[ 2, 8, 14, 20],
[ 3, 9, 15, 21],
[ 4, 10, 16, 22],
[ 5, 11, 17, 23]])
In [7]: t2.swapaxes(1,0)
Out[7]:
array([[ 0, 6, 12, 18],
[ 1, 7, 13, 19],
[ 2, 8, 14, 20],
[ 3, 9, 15, 21],
[ 4, 10, 16, 22],
[ 5, 11, 17, 23]])
- 那么,结合之前的所学的matplotlib把英国和美国的数据呈现出来?
看到这个问题,我们应该考虑什么?
我们想要反映出什么样的结果,解决什么问题?
选择什么样的呈现方式?
数据还需要做什么样的处理?
写代码
numpy索引和切片
- 通用连续取多行多列:
t2[a:b,c:d] 逗号前表示取行,逗号后表示取列,:表示从哪到哪 - 通用取不连续的行或列
t2[:,[1,2,3]] - 取点,相当于一种索引
t2[[a,b,c],[d,e,f]]取出来的是(a,d),(b,e),(c,f)三个点
#取每一行
print(t2[2])
#取连续的多行
print(t2[2:])
#取不连续的多行
print(t2[[2,8,10]])
#取列
print(t2[1,:]) #对列不进行操作,仅仅取第一行
print(t2[2:,:]) #对列不进行操作,取2以后的每一行
print(t2[:,0]) #取第一列
#取连续多列
print(t2[:,2:])
#取不连续的多列
print(t2[:,[0,2]])
#取行和列,取第三行,第四列的值
a=t2[2,3]
print(a)
print(type(a))
#取多行多列的矩阵,第3行到5行,第2到4列,取行和咧交叉部分的数组
b=t2[2:5,1:4]
print(b)
#取多个不相邻的点,用方括号来取
c=t2[[0,2],[0,1]]
print(c)
#如果想选(0,0),(2,1)和(2,3)的点,应当怎么取?
d=t2[[0,2,2],[0,1,3]]
numpy中数值的修改
- 修改行列的值,取完后赋值即可实现,如果条件更复杂?
- 如我们想要把t中小于10的数字替换为3.运用布尔索引切片功能t2[t2<10]=3
In [9]: t2=np.arange(24).reshape(4,6)
In [10]: t2
Out[10]:
array([[ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5],
[ 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11],
[12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17],
[18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23]])
In [11]: t2<10
Out[11]:
array([[ True, True, True, True, True, True],
[ True, True, True, True, False, False],
[False, False, False, False, False, False],
[False, False, False, False, False, False]])
In [12]: t2[t2<10]=3
In [13]: t2[t2>20]
Out[13]: array([21, 22, 23])
- numpy三元运算符
如果想把t2中小于10的数字替换为0,大于20的替换为20,怎么做
np.where(t2<10,0,20) - numpy中的clip操作
**t.clip(10,18)**可以将小于10的替换为10,大于18的替换为18.但nan无法被替换
In [14]: t=np.arange(24).reshape(4,6)
In [15]: t.astype(float)
Out[15]:
array([[ 0., 1., 2., 3., 4., 5.],
[ 6., 7., 8., 9., 10., 11.],
[12., 13., 14., 15., 16., 17.],
[18., 19., 20., 21., 22., 23.]])
In [16]: t[t>20]=nan
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
NameError Traceback (most recent call last)
-input-16-8555a1ff0075> in
----> 1 t[t>20]=nan
NameError: name 'nan' is not defined
In [17]: t[3,3:5]=np.nan
In [18]: t.clip(10,18)
Out[18]:
array([[10, 10, 10, 10, 10, 10],
[10, 10, 10, 10, 10, 11],
[12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17],
[18, 18, 18, 10, 10, 18]])
numpy的nan和inf
nan(NAN,nan):notnan(NAN,Nan):not a number表示不是一个数字
什么时候numpy中会出现nan:
当我们读取本地的文件为float的时候,如果有缺失,就会出现nan
当做了一个不合适的计算的时候(比如无穷大(inf)减去无穷大)
inf(-inf,inf):infinity,inf表示正无穷,-inf表示负无穷
什么时候回出现inf包括(-inf,+inf)
比如一个数字除以0,(python中直接会报错,numpy中是一个inf或者-inf)
- nan是一个浮点型数据
- 两个nan不相等
In [3]: import numpy as np
In [4]:
In [4]: np.nan==np.nan
Out[4]: False
- 利用nan!=nan可以统计nan个数
(1) nan.count_nonzero(统计非0个数,统计布尔索引矩阵中t2!=t2为true也就是1结果的数量,即可统计出nan的个数
In [7]: t[3,3]=np.nan
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
ValueError Traceback (most recent call last)
-input-7-1ed36fdf1edb> in
----> 1 t[3,3]=np.nan
ValueError: cannot convert float NaN to integer
In [8]: t1=t.astype(float)
In [9]: t1[3,3]=np.nan
In [10]: t1
Out[10]:
array([[ 0., 1., 2., 3., 4., 5.],
[ 6., 7., 8., 9., 10., 11.],
[12., 13., 14., 15., 16., 17.],
[18., 19., 20., nan, 22., 23.]])
In [11]: t1!=t1
Out[11]:
array([[False, False, False, False, False, False],
[False, False, False, False, False, False],
[False, False, False, False, False, False],
[False, False, False, True, False, False]])
In [12]: np.count_nonzero(t1!=t1)
Out[12]: 1
(2)np.isnan(t2)统计
4. nan和任值计算都是nan
例如np.sum(t2)计算所有元素和;np.sum(t2,axis=0),计0轴方向上的和,也就是列和
In [16]: np.sum(t3)
Out[16]: 66
In [17]: np.sum(t3,axis=0)
Out[17]: array([12, 15, 18, 21])
In [18]: np.sum(t2,axis=0)
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
NameError Traceback (most recent call last)
-input-18-518805564dc3> in
----> 1 np.sum(t2,axis=0)
NameError: name 't2' is not defined
In [19]: np.sum(t1,axis=0)
Out[19]: array([36., 40., 44., nan, 52., 56.])
- 在一组数据中单纯的把nan替换为0,合适么?会带来什么样的影响?
比如,全部替换为0后,替换之前的平均值如果大于0,替换之后的均值肯定会变小,所以更一般的方式是把缺失的数值替换为均值(中值)或者是直接删除有缺失值的一行
那么问题来了:
- 计算一组数据的中值或者是均值
求和:t.sum(axis=None)
均值:t.mean(a,axis=None) 受离群点的影响较大
中值:np.median(t,axis=None)
最大值:t.max(axis=None)
最小值:t.min(axis=None)
极值:np.ptp(t,axis=None) 即最大值和最小值只差
标准差:t.std(axis=None) (标准差是一组数据平均值分散程度的一种度量。一个较大的标准差,代表大部分数值和其平均值之间差异较大;)
import numpy as np
#定义一种填充缺失值方法
def fill_nanarray(t1):
for i in range(t1.shape[1]):#取出来一共有多少列,遍历每一列
temp_col=t1[:,i] #取出来当前的列
if np.count_nonzero(temp_col!=temp_col)!=0:#判断哪几列包含nan
#得到不为nan的array
temp_not_nan_col=temp_col[temp_col==temp_col]
#选中nan的位置
temp_col[temp_col!=temp_col]=temp_not_nan_col.mean()
return t1
#调用该方法
if __name__ == '__main__':
'''第一是作为脚本直接执行,第二是 import 到其他的 python 脚本中被调用(模块重用)执行。因此 if __name__ == 'main': 的作用就是控制这两种情况执行代码的过程,在 if __name__ == 'main': 下的代码只有在第一种情况下(即文件作为脚本直接执行)才会被执行,而 import 到其他脚本中是不会被执行的。举例说明如下
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/heqiang525/article/details/89879056'''
t1 = np.arange(12).reshape(3, 4).astype("float")
t1[1, 2:] = np.nan
print(t1)
t2=fill_nanarray(t1)
print(t2)
- 如何删除有缺失数据的那一行(列)[在pandas中介绍]
练习
英国和美国各自youtube1000的数据结合之前的matplotlib绘制出各自的评论数量的直方图
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
us_file_path="./youtube_video_data/US_video_data_numbers.csv"
uk_file_path="./youtube_video_data/GB_video_data_numbers.csv"
#导入数据
t_us=np.loadtxt(us_file_path,delimiter=",",dtype="int")
#取评论(最后一列),因此可以-1索引
t_us_comments=t_us[:,-1]
#选择比5000小的数据
t_us_comments = t_us_comments[t_us_comments<=5000]
#查看最大最小值,进而选择合适组数
print(t_us_comments.max(),t_us_comments.min())
#绘制直方图
d=50
num_bins=np.ptp(t_us_comments)//d
plt.figure(figsize=(20,8),dpi=80)
plt.hist(t_us_comments,num_bins)
plt.show()
希望了解英国的youtube中视频的评论数和喜欢数的关系,应该如何绘制改图
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
us_file_path = "./youtube_video_data/US_video_data_numbers.csv"
uk_file_path = "./youtube_video_data/GB_video_data_numbers.csv"
# 导入数据
t_uk = np.loadtxt(uk_file_path, delimiter=",", dtype="int")
#选择喜欢数比50000小的数据
t_uk=t_uk[t_uk[:,1]<=500000]
#取评论和喜欢(最后一列),因此可以-1索引
t_uk_comments=t_uk[:,-1]
t_uk_likes=t_uk[:,1]
#绘制散点图
plt.figure(figsize=(20,8),dpi=80)
plt.scatter(t_uk_likes,t_uk_comments)
plt.show()
数组的拼接与交换
-
水平拼接:np.hstack((t1,t2))#双括号
-
现在希望把之前案例中两个国家的数据方法一起来研究分析,同时保留国家的信息(每条数据的国家来源),应该怎么办
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
#导入两个国家的值
us_file_path = "./youtube_video_data/US_video_data_numbers.csv"
uk_file_path = "./youtube_video_data/GB_video_data_numbers.csv"
us_data=np.loadtxt(us_file_path,delimiter=",",dtype="int")
uk_data=np.loadtxt(uk_file_path,delimiter=",",dtype="int")
#给两个国家的值加上国家列,us用0表示,uk用1表示
zeros_data=np.zeros((us_data.shape[0],1),"int") #np.zeros(shape,dytpe,order),shape应该是一个元祖(a,b),这里应该a是和原数组行数一致,b列数为1
ones_data=np.ones((uk_data.shape[0],1),"int")
us_data=np.hstack((zeros_data,us_data))
uk_data=np.hstack((ones_data,uk_data))
#两个国家的数据拼接起来
final_data = np.vstack((us_data,uk_data))
print(final_data)