【SVM预测】基于鲸鱼算法优化支持向量机SVM实现数据预测附matlab代码
1 简介
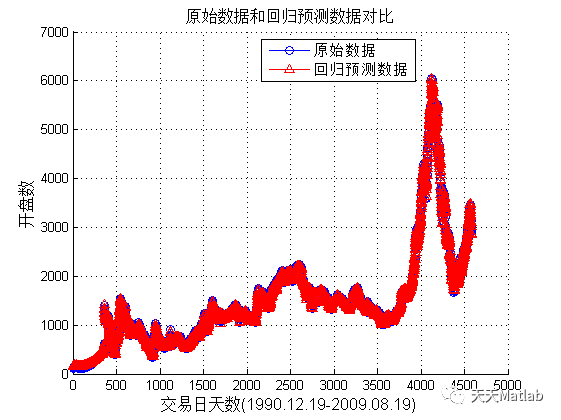
对开盘指数预测的精度与可靠性提出更高要求.为解决支持向量机(SVM)算法中核参数和惩戒参数依赖经验选取导致的大盘指数预测精度较低,收敛速度较慢的问题,提出一种基于鲸鱼算法优化最小二乘支持向量机(WOASVM)的负荷预测方法.首先通过鲸鱼算法对SVM参数进行寻优,最后建立大盘指数预测模型.结合某地区的实测数据进行预测分析,结果表明,相较于SVM改进模型预测精度和收敛速度均有大幅提高,在金融企业中具有良好的实际应用价值.
断阈值p选择包围猎物还是狩猎行为。为了减少控制变量,该算法只有位置向量,去掉了速度向量,所以使得算法的寻优能力得到增强。
2 部分代码
%_________________________________________________________________________%
% Whale Optimization Algorithm (WOA) source codes demo 1.0 %
% %
% %
%_________________________________________________________________________%
% You can simply define your cost in a seperate file and load its handle to fobj
% The initial parameters that you need are:
%__________________________________________
% fobj = @YourCostFunction
% dim = number of your variables
% Max_iteration = maximum number of generations
% SearchAgents_no = number of search agents
% lb=[lb1,lb2,...,lbn] where lbn is the lower bound of variable n
% ub=[ub1,ub2,...,ubn] where ubn is the upper bound of variable n
% If all the variables have equal lower bound you can just
% define lb and ub as two single number numbers
% To run ALO: [Best_score,Best_pos,cg_curve]=ALO(SearchAgents_no,Max_iteration,lb,ub,dim,fobj)
% The Whale Optimization Algorithm
function [Leader_score,Leader_pos,Convergence_curve]=WOA(SearchAgents_no,Max_iter,lb,ub,dim,fobj,handles,value)
% initialize position vector and score for the leader
Leader_pos=zeros(1,dim);
Leader_score=inf; %change this to -inf for maximization problems
%Initialize the positions of search agents
Positions=initialization(SearchAgents_no,dim,ub,lb);
Convergence_curve=zeros(1,Max_iter);
t=0;% Loop counter
% Main loop
while t
% Return back the search agents that go beyond the boundaries of the search space
Flag4ub=Positions(i,:)>ub;
Flag4lb=Positions(i,:)
% Calculate objective function for each search agent
fitness=fobj(Positions(i,:));
All_fitness(1,i)=fitness;
% Update the leader
if fitness
Leader_score=fitness; % Update alpha
Leader_pos=Positions(i,:);
end
end
a=2-t*((2)/Max_iter); % a decreases linearly fron 2 to 0 in Eq. (2.3)
% a2 linearly dicreases from -1 to -2 to calculate t in Eq. (3.12)
a2=-1+t*((-1)/Max_iter);
% Update the Position of search agents
for i=1:size(Positions,1)
r1=rand(); % r1 is a random number in [0,1]
r2=rand(); % r2 is a random number in [0,1]
A=2*a*r1-a; % Eq. (2.3) in the paper
C=2*r2; % Eq. (2.4) in the paper
b=1; % parameters in Eq. (2.5)
l=(a2-1)*rand+1; % parameters in Eq. (2.5)
p = rand(); % p in Eq. (2.6)
for j=1:size(Positions,2)
if p<0.5
if abs(A)>=1
rand_leader_index = floor(SearchAgents_no*rand()+1);
X_rand = Positions(rand_leader_index, :);
D_X_rand=abs(C*X_rand(j)-Positions(i,j)); % Eq. (2.7)
Positions(i,j)=X_rand(j)-A*D_X_rand; % Eq. (2.8)
elseif abs(A)<1
D_Leader=abs(C*Leader_pos(j)-Positions(i,j)); % Eq. (2.1)
Positions(i,j)=Leader_pos(j)-A*D_Leader; % Eq. (2.2)
end
elseif p>=0.5
distance2Leader=abs(Leader_pos(j)-Positions(i,j));
% Eq. (2.5)
Positions(i,j)=distance2Leader*exp(b.*l).*cos(l.*2*pi)+Leader_pos(j);
end
end
end
t=t+1;
Convergence_curve(t)=Leader_score;
if t>2
line([t-1 t], [Convergence_curve(t-1) Convergence_curve(t)],'Color','b')
xlabel('Iteration');
ylabel('Best score obtained so far');
drawnow
end
set(handles.itertext,'String', ['The current iteration is ', num2str(t)])
set(handles.optimumtext,'String', ['The current optimal value is ', num2str(Leader_score)])
if value==1
hold on
scatter(t*ones(1,SearchAgents_no),All_fitness,'.','k')
end
end
3 仿真结果
4 参考文献
[1]张文喜. 基于鲸鱼算法优化LSSVM的抽油井动液面预测[J]. 化工管理, 2018(2):1.
博主简介:擅长智能优化算法、神经网络预测、信号处理、元胞自动机、图像处理、路径规划、无人机等多种领域的Matlab仿真,相关matlab代码问题可私信交流。
部分理论引用网络文献,若有侵权联系博主删除。