目标检测中IOU和NMS的python实现
文章目录
- 1、两个框的IOU
- 2、多框IOU计算
- 3、NMS
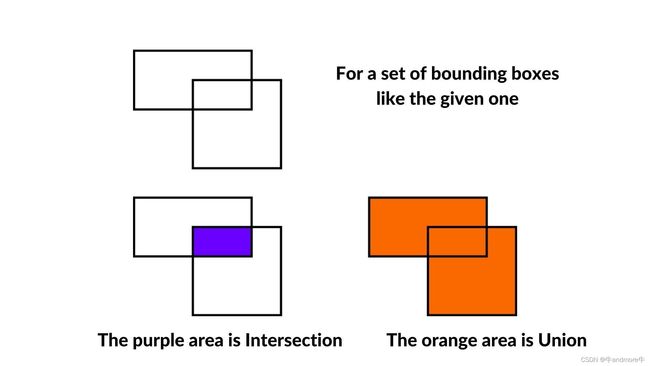
Non Maximum Suppression(NMS)在目标检测中应用广泛,主要是用于目标检测结果从多个重叠边界框中选出一个
1、两个框的IOU
IOU就是intersection over union,交比补,用来计算两个框之间重叠的比例。IOU的数学公式可以是如下:
iou = (target交prediction)/(target并prediction)
也就是:
iou(box1,box2) = intersection(box1,box2)/union(box1,box2)
如下图分别是交集和并集的示意图,蓝色是交集,橙色是并集
用python实现两个框的iou计算如下
import numpy as np
def iou(box1,box2):
"""
box1:(x11,y11,x12,y12)
box2:(x21,y21,x22,y22)
坐标是(左,上,右,下)
"""
#find the area of box
x11,y11,x12,y12 = box1
x21,y21,x22,y22 = box2
width1 = np.maximum(0,x12-x11)
height1 = np.maximum(0,y12-y11)
width2 = np.maximum(0,x22-x21)
height2 = np.maximum(0,y22-y21)
area1 = width1*height1
area2 = width2*height2
#计算交集,需要计算交集部分的左、上、右、下坐标
xi1 = np.maximum(x11,x21)
yi1 = np.maximum(y11,y21)
xi2 = np.minimum(x12,x22)
yi2 = np.minimum(y12,y22)
#计算交集部分面积
w = np.maximum(0,xi2-xi1)
h = np.maximum(0,yi2-yi1)
intersection = w*h
#计算并集
union = area1+area2-intersection
#计算iou
iou = intersection/union
return iou
测试一下结果:
box1=[1,1,3,3]
box2=[2,2,4,4]
a = iou(box1,box2)
print(a) #1/7=0.14285714285714285
2、多框IOU计算
def compute_iou(boxes1,boxes2):
"""[Compute pairwise IOU matrix for given two sets of boxes]
Args:
boxes1 ([numpy ndarray with shape N,4]): [representing bounding boxes with format (xmin,ymin,xmax,ymax)]
boxes2 ([numpy ndarray with shape M,4]): [representing bounding boxes with format (xmin,ymin,xmax,ymax)]
Returns:
pairwise IOU maxtrix with shape (N,M),where the value at ith row jth column hold the iou between ith
box and jth box from box1 and box2 respectively.
"""
lu = np.maximum(boxes1[:,None,:2],boxes2[:,:2]) #lu with shape N,M,2 ; boxes1[:,None,:2] with shape (N,1,2) boxes2 with shape(M,2)
rd = np.minimum(boxes1[:,None,2:],boxes2[:,2:]) # rd same to lu
intersection_wh = np.maximum(0.0,rd-lu)
intersection_area = intersection_wh[:,:,0]*intersection_wh[:,:,1] #with shape (N,M)
boxes1_wh = np.maximum(0.0,boxes1[:,2:]-boxes1[:,:2])
boxes1_area = boxes1_wh[:,0]*boxes1_wh[:,1] #with shape (N,)
boxes2_wh = np.maximum(0.0,boxes2[:,2:]-boxes2[:,:2])
boxes2_area = boxes2_wh[:,0]*boxes2_wh[:,1] # with shape (M,)
union_area = np.maximum(boxes1_area[:,None]+boxes2_area -intersection_area,1e-8) # with shape (N,M)
ious = np.clip(intersection_area/union_area,0.0,1.0)
return ious
如下示例
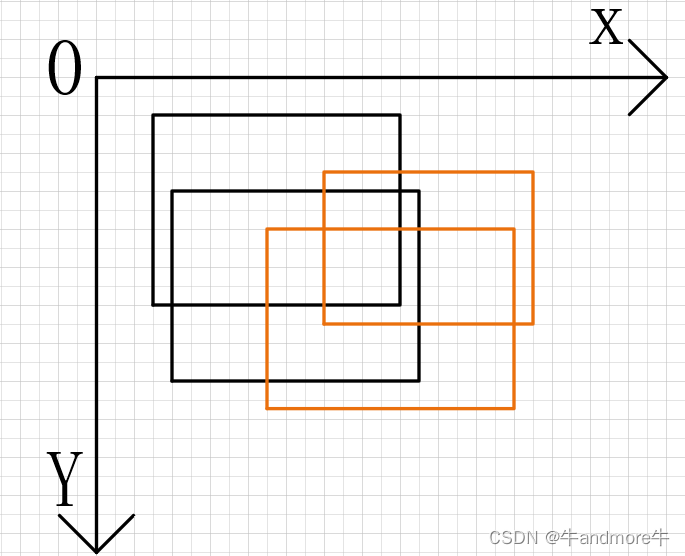
上图黑色是boxes1,另一种颜色是boxes2,计算结是为:
boxes1 = np.array([[3,2,16,12],[4,6,17,16]]).astype(np.float32)
boxes2 = np.array([[9,8,23,17],[12,5,24,13]]).astype(np.float32)
ious=compute_iou(boxes1,boxes2)
print(ious)
#[[0.12280702 0.14141414]
#[0.33333334 0.18324608]]
3、NMS
import numpy as np
def nms_boxes(boxes,nms_threshold):
"""
Apply the Non-Maximum Suppression (NMS) algorithm on the bounding
boxes with their confidence scores and return an array with the
indexes of the bounding boxes we want to keep
boxes: Nx7 numpy array of [[x1,y1,x2,y2,box_confidence,class_id,class_prob]...]
"""
x1 = boxes[:,0]
y1 = boxes[:,1]
x2 = boxes[:,3]
y2 = boxes[:,4]
width = np.abs(x2-x1)
height = np.abs(y2-y1)
box_confidences = boxes[:,4]*boxes[:,6]
areas = width*height
ordered = box_confidences.argsort()[::-1] #从大到小
keep = list()
while ordered.size>0:
# index of the current element
i = ordered[0]
keep.append(i)
# 求当前最大分值框与各个其它框的交集
xx1 = np.maximum(x1[i],x1[ordered[1:]])
yy1 = np.maximum(y1[i],y1[ordered[1:]])
xx2 = np.minimum(x2[i],x2[ordered[1:]])
yy2 = np.minimum(y2[i],y2[ordered[1:]])
width1 = np.maximum(0.0,xx2-xx1+1)
height1 = np.maximum(0.0,yy2-yy1+1)
intersection = width1*height1
union = areas[i] + areas[ordered[1:]]-intersection
iou = intersection/union
indexes = np.where(iou<nms_threshold)[0]
ordered = ordered[indexes+1]
keep = np.array(keep)
return keep
以上就是nms算法,最后返回所有要保留的索引,以yolov3为例,做一个全流程
def postprocess(yolov3_outputs,img_h,img_w,conf_th,nms_threshold):
"""[yolov3输出后处理]
Args:
yolov3_outputs ([type]): [a list of 3 tensors每一个tensor[N,7]的float32 numbers]
the order of [x, y, w, h, box_confidence, class_id, class_prob]
img_h ([type]): [description]
img_w ([type]): [description]
conf_th ([type]): [description] confidence threshold
nms_threshold ([type]): [description]
Returns:
boxes,scores,classes
"""
#过滤低分值的结果并且把所有yolov3的结果合并起来
detections =[]
for o in yolov3_outputs:
dets = o.reshape((-1,7))
#分值是框的分值与分类分值的积
dets = dets[dets[:,4]*dets[:,6]>=conf_th]
detections.append(dets)
detections = np.concatenate(detections,axis=0)
if len(detections)==0:
boxes = np.zeros((0,4),dtype = np.int32)
scores = np.zeros((0,),dtype = np.float32)
classes = np.zeros((0,),dtype=np.float32)
else:
box_scores = detections[:,4]*detections[:,6]
# scale x, y, w, h from [0, 1] to pixel values
old_h = img_h
old_w = img_w
detections[:,:4] *= np.array([old_w,old_h,old_w,old_h],dtype=np.float32)
#convert x,y,w,h to x1,y1,x2,y2
detections = np.concatenate([detections[:,:2]-detections[:,2:4]/2.0,detections[:,:2]-detections[:,2:4]/2.0,
detections[:,:4:]],axis=-1)
#按类NMS
nms_detections = np.zeros((0,7),dtype=detections.dtype)
for class_id in set(detections[:,5]):
idxs = np.where(detectons[:,5]==class_id)
cls_detections = detections[idxs]
keep = nms_boxes(cls_detections,nms_threshold)
nms_detections = np.concatenate([nms_detections,cls_detections[keep]],axis=0)
boxes = nms_detections[:,:4]+0.5
boxes = boxes.astype(np.int32) #shape:(N,)
scores = nms_detections[:,4]*nms_detections[:,6] #shape:(N,)
classes = nms_detections[:,5] #shape:(N,)
return boxes,scores,classes