MySQL 示例数据库 employees 的导入与使用
导入 MySQL 示例数据库 employees
本博客记录将 employees.db 数据库导入本地 MySQL 数据库中。
文章目录
- 导入 MySQL 示例数据库 employees
- 1. 导入示例数据库:employees
-
- 1.1 下载示例数据库:employees
- 1.2 导入 employees
- 2. 使用示例数据库:employees
1. 导入示例数据库:employees
1.1 下载示例数据库:employees
employees 是官方提供的示例数据库,官方下载链接
或者在该链接下下载:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1i_tddrAHSf27u8zI3lDSWA (提取密码:g5au)
1.2 导入 employees
① 将 “employees_db” 解压到任一文件夹下(最好别带中文)
② 修改 employees.sql 文件 (若直接将“employees_db” 解压到 D 盘下则无需修改 ) :
打开employees.sql文件,拉到最后,将下列路径修改为自己解压的路径
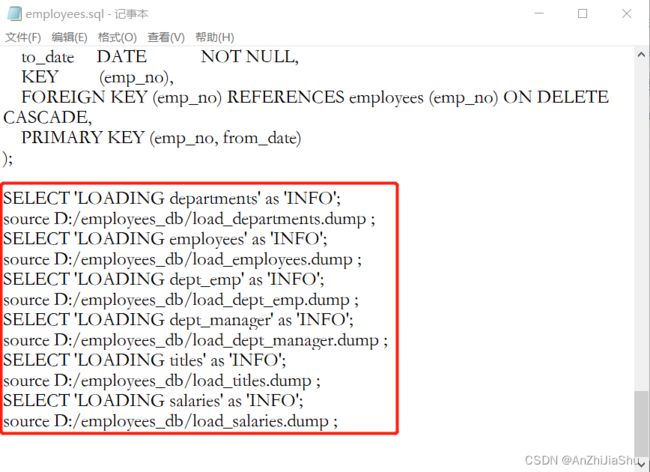
例如我将 “employees_db” 解压至D:\SoftWare\mysql-5.5.56-winx64\example_db 文件夹下,则我修改后为:

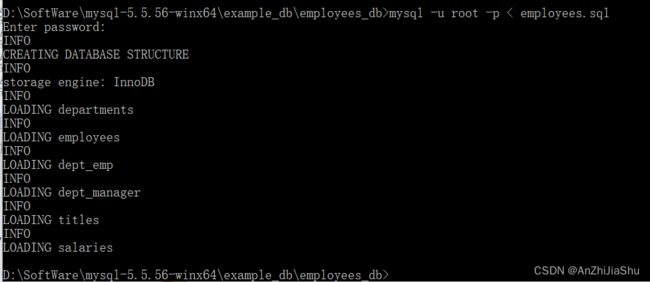
③ 打开 cmd,切到刚刚解压的 “employees_db” 文件夹下,输入以下命令:
mysql -u root -p < employees.sql
无报错则导入成功
④ 查看数据库:激活mysql,输入 show databases; 查看数据库,或者打开MySQL的可视化工具 MySQL Workbench 或 navicat 查看数据库 employees。下图为在 workbench 中查看数据库 employees
2. 使用示例数据库:employees
1.在MySQL样本数据库上完成下列查询,并使用SQL EXPLAIN工具对每一条SQL语句进行分析:
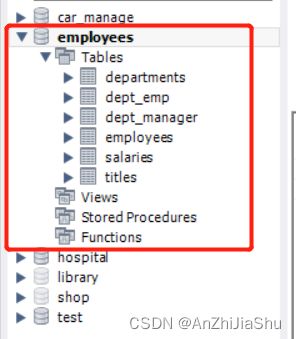
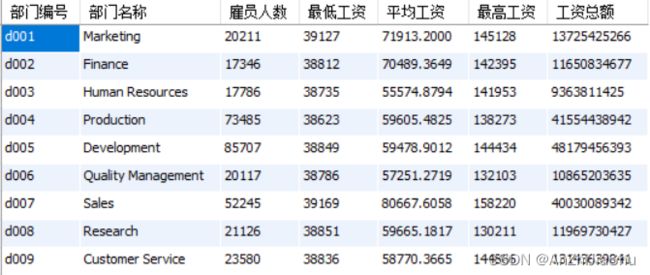
(1). 查询每个部门 (departments) 的编号 (dept_no),名称 (dept_name),在该部门工作过的雇员 (employees) 人数,最低工资 (salary) ,平均工资,最高工资及工资总额;
sql语句如下所示:
select a.dept_no as 部门编号,
a.dept_name as 部门名称,
count(distinct b.emp_no) as 雇员人数,
min(salary) as 最低工资,
avg(salary) as 平均工资,
max(salary) as 最高工资,
sum(salary) as 工资总额
from employees.departments a, employees.dept_emp b, employees.salaries c
where a.dept_no=b.dept_no and b.emp_no=c.emp_no
group by a.dept_no,a.dept_name
查询结果如下图所示:
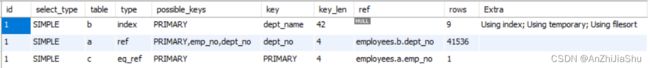
explain+sql 对sql语句进行分析(explain教程详见:MySQL explain 应用详解(吐血整理)):
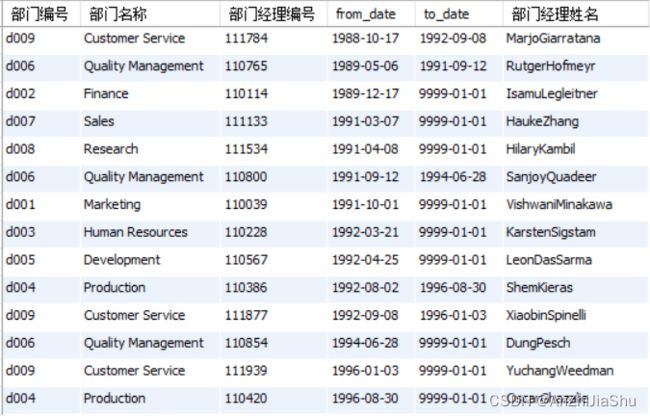
(2). 查询每个部门(departments)的编号(dept_no),名称(dept_name),及各个时间段(from_date,to_date)担任该部门经理(dept_manager)的雇员的编号(emp_no)和姓名(first_name+last_name),并按时间段先后显式;
sql语句如下所示:
select a.dept_no as 部门编号,
a.dept_name as 部门名称,
b.emp_no as 部门经理编号,
b.from_date,
to_date,
concat(c.first_name,c.last_name) as 部门经理姓名
from departments a,
dept_manager b,
employees c
where a.dept_no=b.dept_no
and b.emp_no=c.emp_no
order by b.from_date;
查询结果如下图所示:
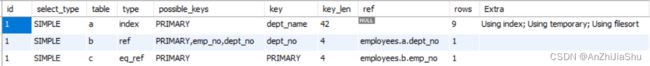
explain sql 结果如下图所示:
(3) 查询每位雇员的编号(emp_no),姓名(first_name+last_name),及各个时间段(from_date,end_data)的工资额(salary),并按时间段先后显式;
sql 语句如下所示
select a.emp_no as 雇员编号,
concat(a.first_name,a.last_name) as 雇员姓名,
b.from_date,
b. to_date,
b.salary as 工资额
from employees a,
salaries b
where a.emp_no=b.emp_no
order by b.from_date;
执行结果如下图所示:
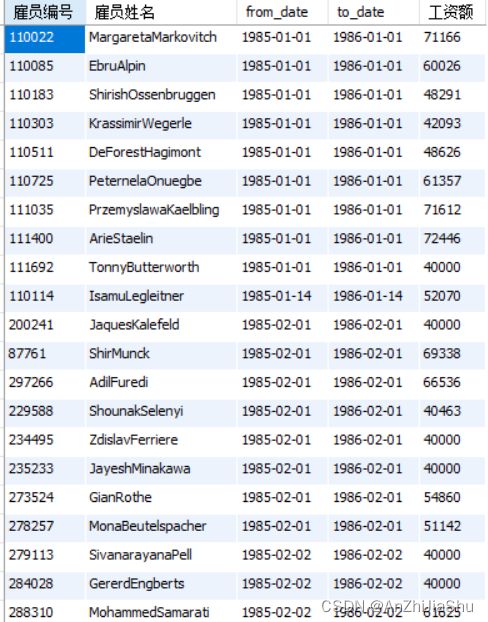
explain+sql 语句分析结果如下图所示:

(4) 查询每位雇员的编号(emp_no),姓名(first_name+last_name),及各个时间段(from_date,end_data)的工作部门名称(dept_name),并按时间段先后显式;
sql语句如下所示:
select a.emp_no as 雇员编号,
concat(c.first_name,c.last_name) as 雇员姓名,
from_date,
to_date,
b.dept_name as 部门名称
from dept_emp a,
departments b,
employees c
where a.dept_no=b.dept_no
and a.emp_no=c.emp_no
order by a.from_date
;
执行结果如下图所示:
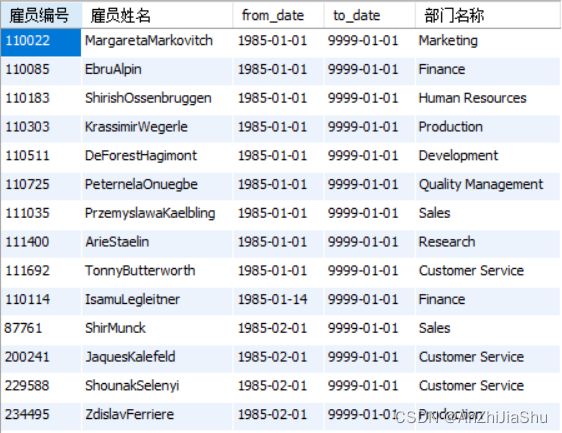
explain+sql 语句分析结果如下图所示:
(5) 查询每位雇员的编号(emp_no),姓名(first_name+last_name),及任职过的部门数;
sql语句如下所示:
select a.emp_no as 雇员编号,
concat(b.first_name,b.last_name) as 雇员姓名,
count(distinct a.dept_no) as 任职过的部门数
from dept_emp a,
employees b
where a.emp_no=b.emp_no
group by a.emp_no ,
concat(b.first_name,b.last_name)
;
执行结果如下图所示:
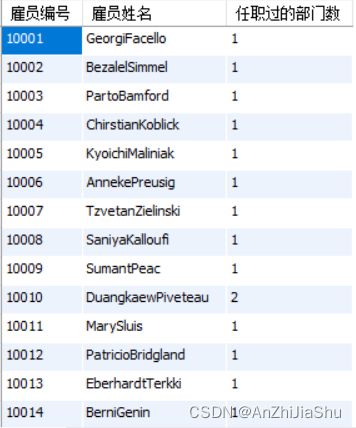
explain sql 结果如下图所示:

(6) 查询每位雇员的编号(emp_no),姓名(first_name+last_name),及各个时间段(from_date,end_data)担任的职务(title),并按时间段先后显式;
sql 语句如下所示:
select a.emp_no as 雇员编号,
concat(a.first_name,a.last_name) as 雇员姓名,
b.from_date,
b.to_date,
b.title as 职务
from employees a,
titles b
where a.emp_no=b.emp_no
order by b.from_date
;
执行结果如下图所示:

explain sql 结果如下图所示:

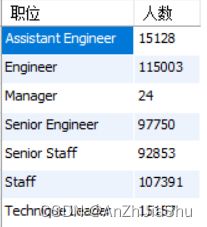
(7) 查询担任每种职务(title)的雇员人数;
sql 语句如下所示:
select title as 职位,
count(distinct emp_no) as 人数
from titles
group by title
;
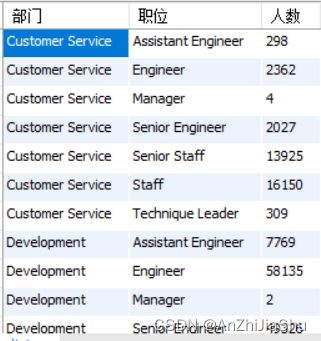
(8) 查询每个部门中担任每种职务(title)的雇员人数;
sql语句如下所示
select a.dept_name as 部门,
c.title as 职位,
count(distinct c.emp_no) as 人数
from departments a,
dept_emp b,
titles c
where a.dept_no=b.dept_no
and b.emp_no=c.emp_no
group by dept_name,title
;
执行结果如下图所示:
explain sql结果如下图所示:

(9) 查询每位雇员的编号(emp_no),姓名(first_name+last_name),及工资额最高的时间段(from_date,end_data)及其工资额;
sql语句如下所示
select a.emp_no as 雇员编号,
concat(a.first_name,a.last_name) as 雇员姓名,
c.from_date,
c.to_date,
b.salary as 最高工资
from employees a,
(select emp_no,max(salary) as salary from salaries group by emp_no) b,
salaries c
where a.emp_no=b.emp_no
and b.emp_no = c.emp_no
and b.salary =c.salary
;
执行结果如下图所示:

explain sql 分析结果如下图所示:

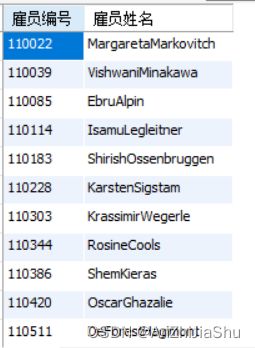
(10) 查询所有曾经担任过部门经理(dept_manager)的雇员的编号(emp_no)和姓名(first_name+last_name);
sql语句如下所示:
select a.emp_no as 雇员编号,
concat(a.first_name,a.last_name) as 雇员姓名
from employees a,
titles b
where b.title="Manager"
and a.emp_no = b.emp_no
;
执行结果如下图所示:
explain sql 分析结果如下图所示:

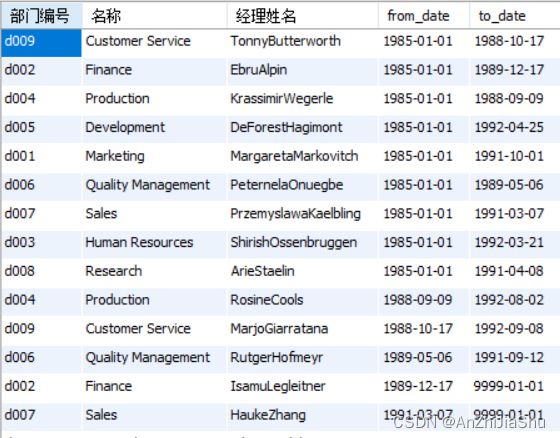
(11) 按时间段(from_date,end_data)先后列出每个部门(departments)的编号(dept_no),名称(dept_name),及其经理的姓名(first_name+last_name);
sql 语句如下所示:
select a.dept_no as 部门编号,
a.dept_name as 名称,
concat(c.first_name,c.last_name) as 经理姓名,
b.from_date,
b.to_date
from departments a,
dept_manager b,
employees c
where a.dept_no=b.dept_no
and b.emp_no=c.emp_no
order by b.from_date
;
执行结果如下图所示:
explain sql 分析结果如下图所示:
(12) 查询所有曾经在‘Development’工作过雇员的编号(emp_no),姓名(first_name+last_name),及时间段(from_date,end_data);
sql 语句如下所示:
select c.emp_no as 雇员编号,
concat(c.first_name,c.last_name) as 姓名,
b.from_date,
b.to_date
from (select dept_no from departments where dept_name="Development") a,
dept_emp b,
employees c
where a.dept_no=b.dept_no
and b.emp_no=c.emp_no
order by b.from_date
;
执行结果如下图所示:
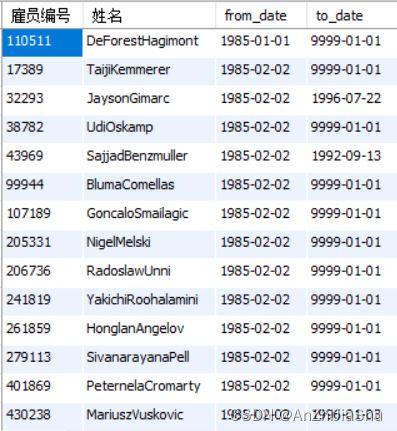
explain sql 分析结果如下图所示:
(13) 查询曾经在所有部门都工作过的雇员的编号(emp_no),姓名(first_name+last_name);
思路1:查找符合下列条件的雇员:不存在一个部门,雇员没有在该部门工作过,sql语句如下所示:
select a.emp_no as 雇员编号,
concat(a.first_name,a.last_name) as 姓名
from employees a
where not exists( -- 不存在这样的部门
select *
from departments b
where not exists( -- 员工没有工作过
select *
from dept_emp c
where b.dept_no=c.dept_no
and c.emp_no=a.emp_no
)
);
思路2:查找符合下列条件的雇员:雇员工作过的部门数 == 所有的部门数,
sql语句如下所示:
select a.emp_no as 雇员编号,
concat(a.first_name,a.last_name) as 姓名
from employees a,
dept_emp b
where a.emp_no=b.emp_no
group by b.emp_no
having count(distinct b.emp_no) = (
select count(distinct dept_no)
from departments);
或者用 all 语句,sql 语句如下所示
select a.emp_no as 雇员编号,
concat(a.first_name,a.last_name) as 姓名
from employees a,
dept_emp b
where a.emp_no=b.emp_no
and b.dept_no = all (select distinct dept_no from departments)
;
(14) 在dept_emp表中插入适当数据使得至少3个以上雇员满足上一题的查询要求。
先在 employees 表中插入 3 个员工信息,sql语句如下所示:
#(1)先插入3个员工
insert into employees(emp_no,birth_date,first_name,last_name,gender,hire_date) values(1,'1985-01-01','Ann','Black','M','2010-01-01');
insert into employees(emp_no,birth_date,first_name,last_name,gender,hire_date) values(2,'1985-01-01','Bnn','Black','M','2010-01-01');
insert into employees(emp_no,birth_date,first_name,last_name,gender,hire_date) values(3,'1985-01-01','Cnn','Black','M','2010-01-01');
执行结果如下图所示:
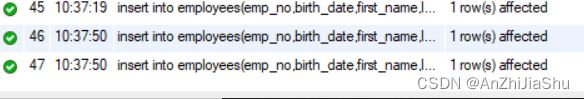
再在 dept_emp 表中插入信息,sql语句如下所示:
#插入员工1
insert into dept_emp(emp_no,dept_no,from_date,to_date) values(1,'d001','2010-01-01','2010-12-01');
insert into dept_emp(emp_no,dept_no,from_date,to_date) values(1,'d002','2011-01-01','2011-12-01');
insert into dept_emp(emp_no,dept_no,from_date,to_date) values(1,'d003','2012-01-01','2012-12-01');
insert into dept_emp(emp_no,dept_no,from_date,to_date) values(1,'d004','2013-01-01','2013-12-01');
insert into dept_emp(emp_no,dept_no,from_date,to_date) values(1,'d005','2014-01-01','2014-12-01');
insert into dept_emp(emp_no,dept_no,from_date,to_date) values(1,'d006','2015-01-01','2015-12-01');
insert into dept_emp(emp_no,dept_no,from_date,to_date) values(1,'d007','2016-01-01','2016-12-01');
insert into dept_emp(emp_no,dept_no,from_date,to_date) values(1,'d008','2017-01-01','2017-12-01');
insert into dept_emp(emp_no,dept_no,from_date,to_date) values(1,'d009','2018-01-01','2018-12-01');
#插入员工2
insert into dept_emp(emp_no,dept_no,from_date,to_date) values(2,'d001','2010-01-01','2010-12-01');
insert into dept_emp(emp_no,dept_no,from_date,to_date) values(2,'d002','2011-01-01','2011-12-01');
insert into dept_emp(emp_no,dept_no,from_date,to_date) values(2,'d003','2012-01-01','2012-12-01');
insert into dept_emp(emp_no,dept_no,from_date,to_date) values(2,'d004','2013-01-01','2013-12-01');
insert into dept_emp(emp_no,dept_no,from_date,to_date) values(2,'d005','2014-01-01','2014-12-01');
insert into dept_emp(emp_no,dept_no,from_date,to_date) values(2,'d006','2015-01-01','2015-12-01');
insert into dept_emp(emp_no,dept_no,from_date,to_date) values(2,'d007','2016-01-01','2016-12-01');
insert into dept_emp(emp_no,dept_no,from_date,to_date) values(2,'d008','2017-01-01','2017-12-01');
insert into dept_emp(emp_no,dept_no,from_date,to_date) values(2,'d009','2018-01-01','2018-12-01');
#插入员工3
insert into dept_emp(emp_no,dept_no,from_date,to_date) values(3,'d001','2010-01-01','2010-12-01');
insert into dept_emp(emp_no,dept_no,from_date,to_date) values(3,'d002','2011-01-01','2011-12-01');
insert into dept_emp(emp_no,dept_no,from_date,to_date) values(3,'d003','2012-01-01','2012-12-01');
insert into dept_emp(emp_no,dept_no,from_date,to_date) values(3,'d004','2013-01-01','2013-12-01');
insert into dept_emp(emp_no,dept_no,from_date,to_date) values(3,'d005','2014-01-01','2014-12-01');
insert into dept_emp(emp_no,dept_no,from_date,to_date) values(3,'d006','2015-01-01','2015-12-01');
insert into dept_emp(emp_no,dept_no,from_date,to_date) values(3,'d007','2016-01-01','2016-12-01');
insert into dept_emp(emp_no,dept_no,from_date,to_date) values(3,'d008','2017-01-01','2017-12-01');
insert into dept_emp(emp_no,dept_no,from_date,to_date) values(3,'d009','2018-01-01','2018-12-01');
2.使用SQL EXPLAIN 工具对下列SQL查询语句进行分析,判断哪些索引将可以对下列查询产生加速作用,并通过实验进行验证。

在红色上的列建索引(个人感觉题目不对,红色的属性本来就自动建了索引)
比较速度:(1).不建索引;(2).建索引;
① explain 分析上述 sql 语句:
explain
SELECT TITLE,
DEPT_NAME,
GENDER,
COUNT(DISTINCT E.EMP_NO)
FROM DEPARTMENTS D,
DEPT_EMP DE,
EMPLOYEES E,
SALARIES S,
TITLES T
WHERE D.DEPT_NO=DE.DEPT_NO
AND DE.EMP_NO=E.EMP_NO
AND E.EMP_NO=S.EMP_NO
AND E.EMP_NO=T.EMP_NO
GROUP BY TITLE,DEPT_NAME,GENDER
ORDER BY TITLE,DEPT_NAME,GENDER;
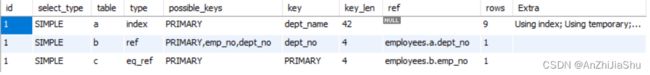
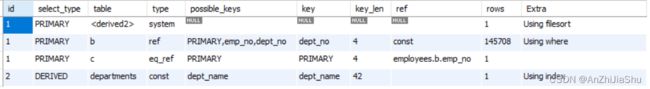
分析结果如下图所示;

♥ 根据 explain 的 possible key 结果可知:
- departments 表可能使用的索引为:主键索引,即dept_no;
- dept_emp 表可能使用的索引为:主键索引(emp_no, dept_no)、emp_no 以及dept_no索引;
- employees 表可能使用的索引为:主键索引,即 emp_no;
- title 表可能使用的索引为:主键索引,即(emp_no, title, from_date) 以及 emp_no
- salaries 表可能使用的索引为:主键索引,即(emp_no, from_date)以及 emp_no
♥ 根据 explain 的 key 结果可知:
- 使用了 departments 表的 dept_name 索引(unique 索引);
- 使用了 dept_emp 表的dept_no索引;
- 使用了 employees 表的主键索引,即 emp_no;
- 使用了 title 表的主键索引,即(emp_no, title, from_date)
- 使用了salaries 表的主键索引,即(emp_no, from_date)
♥ 对 explain 的 extra 分析:
Using filesort 表示当SQL中有一个地方需要对一些数据进行排序的时候,优化器找不到能够使用的索引,所以只能使用外部的索引排序,外部排序就不断的在磁盘和内存中交换数据,这样就摆脱不了很多次磁盘IO,以至于SQL执行的效率很低。反之,由于索引的底层是B+Tree实现的,他的叶子节点本来就是有序的,能加快查询。
Using tempporary 表示在对MySQL查询结果进行排序时,使用了临时表,这样的查询效率是比外部排序更低的,常见于 order by 和 group by 。
在对 departments 的 dept_name 进行order by以及group by时没有使用索引导致了Using filesort 和 Using tempporary,但是经过查看发现,departments的 dept_name 上是有 unique 索引的(如下图所示),因为 order by 和 group by的时候用到了其他表的属性,索引导致 dept_name 索引失效了。

order by 使用索引失败原因:在联表查询中order by后面跟的索引只对驱动表才起作用。
- 驱动表(谁查出来符合来签合条件的数据量少,谁就最有资格做驱动表): 在多表查询的时候,sql 查的第一张表数据再去匹配第二张表,此时第一张表 就是驱动表。
- 如果orderby 后的排序字段用的是驱动表的排序字段,那么这个字段的索引是不失效的,效率高。
- 如果 order by 后的排序字段用的不是驱动表的字段,那么索引不会起作用,数据库会将驱动表查出来的数据和其他表进行关联,关联后的结果集创建一个临时表进行存储,然后对这个临时表按非驱动表的列进行排序,这样 sql 效率会变慢。