PyTorch学习笔记
文章目录
- 1 PyTorch基本数据类型
-
- 1.1 与Python的比较
- 1.2 标量(dim=0)
- 1.3 张量/向量(dim=1)
- 1.4 dim,size and shape
- 1.5 dim = 3的tensor
- 1.6 dim = 4的tensor
- 1.7 一些其他知识
- 2 创建Tensor
-
- 2.1 从Numpy中导入
- 2.2 使用其他方式创建Tensor
- 3 nn.Module
-
- 3.1 nn.Module的好处
-
- 3.1.1 embed current layers
- 3.1.2 Container
- 3.1.3 parameters
- 3.1.4 modules
- 3.1.5 to(device)
- 3.1.6 save and load
- 3.1.7 train/test
- 3.1.8 implement own layer
- 4 Merge or split
-
- 4.1 Cat
- 4.2 Stack
- 4.3 Split
- 4.4 Chunk
1 PyTorch基本数据类型
1.1 与Python的比较

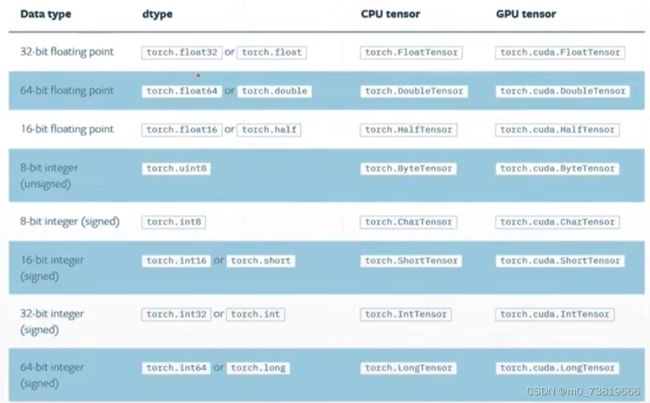
※PyTorch无法对str类型表示
Pytorch只能用以下两种方法来表示string:
① One-Hot
[0,1]——猫
[1,0]——狗
②Embedding
·Word2vec
·glove
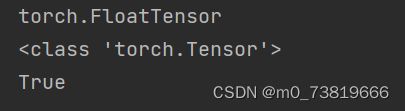
a = torch.randn(2, 3)
print(a.type())
print(type(a))
print(isinstance(a, torch.FloatTensor))#合法化检验
1.2 标量(dim=0)
a = torch.tensor(1.)
print(a)
print(torch.tensor(1.3))
print(a.shape)
print(len(a.shape))
print(a.size())
1.3 张量/向量(dim=1)
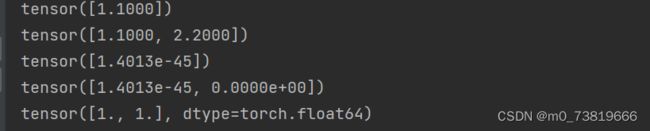
a = torch.tensor([1.1])
b = torch.tensor([1.1,2.2])
c = torch.FloatTensor(1)
d = torch.FloatTensor(2)
e = torch.from_numpy(np.ones(2))
print(a)
print(b)
print(c)
print(d)
print(e)
dim = 1的向量经常用于Bias,Linear Input
1.4 dim,size and shape
通常说的二维,指的是dimension,数学中称为Rank
dim指的是size/shape的长度
size/shape指的是tensor的形状
a = torch.randn(3, 4)
print(a.shape)
print(a.size(0),a.size(1))
print(a.shape[0], a.shape[1])

区别于Numpy库,Pytorch中的size(),shape()函数用法都是返回Tensor大小。
可以说,size(0) = shape[0]
附Numpy库:
size():返回矩阵元素的总个数
shape():返回矩阵的形状大小
此处常用于:Linear,Input,Batch
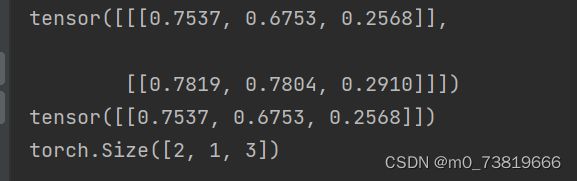
1.5 dim = 3的tensor
a = torch.rand(2,1, 3)
print(a)
print(a[0])
print(a.shape)
1.6 dim = 4的tensor
四维Tensor最常用的场合即是图片处理了。
torch.size([2,3,28,28])代表了:[b,c,h,w]
2张图片,三个通道,28*28的图片大小
1.7 一些其他知识
a = torch.rand(2,1, 3)
print(a.numel())#number of element
print(a.dim())
2 创建Tensor
2.1 从Numpy中导入
可以使用torch.from_numpy()将numpy中创建的array转换为Tensor
2.2 使用其他方式创建Tensor
直接使用torch.tensor().
需要注意Tensor()和FloatTensor()作用一致,均需要传入shape参数进行创建Tensor,ch
tensor()需要传入具体数值
3 nn.Module
nn.Module是Pytorch中所有网络层次类的父类,如果我们需要实现一个层的时候,必须要继承这个类。当我们实现一些现有的层,也是要继承自nn.Module
Magic
- Every Layer in nn.Module
nn.Linear
nn.BatchNorm2d
nn.Conv2d - nn.Module nested in nn.Module
3.1 nn.Module的好处
3.1.1 embed current layers
- Linear
- ReLU
- Sigmoid
- Conv2d
- ConvTransposed2d
- Dropout
- etc.
3.1.2 Container
- sele.net() = nn.Sequential()
可以自动完成forward操作
3.1.3 parameters
- list(net.parameters())
可以查看参数 - list(net.named_parameters())
可以返回字典,PyTorch自动为参数命名 - 可以直接将参数传入优化器中
optimizer = optim.SGD(net.parameters())
3.1.4 modules
- modules: all nodes
- children: direct children
3.1.5 to(device)
device = torch.device(‘cuda’)
net = Net()
net.to(device)
将函数转移至cuda上工作
3.1.6 save and load
在训练过程中,为防止意外事故发生,PyTorch可以自动保存中间状态
torch.save(net.state_dict(),‘ckpt.mdl’)
同时网络开始工作时,也可以检查是否有checkpoint
net.load_state_dict(torch.load(‘ckpt.mdl’))
3.1.7 train/test
对于dropout和BN来说,train和test数据是不太一样的,所以可以在train和test中切换
net.train()
net.eval()
3.1.8 implement own layer
4 Merge or split
4.1 Cat
a = torch.rand(4, 32, 8)
b = torch.rand(5, 32, 8)
print(torch.cat([a, b], dim=0).shape)
4.2 Stack
与concat不同的是,stack会创建一个新的维度
a = torch.rand(4, 32, 8)
b = torch.rand(4, 32, 8)
print(torch.cat([a, b], dim=0).shape)
print(torch.stack([a, b], dim=0).shape)
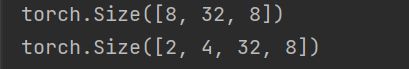
可以理解为:当新维度取0,后面是a的数值,新维度取1,后面是b的数值
4.3 Split
根据长度进行拆分
a = torch.rand(4, 32, 8)
aa, bb, cc, dd = a.split(1, dim=0)
print(aa.shape, bb.shape, cc.shape, dd.shape)
![]()
指定长度进行拆分
a = torch.rand(4, 32, 8)
aa, bb = a.split([1,3], dim=0)
print(aa.shape, bb.shape)
4.4 Chunk
根据数量进行拆分
a = torch.rand(4, 32, 8)
aa, bb = a.chunk(2, dim=0)
print(aa.shape, bb.shape)