Faster-RCNN原理笔记
摘要
详细记录了 Faster RCNN 网络原理和个人的理解
- 论文下载
- 论文源码
前期
Tensorflow 2.0 基础
RCNN 原理
Fast RCNN 原理
原理
论文中的网络结构图解
主要步骤是
- 输入图片
- 对图片进行卷积,提取特征
- 使用 RPN 网络生成 Anchor box,对其裁剪过滤后,通过 softmax 对前景和后景分类,同时,bounding box regression 修正 anchor box,形成校正后的 proposals
- 将 proposals 映射到 feature maps 上
- 通过 RoI pooling 层使每个 RoI 生成固定尺寸的 feature map
- 利用 Softmax Loss 和 Smooth L1 Loss 对分类概率和边框回归联合训练
Faster RCNN 具体的网络结构图
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-TKdQIUEE-1649642178369)(https://aeeeeeep.top/image/Faster-RCNN%E5%8E%9F%E7%90%86%E7%AC%94%E8%AE%B0/construction.png)]
主干特征提取网络
可选 ResNet,MobileNet,VGG16 等网络,本模型使用的是 VGG16 网络,由卷积层模块后接全连接层模块构成,每个卷积层的参数分别为 kernel_size=(3,3), padding='same', activation='relu', kernel_regularizer='l2',最大池化层的参数为 pool_size=(2,2), padding='same'
____________________________________________________________________________________________________
Layer (type) Output Shape Param #
====================================================================================================
input_1 (InputLayer) [(None, 500, 500, 3)] 0
____________________________________________________________________________________________________
conv2d (Conv2D) (None, 500, 500, 64) 1792
____________________________________________________________________________________________________
conv2d_1 (Conv2D) (None, 500, 500, 64) 36928
____________________________________________________________________________________________________
max_pooling2d (MaxPooling2D) (None, 250, 250, 64) 0
____________________________________________________________________________________________________
conv2d_2 (Conv2D) (None, 250, 250, 128) 73856
____________________________________________________________________________________________________
conv2d_3 (Conv2D) (None, 250, 250, 128) 147584
____________________________________________________________________________________________________
max_pooling2d_1 (MaxPooling2D) (None, 125, 125, 128) 0
____________________________________________________________________________________________________
conv2d_4 (Conv2D) (None, 125, 125, 256) 295168
____________________________________________________________________________________________________
conv2d_5 (Conv2D) (None, 125, 125, 256) 590080
____________________________________________________________________________________________________
conv2d_6 (Conv2D) (None, 125, 125, 256) 590080
____________________________________________________________________________________________________
max_pooling2d_2 (MaxPooling2D) (None, 63, 63, 256) 0
____________________________________________________________________________________________________
conv2d_7 (Conv2D) (None, 63, 63, 512) 1180160
____________________________________________________________________________________________________
conv2d_8 (Conv2D) (None, 63, 63, 512) 2359808
____________________________________________________________________________________________________
conv2d_9 (Conv2D) (None, 63, 63, 512) 2359808
____________________________________________________________________________________________________
max_pooling2d_3 (MaxPooling2D) (None, 32, 32, 512) 0
____________________________________________________________________________________________________
conv2d_10 (Conv2D) (None, 32, 32, 512) 2359808
____________________________________________________________________________________________________
conv2d_11 (Conv2D) (None, 32, 32, 512) 2359808
____________________________________________________________________________________________________
conv2d_12 (Conv2D) (None, 32, 32, 512) 2359808
____________________________________________________________________________________________________
dense (Dense) (None, 32, 32, 10) 5130
====================================================================================================
Total params: 14,719,818
Trainable params: 14,719,818
Non-trainable params: 0
____________________________________________________________________________________________________
使用 VGG16 网络不像resnet那么复杂,更深的网络理论上效果也更好
RPN (Region Proposal Networks)
在图像中产生所有可能为目标的候选区域,用来解决生成检测框耗时较多的问题。RPN 根据 CNN 生成的特征图,在 img 的尺度上生成多个锚框,对生成的锚框进行分类和回归。
网络分为2条线,上面一条通过softmax分类 anchors 获得positive 和 negative 分类,下面一条用于计算对于 anchors 的 bounding box regression 偏移量,获得精确的 proposal。最后的 Proposal layer 负责综合 positive anchors 和对应 bounding box regression 偏移量获取 proposals,同时剔除太小和超出边界的 proposals
ahchors
是一种多尺度方法,以一个像素点为中心,生成一组描述 9 个矩形的矩阵,每行4个值 ( x m i n , y m i n , x m a x , y m a x ) (x_min, y_min, x_max, y_max) (xmin,ymin,xmax,ymax) 表示矩形左上和右下角点坐标,长宽比为 $ width:height \in { 1:1, 1:2, 2:1 } $
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-WA83duQ9-1649642178370)(https://aeeeeeep.top/image/Faster-RCNN%E5%8E%9F%E7%90%86%E7%AC%94%E8%AE%B0/anchors.jpg)]
其中,anchors size 是根据检测图像设置的,Faster RCNN网络会把所有输入的图像 reshape 成固定大小,在论文中,会为 feature map 中的每个像素点生成 anchors,后面的2次 bounding box regression 会修正 anchors 检测框位置
上图截取自论文,其中
- 256-d: 论文中主干特征提取网络的最后一层 num_output=256,对应生成的 feature map 是256维的
- sliding window: feature map 在进入 RPN 网络后,又进行了一次 3x3 的卷积,256-d 没有变
- c l s l a y e r cls \quad layer clslayer: 已知每个像素点上有 k 个 anchor(图中 k = 9),每个 anchor 要分前景(positive)和背景(negative),所以每个点由 256-d 的 feature map 转化为 2k scores
- r e g l a y e r reg \quad layer reglayer: 已知每个像素点上有 k 个 anchor(图中 k = 9),每个 anchor 有 ( x , y , w , h ) (x, y, w, h) (x,y,w,h) 对应的4个偏移量,所以每个点由 256-d 的 feature map 转化为 4k coordinates
上图以 图片大小 500x500 为例,计算生成的 gernerate anchors 的数量
ceil ( 500 / 16 ) × ceil ( 500 / 16 ) × 9 = 32 × 32 × 9 = 9216 \operatorname{ceil}(500 / 16) \times \operatorname{ceil}(500 / 16) \times 9=32 \times 32 \times 9= 9216 ceil(500/16)×ceil(500/16)×9=32×32×9=9216
ceil()为向上取整,因为图中VGG16网络输出的 feature map size 为整数
判定 positive/negative
主要步骤:
- RPN 网络图中上面一条输入为共享层卷积的输出
- 进行通道数为2k(k=num_anchors)的 1x1 卷积
- reshape 成两个通道
- 对通道层做归一化,使类别预测的概率和为 1
- 取最终的预测类别和概率
- reshape 回复原状
[1, h, w, 9*2]
论文作者在源码中的 softmax_loss_layer.cpp 对最后 reshape层 的解释:
"Number of labels must match number of predictions; "
"e.g., if softmax axis == 1 and prediction shape is (N, C, H, W), "
"label count (number of labels) must be N*H*W, "
"with integer values in {0, 1, ..., C-1}.";
bounding box regression
图中所示,绿色框为苹果的 ground truth,红色为提取的 positive anchors,即便红色的框被分类器识别为苹果,但是由于红色的框定位不准,这张图相当于没有正确的检测出苹果。所以需要采用一种方法对红色的框进行微调,使得 positive anchors 和 ground truth 更加接近
对于窗口一般使用四维向量 ( x , y , w , h ) (x, y, w, h) (x,y,w,h) 表示,分别表示窗口的中心点坐标和宽高,红框代表原始的positive anchors,绿框代表目标的 ground truth,使得输入原始的 anchor 经过映射得到一个跟 ground truth 更接近的回归窗口,即
positive anchors: A = ( A x , A y , A w , A h ) A = (A_x, A_y, A_w, A_h) A=(Ax,Ay,Aw,Ah)
ground truth: G T = ( G x , G y , G w , G h ) GT = (G_x, G_y, G_w, G_h) GT=(Gx,Gy,Gw,Gh)
寻找 F F F,使 F ( A ) = ( G x ′ , G y ′ , G w ′ , G h ′ ) F(A) = (G_{x}^{\prime}, G_{y}^{\prime}, G_{w}^{\prime}, G_{h}^{\prime}) F(A)=(Gx′,Gy′,Gw′,Gh′)
其中 ( G x ′ , G y ′ , G w ′ , G h ′ ) ≈ ( G x , G y , G w , G h ) (G_{x}^{\prime}, G_{y}^{\prime}, G_{w}^{\prime}, G_{h}^{\prime}) \approx (G_{x}, G_{y}, G_{w}, G_{h}) (Gx′,Gy′,Gw′,Gh′)≈(Gx,Gy,Gw,Gh)
通过变换 F F F从 A A A 变换到 G ′ G' G′,我们要做的是
平移
G x ′ = A w ⋅ d x ( A ) + A x G y ′ = A h ⋅ d y ( A ) + A y G_x^\prime = A_w \cdot d_x(A) + A_x \\ G_y^\prime = A_h \cdot d_y(A) + A_y Gx′=Aw⋅dx(A)+AxGy′=Ah⋅dy(A)+Ay
缩放
G w ′ = A w ⋅ e x p ( d w ( A ) ) G h ′ = A h ⋅ e x p ( d h ( A ) ) G_w^\prime = A_w \cdot exp(d_w(A))\\ G_h^\prime = A_h \cdot exp(d_h(A)) Gw′=Aw⋅exp(dw(A))Gh′=Ah⋅exp(dh(A))
需要学习的是 d x ( A ) , d y ( A ) , d w ( A ) , d h ( A ) d_x(A), d_y(A), d_w(A) ,d_h(A) dx(A),dy(A),dw(A),dh(A) 这四个变换。当输入的 A A A 与 G T GT GT 相差较小时,认为这种变换是一种线性变换, 用线性回归来建模对窗口进行微调,当 A A A 和 G T GT GT 比较接近时,认为是复杂的非线性问题
已知线性回归公式 Y = W X Y = WX Y=WX, X X X 为 feature map,定义为 ϕ \phi ϕ,训练传入 A A A与 G T GT GT之间的变换量 ( t x , t y , t w , t h , ) (t_x, t_y, t_w, t_h, ) (tx,ty,tw,th,), Y Y Y为 ( d x ( A ) , d y ( A ) , d w ( A ) , d h ( A ) ) (d_x(A), d_y(A), d_w(A) ,d_h(A)) (dx(A),dy(A),dw(A),dh(A)),则目标函数为
d ∗ ( A ) = W ∗ T ϕ ( A ) d_*(A) = W_*^T\phi(A) d∗(A)=W∗Tϕ(A)
其中 ϕ ( A ) \phi(A) ϕ(A) 是对应 anchor 的 feature map 组成的特征向量, W ∗ W_{*} W∗ 是需要学习的参数, d ∗ ( A ) d_{*}(A) d∗(A) 是得到的预测值
在 Faster RCNN 论文中,positive anchor 与 ground truth 之间的平移量 ( t x , t y ) (t_x, t_y) (tx,ty) 与尺度因子 ( t w , t h ) (t_w, t_h) (tw,th) 如下
t x = ( x − x a ) / w a t y = ( y − y a ) / h a t w = log ( w / w a ) t h = log ( h / h a ) t_x = (x-x_a)/w_a \quad t_y = (y-y_a)/h_a \\ t_w = \log(w/w_a) \quad t_h = \log(h/h_a) tx=(x−xa)/waty=(y−ya)/hatw=log(w/wa)th=log(h/ha)
为了让预测值 $ {d_{*}(A) }$ 与真实值差距最小, smooth L 1 {\operatorname{smooth}_{L_{1}}} smoothL1 损失函数为
L o s s = { 0.5 ⋅ ( ∑ i N ( t ∗ i − W ∗ T ⋅ ϕ ( A i ) ) 2 if ∣ x ∣ < 1 ∑ i N ∣ t ∗ i − W ∗ T ⋅ ϕ ( A i ) ∣ − 0.5 otherwise Loss = \begin{cases} 0.5 \cdot (\sum_i^N (t_*^i -W_*^T \cdot \phi(A^i))^2 & \text{if}|x| <1 \\ \sum_i^N |t_*^i -W_*^T \cdot \phi(A^i)| - 0.5 & \text{otherwise} \\ \end{cases} Loss={0.5⋅(∑iN(t∗i−W∗T⋅ϕ(Ai))2∑iN∣t∗i−W∗T⋅ϕ(Ai)∣−0.5if∣x∣<1otherwise
优化目标函数为
W ^ ∗ = a r g m i n W ∗ ∑ i n ( t ∗ i − W ∗ T ⋅ ϕ ( A i ) ) 2 + λ ∥ W ∗ ∥ \hat{W}_* = {argmin}_{W_*} \sum_i^n (t_*^i -W_*^T \cdot \phi(A^i))^2 + \lambda \| W_* \| W^∗=argminW∗i∑n(t∗i−W∗T⋅ϕ(Ai))2+λ∥W∗∥
之后可通过梯度下降等方法修正 anchor 位置,注意当 A A A 和 G T GT GT 比较接近时,才可近似认为上述线性变换及优化目标函数成立
对 proposals 进行 bounding box regression
在第二条线路中,num_output=36,即经过该卷积输出图像为 WxHx36,存储为 [1, 4x9, H, W],这里相当于 feature maps 每个点都有9个 anchors,每个 anchors 又都有4个用于回归的 ( d x ( A ) , d y ( A ) , d w ( A ) , d h ( A ) ) (d_x(A), d_y(A), d_w(A) ,d_h(A)) (dx(A),dy(A),dw(A),dh(A)) 变换量
VGG16 网络输出 32 ∗ 32 ∗ 512 32 * 32 * 512 32∗32∗512 的特征,对应设置 32 ∗ 32 ∗ k 32*32*k 32∗32∗k 个 anchors,因此RPN输出
-
大小为 32 ∗ 32 ∗ 2 k 32 * 32 * 2k 32∗32∗2k 的 positive/negative softmax 分类特征矩阵
-
大小为 32 ∗ 32 ∗ 4 k 32 * 32 * 4k 32∗32∗4k 的 regression 坐标回归特征矩阵
对应 RPN 的 positive/negative 分类和 bounding box regression 坐标回归
Proposal Layer
Proposal Layer负责综合所有 ( d x ( A ) , d y ( A ) , d w ( A ) , d h ( A ) ) (d_x(A), d_y(A), d_w(A), d_h(A)) (dx(A),dy(A),dw(A),dh(A)) 变换量和 positive anchors,计算出精准的proposal,送入后续 RoI Pooling Layer
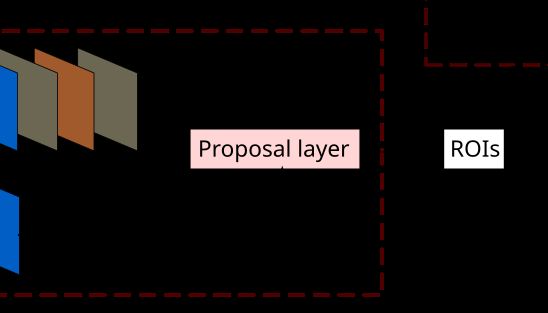
Proposal Layer有3个输入:positive/negative anchors 分类器结果 rpn_cls_score, ( d x ( A ) , d y ( A ) , d w ( A ) , d h ( A ) ) (d_x(A), d_y(A), d_w(A), d_h(A)) (dx(A),dy(A),dw(A),dh(A)) 的变换量 rpn_bbox_pred,img_info(包含 feat_stride = 16)
img_info: 对于一副任意大小 PxQ 图像,传入 Faster RCNN 前_prob概首先reshape到固定 MxN,im_info=[M, N, scale_factor] 保存了此次缩放的所有信息。然后经过 VGG16,经过4次 max_pooling2d 变为 WxH=(M/16)x(N/16) 大小,其中 feature_stride=16 则保存了该信息,用于计算 anchor 偏移量
Proposal Layer forward(前传函数)按照以下顺序依次处理:
- 生成anchors,利用 $ (d_x(A), d_y(A), d_w(A), d_h(A)) $ 对所有的 anchors 做 bbox regression 回归(这里的 anchors 生成和训练时相同)
- 按照输入的 positive softmax scores 由大到小排序 anchors,提取前 pre_nms_top N(e.g. 5000) 个anchors,即提取修正位置后的 positive anchors
- 限定超出图像边界的 positive anchors 为图像边界,防止后续 ROIpooling 时 proposal 超出图像边界
- 剔除尺寸非常小的 positive anchors
- 对剩余的 positive anchors 进行NMS(极大值抑制)
- Proposal Layer 有3个输入: positive 和 negative anchors 分类器结果 rpn_cls_score,对应的 bbox reg 的 (e.g. 300) 结果作为 proposal 输出
输出 proposal 为 [x_min, y_min, x_max, y_max],由于需要将 anchors 映射回原图判断是否超出边界,所以 proposal 对应的图像尺度为 MxN
ROIHead
在传统的CNN网络中,当训练好后输入的图像尺寸必须是固定值,同时网络输出也是固定大小的 vector or matrix,如果输入图像大小不定,过去有2种解决办法:
- 从图像中 crop 一部分传入网络
- 将图像warp成需要的大小后传入网络
crop后破坏了图像的完整结构,warp后破坏了图像原始形状信息,两种方法都不好
为了使网络可以接收不同大小的图像,Faster RCNN 中提出了 ROIPooling,ROIPooling 从 Spatial Pyramid Pooling 发展而来,这里不展开讨论
ROI pooling
ROIpooling 对 proposal 对 feature map 裁剪后的 ROIs 进行 maxpooling 使输入的 shape 相同,生成 proposal feature maps,它有3个参数:
- pooled_w: proposal feature maps 的 width
- pooled_h: proposal feature maps 的 width
- spatial_scale: 是 VGG16 提取 feature map 后对图像尺度的改变,也就是 feature_stride=16
由于 proposal 是对应 MxN 尺度的,所以首先使用 spatial_scale 将其映射回 (M/16)x(N/16) 大小的 feature map 尺度,再将每个 proposal 对应的 feature map 区域水平分为 pooled_w x pooled_h 的网格,对网格的每一份都进行max pooling处理
例:
假定输入 feature map 为
假定区域建议为
假定 pooled_w=2, pooled_h=2
对网格的每一份都进行 max pooling 处理
这种方法显著加快了训练和测试时间
Classification
利用 ROIpooling 输出的 proposal feature maps,通过 1x1的conv2d 层与 softmax 计算每个 proposal 具体属于那个类别,输出 cls_prob 概率向量,同时再次利用 bounding box regression 获得每个 proposal 的位置偏移量 bbox_pred,用于回归更加精确的目标检测框
训练过程
论文源码中训练 Faster RCNN 有两种方式,一种是四步交替训练法,一种是 end-to-end 训练法,本文只讨论四步交替训练法
由前面我们可知,Faster RCNN 大概可以分为 RPN 网络和 Fast RCNN 网络部分
-
训练 RPN,用 feature map 初始化 RPN 网络,并端到端微调,生成 region proposal
-
用 feature map 初始化 Fast RCNN 网络部分,利用第一步的 RPN 生成的 region proposals 作为输入数据,接着训练 Fast RCNN部分,这时两个网络没有共享卷积层
-
用第二步的 Fast RCNN model 初始化 RPN 第二次进行训练,但固定共享的卷积层,并且只微调 RPN 独有的层,现在两个网络共享卷积层
-
由第三步的 RPN model 初始化 Fast RCNN 网络部分,输入数据为第三步生成的 proposals,保持共享的卷积层固定,微调 Fast RCNN 网络部分 Classification 中的卷积层,两个网络共享相同的卷积层,构成一个统一的网络,也就是论文中的 unified network
文中提到的共享卷积层的方法为迁移学习中的技术: 微调(fine tunin)
参考
-
Faster R-CNN: Towards Real-Time Object Detection with Region Proposal Networks Shaoqing Ren; Kaiming He; Ross B. Girshick; Jian Sun 0001
-
Fast R-CNN Ross Girshick; Microsoft Research
-
Research on Apple Detection Classification and Location Technology in Complex Environment Based on Deep Learning Tian Bokai; Professor Yue Youjun
-
Apple Target Detection Based on Improved Faster - RCNN Framework of Deep Learning LI Linsheng; ZENG Pingping
-
https://github.com/FurkanOM/tf-faster-rcnn
-
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_43198141/article/details/90178512
-
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/31426458
-
https://github.com/jinfagang/keras_frcnn
-
https://github.com/bubbliiiing/faster-rcnn-keras
-
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_40449426/article/details/78141635