【论文笔记】API-Net:Learning Attentive Pairwise Interaction for Fine-Grained Classification
API-Net
- 简介
- 创新点
-
- mutual vector learning(互向量学习)
- gate vector generation(门向量生成器)
- pairwise interaction(成对交互)
- 队构造(Pair Construction)
- 实验结果
- 总结
简介
- 2020年发表在AAAI的一篇细粒度分类论文。
- 人类在区分不同子类的图像时,会成对地进行比较。本文模仿这一行为,同时提取并融合一对图片的特征,提高了网络辨别不同目标的能力。
- 槽点:开源代码环境居然用的 pyton2.7 + torch0.4.1 的远古版本,实验室服务器CUDA10.0完全没法跑,以后有机会尝试自己复现吧。。。
- 论文地址
- 代码地址
创新点
mutual vector learning(互向量学习)
-
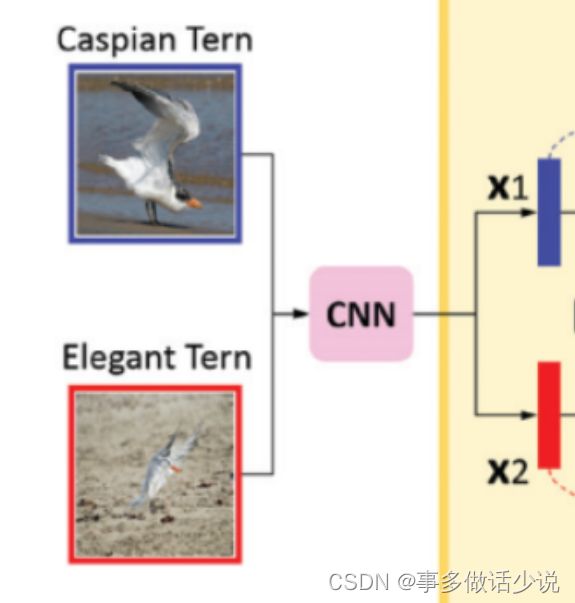
训练过程首先把两张图片输入骨干网络 (ResNet101),分别提取D维度的特征 x 1 x_1 x1 和 x 2 x_2 x2,即: x 1 a n d x 2 ∈ R D x_1\space and \space x_2\in \mathbb{R}^D x1 and x2∈RD
示意图:
-
之后进入 互向量学习 阶段,将 x 1 x_1 x1 和 x 2 x_2 x2 连接,对其使用MLP,即两个全连接加一个Dropout,得到 x m ∈ R D x_m\in \mathbb{R}^D xm∈RD。
x m = f m ( [ x 1 , x 2 ] ) , f m 为 M L P 操 作 x_m=f_m([x_1,x_2]),f_m为MLP操作 xm=fm([x1,x2]),fm为MLP操作
代码:
# 定义
self.map1 = nn.Linear(2048 * 2, 512)
self.map2 = nn.Linear(512, 2048)
self.drop = nn.Dropout(p=0.5)
# concat和两个全连接
mutual_features = torch.cat([features1, features2], dim=1)
map1_out = self.map1(mutual_features)
map2_out = self.drop(map1_out)
map2_out = self.map2(map2_out)
gate vector generation(门向量生成器)
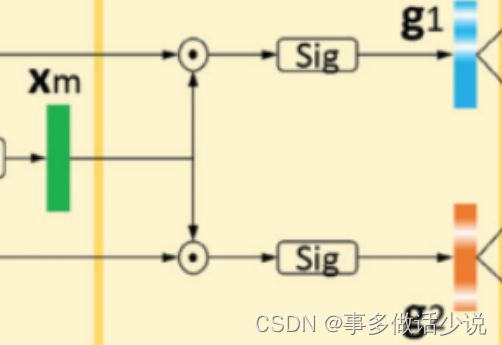
- 先将 xm 与x1 和 x2 作比较,从单独的图片中进一步提取有区别的线索(clue),为后续区分这一对做准备。
- 将 xm 和xi 做通道乘积,对结果用sigmoid,生成门函数(gate vector) g i ∈ R D g_i\in R^D gi∈RD
g i = s i g m o i d ( x m ⊙ x i ) , i ∈ { 1 , 2 } g_i=sigmoid(x_m\odot x_i),i\in \left\{1,2 \right\} gi=sigmoid(xm⊙xi),i∈{1,2}
gi 作为一种区分注意力( discriminative attention),原文说是通过每个个体 xi 的不同视角来突出语义差异。其实就是把 xm 和 xi 点乘后做 sigmoid,我不认为这一步有多大用。
代码:
gate1 = torch.mul(map2_out, features1) # 点乘
gate1 = self.sigmoid(gate1)
gate2 = torch.mul(map2_out, features2)
gate2 = self.sigmoid(gate2)
示意图:
pairwise interaction(成对交互)
- 原文:为了捕捉一对细粒度图像中的细微差异,人类检查每幅图像,不仅有其突出的部分,而且有与其他图像不同的部分。
- 实现:将向量与门两两组合,进行一些操作,得到四个向量:
- x i s e l f x^{self}_i xiself 用自己的门向量进行加强, x i o t h e r x_i^{other} xiother 用自己的门向量和pair中另一副图像进行激活。
- 用来自这两幅图像的鉴别线索( discriminative clues)来增强 xi 。
x 1 s e l f = x 1 + x 1 ⊙ g 1 , x 2 s e l f = x 2 + x 2 ⊙ g 2 , x 1 o t h e r = x 1 + x 1 ⊙ g 2 , x 2 o t h e r = x 2 + x 2 ⊙ g 1 , x_1^{self}=x_1+x_1\odot g_1,\\ x_2^{self}=x_2+x_2\odot g_2,\\ x_1^{other}=x_1+x_1\odot g_2,\\ x_2^{other}=x_2+x_2\odot g_1, x1self=x1+x1⊙g1,x2self=x2+x2⊙g2,x1other=x1+x1⊙g2,x2other=x2+x2⊙g1,
代码:
# 点乘后相加
features1_self = torch.mul(gate1, features1) + features1
features1_other = torch.mul(gate2, features1) + features1
features2_self = torch.mul(gate2, features2) + features2
features2_other = torch.mul(gate1, features2) + features2
#全连接后dropout,得到结果
logit1_self = self.fc(self.drop(features1_self))
logit1_other = self.fc(self.drop(features1_other))
logit2_self = self.fc(self.drop(features2_self))
logit2_other = self.fc(self.drop(features2_other))
之后便是常规的softmax以及计算损失,得到最终结果。
值得一提的是,计算损失过程中除了交叉熵损失,还添加了一个排序损失 L r k L_{rk} Lrk 。
作用是让 p i o t h e r p_i^{other} piother 的优先级更低。
其实就是MarginRankingLoss:
L r k = ∑ i ∈ { 1 , 2 } m a x ( 0 , p i o t h e r ( c i ) − p i s e l f ( c i ) + ξ ) L_{rk}=\sum_{i\in \left \{ 1,2 \right\}}max(0,p^{other}_i(c_i)-p^{self}_i(c_i)+\xi) Lrk=i∈{1,2}∑max(0,piother(ci)−piself(ci)+ξ)
# 定义
criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss().to(device)
rank_criterion = nn.MarginRankingLoss(margin=0.05)
# 实现
softmax_loss = criterion(logits, targets)
rank_loss = rank_criterion(self_scores, other_scores, flag)
loss = softmax_loss + rank_loss
队构造(Pair Construction)
利用欧氏距离找到每张图像和batch中类间图象以及类内图像最接近的两对
细节如下:
- 在一批(batch)中随机抽取 N c l N_{cl} Ncl 个类,在每个类中随机抽取 N i m N_{im} Nim 个训练图像;
- 我们将所有这些图像输入CNN主干,生成它们的特征向量;
- 根据欧氏距离,将每幅图像的特征和batch中其他图像的特征进行比较;
- 对每张图像构造出1)类内/类间pair,包含本身的特征,2)batch中类内/类间最相近的特征组成;
- 所以,每一个batch中有 2 × N c l × N i m 2\times N_{cl}\times N_{im} 2×Ncl×Nim 个pair;
- 把它们所有的损失L进行总结并进行端到端训练。
代码:
def get_pairs(self, embeddings, labels): # 得到的结果不影响网络梯度
distance_matrix = pdist(embeddings).detach().cpu().numpy() # detach():不计算梯度 转到numpy
labels = labels.detach().cpu().numpy().reshape(-1,1)# 变成一列
num = labels.shape[0] # 个数
dia_inds = np.diag_indices(num) # 得到num维数组的对角线的索引
lb_eqs = (labels == labels.T)
lb_eqs[dia_inds] = False
dist_same = distance_matrix.copy()
dist_same[lb_eqs == False] = np.inf
intra_idxs = np.argmin(dist_same, axis=1) # 按行取最小值
dist_diff = distance_matrix.copy()
lb_eqs[dia_inds] = True
dist_diff[lb_eqs == True] = np.inf
inter_idxs = np.argmin(dist_diff, axis=1)
intra_pairs = np.zeros([embeddings.shape[0], 2])
inter_pairs = np.zeros([embeddings.shape[0], 2])
intra_labels = np.zeros([embeddings.shape[0], 2])
inter_labels = np.zeros([embeddings.shape[0], 2])
for i in range(embeddings.shape[0]):
intra_labels[i, 0] = labels[i]
intra_labels[i, 1] = labels[intra_idxs[i]]
intra_pairs[i, 0] = i
intra_pairs[i, 1] = intra_idxs[i]
inter_labels[i, 0] = labels[i]
inter_labels[i, 1] = labels[inter_idxs[i]]
inter_pairs[i, 0] = i
inter_pairs[i, 1] = inter_idxs[i]
intra_labels = torch.from_numpy(intra_labels).long().to(device)
intra_pairs = torch.from_numpy(intra_pairs).long().to(device)
inter_labels = torch.from_numpy(inter_labels).long().to(device)
inter_pairs = torch.from_numpy(inter_pairs).long().to(device)
return intra_pairs, inter_pairs, intra_labels, inter_labels
实验结果
CUB-200-2011
总结
- 我个人认为本文的实验结果不算惊艳,网络中的很多步骤我也不明白为啥能够得到正反馈,包括作者自己也只是概括地介绍。
- 但必须承认API-Net的思路很有创新性,并且也能够取得较高的精度。