多项式回归
- 多项式回归基本概念
- Scikit-Learn中多项式回归
- 关于PolynomialFeatures
多项式回归基本概念
- 对于线性回归,数据都是线性的,目标是寻找一条直线,尽可能的拟合样本。但实际任务中,数据往往是非线性,因此需对线性回归算法进行一些转换改造,即多项式回归。
- 多项式回归中,数据不太具有线性关系,因此应寻找一些非线性曲线去拟合。如下图,用一条二次曲线去拟合数据,效果更好。
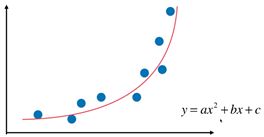
- 对于上面的数据,原本是只有x一个特征,但是我们可以构造一个新的特征 x 2 x^2 x2,即构成了二次函数。将二次函数看成 y = a x 1 + b x + c y=ax_1+bx+c y=ax1+bx+c 其中( x 1 = x 2 x_1= x^2 x1=x2)。这样就又变成解多元线性回归的问题了。
Scikit-Learn中多项式回归
- scikit-learn 中并没有直接封装多项式回归。
- 通过使用 sklearn.preprocessing.PolynomialFeatures 改变样本幂次,构造新特征,再调用线性回归来实现多项式回归。
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.preprocessing import PolynomialFeatures
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
x = np.random.uniform(-3, 3, size=100)
X = x.reshape(-1, 1)
y = 0.5 * x**2 + x + 2 + np.random.normal(0, 1, 100)
poly = PolynomialFeatures(degree=2)
poly.fit(X)
X2 = poly.transform(X)
>>>X2[:5,:]
>>>'''第一例是x0特征,第二列原样本,第三列原样本2次幂样本'''
array([[ 1. , 0.14960154, 0.02238062],
[ 1. , 0.49319423, 0.24324055],
[ 1. , -0.87176575, 0.75997552],
[ 1. , -1.33024477, 1.76955114],
[ 1. , 0.47383199, 0.22451675]])
lin_reg2 = LinearRegression()
lin_reg2.fit(X2, y)
y_predict2 = lin_reg2.predict(X2)
plt.scatter(x, y)
plt.plot(np.sort(x), y_predict2[np.argsort(x)], color='r')
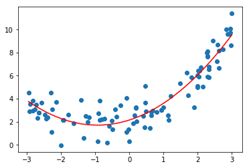
'''创建模拟数据使用的方程 y = 0.5 * x**2 + x + 2 + np.random.normal(0, 1, 100)'''
>>>lin_reg2.coef_
'''得到系数与原方程1和0.5相当接近'''
array([ 0. , 0.9460157 , 0.50420543])
'''得到截距与原方程2相当接近'''
>>>lin_reg2.intercept_
2.1536054095953823
关于PolynomialFeatures
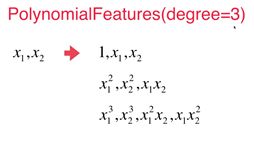
- 对于原样本不只一个特征时,PolynomialFeatures 构造新样本特征采用如下规则:
X = np.arange(1, 11).reshape(-1, 2)
>>> X.shape
(5,2)
>>> X
array([[ 1, 2],
[ 3, 4],
[ 5, 6],
[ 7, 8],
[ 9, 10]])
poly = PolynomialFeatures(degree=2)
poly.fit(X)
X2 = poly.transform(X)
>>> X2.shape
(5, 6)
>>> X2
array([[ 1., 1., 2., 1., 2., 4.],
[ 1., 3., 4., 9., 12., 16.],
[ 1., 5., 6., 25., 30., 36.],
[ 1., 7., 8., 49., 56., 64.],
[ 1., 9., 10., 81., 90., 100.]])
''' 第1例x0特征,第2、3列原样本,第4、6列原样本2次幂,第5列两个原样本乘积
x1 ,x2 --> 1, x1, x2, x1^2, x1x2, x2^2
'''
- 当PolynomialFeatures(degree=3)时,有10项: