python模块学习记录1------argparse函数
这个函数的官方解释是用于解析命令行参数。
有三个步骤:
- 创建 ArgumentParser() 对象
- 调用 add_argument() 方法添加参数
- 使用 parse_args() 解析添加的参数
但到底它的作用是什么,该如何使用?
目录
写一个计算圆柱体积的程序:
用argparse函数完成上面的工作:
二者区别:
调用help命令看看:
编辑使用选择性参数:
让help命令下的文字简洁一点:
如果只赋值了一个参数:
互斥参数:
总结:
写一个计算圆柱体积的程序:
计算半径为2,高度为4的圆柱体积
import math
def cylinder_volume(radius, height):
vol = (math.pi) * (radius ** 2) * (height)
return vol
if __name__ == '__main__':
print(cylinder_volume(2,4))在cmd上运行结果:
用argparse函数完成上面的工作:
import math
import argparse
# 创建一个解析对象parser
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description='Calculate volume of a Cylinder')
# 添加命令行参数。type默认的是字符串类型,help用来描述这个命令行参数
parser.add_argument('radius', type=int, help='Radius of Cylinder')
parser.add_argument('height', type=int, help='Height of Cylinder')
# 进行解析
args = parser.parse_args()
def cylinder_volume(radius, height):
vol = (math.pi) * (radius ** 2) * (height)
return vol
if __name__ == '__main__':
print(cylinder_volume(args.radius, args.height))二者区别:
对比在cmd的命令会发现,使用argparse函数时,可以在命令里面随时修改参数,而不用每次都打开python原始程序进行修改。
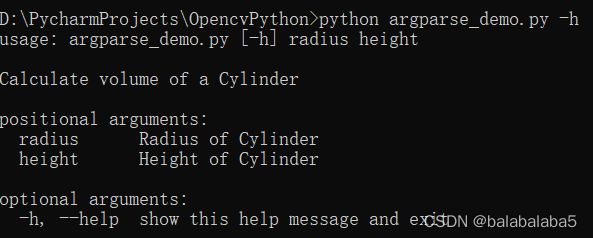
调用help命令看看:
第一个参数必须是半径radius,第二个参数必须是高度height。
再对比一下其他的内容:
 使用选择性参数:
使用选择性参数:
程序修改如下:
# 创建一个解析对象parser
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description='Calculate volume of a Cylinder')
# 添加命令行参数。type默认的是字符串类型,help用来描述这个命令行参数
parser.add_argument('-r', '--radius', type=int, help='Radius of Cylinder')
parser.add_argument('-H', '--height', type=int, help='Height of Cylinder')
# 进行解析
args = parser.parse_args()结果:
这样修改它们的位置也不会颠倒了。
让help命令下的文字简洁一点:
用空的字符串代替
# 创建一个解析对象parser
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description='Calculate volume of a Cylinder')
# 添加命令行参数。type默认的是字符串类型,help用来描述这个命令行参数
parser.add_argument('-r', '--radius', type=int, metavar='', help='Radius of Cylinder')
parser.add_argument('-H', '--height', type=int, metavar='', help='Height of Cylinder')
# 进行解析
args = parser.parse_args()原来:
现在:
如果只赋值了一个参数:
该程序本应该要两个参数才能求出体积,但如果只赋值了一个参数,另一个参数就会赋值为None。那程序肯定会出现错误。
如何避免这一现象?使用required属性。
# 创建一个解析对象parser
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description='Calculate volume of a Cylinder')
# 添加命令行参数。type默认的是字符串类型,help用来描述这个命令行参数
parser.add_argument('-r', '--radius', type=int, metavar='', required=True,help='Radius of Cylinder')
parser.add_argument('-H', '--height', type=int, metavar='', required=True,help='Height of Cylinder')
# 进行解析
args = parser.parse_args()互斥参数:
import math
import argparse
# 创建一个解析对象parser
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description='Calculate volume of a Cylinder')
# 添加命令行参数。type默认的是字符串类型,help用来描述这个命令行参数
parser.add_argument('-r', '--radius', type=int, metavar='', required=True,help='Radius of Cylinder')
parser.add_argument('-H', '--height', type=int, metavar='', required=True,help='Height of Cylinder')
# 添加互斥组
group = parser.add_mutually_exclusive_group()
# 给action赋值store_true的时候程序默认为False。当执行这个命令的时候默认值就会被激活成True
group.add_argument('-q', '--quiet', action='store_true', help='print quiet')
group.add_argument('-v', '--verbose', action='store_true', help='print verbose')
# 进行解析
args = parser.parse_args()
def cylinder_volume(radius, height):
vol = (math.pi) * (radius ** 2) * (height)
return vol
if __name__ == '__main__':
volume = cylinder_volume(args.radius, args.height)
if args.quiet:
print(volume)
elif args.verbose:
print("volume of a Cylinder with radius %s and height %s is %s" % (args.radius, args.height, volume))
else:
print("volume of Cylinder = %s" % volume)在主程序这里的条件语句就大概能猜到这个互斥是什么意思了。
不能同时执行两个命令,可以执行一个,可以一个都不执行,就是不能同时执行两个。
结果:
总结:
argparse函数是让你可以在命令行快速地运行程序,通过-h命令来查看需要的参数和参数的含义。不用再返回pycharm或者其他的编辑器里去修改参数了。