【北邮国院大三上】电子商务法(e-commerce law)知识点整理——Jurisdiction&ISP liability
北邮国院大三电商在读,随课程进行整理知识点。仅整理PPT和相关法条中相对重要的知识点,个人认为相对不重要的细小的知识点不列在其中。如有错误请指出。转载请注明出处,祝您学习愉快。
jurisdiction
管辖权
- 两个定义:
- Power to Regulate or prescribe laws –by a state within its territorial borders
- 一个国家在其领土边界内规定或制定法律的权力
- Power of a court to adjudicate cases and issue and enforce its orders
- 法院裁决案件、发布和执行其命令的权力
legislative jurisdiction
立法管辖权
- Person within a territory must obey the law or face sanctions
- 在一个领土内的人必须遵守法律,否则将面临制裁
Disputes: many ‘causes of action’
有三种cause
- Contractual
- 契约性的
- non-contractual
- 非契约的
- e.g.: harm/injury caused to another – ‘tort’ law, such as ‘defamation’ (injuring the good reputation of a person) or Intellectual Property Violations
- 对他人造成的伤害——“侵权法”,如“诽谤”(损害某人的良好声誉)或侵犯知识产权
- criminal
- 犯法的
Adjudicatory & Enforcement Jurisdiction
When a court decides a case and issues orders against any person, the person has to obey or appeal
当法院判决一个案件并发布针对任何人的命令时,该人必须服从或上诉
- If Appealed: Final order obey
- 如果上诉:服从最终命令
- If not, court can compel enforcement
- 如果没有,法院可以强制执行
Court’s power
- Seize and freeze assets
- 扣押和冻结资产
- Compel attendance
- 强迫出席
- Hear cases ‘ex parte’
- “单方面”审理案件
- Etc… (a range of powers)
Adjudicatory jurisdiction
审判管辖
有两个特点:
- Subject matter
与事件相关(每个court有每个court负责的事务/方面) - Over the person(personal)
- General rule: A court has jurisdiction over a person within its ‘territory’ (personal jurisdiction)
- 一般规则:法院对其“领土”内的人有管辖权(属人管辖权)
Some terms
- Person who initiates action in court –plaintiff
- 在法庭上提起诉讼的人——原告
- Person against whom action is initiated in court - defendant
- 在法庭上被提起诉讼的人-被告
各地都有法院,我们的问题是什么时候可以让被告在原告选择的法院进行诉讼?
接下来涉及的法律为China Civil Procedure Law
Location based rules
一共有三个rules
- Default
- Contract
- Tort
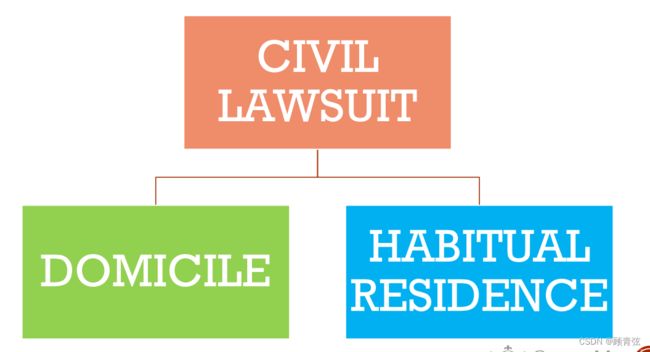
Default rule(Art.22)
Article 22
A civil lawsuit brought against a citizen shall be under the jurisdiction of the people’s court of the place where the defendant has his domicile; if the place of the defendant’s 5 domicile is different from that of his habitual residence, the lawsuit shall be under the jurisdiction of the people’s court of the place of his habitual residence. A civil lawsuit brought against a legal person or any other organization shall be under the jurisdiction of the people’s court of the place where the defendant has his domicile.
对公民提起的民事诉讼,由被告住所地人民法院管辖;被告住所地与经常居所地不一致的,由被告经常居所地人民法院管辖。对法人或者其他组织提起的民事诉讼,由被告住所地人民法院管辖。
【反正就是原告被告不在一个地方就去被告那】
domicile
永久居住地
- a person can have only one ‘domicile’
- 一个人只能有一个“住所”
- A person must intend to reside in a place permanently or indefinitely
- 一个人必须打算永久或无限期地居住在一个地方
habitual residence
通常住址
- Habitual residence in two or more places possible
- 可能在两个或两个以上的地方经常居住
- Regular physical presence in a place, over time
- 随着时间的推移,经常出现在一个地方
【这两个定义在法律中没有明确给出】
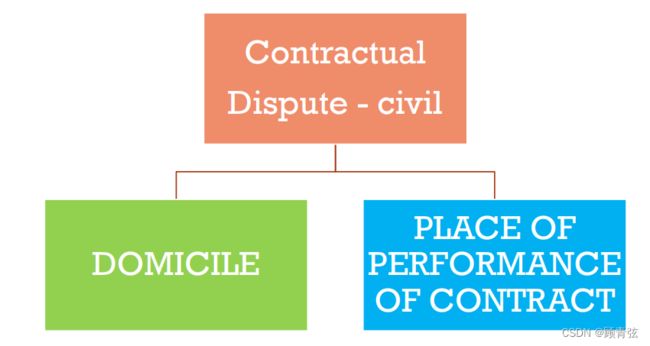
Contract rule(Art.24,25)
Article 24 A lawsuit brought on a contract dispute shall be under the jurisdiction of the people’s court of the place where the defendant has his domicile or where the contract is performed.
因合同纠纷提起的诉讼,由被告住所地或者合同履行地人民法院管辖。
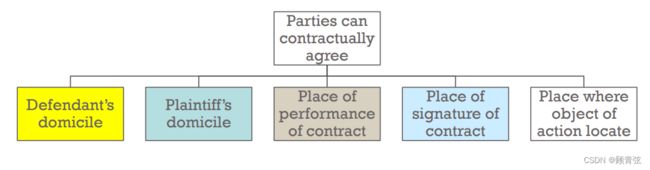
Article 25 The parties to a contract may agree to choose in their written contract the people’s court of the place where the defendant has his domicile, where the contract is performed, where the contract is signed, where the plaintiff has his domicile or where the object of the action is located to exercise jurisdiction over the case, provided that the provisions of this Law regarding jurisdiction by forum level and exclusive jurisdiction are not violated
当事人可以在书面合同中约定,由被告住所地、合同履行地、合同签订地、原告住所地、诉讼对象所在地的人民法院管辖,但不违反本法有关地级管辖和专属管辖的规定
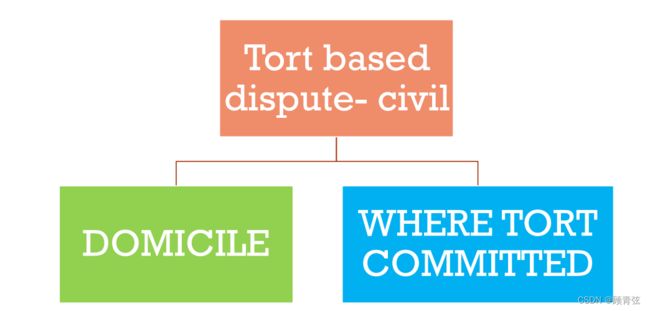
Tort rule(Art.29)
Article 29
A lawsuit brought on a tortious act shall be under the jurisdiction of the people’s court of the place where the tort is committed or where the defendant has his domicile.
因侵权行为提起的诉讼,由侵权行为地或者被告住所地人民法院管辖。
Court can only take case if within its jurisdiction——CPL(Art.36)
- CPL gives the court (i.e. the judges) many powers
- 就是我们上面说的那些court的权利都是CPL给的
涉及到境外的该去哪个法院(Art.243,244,245)
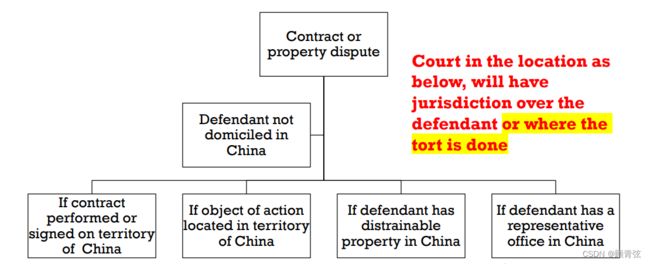
Article 243
In the case of an action concerning a contract dispute or other disputes over property rights and interests, brought against a defendant who has no domicile within the territory of the People’s Republic of China, if the contract is signed or performed within the territory of the People’s Republic of China, or if the object of the action is located within the territory of the People’s Republic of China, or if the defendant has distrainable property within the territory of the People’s Republic of China, or if the defendant has its representative office within the territory of the People’s Republic of China, the people’s court of the place where the contract is signed or performed, or where the object of the action is, or where the defendant’s distrainable property is located, or where the torts are done, or where the defendant’s representative office is located, shall have jurisdiction
对在中华人民共和国境内没有住所的被告提起的合同纠纷或其他财产权益纠纷诉讼,如果合同是在中华人民人民共和国境外签订或履行的,或者,如果诉讼标的位于中华人民共和国境内,或者被告在中华人民共和国境内有可扣押的财产,或者被告的代表机构在中华人民国境内,则由合同签订地或履行地的人民法院,或诉讼对象所在地、被告可扣押财产所在地、侵权行为发生地或被告代表处所在地具有管辖权
Article 244 Parties to a dispute over a contract concluded with foreign element or over property rights and interests involving foreign element may, through written agreement, choose the court of the place which has practical connections with the dispute to exercise jurisdiction. If a people’s court of the People’s Republic of China is chosen to exercise jurisdiction, the provisions of this Law on jurisdiction by forum level and on exclusive jurisdiction shall not be violated.
涉外合同或者涉外财产权益纠纷的当事人,可以通过书面协议选择与纠纷有实际联系的地方法院管辖。选择中华人民共和国人民法院管辖的,不得违反本法关于法院级管辖和专属管辖的规定。

Article 245 If in a civil action in respect of a case involving foreign element, the defendant raises no objection to the jurisdiction of a people’s court and responds to the action by making his defence, he shall be deemed to have accepted that this people’s court has jurisdiction over the case.
在涉外民事诉讼中,被告人对人民法院管辖不提出异议,并作出答辩的,视为接受人民法院管辖。

-
Foreign court judgments are rarely recognised and enforced in China.
-
外国法院的判决在中国很少得到承认和执行。
由于: -
multilateral treaty required
-
多边条约要求
-
Bilateral judicial assistance treaty required
-
需要签订双边司法协助条约
-
Or principle of reciprocity
-
或者互惠原则
-
In practice, China has few treaties and reciprocity basis is limited
-
在实践中,中国条约很少,互惠基础有限
-
Under PRC law, parties to a foreign-related contract are free to choose PRC law or any other law to govern their contract, regardless of whether the chosen law has a connection to their transaction
根据中国法律,涉外合同的当事人可以自由选择中国法律或任何其他法律管辖其合同,无论所选择的法律是否与交易有关
【相关法律:Art.3,7 】
Foreign related contract
- at least one party is a foreign national/corporation;
- 至少有一方是外国国民/公司;
- at least one party has its habitual residence outside PRC;
- 至少一方当事人在中国境外有经常居所;
- the object of the contract is located outside PRC;
- 合同标的在中国境外;
- the contractual relationship was made, amended or ended outside PRC; or
- 合同关系在中国境外订立、修改或终止的
- other circumstances which may be construed as foreign related.
- 其他可解释为涉外的情形。
Note:
(1) this rule only applies to contractual matters. Chinese law will apply where ‘mandated’ – such as product liability and other laws.
这条规则只适用于合同事项。中国法律将适用于“强制”的地方,比如产品责任和其他法律。
(2) Choice of foreign law may be construed against “public interest” or rejected on other grounds.
选择外国法律可能被解释为违背“公共利益”或以其他理由拒绝。
Regulation is based on territory
监管以地域为基础
- State can regulate what occurs within its territory. Location is the criterion for the regulation of activities
国家可以监管其领土内发生的事情。位置是活动调节的标准
【不涉及法条,这三句话可以拿来当相应事件的凑字数用的话】
Sovereignty:Each country has power to conduct its own affairs (legal, political, etc.)within its borders
主权:每个国家都有权在其边界内处理自己的事务(法律、政治等)
Comity:States to recognize the jurisdiction of other states (not interfere)
礼让:各国承认其他国家的管辖权(不干涉)
Transnational Jurisdiction——3 types
- Prescriptive regulation – right to make laws within territory
- Right to adjudicate – when there is a dispute, the right to adjudicate the dispute
- Enforcement – right to enforce its judgment (within its territory)- no State can send its police or other agents into another state’s territory to enforce a judgment given by its court
1)规定性的规制——在领土内制定法律的权利 2)审判权——当存在争议时,对争议进行裁决的权利
3)执行——(在其领土内)执行其判决的权利——任何国家都不能派遣其警察或其他代理人进入另一个国家的领土执行其法院作出的判决
不同国家之间的jurisdiction
Each country determines the jurisdiction of its courts to entertain a civil law suit
In China the national – CPL – dictates jurisdiction
in other countries, it may be a national law or state law (as in the U.S., GERMANY, U.K. ETC)
Most countries allow the parties to agree to the jurisdiction of a court
which court has jurisdiction in a civil action when the parties have not agreed on or submitted to the forum – decided by PLACE OF PERFORMANCE/ SIGNATURE OF CONTRACT OR WHERE tort was committed or where its effects were felt
每个国家决定其法院受理民事诉讼的管辖权在中国,国家- CPL -规定管辖权
在其他国家,它可能是国内法或州法(如美国、德国、大多数国家允许当事人同意某一法院的管辖权,
当当事人未就民事诉讼达成协议或提交法庭时,该法院对民事诉讼具有管辖权——由合同履行/签署地点或侵权行为发生地或侵权影响感受到地决定
基于互联网的jurisdiction
【案例:Yahoo案,简单来说就是Yahoo卖的东西(带有纳粹标识的东西)违背了法国法律,理论上在美国运营的网站是不需要为法国的法律买单的,但是由于法国法院判定这个事情对法国产生了影响,就勒令Yahoo限制法国的用户访问相关商品,如果不改的话就罚款,但是Yahoo向美国法院起诉说我们做不到,而且这样的禁令侵犯权利,认为不应该执行。但是如果不改/不交罚款,Yahoo的高管还是会面临一些问题,比如在法国可能会被逮捕。所以Yahoo用了尽可能多的限制器来限制访问】
【所以就引出了最核心的争论,一个全球都可以访问的网站究竟应该遵守什么法律呢?】
-
States now consistently applying traditional territorially based rules to online activity
-
各州现在一贯地对网络活动适用传统的以领土为基础的规则
-
China: websites not in compliance with Chinese laws cannot be accessed within China. Blocked by the government itself (how effectively, that’s another issue)
-
中国:不符合中国法律的网站不能在中国境内访问。被政府本身阻塞(有效程度如何,这是另一个问题)
接下来是ISP LIABILITY部分
Legal liability
法律责任
有两种分类
- We are liable for our acts that harm others
我们要对自己伤害他人的行为负责
2.We can also be liable to others for harm done to them by someone else. From authority, control or participation in the act that caused the harm
我们也可以为他人对他人造成的伤害承担责任。不受权威、控制或参与造成伤害的行为的影响
【这里机翻有点问题,我的理解是间接参与了harm,或者说对这个harm有间接责任,比如雪天你的店门口没有警示标示而且没扫雪导致客人摔倒等等】
Sources of liability
- tort law 侵权行为法
- privacy law 隐私权法
- IP laws (Intellectual property law) 知识产权法
- Criminal laws 刑法
- Specific laws - e.g. laws against hate speech etc.
具体的法律,例如反对仇恨言论的法律等
Tort
Tort From French for “wrong,” a civil wrong or wrongful act, whether intentional or accidental, from which injury occurs to another.
源自法语,意为“错误”,一种民事错误或不正当的行为,无论是有意的还是偶然的,由此对他人造成伤害。
Torts include all negligence cases as well as intentional wrongs which result in harm.
侵权行为包括所有过失案件以及导致损害的故意错误行为。
Tort law is one of the major areas of law (along with contract, real property and criminal law) and results in more civil litigation than any other category.
侵权法是法律的主要领域之一(与合同法、不动产法和刑法一样),比其他任何类别的法律都导致更多的民事诉讼。
Tort liability arises from
- Duty of care 注意义务
- Failure to fulfil that duty 未能履行这一职责
- Connection (proximate cause) of that failure to some injury or harm to a person
失败与某人受到的某种伤害或伤害有关(近因)
Reputation Tort——Defamation
侵权
False statement relating to another person that causes injury to reputation. Speech that is harmful to the reputation of others, be it a natural person or a legal person.
关于他人造成名誉损害的虚假陈述。损害他人名誉的言论,无论是自然人还是法人。
Defamation, including intentionally telling harmful untruths about another-either by print or broadcast (libel) or orally (slander)-is a type of tort and in some countries it can be a crime as well (Singapore, China for e.g.)
诽谤,包括故意讲述他人的有害的谎言——通过印刷或广播(诽谤)或口头(诽谤)——是一种侵权行为,在一些国家也可能是一种犯罪(例如新加坡、中国)。
【这里的案例就是说你在广告板/报纸上诽谤一个人,投广告的人/写文章的人肯定有责任,但是广告公司、做广告的人/报社也承担责任】
【注意一点,这里说广告公司/报社都有责任的时候,都用了一句话,叫做“If acting with knowledge” ,我的理解是因为他们知道这个消息,虽然不知道真假,但是有义务去查验真假,但是他们没有而是传播了这个诽谤消息所以有责任】
Publisher Liability
Factors that indicate publisher liability include evidence of exercising editorial control and judgment over the choice of material
显示出版商责任的因素包括行使编辑控制的证据和对材料选择的判断
Distributor Liability
Distributors are rarely aware of the content of the material they distribute
分发者很少知道他们分发的材料的内容
• If aware, cannot check if statements are false
如果意识到,不能检查语句是否为假
‘Distributor Defence’: No liability if distributor can show that took reasonable care, did not know, had no reason to believe that caused publication of a defamatory statement
“经销商辩护”:如果经销商能够证明其采取了合理的谨慎措施,不知道,没有理由相信这导致了诽谤声明的发表,则无需承担责任
No actual knowledge of a defamatory statement
对诽谤性言论一无所知
user generated content – UGC
用户生成的内容【这个词以后会见很多次,记住UGC是什么】
接下来的重点就是China,EU,US这三个地方的ISP liability。
先从China开始
- 首先说的就是中国有60种定义有害内容的法律/指南,比如PRC Tort Law,但不做重点,我们的重点还是ISP相关
- 简单说一下ISP是啥,Internet Service Provider,和互联网协议中的ISP是一个东西
Joint liability
连带责任
The Civil Law: Art.130
- If two or more persons jointly infringe upon another person’s rights and cause him damage, they shall bear joint liability.
- 二人以上共同侵犯他人权利造成损害的,应当承担连带责任。
China Tort Law: Art.6,8
-
Article 6 One who is at fault for infringement upon a civil right or interest of another person shall be subject to the tort liability.
侵犯他人民事权利、利益有过错的,应当承担侵权责任。 -
Article 8 Where two or more persons jointly commit a tort, causing harm to another person, they shall be liable jointly and severally.
二人以上共同实施侵权行为,给他人造成损害的,应当承担连带责任。
ISP jointly liable
China Tort Law: Art.36 (ISP相关的Joint Liability)
-
Article 36 Where network users or Internet service providers utilize network to commit a tort to other’s civil rights and interests, they shall be subject to tort liability
网络用户或者互联网服务提供者利用网络对他人民事权益实施侵权的,应当承担侵权责任 -
A. 36 Where a network service provider knows that a network user is infringing upon a civil right or interest of another person through its network services, and fails to take necessary measures, it shall be jointly and severally liable for any additional harm with the network user
网络服务提供者知道网络用户通过其网络服务侵犯他人民事权利、利益而不采取必要措施的,应当与网络用户承担额外损害的连带责任
那么我们如何判断ISP是不是“know”呢?
SPC (Supreme People’s Court, 最高人民法院)给了一些判断条件
- Article 9 of the SPC Regulations provide a number of possible factors
– did the ISP actively process the information?
– could the ISP reasonably be expected to have had the ability to identify that kind of information?
– the degree to which it is clear that the information is unlawful
– its influence and hit rate
– the extent to which it is possible to carry out remedial measures
– whether a case concerns repeated infringement by the same user or through the same information
- ISP是否积极处理信息?
-是否可以合理地期望ISP有能力识别这类信息?
-该资料非法的明确程度
-其影响力和命中率
-可采取补救措施的程度
-案件是否涉及同一用户或通过同一信息进行的重复侵权
China Tort Law 对于ISP的要求
-
核心词语:notice and take down(注意并删除)
-
Where network users utilize the network to commit a tort, the infringee shall
– have the right to notify the Internet service provider to take necessary measures such as deleting, blocking, disconnecting, etc.
– If the Internet service provider fails to take necessary measures in a timely manner after receipt of the notice, it shall be subject to joint and several liability with the users for the expanded damages.
网络用户利用网络实施侵权行为的,被侵权人应当
-有权通知互联网服务供应商采取必要措施,如删除、屏蔽、断开连接等。
-互联网服务提供商在接到通知后未及时采取必要措施的,应当就扩大的损害赔偿与用户承担连带责任。
Art.36 Tort Liability Law
(1) jointly liable due to the failure of taking necessary measures expeditiously upon receiving the notification of victim (within the scope of further loss )
(2) jointly liable if it knows that the internet user is conducting illegal activity by using its internet service and it doesn’t take any necessary measures
(一)在收到受害人通知后未及时采取必要措施的(在进一步损失范围内),承担连带责任的
(二)明知互联网用户利用其互联网服务进行违法活动而不采取必要措施的,承担连带责任
SPC的一些解释
- A.5 Notice has to be in proper form, otherwise does not have to be considered
- 通知必须是正确的形式,否则就不必考虑
- A.6 What is ‘expeditious’ removal clarified
on the basis of factors such as the nature of the network service, the form of valid notification and its degree of accuracy, the type and extent of the infringement of rights and interests through online information, etc
- 什么是“快速”转移
基于网络服务的性质、有效通知的形式及其准确程度、通过网络信息侵犯权益的类型和程度等因素
上面都可以不知道,但是下面这两点要明白
核心要点:Chinese ISPs are highly regulated
Must have manpower and technologies to monitor and filter the information hosted on their platforms - a mix of human reviews and machine filtering.
必须有人力和技术来监控和过滤他们平台上的信息——一种人工审查和机器过滤的混合
Summary of China
-
China imposes tight regulation on harmful or illegal content online
-
Online companies must monitor content and remove any content considered harmful
-
Also, notice and takedown procedures provide some immunity
-
中国对网上有害或非法内容实施严格监管
-
网络公司必须监控内容并删除任何被认为有害的内容
-
此外,通知和下架程序提供了一些豁免
US ISP Liability
ISP Liability(Early case)
Internet Hosts Liability:
– ISPs who monitor, filter and edit content: may have liability as publisher
– ISPs who have a ‘hands off’ approach to hosting content : no liability unless they had actual knowledge
互联网主机责任:
-监控、过滤和编辑内容的isp:可能作为发布者负有责任
-对托管内容采取“不干涉”方式的isp:没有责任,除非他们有实际知识
经过balabalabala的辩论和谈判,关于ISP Liability的法律修改了
核心法律:United States: Communication Decency Act Section 230: Safe Harbour
核心法条:CDA S230 Immunity (1996)
47 U.S.C. §230©(1)
- "No provider or user of an interactive computer service shall be treated as the publisher or speaker of any information provided by another information content provider.“
- “交互式计算机服务的提供者或用户不应被视为另一信息内容提供者提供的任何信息的发布者或发布者。”
Note: Immunity does not extend to ‘Information Content Provider’
注:豁免不适用于“信息内容提供者”
术语解释:
- Interactive computer service (ICS): information service, system, or access software provider that provides or enables computer access by multiple users to a computer server
- 交互式计算机服务:信息服务、系统或访问软件提供者,它提供或使多个用户能够访问计算机服务器
- Information Content Provider(ICP): Responsible for creating or developing (in whole or in part) information & providing it through the internet or through Interactive Computer Services
- 信息内容提供者:负责创建或开发(全部或部分)信息并通过互联网或交互式计算机服务提供信息
US ISP Immunity 核心(省流版)
一句话概括就是ISP无罪,作为信息发布的平台,无论你发了什么信息,只要这个信息不是你写的,你单纯的只是发布了这个信息,无论这个信息是诽谤还是什么,你都无罪。
【这里建议去PPT ISP Liability1 看一看案例,这里面给了很多案例,甚至ISP简单的修改一下再发都是无责任,你在平台上发别人诽谤另一个人的信息,这个人来找你你也是无责任。反正就是很奇妙。给的案例里甚至没有一个ISP有责任的】
EU ISP Liability
EU E-Commerce Directive
- Graduated responsibility, linked to ability to control content
- 逐步递进的责任,与控制内容的能力相关
EU法律将ISP分为三类:
- Mere conduit ISPs / Carrying ISPs (transmission in network)
纯粹的管道isp(网络传输) - Caching ISP (temporary storage of data)
缓存ISP(数据的临时存储) - Hosting ISP (storage of information provided by a recipient of the service)
托管ISP(由服务接收者提供的信息的存储)
Liability of ISPs for Content
- Mere conduit: Must not originate or modify content
不能创造或修改内容 - Caching: Must not originate or modify, must remove material or disable access upon actual knowledge that material removed at original source or court has ordered removal or disablement.
不得原创或修改,必须删除材料或禁止访问的实际知识,材料删除的原始来源或法院已下令删除或禁用。 - Hosting (Distributor defence): Must not have actual knowledge of harmful content, is not aware of harmful content and acts expeditiously to remove or disable access to the harmful content
托管(分销商辩护):必须对有害内容没有实际了解,不知道有害内容,并迅速行动删除或禁止对有害内容的访问
以上这三个除了mere conduit是完全没有责任以外,其余两个只要违反了后面的条件,就有责任,如果完全遵守则没有责任
但是这就引出了一个很大的问题,就是如果平台不知道这个是illegal content,那么平台就没有责任,那么平台就没有意愿去审查监管:
Under current EU law, a platform is not liable for illegal content if it is unaware of hosting it, which has disincentivized platforms to voluntarily act on content
根据现行的欧盟法律,如果一个平台不知道它托管了非法内容,它就无需对非法内容负责,这削弱了平台自愿对内容采取行动的动力
一个很理想化的解决办法:‘self –regulation encouraged’
Exclusion of the Obligation to Monitor for illegal or harmful activity – ‘self –regulation encouraged’
排除监督非法或有害活动的义务——“鼓励自我监管”
Article 15 of the Directive states that Member States shall not impose a general obligation on providers to monitor the information they transmit or store when they are performing one of the services analyzed above, namely mere conduit, caching, and hosting, and also cannot compel them to seek facts or circumstances indicating illegal activity
该指令第15条规定,当供应商执行上述分析的服务之一,即仅仅是管道、缓存和托管时,成员国不应强制供应商监测其传输或存储的信息,也不能强迫他们寻找表明非法活动的事实或情况
【反正就是法律没办法了,只能靠平台自己的义务】
————————————————————
对以上的三个地方进行一个总结
Summary
- US: Focus on freedom of speech, free flow of information
- EU: Balances freedom of speech with dignity and respect for the individual, protection of social interests
- China: Focus on dignity and respect, civil rights and interests, protection for social interests
美国:关注言论自由和信息自由流动
欧盟:在言论自由与尊重个人、保护社会利益之间取得平衡
中国:注重尊严与尊重、公民权利与利益、保护社会利益
【可以理解为中美是两个极端,欧盟比较中庸】
接下来是Consumer Protection Law
E-Commerce Types: B2B v B2C
- B2B contracts: more freedom
- B2B合同:更自由
- B2C contracts: B has obligations to protect the consumer
- B2C契约:B有义务保护消费者
记住消费者比商家弱势就行
Who is a ‘Consumer’ ?
- A person who buys the goods/ services for own consumption
- 为自己消费而购买商品/服务的人
PRC Consumer Protection Law 给consumer的定义(Art.2)
- Article 2 The rights and interests of consumers in purchasing and using commodities or receiving services for daily consumption shall be under the protection of the present Law, or under the protection of other relevant laws and regulations in absence of stipulations in this Law
- 第二条消费者购买、使用商品或者接受日常消费服务的权益,由本法保护;本法未作规定的,由其他有关法律、法规保护
PRC Consumer Protection Law 给Business Operators Obligations(经营者的义务)的规定(Art.3, 4)
- Article 3 Business operators shall, in their supply of commodities produced and sold by them or services to consumers, abide by the present Law……
- 第三条经营者向消费者提供其生产、销售的商品或者服务,应当遵守本法
- Article 4 In transactions between business operators and consumers a principle of voluntariness, equality, fairness, honesty and credibility shall be followed
- 第四条经营者与消费者进行交易,应当遵循自愿、平等、公平、诚实信用的原则
不能强制交易
Online Information Disclosure to Consumers (A.27)
向消费者披露网上信息
- Identify the business
- 确定业务
- Enable prompt and effective communication
- 进行及时有效的沟通
- Accurate, clear and easily accessible information about the goods or services offered
- 关于所提供的商品或服务的准确、清晰和容易获取的信息
- Information about terms, conditions, costs to enable consumers to make informed decisions
- 关于条款、条件和成本的信息,使消费者能够做出明智的决定
【这段介绍的有点模糊,我的理解是商家需要在网上提供给消费者这些信息,然后消费者可以和商家进行沟通。在此附上E-commerce Law的Art.27,以供对照】
Article 27 E-commerce platform operators shall require business operators who apply to sell goods or provide services on the platforms to provide their identity information, address, contact details, administrative licensing information etc for verification and registration, establish registration files, and verify and update regularly.E-commerce platform operators providing services for non-business users who enter the platforms for sale of goods or provision of services shall comply with the relevant provisions of this Section.
第二十七条 电子商务平台经营者应当要求申请进入平台销售商品或者提供服务的经营者提交其身份、地址、联系方式、行政许可等真实信息,进行核验、登记,建立登记档案,并定期核验更新。
电子商务平台经营者为进入平台销售商品或者提供服务的非经营用户提供服务,应当遵守本节有关规定。
【最后一点根据的是Art.17,这里也给出双语的条文】
Article 17 E-commerce business operators shall disclose information of goods or services fully, truthfully, accurately and promptly, and protect consumers’ right to know and right to choose. E-commerce business operators shall not use false transactions, fabricated user review etc to conduct false or misleading business promotion, so as to defraud or mislead consumers.
第十七条 电子商务经营者应当全面、真实、准确、及时地披露商品或者服务信息,保障消费者的知情权和选择权。电子商务经营者不得以虚构交易、编造用户评价等方式进行虚假或者引人误解的商业宣传,欺骗、误导消费者。
Full disclosure 充分披露
【我觉得很重要的一个词,考试写这方面的题的话肯定会用】
【这里举的例子是Art.17, 18,Art.17上面有,这里给出Art.18】
Article 18 Where an e-commerce business operator provides consumers with search results for goods or services based on consumers’ preference or consumption habit, it shall also provide consumers with options which are not targeted at their personal characteristics, to respect and equally protect the legitimate rights and interests of consumers.E-commerce business operators sending ads to consumers shall comply with the relevant provisions of the Advertising Law of the People’s Republic of China.
第十八条 电子商务经营者根据消费者的兴趣爱好、消费习惯等特征向其提供商品或者服务的搜索结果的,应当同时向该消费者提供不针对其个人特征的选项,尊重和平等保护消费者合法权益。
电子商务经营者向消费者发送广告的,应当遵守《中华人民共和国广告法》的有关规定。
confirmation process(Art.50, 56)
确认过程
Article 50 E-commerce business operators shall notify users of the steps for conclusion of contract, points to note, download method etc in a clear, complete and specific manner, and ensure that the users are able to read and download conveniently and fully.E-commerce business operators shall ensure that a user may correct input error prior to submission of an order.
第五十条 电子商务经营者应当清晰、全面、明确地告知用户订立合同的步骤、注意事项、下载方法等事项,并保证用户能够便利、完整地阅览和下载。
电子商务经营者应当保证用户在提交订单前可以更正输入错误。
Article 56 Upon completion of electronic payment by the electronic payment service provider, it shall provide information on payment confirmation to the user promptly and accurately in accordance with the agreed method.
第五十六条 电子支付服务提供者完成电子支付后,应当及时准确地向用户提供符合约定方式的确认支付的信息。
dispute resolution(Art.59-63)
- Businesses should provide consumers with fair and timely means to settle disputes and obtain redress without undue cost or burden.
- 企业应当为消费者提供公平、及时的解决纠纷的途径,并在不产生不必要费用或负担的情况下获得赔偿。
- Dispute resolution mechanisms include internal mechanisms to address consumer complaints and participation by the business in third party dispute resolution programs.
- 纠纷解决机制包括处理消费者投诉的内部机制和企业参与第三方纠纷解决方案的机制。
【以上两个是PPT给出的重点,为了便于理解,这里给出Art.59-63的原文】
Article 59 E-commerce business operators shall establish a convenient and effective mechanism for receiving complaints and reports, announce information on complain and report methods, promptly accept and deal with complaints and reports.
Article 60 E-commerce disputes may be resolved via negotiation and settlement, mediation by a consumers’ association, an industry association or any other lawfully established mediation organisation, lodgement of a complaint to the relevant authorities, arbitration or litigation etc.
Article 61 In the event of a dispute between a consumer purchasing goods or receiving services on an e-commerce platform and a business operator using the platform, thee-commerce platform operator shall actively assist the consumer to protect his/her legitimate rights and interests.
Article 62 When handling an e-commerce dispute, the e-commerce business operator shall provide the original contract and transaction record. Where the aforesaid materials are lost, forged, altered, destroyed or concealed by the e-commerce business operator or the e-commerce business operator refuses to provide, and the People’s Court, arbitration organisation or the relevant agency is thus unable to verify the facts, the e-commerce business operator shall bear the corresponding legal liability.
Article 63 E-commerce platform operators may establish an online dispute resolution mechanism, formulate and announce dispute resolution rules, and resolve disputes between e-commerce participants fairly and equitably in accordance with voluntary participation principle.
第五十九条 电子商务经营者应当建立便捷、有效的投诉、举报机制,公开投诉、举报方式等信息,及时受理并处理投诉、举报。
第六十条 电子商务争议可以通过协商和解,请求消费者组织、行业协会或者其他依法成立的调解组织调解,向有关部门投诉,提请仲裁,或者提起诉讼等方式解决。
第六十一条 消费者在电子商务平台购买商品或者接受服务,与平台内经营者发生争议时,电子商务平台经营者应当积极协助消费者维护合法权益。
第六十二条 在电子商务争议处理中,电子商务经营者应当提供原始合同和交易记录。因电子商务经营者丢失、伪造、篡改、销毁、隐匿或者拒绝提供前述资料,致使人民法院、仲裁机构或者有关机关无法查明事实的,电子商务经营者应当承担相应的法律责任。
第六十三条 电子商务平台经营者可以建立争议在线解决机制,制定并公示争议解决规则,根据自愿原则,公平、公正地解决当事人的争议。
商家不遵守消费者保护法的后果
- Failure to comply: serious consequences – heavy fines –closure of business – loss of business reputation
- 未能遵守:严重后果-巨额罚款-关闭企业-丧失商业信誉
接下来是Advertising Law
主要法律:Advertisement Law of the People’s Republic of China - 2015
AD content (Art.3, 4)
-
Article 3 An advertisement shall be true to facts, lawful, and in compliance with the requirements for the socialist cultural and ideological development.
-
Article 4 An advertisement shall not contain any false information, and shall not cheat or mislead consumers.
-
第三条 广告应当真实、合法,以健康的表现形式表达广告内容,符合社会主义精神文明建设和弘扬中华民族优秀传统文化的要求。
-
第四条 广告不得含有虚假或者引人误解的内容,不得欺骗、误导消费者。
中国对于儿童的广告政策
- China : Children below 10 not to endorse products
- 中国:10岁以下儿童不得为产品代言
- Also, Ads targeting children must not:
- 此外,针对儿童的广告不能:
- Be harmful to child’s mental & physical health or moral standard
- 有害于儿童的身心健康或道德水准
- Induce child to put pressure on parents to buy the advertised product
- 诱导孩子向父母施加压力,让他们购买广告产品
- Reduce child’s respect for elders or friendly behaviour
- 减少孩子对长辈的尊重或友好行为
- Interrupt parents’/elders/ education of their child
- 打断父母/长辈/对孩子的教育
definition of online advertising
commercial advertisements that sell goods or services directly or indirectly through text, images, audio, video or other forms through internet media such as websites, web pages, internet applications, etc.
通过网站、网页、网络应用等互联网媒体,直接或者间接地以文字、图像、音频、视频或者其他形式销售商品或者服务的商业广告。
In whatever form, must comply with the law
- Online advertising should be identifiable, with the mark ‘advertising’, so that consumers can identify it as an advertisement.
- 网络广告应该是可识别的,标有“广告”的标志,这样消费者就可以识别它是广告。
- Paid search advertising shall be significantly different from natural search results, so that the consumers will not misunderstand the nature of the search results
- 付费搜索广告要与自然搜索结果有明显区别,这样消费者才不会对搜索结果的性质产生误解
PRC Advertising law 关于Product endorsement(产品代言)的规定
- Celebrity endorsers can be held responsible if they endorse a product or service in an advert that contains false claims and breaches the new advertising law, if they were aware or should have been aware that the product or service contained the false claims. Anyone guilty of this can be banned from endorsing products or services for three years
- 如果明星代言人在广告中代言的产品或服务含有虚假宣传,违反了新广告法,如果他们知道或应该知道产品或服务含有虚假宣传,他们将被追究责任。违反此规定的人将被禁止在三年内为产品或服务代言
PRC Advertising law 关于Online advertising rules的规定
- Internet adverts must not interfere with the user’s “normal use of the internet”.
- 网络广告不得干扰用户“正常使用互联网”
- With regards pop-up adverts, it must be clear to a user how to close a pop-up advert and this must be achievable with one click only. Electronically sent adverts, so by email for example, must include the sender’s true identity, the contact details of the sender and provide the recipient with an option to reject continuing to receive the advertising.
- 关于弹出式广告,用户必须清楚如何关闭弹出式广告,这必须通过一次点击即可实现。以电子邮件为例,通过电子邮件发送的广告必须包含发送者的真实身份、发送者的联系方式,并向接收者提供拒绝继续接收广告的选项。