python二手车价格预测_数据挖掘实战--二手车交易价格预测(四)建模调参
建模调参的过程中,尝试了两种不同的调参方式——贪心调参和贝叶斯调参。
最近事情太多,就划个水给自己记录一下即可。
贪心调参
把求解的问题分成若干个子问题;对每个子问题求解,得到子问题的局部最优解;把子问题的解局部最优解合成原来问题的一个解。
objective = ['regression', 'regression_l1', 'mape', 'huber', 'fair']
num_leaves = [3,5,10,15,20,40, 55]
max_depth = [3,5,10,15,20,40, 55]
bagging_fraction = []
feature_fraction = []
drop_rate = []
# 1_turning_obj
best_obj = dict()
for obj in objective:
model = LGBMRegressor(objective=obj)
score = np.mean(cross_val_score(model, X=train_X, y=train_y_ln, verbose=0, cv = 5, scoring=make_scorer(mean_absolute_error)))
best_obj[obj] = score
# 2_turning_leaves
best_leaves = dict()
for leaves in num_leaves:
model = LGBMRegressor(objective=min(best_obj.items(), key=lambda x:x[1])[0], num_leaves=leaves)
score = np.mean(cross_val_score(model, X=train_X, y=train_y_ln, verbose=0, cv = 5, scoring=make_scorer(mean_absolute_error)))
best_leaves[leaves] = score
# 3_turning_depth
best_depth = dict()
for depth in max_depth:
model = LGBMRegressor(objective=min(best_obj.items(), key=lambda x:x[1])[0],
num_leaves=min(best_leaves.items(), key=lambda x:x[1])[0],
max_depth=depth)
score = np.mean(cross_val_score(model, X=train_X, y=train_y_ln, verbose=0, cv = 5, scoring=make_scorer(mean_absolute_error)))
best_depth[depth] = score
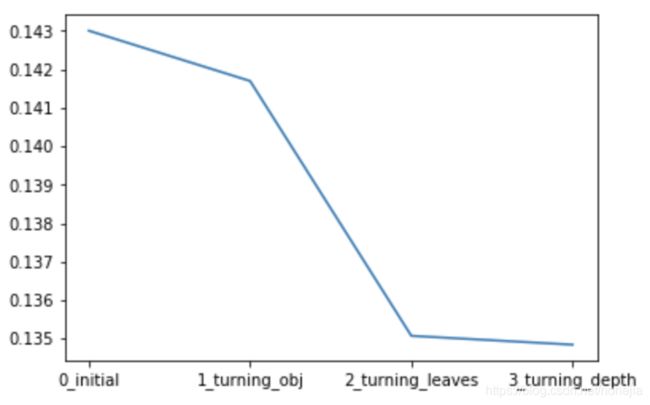
sns.lineplot(x=['0_initial','1_turning_obj','2_turning_leaves','3_turning_depth'], y=[0.143 ,min(best_obj.values()), min(best_leaves.values()), min(best_depth.values())])
贝叶斯调参
from bayes_opt import BayesianOptimization
def rf_cv(num_leaves, max_depth, subsample, min_child_samples):
val = cross_val_score(
LGBMRegressor(objective = ‘regression_l1’,
num_leaves=int(num_leaves),
max_depth=int(max_depth),
subsample = subsample,
min_child_samples = int(min_child_samples)
),
X=train_X, y=train_y_ln, verbose=0, cv = 5, scoring=make_scorer(mean_absolute_error)
).mean()
return 1 - val
rf_bo = BayesianOptimization(
rf_cv,
{
‘num_leaves’: (2, 100),
‘max_depth’: (2, 100),
‘subsample’: (0.1, 1),
‘min_child_samples’ : (2, 100)
}
)
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/nonejia/article/details/105255231