【pytorch学习实战】第二篇:多项式回归
往期相关文章列表:
- 【pytorch学习实战】第一篇:线性回归
- 【pytorch学习实战】第二篇:多项式回归
- 【pytorch学习实战】第三篇:逻辑回归
- 【pytorch学习实战】第四篇:MNIST数据集的读取、显示以及全连接实现数字识别
- 【pytorch学习实战】第五篇:卷积神经网络实现MNIST手写数字识别
- 【pytorch实战学习】第六篇:CIFAR-10分类实现
- 【pytorch实战学习】第七篇:tensorboard可视化介绍
文章目录
- 1. 理论基础
- 2. 代码示例
1. 理论基础
在上一篇文章中我们讲了线性回归,但是很多时候,仅仅使用线性回归拟合出来的直线并不能满足我们的需求,也就是精度欠佳,所以更多的时候我们使用多项式回归来处理拟合问题。其实多项式回归,原理和线性回归是一样的。
比如我们要拟合下列函数:
y = 2 x 3 + 3 x 2 + 4 x + 0.5 y = 2x^3 + 3x^2 + 4x + 0.5 y=2x3+3x2+4x+0.5
我们可以设置如下所示的参数类型方程:
y = w 3 x 3 + w 2 x 2 + w 1 x + b y = w_3x^3 + w_2x^2 + w_1x + b y=w3x3+w2x2+w1x+b
2. 代码示例
下列示例的步骤:
数据生成:生成 y = 2 x 3 + 3 x 2 + 4 x + 0.5 y = 2x^3 + 3x^2 + 4x + 0.5 y=2x3+3x2+4x+0.5的数据,注意这里没有携带误差。自定义模型:使用nn.Linear(3,1)指定输入输出的维度。注意这里的输入的维度是3,输入数据分别为x的一次、二次和三次。损失函数和优化器的选择:MSE损失和SGD优化器。开始训练:因为没有携带误差,直接指定损失误差比较好,所以没有指定迭代次数。显示结果:显示最终的多项式回归效果。
'''
功能:多项式回归
'''
import torch
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from torch import nn
#-------------------------------------数据准备--------------------------------------
# 目标权重和偏置
w = torch.FloatTensor([2.0, 3.0, 4.0]).unsqueeze(1)
b = torch.FloatTensor([0.5])
#一次生成32个数据
def create_data(batch_size=32):
random = torch.randn(batch_size)
random = random.unsqueeze(1) # 添加一个维度
# 纵向连接tensor
x = torch.cat([random**i for i in range(1,4)], 1) # b/x/^2/x^3
# 矩阵乘法
y = x.mm(w) + b[0] # mm表示矩阵相乘,mul为对应元素相乘
if torch.cuda.is_available():
return x.cuda(), y.cuda()
return x, y
#-------------------------------------自定义模型--------------------------------------
class PloyRegression(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(PloyRegression, self).__init__()
self.ploy = nn.Linear(3,1) #输入3维(分别表示x/x^2/x^3),输出1维
def forward(self, x):
out = self.ploy(x)
return out
model = PloyRegression()
if torch.cuda.is_available():
model = model.cuda()
#------------------------损失函数、优化器的选择----------------------------
criterion = torch.nn.MSELoss()
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=1e-3)
#------------------------开始训练----------------------------
epoch = 0
while True:
# 创建数据
batch_x, batch_y = create_data() #一次生成32个数据
# 前向传播
output = model(batch_x)
# 损失计算
loss = criterion(output, batch_y)
# 获取损失值
loss_value = loss.data.cpu().numpy()
# 梯度置零
optimizer.zero_grad()
# 反向传播
loss.backward()
# 更新参数
optimizer.step()
epoch += 1
#损失函数小于一定的值才会退出来
if loss_value < 1e-3:
break
# 每100步打印一次损失
if (epoch+1)%100==0:
print("Epoch{}, loss:{:.6f}".format(epoch+1, loss_value))
#-------------------------------------测试--------------------------------------
print("start eval!!!")
model.eval() # 开启验证模式
# 构造数据
x_train = np.array([ [i] for i in range(20) ],dtype = np.float32)
x_train = torch.from_numpy(x_train)
x = torch.cat([x_train**i for i in range(1,4)], 1)
y = x.mm(w) + b
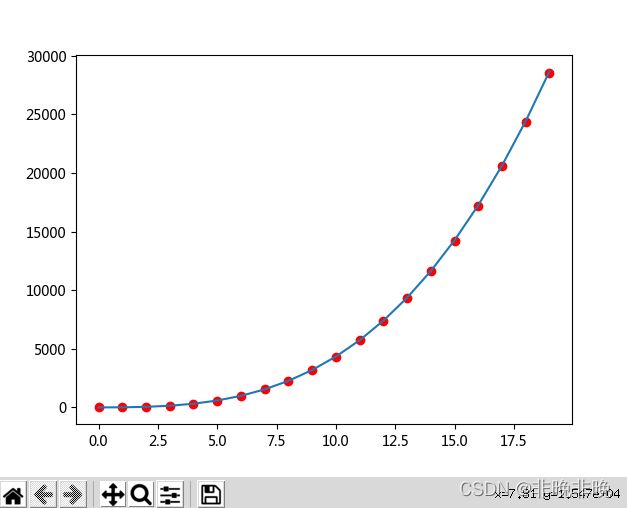
# 绘制数据点
plt.plot(x_train.numpy(),y.numpy(),'ro')
# 提取拟合参数
w_get = model.ploy.weight.data.T
b_get = model.ploy.bias.data
print('w:{},b:{}'.format(w_get.cpu().numpy(), b_get.cpu().numpy()))
# 计算预测值
Y_get = x.mm(w_get.cpu()) + b_get.cpu()
plt.plot(x_train.numpy(), Y_get.numpy(), '-')
plt.show()