语音学发音语音学笔记
词汇表
articulators 咬合架发音器
cochlea 耳蜗
consonants 元音
dialect 方言
eardrum 鼓膜
endolymph 内淋巴
Epiglottis 喉头盖
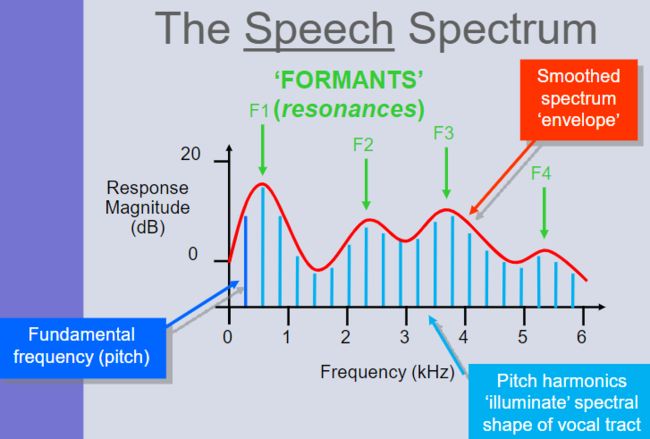
formants 共振峰
fricative 摩擦音
Larynx 喉
meatus 耳道
monosyllabic 单音节
pinna 耳廊
pitch 音调
pitch harmonics 音高泛音
phonation 发声
plosive 爆破音
perilymph 外淋巴
polysyllabic 多音节
Phonetic Transcription 音标
Phonology 音位学, 音韵学
Prosody 韵律学
resonator 谐振器
Response Magnitude 响应幅度
Spectrum 光谱图
Syllable 音节
vibration 振动
Vocalisation 发声
Vocal Tract 声道
vocal folds/cords 声带
voiced 浊音
vowels 辅音
unvoiced 清音
utterances 话语
L10 Speaking
Voice Source
Air pressure from the lungs builds up behind closed ‘vocal folds’ (often called ‘vocal cords’)来自肺部的气压在闭合的“声带”(通常称为“声带”)后面积聚
The vocal folds are repeatedly forced apart and pulled together again, producing a series of small pulses of air, This modulation of the airstream is known as phonation 声带反复被迫分开并再次拉在一起,产生一系列小的空气脉冲
The tension in the muscles attached to the vocal folds determines their rate of vibration and hence the ‘fundamental frequency’ (FX or F0) of the speech waveform 附着在声带上的肌肉的张力决定了它们的振动速率,因此决定了语音波形的“基频”(FX 或 F0)
The fundamental frequency contributes to the perceived pitch of the voice 基频有助于感知声音的音调
Because the vibration is not a pure sine wave, there is energy at frequencies that are multiples of the fundamental frequency (known as the pitch harmonics
Voice Filter
The vocal tract forms a resonator with a complex shape 声道形成一个形状复杂的共鸣器
Resonances are known as formants 共振称为共振峰
Speech is produced by using the articulators to change the shape of the vocal tract, hence modifying its resonant characteristics语音是通过使用发音器来改变声道的形状,从而改变其共振特性而产生的
Different configurations of the vocal tract enhance some of the harmonics of the pitch, and suppress (damp) others声道的不同配置增强了音高的一些谐波,并抑制(抑制)其他谐波
The principal articulator is the tongue, but the jaw, lips, soft palate and teeth are also involved 主要的发音器官是舌头,但下颌、嘴唇、软腭和牙齿也参与其中
The Excitation Spectrum
The Speech Spectrum
Sound Source
exciting a resonance (e.g. a whistle) 激发共鸣(例如口哨声)
vibrating an articulator (e.g. the tongue) 振动咬合架(例如舌头)
releasing a blockage (e.g. the lips)
• A voiced sound is one in which the vocal cords are vibrating 浊音是声带振动的声音
• An unvoiced sound is one in which the vocal cords are not vibrating 清音是声带不振动的声音
• A fricative sound results from a turbulent air flow at a constriction 摩擦声是由收缩处的湍流气流产生的
• A plosive sound occurs after a blockage is released 堵塞解除后发出爆破音
L11 Hearing
人耳主要功能是频率分析
The main percepts are …
– pitch 音高
– loudness 响度
– timbre 音色
Outer Ear
The pinna protects the entrance to the ear canal, and its shape makes it directionally sensitive at high frequencies耳廓保护耳道入口,其形状使其对高频方向敏感
The external canal - meatus - is a tube (~2.7 cm long, ~0.7 cm in diameter) that leads from the pinna to the middle ear 外耳道 - 耳道 - 是一条从耳廓通向中耳的管子(长约 2.7 厘米,直径约 0.7 厘米)
The meatus terminates at the cone shaped tympanic membrane (eardrum)耳道终止于锥形鼓膜(鼓膜)
Sound waves entering the ear impinge upon the eardrum and cause it to vibrate进入耳朵的声波撞击鼓膜并使其振动
Middle Ear
The middle ear transforms the vibration of the eardrum into oscillations of the liquid in the inner ear by vibrating the oval window 中耳通过振动卵圆窗将鼓膜的振动转化为内耳液体的振动
The necessary impedance matching (between air and liquid) is achieved by a group of bones - the ossicles - acting as a system of mechanical levers
The pressure at the oval window is ~35x greater than that arriving at the eardrum
This mechanical amplification allows us to hear sounds 1000x weaker than otherwise
Muscles attached to the ossicles protect the inner ear from potential damage due to high sound levels 附着在小骨上的肌肉保护内耳免受高音量的潜在伤害
Inner Ear
The transformation from mechanical vibrations to electrical nerve impulses (neural transduction) takes place in the snail-like structure of the cochlea 从机械振动到电神经冲动(神经转导)的转变发生在耳蜗的蜗牛状结构中
The cochlea is ~35 mm long and is filled with a colourless liquid called perilymph 耳蜗长约 35 毫米,充满了一种称为外淋巴液的无色液体
The cochlea is divided into two regions along its length by a membrane structure called the cochlea partition (a channel filled with a liquid called endolymph 耳蜗沿其长度被称为耳蜗分区的膜结构分为两个区域(一个充满液体的通道,称为内淋巴
耳蜗隔板以 basilar membrane 基底膜 和 Reissner’s membrane为界
耳蜗的作用
• The mechanical properties of the basilar membrane determine how the cochlea responds to sound
• Vibrations entering at the oval window set up travelling waves which lead to peaks of energy at different places along the cochlea depending on the frequency
• The vibration is nearest the oval window for high- frequency sounds
• The organ of corti transform the mechanical movements into electrochemical pulses by bending the outer hair cells (of which there are ~25,000)
• These actions are equivalent to a bank of bandpass filters 相当于一组带通滤波器
Frequency Selectivity
• Low frequency sounds can mask higher frequency sounds because of the overlap between auditory filters 由于听觉滤波器之间的重叠,低频声音可以掩盖高频声音
• The bandwidth over which masking operates is termed the critical band 掩蔽操作的带宽被称为临界带
• The shapes of the auditory filters are revealed by deriving psychophysical tuning curves 听觉滤波器的形状通过导出心理物理调谐曲线来揭示
Spectrogram vs. Cochleogram
• Spectrogram
– Plot of log energy across time and frequency (linear frequency scale)
• Cochleogram
– Cochlear filtering by the gammatone filterbank (or other models of cochlear filtering)
– Quasi-logarithmic frequency scale, and filter bandwidth is frequency-dependent
Binaural Auditory Processing
Possible mechanism:
– inter-aural time differences (ITD) 耳间时间差
– inter-aural level differences (ILD) 耳间电平差
Hearing Aids
Basic-Components of hearing aids
• Microphone
• Amplifier (in digital also DSP)
• Loudspeaker
• Battery
Cochlear Implants 人工耳蜗
A dialect is when different words are used 方言
An accent is when different sounds are used
Accents and dialects reflect regional and/or social differences
L13 Sounds and Symbols
Writing allows information to be:
– transmitted over space
– stored over time
The Syllable
The syllable is the shortest stretch of speech
Syllables consist of
– vowels: sound segments produced using an unobstructed configuration of the vocal tract 使用畅通无阻的声道配置产生的声音片段
– consonants: sound segments in which the airflow is at least partly obstructed 气流至少部分受阻的声音片段
A simple CVC (consonant-vowel-consonant) syllable corresponds to the opening and closing of the mouth
Words can be
– monosyllabic (having one syllable) 单音节
– polysyllabic (having two or more syllables) 多音节
Consonants and vowels 元音和辅音
Phonetic Transcription
International Phonetic Association (IPA) 国际语音协会
L14 Articulatory Phonetics 发音语音学
The Resonant Cavities 谐振腔
Nasal Cavity 鼻腔
Pharyngial Cavity 咽腔
Laryngial Cavity 喉腔
Oral Cavity 口腔
The Articulators 发音器
Alveolar Ridge 牙床
Hard Palate 硬腭
Soft Palate (Velum) 软腭
Upper Teeth 上牙
Upper Lip 上唇
Lower Lip 下唇
Uvula 小舌
Vocal Cords 声带
Speech sounds are classified in articulatory phonetics as follow
– vowels & consonants (i.e. all sounds)
• where the air stream comes from
• whether air is going in or out
– consonants
• whether the vocal cords are vibrating: voice
• where the constriction is: the place of articulation
• how the sound is made: the manner of articulation
– vowels
• the position of the tongue
• the shape of the lips
• Articulation refers to the constriction of the vocal tract during speech production 是指发音过程中声道的收缩
• Articulation involves the movement of an active articulator (e.g. the tongue) towards a passive articulator (e.g. the top of the mouth)
• The place of articulation refers to the physical location of the constriction in the vocal tract
**Place of Articulation: **
- Bilabial
- Labiodental
- Dental
- Alveolar
- Postalveolar
- Retroflex
- Palatal
- Velar
- Uvular
- Pharyngeal
- Glottal
Manner of Articulation
The manner of articulation refers to the way in which the airstream is modified by the primary and secondary articulators 发音方式是指气流被初级和次级发音器修改的方式
• Degrees of stricture …
– closure: articulators in firm contact (stops)
– narrowing: articulators close together but not touching (fricatives)
– approximation: wide gap between articulators (approximants)
Stops
– complete blockage of the airstream
– can be produced at many different places of articulation
– stops made with a velic closure are called oral stops
– stops made without a velic closure (and with airflow through the nasal cavity) are called nasal stops
plosives 爆破音
slower release sounds are called affricates 塞擦音
Voice, Place, Manner (VPM) labels are the standard method of specifying consonants
voiceless,voiced,bilabial ,velar ,alveolar ,postavelar ,glottal ,plosive ,fricative ,affricate ,nasal ,lateral-approximant


元音
Vowel quality is governed by …
– vowel height: high / low
– vowel location: front / back
– lip position: rounded / unrounded
The height of a vowel refers to the relationship between the highest point of the tongue and the roof of the oral cavity 元音的高度是指舌头最高点与口腔顶部的关系
close [i] /high [u]
open [æ] /low [ɑ]
mid ([ə]) /half-close ([e]) / half-open ([ʌ])
The location of a vowel refers to the part of the tongue which is highest 元音的位置指的是舌头最高的部分
front vowel [i]
back vowel [u]
central vowel
The mid-central vowel [ə] is called schwa
Vowel quality can be indicated by
– placing a dot on the vowel quadrilatera
– relating it to a set of language-independent cardinal vowels
Vowels seem to act as a carrier signal that is modulated by the consonants 元音似乎充当由辅音调制的载波信号
For these reasons, vowel quality is very variable and can drift over time (hence giving rise to different historical and contemporary accents)
由于这些原因,元音质量变化很大,并且会随着时间的推移而漂移(因此产生不同的历史和现代口音)
L15 Acoustic Phonetics 语音学
Articulatory Phonetics is a description of speech sounds in terms of the physical actions performed in their production 物理动作
Acoustic Phonetics is a description of speech sounds in terms of the acoustic consequences of their production 声学结果
Voice Onset Time (VOT) 发声时间
频谱图
Coarticulation 联合发音 refers to the influence of one sound on another
To a speech technologist/engineer, this is a form of context-dependency
To a phonetician, it is a consequence of efficient motor planning
L16 Phonology and Prosody 音系学和韵律学
Phonemic Contrast 音位对比
The contrastive phones in a language are called phonemes 音素
minimal pair in english contains the words
– “fussy” [fʌsɪ]
– “fuzzy” [fʌzɪ]
Therefore the [s] and [z] sounds are phonemes in English
The Phoneme 音素
Daniel Jones defined the phoneme as “a family of uttered sounds (segmental elements of speech) in a particular language which count for practical purposes as if they were one and the same
The phonemic inventory of a language is found by exploring all of the possible minimal pairs 一种语言的音位清单是通过探索所有可能的最小对来找到的
Phonemes are written using IPA symbols
A phonemic transcription is an idealised representation of an utterance (whereas a phonetic transcription represents the actual sounds used) 音位转录是话语的理想化表示(而语音转录表示实际使用的声音)
Phonological Processes
– Assimilation (feature spreading)
– Elision (deletion)
– Epenthesis (insertion)
– Reduction (neutralised vowel quality)
Prosody
Lexical stress refers to the prominence of syllables in words
The location of the stress can be marked using a diacritic, e.g. [ˈbɪləʊ] vs. [bɪˈləʊ]
About half of the world’s languages use the pitch pattern (called lexical tone) to distinguish between one word and another
Languages with moving pitch patterns (such as Modern Standard Chinese) are called contour tone languages
Languages with entirely level tones (such as Yoruba) are called register tone languages
经典施氏食獅史
intonation
Pitch variation that doesn’t affect the meaning of the words, but does affect the meaning of an utterance is known as intonation