使用 MySQL、Thymeleaf 和 Spring Boot Framework 上传、存储和查看图像
在本文中,我们将使用 Spring Boot 框架从头开始构建映像库应用程序,用户可以在其中列出其映像。
以下是我们将在应用程序中实现的功能。
- 用户可以列出他们的图像以及详细信息,例如,
- 名字
- 描述
- 图像
- 价格。(如果他们想卖)。
- 任何人都可以查看列出的图像以及所有详细信息。
注意:我们将使用 MySQL 数据库来存储所有图像详细信息。
最终应用
注意:视频教程可在底部找到。
您可以在本文的底部找到源代码。
请严格按照以下提及的步骤从头开始构建应用程序。
第 1 步:从 Spring Initializr 创建一个项目。
- 转到 Spring 初始化器。
- 输入组名称 com.pixeltrice。
- 提及工件 ID,spring-boot-image-gallery-app
- 添加以下依赖项。
- 春网
- 春季数据 JPA
- MySQL 驱动程序
- 百里香叶
第 2 步:按“生成”按钮,该项目将下载到您的本地系统上。
第 3 步:现在解压缩项目并将其解压缩到本地系统。
第 4 步:之后,将项目导入 IDE 中,例如 Eclipse。
选择文件 -> 导入 -> 现有 Maven 项目 -> 浏览 -> 选择文件夹 spring-boot-image-gallery-app-> 完成。
第 5 步:在应用程序中配置属性。属性
应用程序属性
# Set here configurations for the database connection
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/imageGalleryApp?autoReconnect=true&useSSL=false
spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
spring.datasource.username=root
spring.datasource.password=your MySQL Password
# Specify the DBMS
spring.jpa.database = MYSQL
# Show or not log for each sql query
spring.jpa.show-sql = true
#create-drop| update | validate | none
spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto = update
# SQL dialect for generating optimized queries
spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.dialect = org.hibernate.dialect.MySQL5Dialect
uploadDir=/resources
#Enable multipart uploads
spring.servlet.multipart.enabled=true
# Threshold after which files are written to disk.
spring.servlet.multipart.file-size-threshold=2KB
# Max file size.
spring.servlet.multipart.max-file-size=200MB
# Max Request Size
spring.servlet.multipart.max-request-size=215MB所有属性都是不言自明的,您通过查看它很容易理解。
第 6 步:为图像创建实体类。
在此步骤中,我们将定义实体类,该实体类将与数据库中存在的表进行映射。
ImageGallery.java
package com.pixeltrice.springbootimagegalleryapp.entity;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Date;
import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.GenerationType;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import javax.persistence.Lob;
import javax.persistence.Table;
import javax.persistence.Temporal;
import javax.persistence.TemporalType;
@Entity
@Table(name = "image_gallery")
public class ImageGallery {
@Id @GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
@Column(name = "id", nullable = false, unique = true)
private Long id;
@Column(name = "name", nullable = false)
private String name;
@Column(name = "description", nullable = false)
private String description;
@Column(name = "price",nullable = false, precision = 10, scale = 2)
private double price;
@Lob
@Column(name = "Image", length = Integer.MAX_VALUE, nullable = true)
private byte[] image;
@Temporal(TemporalType.TIMESTAMP)
@Column(name = "create_date", nullable = false)
private Date createDate;
public ImageGallery() {}
public Long getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Long id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getDescription() {
return description;
}
public void setDescription(String description) {
this.description = description;
}
public double getPrice() {
return price;
}
public void setPrice(double price) {
this.price = price;
}
public byte[] getImage() {
return image;
}
public void setImage(byte[] image) {
this.image = image;
}
public Date getCreateDate() {
return createDate;
}
public void setCreateDate(Date createDate) {
this.createDate = createDate;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Product [id=" + id + ", name=" + name + ", description=" + description + ", price=" + price + ", image="
+ Arrays.toString(image) + ", createDate=" + createDate + "]";
}
}在实体上方,该类将与 MySQL 数据库中名为“image_gallery”的表进行映射。由于该类带有@Entity注释标记,因此它是一个持久 Java 类。
@Table注解指示与上述实体类映射的数据库表名。 @Id注解用于将变量表示为表中的主键。
@Column注释用于表示与上述变量或字段映射的列的名称。
@Lob注释用于将大型对象存储到数据库中,例如字节数组或大型字符串。在我们的例子中,我们以字节数组的形式存储图像。
此注释用于指定使用 Lob 标记或批注的字段应在数据库表中以 BLOB(二进制大对象)数据类型的形式表示。
第 7 步:为 ImageGallery 实体类创建存储库接口
在这里,我们将创建存储库,该存储库将与我们的数据库通信并执行所有类型的 CRUD 操作。在此步骤中,我们将扩展一个名为 JpaRepository 的预定义类,该类提供了创建、删除、更新和从数据库表中获取数据所需的所有可能方法。
ImageGalleryRepository.java
package com.pixeltrice.springbootimagegalleryapp.repository;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
import com.pixeltrice.springbootimagegalleryapp.entity.ImageGallery;
@Repository
public interface ImageGalleryRepository extends JpaRepository{
} JpaRepository
@Repository:此注释指示类或接口完全专用于执行各种 CRUD 操作,例如创建、更新、读取或删除数据库中的数据。
第 8 步:创建图像库服务类
ImageGalleryService.java
package com.pixeltrice.springbootimagegalleryapp.service;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Optional;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import com.pixeltrice.springbootimagegalleryapp.entity.ImageGallery;
import com.pixeltrice.springbootimagegalleryapp.repository.ImageGalleryRepository;
@Service
public class ImageGalleryService {
@Autowired
private ImageGalleryRepository imageGalleryRepository;
public void saveImage(ImageGallery imageGallery) {
imageGalleryRepository.save(imageGallery);
}
public List getAllActiveImages() {
return imageGalleryRepository.findAll();
}
public Optional getImageById(Long id) {
return imageGalleryRepository.findById(id);
}
} 第 9 步:创建控制器类
在控制器类中,我们将创建 API,以存储和获取来自 MySQL 数据库的图像。
ImageGalleryController.java
package com.pixeltrice.springbootimagegalleryapp.controller;
import java.io.BufferedOutputStream;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.file.Paths;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Optional;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.ui.Model;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
import org.springframework.web.multipart.MultipartFile;
import com.pixeltrice.springbootimagegalleryapp.entity.ImageGallery;
import com.pixeltrice.springbootimagegalleryapp.service.ImageGalleryService;
@Controller
public class ImageGalleryController {
@Value("${uploadDir}")
private String uploadFolder;
@Autowired
private ImageGalleryService imageGalleryService;
private final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(this.getClass());
@GetMapping(value = {"/", "/home"})
public String addProductPage() {
return "index";
}
@PostMapping("/image/saveImageDetails")
public @ResponseBody ResponseEntity createProduct(@RequestParam("name") String name,
@RequestParam("price") double price, @RequestParam("description") String description, Model model, HttpServletRequest request
,final @RequestParam("image") MultipartFile file) {
try {
//String uploadDirectory = System.getProperty("user.dir") + uploadFolder;
String uploadDirectory = request.getServletContext().getRealPath(uploadFolder);
log.info("uploadDirectory:: " + uploadDirectory);
String fileName = file.getOriginalFilename();
String filePath = Paths.get(uploadDirectory, fileName).toString();
log.info("FileName: " + file.getOriginalFilename());
if (fileName == null || fileName.contains("..")) {
model.addAttribute("invalid", "Sorry! Filename contains invalid path sequence \" + fileName");
return new ResponseEntity<>("Sorry! Filename contains invalid path sequence " + fileName, HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST);
}
String[] names = name.split(",");
String[] descriptions = description.split(",");
Date createDate = new Date();
log.info("Name: " + names[0]+" "+filePath);
log.info("description: " + descriptions[0]);
log.info("price: " + price);
try {
File dir = new File(uploadDirectory);
if (!dir.exists()) {
log.info("Folder Created");
dir.mkdirs();
}
// Save the file locally
BufferedOutputStream stream = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(new File(filePath)));
stream.write(file.getBytes());
stream.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
log.info("in catch");
e.printStackTrace();
}
byte[] imageData = file.getBytes();
ImageGallery imageGallery = new ImageGallery();
imageGallery.setName(names[0]);
imageGallery.setImage(imageData);
imageGallery.setPrice(price);
imageGallery.setDescription(descriptions[0]);
imageGallery.setCreateDate(createDate);
imageGalleryService.saveImage(imageGallery);
log.info("HttpStatus===" + new ResponseEntity<>(HttpStatus.OK));
return new ResponseEntity<>("Product Saved With File - " + fileName, HttpStatus.OK);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
log.info("Exception: " + e);
return new ResponseEntity<>(HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST);
}
}
@GetMapping("/image/display/{id}")
@ResponseBody
void showImage(@PathVariable("id") Long id, HttpServletResponse response, Optional imageGallery)
throws ServletException, IOException {
log.info("Id :: " + id);
imageGallery = imageGalleryService.getImageById(id);
response.setContentType("image/jpeg, image/jpg, image/png, image/gif");
response.getOutputStream().write(imageGallery.get().getImage());
response.getOutputStream().close();
}
@GetMapping("/image/imageDetails")
String showProductDetails(@RequestParam("id") Long id, Optional imageGallery, Model model) {
try {
log.info("Id :: " + id);
if (id != 0) {
imageGallery = imageGalleryService.getImageById(id);
log.info("products :: " + imageGallery);
if (imageGallery.isPresent()) {
model.addAttribute("id", imageGallery.get().getId());
model.addAttribute("description", imageGallery.get().getDescription());
model.addAttribute("name", imageGallery.get().getName());
model.addAttribute("price", imageGallery.get().getPrice());
return "imagedetails";
}
return "redirect:/home";
}
return "redirect:/home";
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return "redirect:/home";
}
}
@GetMapping("/image/show")
String show(Model map) {
List images = imageGalleryService.getAllActiveImages();
map.addAttribute("images", images);
return "images";
}
} 控制器类中存在的每个 API 的说明。
- @GetMapping(value = {“/”, “/home”}):每当请求到达此 API 时,它都会返回索引,由于我们已经在应用程序中实现了百里香叶,因此它将返回 index.html 页面。
2. @PostMapping(“/image/saveImageDetails”):用于将新的图像详细信息存储到MySQL数据库中。
request.getServletContext().getRealPath(uploadFolder):如您所见,我们已经通过从 application.properties 文件中分配值 /resources 来初始化变量 uploadFolder。
我们将参数传递给 getRealPath(),因此它将返回您在本地系统中创建工作区的完整路径。因此对我来说
file.getOriginal文件名():它将返回产品图片的实际名称,例如image.png,这取决于您上传的产品名称。
Paths.get(uploadDirectory, fileName).toString():它将返回系统上保存上传图像的确切位置。
之后,我们将图像转换为字节数组,并将所有与图像相关的详细信息(例如名称,描述,图像等)存储到MySQL数据库中。
如您所见,我们将图像以 byte[] 形式存储在数据库表中,这就是为什么在实体类中我们必须使用注释@Lob。
3. @GetMapping(“/image/display/{id}”):该接口用于从数据库中获取特定图像的 byte[] 形式,并将其转换为 jpeg、png、jpg 或 gif 格式以显示在浏览器中。
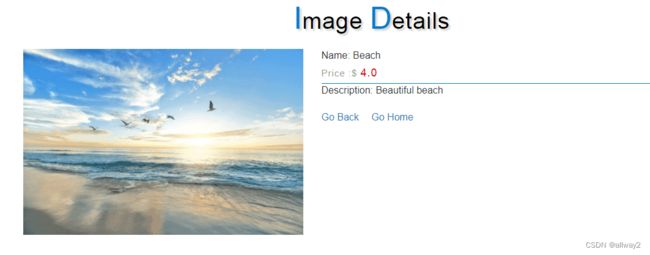
4. @GetMapping(“/image/imageDetails”):它根据镜像 ID 从数据库中获取镜像详情,并显示在镜像详情中.html
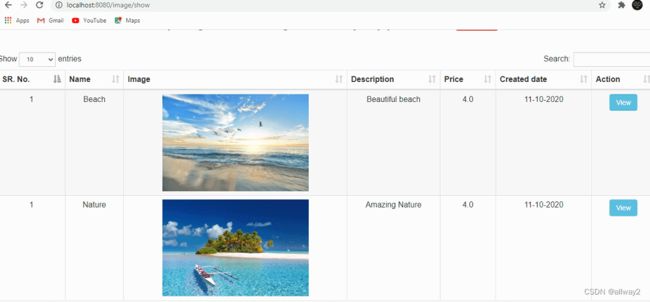
5. @GetMapping(“/image/show”):这是控制器类中的最后一个API,用于在images.html页面中显示产品列表及其详细信息。
第 10 步:创建 HTML 页面
在最后一步中,我们看到我们的应用程序需要三个 HTML 页面。让我们创建它。
注意:确保你应该在\src\main\resources\templates中创建所有HTML页面
index.html
PixelTrice
Spring Boot Image Gallery Application

images.html
PixelTrice
Spring Boot Image Gallery Application
Go Home
SR. No.
Name
Image
Description
Price
Created date
Action
![]()
View
imagedetails.html
PixelTrice
第 11 步:创建 css 和 javascript 文件
在此步骤中,我们将为我们的应用程序创建样式.css和产品.js。还在图像文件夹中放置了一个加载图像。
确保你应该在 src\main\resources\static\css 和 product.js 在路径 src\main\resources\static\js 中创建 style.css
注意我们需要在路径 src\main\resources 上再创建一个包含命名图像的文件夹,我们必须在其中存储加载图像。 您可以从我的 GitHub 帐户上提供的源代码下载它。
product.js
$(document).ready(function() {
$('#loader').hide();
$("#submit").on("click", function() {
$("#submit").prop("disabled", true);
var name = $("#name").val();
var file = $("#image").val();
var price = $("#price").val();
var description = $("#description").val();
var form = $("#form").serialize();
var data = new FormData($("#form")[0]);
data.append('name', name);
data.append('price', price);
data.append('description', description);
//alert(data);
$('#loader').show();
if (name === "" || file === "" || price === "" || description === "") {
$("#submit").prop("disabled", false);
$('#loader').hide();
$("#name").css("border-color", "red");
$("#image").css("border-color", "red");
$("#price").css("border-color", "red");
$("#description").css("border-color", "red");
$("#error_name").html("Please fill the required field.");
$("#error_file").html("Please fill the required field.");
$("#error_price").html("Please fill the required field.");
$("#error_description").html("Please fill the required field.");
} else {
$("#name").css("border-color", "");
$("#image").css("border-color", "");
$("#price").css("border-color", "");
$("#description").css("border-color", "");
$('#error_name').css('opacity', 0);
$('#error_file').css('opacity', 0);
$('#error_price').css('opacity', 0);
$('#error_description').css('opacity', 0);
$.ajax({
type: 'POST',
enctype: 'multipart/form-data',
data: data,
url: "/image/saveImageDetails",
processData: false,
contentType: false,
cache: false,
success: function(data, statusText, xhr) {
console.log(xhr.status);
if(xhr.status == "200") {
$('#loader').hide();
$("#form")[0].reset();
$('#success').css('display','block');
$("#error").text("");
$("#success").html("Product Inserted Succsessfully.");
$('#success').delay(2000).fadeOut('slow');
}
},
error: function(e) {
$('#loader').hide();
$('#error').css('display','block');
$("#error").html("Oops! something went wrong.");
$('#error').delay(5000).fadeOut('slow');
location.reload();
}
});
}
});
});注意:请参考我的Github帐户了解样式.css代码。
现在我们可以运行应用程序了,但在此之前,请确保您提供了正确的 MySQL 用户名、密码和架构名称。
还要验证文件夹结构,如图所示。
第 12 步:运行应用程序
运行应用程序后,添加图像详细信息和视图,如图所示。
进入本地主机:8080上传图片,如图所示。
按提交按钮将图像详细信息存储在MySQL数据库中。点击 全部显示 按钮查看图像。
单击“查看”按钮以查看图像的详细信息。
下载源代码
总结
在本教程中,我们学习并构建了使用 MySQL、Thymeleaf 和 Spring Boot Framework 上传、存储和查看图像的应用程序。源代码在我的 Github 帐户上可用,如果卡在任何地方或遇到一些错误,请通过它。您也可以在下面的评论部分提出任何疑问。