Python使用Opencv图像处理方法完成手势识别(二)
Opencv完成手势识别
- 根据坐标识别
-
- 寻找最低点
- 计算其他点与最低点的距离
- 通过距离阈值判断手指根数和手势
- 效果展现
- 完整代码
当我们把手近似出来后会得到一组轮廓的点坐标,我自己手势识别的思路就是根据点坐标来判断手势。
根据坐标识别
寻找最低点
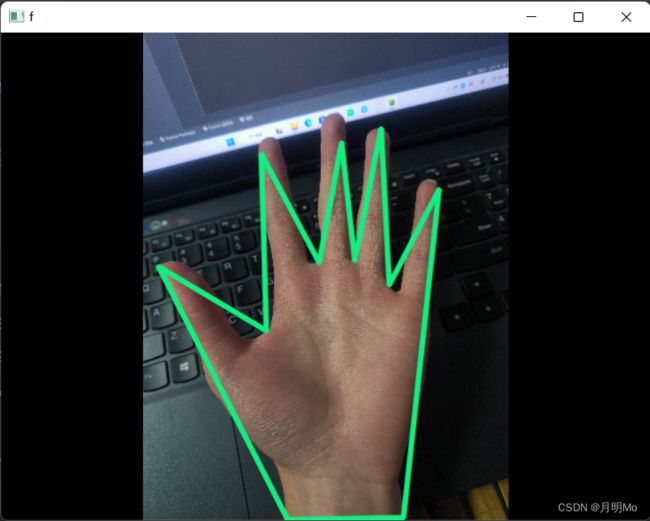
比如这幅图,最左下角的点就是手掌的最低点,获得的方法是使用numpy的np.argmax函数,将维度设置为图片高的维度,获得最大的高就是获得最低的点。
maxindex = np.argmax(allpoint)
计算其他点与最低点的距离
获取成功之后就将最低点与其他点的距离计算出来:
#pt1点一
#pt2点二
def get_distance(pt1, pt2):
distance = ((pt2[0] - pt1[0]) ** 2 + (pt2[1] - pt1[1]) ** 2) ** (0.5)
return distance
for point in allpoint:
distance = self.get_distance(self.allpoint[maxindex [1], :], point)
if distance > 300:
cv2.line(img,all_point[maxindex [1],:],point,bgr,4,16)
通过距离阈值判断手指根数和手势
然后通过这个距离阈值排除两根手指中间的点:
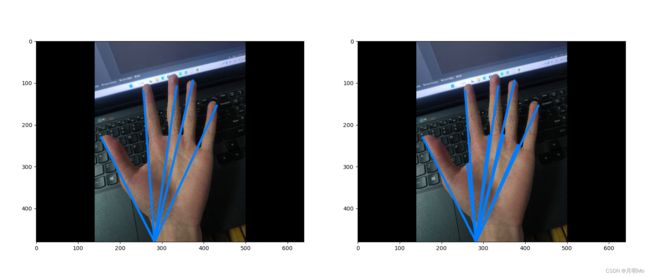
可以发现左边的图片线的数量比右边少了几根双指中间的。
最后我们只需要通过手指线的根数来判断手势就行了。
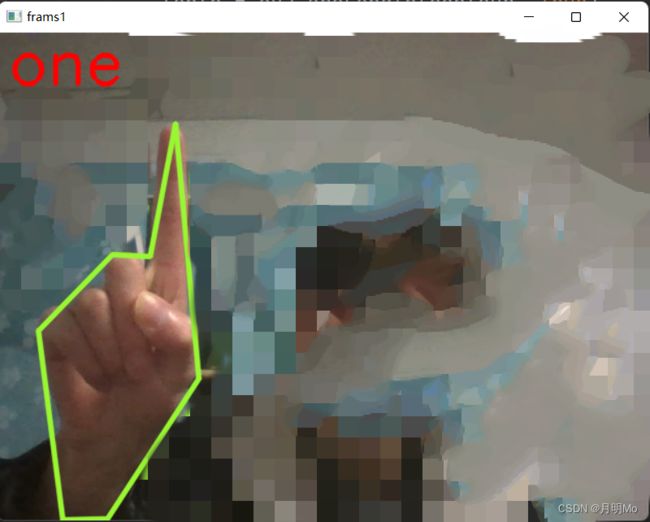
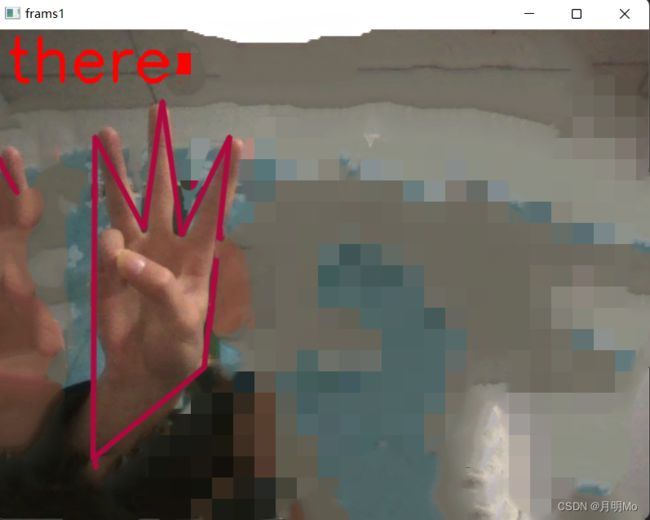
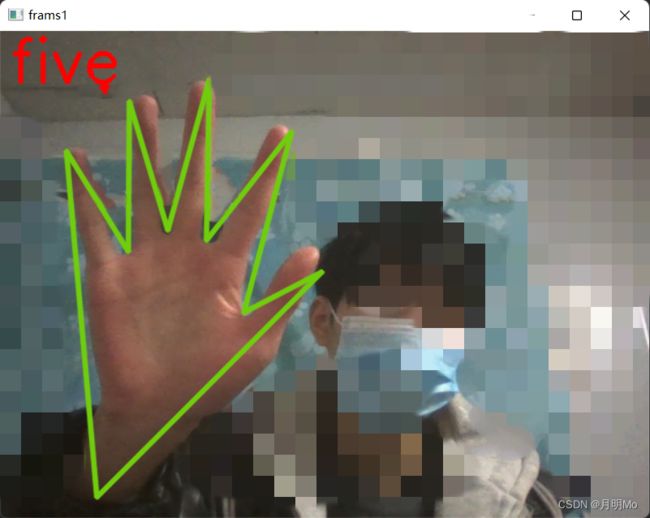
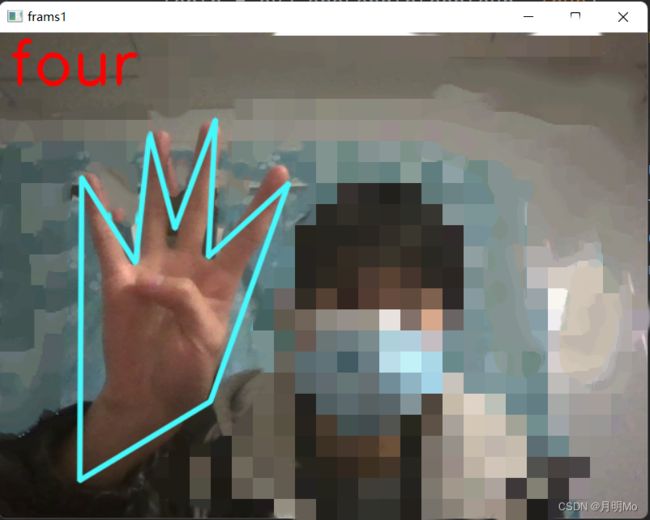
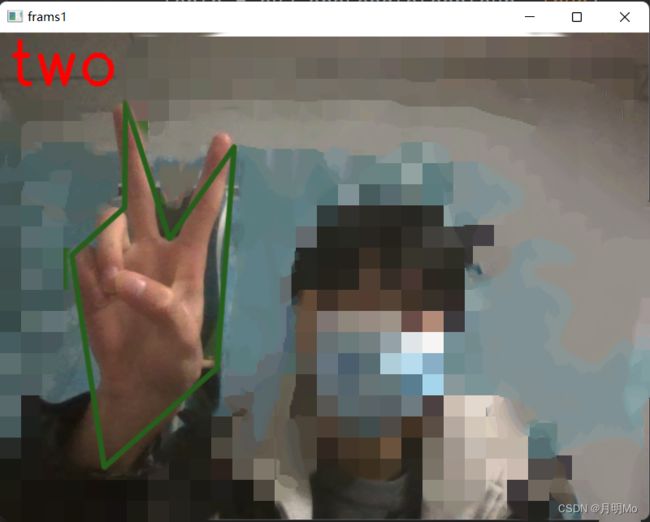
效果展现
完整代码
import cv2
import numpy as np
import random
class Img_handle:
def __init__(self,area_min,lenth_min,distance,drawtype=0,area_max=100000,lenth_max=100000):
#default area_min=20000 lenth_min=1000 distance=300
#writer:csdn月明Mo
#area_min 轮廓面积最小值
#area_max 轮廓面积最大值
#lenth_min 轮廓周长最小值
#lenth_max 轮廓周长最大值
#distance 距离阈值
#drawtype 手势描绘类型,0为近似描绘 1为直线描绘
self.area_min=area_min
self.area_max=area_max
self.lenth_min=lenth_min
self.lenth_max=lenth_max
self.distance=distance
self.allpoint = []
self.highHSV = np.array([15, 255, 255])
self.lowHSV = np.array([0, 50, 50])
self.drawtype=drawtype
#writer:csdn月明Mo
#Hsv阈值改变函数
def change_Hsv(self,lowHSV,highHSV):
self.highHSV=highHSV
self.lowHSV=lowHSV
#writer:csdn月明Mo
#图片不失真resize函数
def resize_img(self,size=list,img=None):
size = [size[1], size[0], size[2]]
mask = np.zeros(size, dtype=np.uint8)
h, w = self.img.shape[0:2]
dwh = min([size[0] / h, size[1] / w])
self.img = cv2.resize(self.img, None, fx=dwh, fy=dwh)
if h > w:
dxy = int((size[1] - self.img.shape[1]) / 2)
mask[:, dxy:self.img.shape[1] + dxy, :] = self.img
else:
dxy = int((size[0] - self.img.shape[0]) / 2)
mask[dxy:self.img.shape[0] + dxy, :, :] = self.img
return mask
#writer:csdn月明Mo
#图片处理函数
def img_handle(self):
self.img = cv2.cvtColor(self.img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2HSV)
cv2.GaussianBlur(self.img, [5, 5], 0)
self.img = cv2.inRange(self.img, self.lowHSV, self.highHSV)
kernel = np.ones([3, 3], dtype=np.uint8)
self.img = cv2.morphologyEx(self.img, cv2.MORPH_CLOSE, kernel, iterations=1)
kernel = np.ones([3, 3], dtype=np.uint8)
self.img = cv2.morphologyEx(self.img, cv2.MORPH_DILATE, kernel, iterations=1)
contours, num = cv2.findContours(self.img, cv2.RETR_TREE, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
for contour in contours:
area = cv2.contourArea(contour)
lenth = cv2.arcLength(contour, True)
if self.area_max >area > self.area_min and self.lenth_max >lenth > self.lenth_min:
epsilon = 0.02 * cv2.arcLength(contour, True)
self.allpoint = cv2.approxPolyDP(contour, epsilon, True)
self.allpoint = self.allpoint.reshape(len(self.allpoint), 2)
self.allpoint = np.array(self.allpoint, dtype=np.int32)
if self.drawtype==0:
b = random.randint(0, 255)
g = random.randint(0, 255)
r = random.randint(0, 255)
cv2.polylines(self.output_img, [self.allpoint], True, [b, g, r], 4, 16)
#writer:csdn月明Mo
#距离计算函数
def get_distance(self, pt1, pt2):
distance = ((pt2[0] - pt1[0]) ** 2 + (pt2[1] - pt1[1]) ** 2) ** (0.5)
return distance
#writer:csdn月明Mo
#手势判断函数
def detect(self):
num = 0
if np.any(self.allpoint):
maxindex = np.argmax(self.allpoint, axis=0)
for point in self.allpoint:
distance = self.get_distance(self.allpoint[maxindex [1], :], point)
if distance > self.distance:
if self.drawtype ==1:
b = random.randint(0, 255)
g = random.randint(0, 255)
r = random.randint(0, 255)
cv2.line(self.output_img,self.allpoint[maxindex [1],:],point,[b, g, r],4,16)
num += 1
if num == 1:
cv2.putText(self.output_img, 'one', [10, 50], cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 2, [0, 0, 255], thickness=4)
elif num == 2:
cv2.putText(self.output_img, 'two', [10, 50], cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 2, [0, 0, 255], thickness=4)
elif num == 3:
cv2.putText(self.output_img, 'there', [10, 50], cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 2, [0, 0, 255], thickness=4)
elif num == 4:
cv2.putText(self.output_img, 'four', [10, 50], cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 2, [0, 0, 255], thickness=4)
elif num == 5:
cv2.putText(self.output_img, 'five', [10, 50], cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 2, [0, 0, 255], thickness=4)
#writer:csdn月明Mo
#获取手势函数
def get_hand(self,img):
self.img = img
if self.img.shape[0] != 480 and self.img.shape[1] != 640:
self.img = self.resize_img([640,480,3])
self.output_img=np.copy(self.img)
self.img_handle()
self.detect()
return self.output_img
def main():
video=cv2.VideoCapture(0)
hand=Img_handle(20000,1000,280)
while video.isOpened():
res,img=video.read()
if res== True:
newimg=hand.get_hand(img)
cv2.imshow('frams1', newimg)
if cv2.waitKey(1)==ord('q'):
break
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
video.release()
if __name__=='__main__':
main()
下一章讲解GUI界面的制作和识别精度的问题
Python使用Opencv图像处理方法完成手势识别(三)