Gmapping的个人理解
Gmapping
第0章 源码阅读的一些预准备
0.1、算法简介
对于建图,SLAM,也称为 CML (Concurrent Mapping and Localization), 我们从名字就可以得知,其包含机器人的定位与地图的构建两部分,或者说并发建图与定位。对于这个问题的模型,就是如果将一个机器人放入未知环境中的未知位置,是否有办法让机器人一边移动一边逐步描绘出此环境完全的地图(完全的地图是指不受障碍行进到房间可进入的每个角落,也就是熟知地图的障碍点)。定位与建图相辅相成、互相影响。
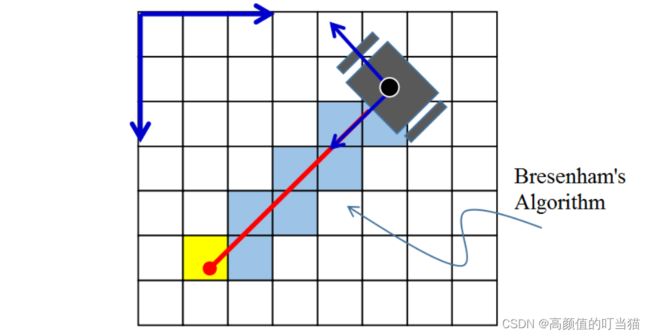
首先,构建地图要知道机器人的精确位姿,精确定位又需要给定的地图做参考。先讲已知精确位姿(坐标和朝向)的地图创建,机器人位置已知,通过激光雷达扫描到环境特征,即障碍物距离。可通过机器人坐标和朝向以及障碍物距离计算出障碍物的坐标,采用bresenham直线段扫面算法,障碍物所处的栅格标注为 occupy,机器人所处的栅格与障碍物所处的栅格之间画直线,直线所到之处都为 free。当然每个栅格并不是简单的非 0 即 1,栅格的占据可用概率表示,若某一个栅格在激光束 a 扫描下标识为 occupy,在激光束 b 扫描下也标识为 occupy,那该栅格的占据概率就变大,反之,则变小。这样,机器人所处的环境就可以通过二维栅格地图来表征。
0.2、gmapping安装
运行指令:sudo apt-get install ros-kinetic-slam-gmapping
运行gmapping:
1.运行roscore
roscore
2.新开终端,设置参数,确保在任何节点使用前设定use_sim_time参数true,这个参数当回放bag数据集是设置为true,此时说明系统使用的是仿真时间
rosparam set use_sim_time true
3.新开终端,运行slam_gmapping节点,它将在base_scan主题上收听激光扫描数据
rosrun gmapping slam_gmapping scan:=base_scan
4.新开终端,进入下载的数据的位置,并play,例如我的是test.bag,把它改成你下载的数据的名字,它的作用是把激光数据发送给slam_gmapping节点。
rosbag play --clock test.bag
0.3、测试结果
第1章 源码阅读的一些预准备
从本文开始,我们会开始对gmapping源码的阅读。我会试图给出逐行或逐块的注释,来说明代码在做什么以及如何跳转。通常,我阅读一个大的project的源码最困难的地方就是难以理解程序跳转来转去的关系。
1.1、代码框架
代码中主要包含slam_gmapping和openslam_gmapping两个包,里面有大量的辅助文件,重点便是以上两个框里面的函数。
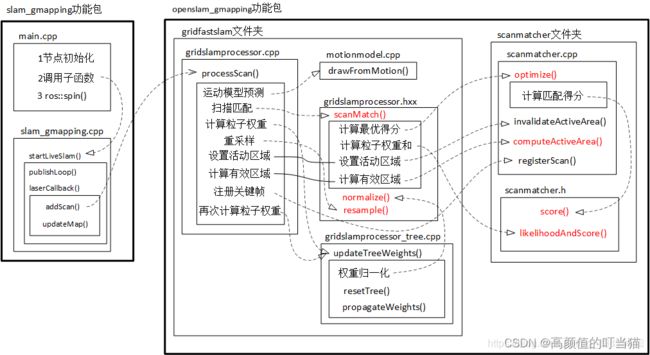
接下来便主要分析各个函数的全部作用以及其实现原理。
第2章 代码核心部分
2.1、main函数
#include 主函数的目的主要是初始化节点,以及订阅一些话题,等待回调函数中实现对应算法功能。
这里着重介绍一下gn.startLiveSlam()函数的作用以及下一步跳转。
*/*订阅一些主题* *发布一些主题*/*
void SlamGMapping::startLiveSlam()
{
entropy_publisher_ = private_nh_.advertise<std_msgs::Float64>("entropy", 1, true);
sst_ = node_.advertise<nav_msgs::OccupancyGrid>("map", 1, true);
sstm_ = node_.advertise<nav_msgs::MapMetaData>("map_metadata", 1, true);
ss_ = node_.advertiseService("dynamic_map", &SlamGMapping::mapCallback, this);
{
*//订阅激光数据* *同时和odom_frame之间的转换同步*
scan_filter_sub_ = new message_filters::Subscriber<sensor_msgs::LaserScan>(node_, "scan", 5);
scan_filter_ = new tf::MessageFilter<sensor_msgs::LaserScan>(*scan_filter_sub_, tf_, odom_frame_, 5);
scan_filter_->registerCallback(boost::bind(&SlamGMapping::laserCallback, this, _1));//最大的重点,这里订阅了/scan话题,在它的回调函数里面对他进行处理
*//成功订阅LaserScan*
std::cout <<"Subscribe LaserScan & odom!!!"<<std::endl;
}
*/*发布转换关系的线程*/*
transform_thread_ = new boost::thread(boost::bind(&SlamGMapping::publishLoop, this, transform_publish_period_));
}
这里我们开始阅读它的回调函数SlamGMapping::laserCallback()
2.2、laserCallback()函数
*/**
*** *接受到激光雷达数据的回调函数* *在这里面调用addScan()函数*
*** *如果addScan()函数调用成功,也就是说激光数据被成功的插入到地图中后,*
*** *如果到了地图更新的时间,则对地图进行更新,通过调用updateMap()函数来进行相应的操作。*
***
*** *laserCallback()->addScan()->gmapping::processScan()*
*** *->updateMap()*
***
**/*
void SlamGMapping::laserCallback(const sensor_msgs::LaserScan::ConstPtr& scan)
{
laser_count_++;
if ((laser_count_ % throttle_scans_) != 0)
return;
*//初始化地图更新计算时间为0,因为函数运行完成后这个计数值依然需要一直增加来计算地图是否需要更新*
static ros::Time last_map_update(0,0);
*//* *We* *can't* *initialize* *the* *mapper* *until* *we've* *got* *the* *first* *scan*
if(!got_first_scan_)
{
if(!initMapper(*scan))
return;
got_first_scan_ = true;
}
GMapping::OrientedPoint odom_pose;*//OrientedPoint为机器人位姿的类,包含机器人坐标以及方向*
if(addScan(*scan, odom_pose))*//addScan()即为下一个核心函数作用下面会着重介绍*
{
ROS_DEBUG("scan processed");
GMapping::OrientedPoint mpose = gsp_->getParticles()[gsp_->getBestParticleIndex()].pose;
*//ROS_DEBUG相当于printf的作用*
ROS_DEBUG("new best pose: %.3f %.3f %.3f", mpose.x, mpose.y, mpose.theta);
ROS_DEBUG("odom pose: %.3f %.3f %.3f", odom_pose.x, odom_pose.y, odom_pose.theta);
ROS_DEBUG("correction: %.3f %.3f %.3f", mpose.x - odom_pose.x, mpose.y - odom_pose.y, mpose.theta - odom_pose.theta);
tf::Transform laser_to_map = tf::Transform(tf::createQuaternionFromRPY(0, 0, mpose.theta), tf::Vector3(mpose.x, mpose.y, 0.0)).inverse();
tf::Transform odom_to_laser = tf::Transform(tf::createQuaternionFromRPY(0, 0, odom_pose.theta), tf::Vector3(odom_pose.x, odom_pose.y, 0.0));
*//这里我的理解是打开互斥锁,加快程序运行速度*
map_to_odom_mutex_.lock();
map_to_odom_ = (odom_to_laser * laser_to_map).inverse();
map_to_odom_mutex_.unlock();
*/*如果没有地图那肯定需要直接更新,如果有地图了则需要到时间了,才更新地图了*/*
*/*map_update_interval_为更新地图的时间设置,这个参数通过gmapping_sim.launch文件中的map_update_interval设置*/*
if(!got_map_ || (scan->header.stamp - last_map_update) > map_update_interval_)
{
*/*多久更新一次地图*/*
updateMap(*scan);
*//时间更新回到初始值*
last_map_update = scan->header.stamp;
*//输出更新地图*
ROS_DEBUG("Updated the map");
}
}
else
ROS_DEBUG("cannot process scan");
}
下面从这个函数跳转到add_scan()
2.3、add_scan()函数
*/**
*** *加入一个激光雷达的数据* *主要函数* *这里面会调用processScan()函数*
*** *这个函数被laserCallback()函数调用*
*** *不难看出这里在laserCallback中的调用形式是addScan(*scan,* *odom_pose),*
*** *scan为雷达的扫描返回值,*
**/*
bool SlamGMapping::addScan(const sensor_msgs::LaserScan& scan, GMapping::OrientedPoint& gmap_pose)
{
*//得到与激光的时间戳相对应的机器人的里程计的位姿*
if(!getOdomPose(gmap_pose, scan.header.stamp))
return false;
*//检测是否所有帧的数据都是相等的* *如果不相等就进行计算* *不知道为什么* *感觉完全没必要啊。*
*//特别是对于champion_nav_msgs的LaserScan来说* *激光束的数量经常变*
if(scan.ranges.size() != gsp_laser_beam_count_)
return false;
*//* *创建一个结构体储存激光的角度数据*
double* ranges_double = new double[scan.ranges.size()];
*//* *如果激光是反着装的,这激光的顺序需要反过来,同时这里会排除掉所有激光距离小于range_min的值。*
*//* *排除的方式是把他们设置为最大值*
if (do_reverse_range_)
{
ROS_DEBUG("Inverting scan");
int num_ranges = scan.ranges.size();
for(int i=0; i < num_ranges; i++)
{
*//* *Must* *filter* *out* *short* *readings,* *because* *the* *mapper* *won't*
if(scan.ranges[num_ranges - i - 1] < scan.range_min)
ranges_double[i] = (double)scan.range_max;
else
ranges_double[i] = (double)scan.ranges[num_ranges - i - 1];
}
}
else
{
for(unsigned int i=0; i < scan.ranges.size(); i++)
{
*//* *将全部读取到的点储存到ranges_double这个数组里面*
if(scan.ranges[i] < scan.range_min)*//判断是否超过阈值,如果超过则为最大阈值,常规操作*
ranges_double[i] = (double)scan.range_max;
else
ranges_double[i] = (double)scan.ranges[i];
}
}
*//把ROS的激光雷达数据信息* *转换为* *GMapping算法看得懂的形式*
*/**
*** *这里第一个参数代表雷达光束的数量*
*** *第二个参数代表雷达扫描返回距离*
*** *第三和第四个在SensorReading(rs,time)中调用的第一个参数以及第二个参赛*
*** *最终读到类RangeReading实体中的距离以及角度中储存起来*
**/*
GMapping::RangeReading reading(scan.ranges.size(),
ranges_double,
gsp_laser_,
scan.header.stamp.toSec());
*//* *...but* *it* *deep* *copies* *them* *in* *RangeReading* *constructor,* *so* *we* *don't*
*//* *need* *to* *keep* *our* *array* *around.*
*//* *上面的初始话是进行深拷贝* *因此申请的内存可以直接释放。*
delete[] ranges_double;
*//设置和激光数据的时间戳匹配的机器人的位姿*
reading.setPose(gmap_pose);
*//输出processing* *scan证明函数正常进入,在大工程需要经常使用的代码思路,可以在有bug时快速定位bug位置*
ROS_DEBUG("processing scan");
*//调用gmapping算法进行处理*
return gsp_->processScan(reading);
}
这时候就进入processScan函数中了,这个函数里面放着SLAM算法,也是算法的核心函数。
2.4、processScan()函数
*/**
*** *在scanmatcherprocessor里面也有一个这样的函数* *但是那个函数是没有使用的*
*@desc* *处理一帧激光数据* *这里是gmapping算法的主要函数。*
*在这个函数里面调用其他的函数,包括里程计预测、激光测量更新、粒子采样等等步骤。*
*主要步骤如下:*
*利用运动模型更新里程计分布*
*利用最近的一次观测来提高proposal分布。(scan-match)*
*利用proposal分布+激光雷达数据来确定各个粒子的权重*
*对粒子进行重采样*
**/*
bool GridSlamProcessor::processScan(const RangeReading & reading, int adaptParticles)
{
*/**retireve* *the* *position* *from* *the* *reading,* *and* *compute* *the* *odometry*/*
*/*得到当前的里程计的位置,m_pose*/*
OrientedPoint relPose=reading.getPose();
*//relPose.y* *=* *m_odoPose.y;*
*/*m_count表示这个函数被调用的次数* *如果是第0次调用,则所有的位姿都是一样的*/*
if (!m_count)
{
m_lastPartPose=m_odoPose=relPose;
}
*//write* *the* *state* *of* *the* *reading* *and* *update* *all* *the* *particles* *using* *the* *motion* *model*
*/*对于每一个粒子,都从里程计运动模型中采样,得到车子的初步估计位置* *这一步对应于* *里程计的更新* **/*
int tmp_size = m_particles.size();
*//这个for循环显然可以用OpenMP进行并行化*
*//#pragma* *omp* *parallel* *for*
for(int i = 0; i < tmp_size;i++)
{
OrientedPoint& pose(m_particles[i].pose);
*//对所有的粒子进行采样函数,这个函数的原理来源于《概率机器人》93页的采样算法*
pose = m_motionModel.drawFromMotion(m_particles[i],relPose,m_odoPose);
}
*//invoke* *the* *callback*
*/*回调函数* *实际上什么都没做*/*
*onOdometryUpdate*();
*//m_***均为代码的核心变量*
*//* *accumulate* *the* *robot* *translation* *and* *rotation*
*/*根据两次里程计的数据* *计算出来机器人的线性位移和角度位移的累积值* *m_odoPose表示上一次的里程计位姿* *relPose表示新的里程计的位姿*/*
OrientedPoint move=relPose-m_odoPose;
move.theta=atan2(sin(move.theta), cos(move.theta));
*//统计机器人在进行激光雷达更新之前* *走了多远的距离* *以及* *平移了多少的角度*
m_linearDistance+=sqrt(move*move);
m_angularDistance+=fabs(move.theta);
*//* *cerr* *<<"linear* *Distance:"<
*//* *cerr* *<<"angular* *Distance:"<
*//* *if* *the* *robot* *jumps* *throw* *a* *warning*
*/**
*** *如果机器人在走了m_distanceThresholdCheck这么远的距离都没有进行激光雷达的更新*
*** *则需要进行报警。这个误差很可能是里程计或者激光雷达的BUG造成的。*
*** *例如里程计数据出错* *或者* *激光雷达很久没有数据等等*
*** *每次进行激光雷达的更新之后* *m_linearDistance这个参数就会清零*
**/*
if (m_linearDistance>m_distanceThresholdCheck)
{
cerr << "***********************************************************************" << endl;
cerr << "********** Error: m_distanceThresholdCheck overridden!!!! *************" << endl;
cerr << "m_distanceThresholdCheck=" << m_distanceThresholdCheck << endl;
cerr << "Old Odometry Pose= " << m_odoPose.x << " " << m_odoPose.y
<< " " <<m_odoPose.theta << endl;
cerr << "New Odometry Pose (reported from observation)= " << relPose.x << " " << relPose.y
<< " " <<relPose.theta << endl;
cerr << "***********************************************************************" << endl;
cerr << "** The Odometry has a big jump here. This is probably a bug in the **" << endl;
cerr << "** odometry/laser input. We continue now, but the result is probably **" << endl;
cerr << "** crap or can lead to a core dump since the map doesn't fit.... C&G **" << endl;
cerr << "***********************************************************************" << endl;
}
*//更新* *把当前的位置赋值给旧的位置*
m_odoPose=relPose;
bool processed=false;
*//* *process* *a* *scan* *only* *if* *the* *robot* *has* *traveled* *a* *given* *distance* *or* *a* *certain* *amount* *of* *time* *has* *elapsed*
*/*只有当机器人走过一定的距离* *或者* *旋转过一定的角度* *或者过一段指定的时间才处理激光数据*/*
if (! m_count
|| m_linearDistance>=m_linearThresholdDistance
|| m_angularDistance>=m_angularThresholdDistance
|| (period_ >= 0.0 && (reading.getTime() - last_update_time_) > period_))
{
last_update_time_ = reading.getTime();
std::cout <<std::endl<<"Start to Process Scan##################"<<std::endl;
if (m_outputStream.is_open())
{
m_outputStream << setiosflags(ios::fixed) << setprecision(6);
m_outputStream << "FRAME " << m_readingCount;
m_outputStream << " " << m_linearDistance;
m_outputStream << " " << m_angularDistance << endl;
}
*//* *if* *(m_infoStream)*
*//* *{*
*//* *m_infoStream* *<<* *"update* *frame* *"* *<<* *m_readingCount* *<<* *endl*
*//* *<<* *"update* *ld="* *<<* *m_linearDistance* *<<* *"* *ad="* *<<* *m_angularDistance* *<<* *endl;*
*//* *m_infoStream* *<<* *"FRAME* *"* *<<* *m_readingCount<
*//* *m_infoStream* *<<"Scan-Match* *Number:* *"<
*//* *}*
*//* *cerr* *<<* *"Laser* *Pose=* *"* *<<* *reading.getPose().x* *<<* *"* *"* *<<* *reading.getPose().y*
*//* *<<* *"* *"* *<<* *reading.getPose().theta* *<<* *endl;*
*//this* *is* *for* *converting* *the* *reading* *in* *a* *scan-matcher* *feedable* *form*
*/*复制一帧数据* *把激光数据转换为scan-match需要的格式*/*
*//* *if(reading.getSize()* *!=* *m_beams)*
*//* *{*
*//* *cerr<<"********************************************"<
*//* *cerr<<"********************************************"<
*//* *cerr<<"reading_size:"<
*//* *cerr<<"********************************************"<
*//* *cerr<<"********************************************"<
*//* *}*
int beam_number = reading.getSize();
double * plainReading = new double[beam_number];
for(unsigned int i=0; i<beam_number; i++)
{
plainReading[i]=reading.m_dists[i];
}
*//这个备份主要是用来储存的。*
RangeReading* reading_copy;
*//champion_nav_msgs激光数据*
if(reading.m_angles.size() == reading.m_dists.size())
{*//将激光雷达数据转换为可以读得数据*
reading_copy = new RangeReading(beam_number,
&(reading.m_dists[0]),
&(reading.m_angles[0]),
static_cast<const RangeSensor*>(reading.getSensor()),
reading.getTime());
}
*//ros的激光数据*
else
{
reading_copy = new RangeReading(beam_number,
&(reading.m_dists[0]),
static_cast<const RangeSensor*>(reading.getSensor()),
reading.getTime());
}
*/*如果不是第一帧数据*/*
if (m_count>0)
{
*/**
*为每个粒子进行scanMatch,计算出来每个粒子的最优位姿,同时计算改最优位姿的得分和似然* *对应于gmapping论文中的用最近的一次测量计算proposal的算法*
*这里面除了进行scanMatch之外,还对粒子进行了权重的计算,并计算了粒子的有效区域* *但不进行内存分配* *内存分配在resample()函数中*
*这个函数在gridslamprocessor.hxx里面。*
**/*
scanMatch(plainReading);
*//至此* *关于proposal的更新完毕了,接下来是计算权重*
*onScanmatchUpdate*();
*/**
*由于scanMatch中对粒子的权重进行了更新,那么这个时候各个粒子的轨迹上的累计权重都需要重新计算*
*这个函数即更新各个粒子的轨迹上的累计权重是更新*
*GridSlamProcessor::updateTreeWeights(bool* *weightsAlreadyNormalized)* *函数在gridslamprocessor_tree.cpp里面实现*
**/*
updateTreeWeights(false);
*/**
*** *粒子重采样* *根据neff的大小来进行重采样* *不但进行了重采样,也对地图进行更新*
*** *GridSlamProcessor::resample* *函数在gridslamprocessor.hxx里面实现*
**/*
std::cerr<<"plainReading:"<<m_beams<<std::endl;
resample(plainReading, adaptParticles, reading_copy);
}
*/*如果是第一帧激光数据*/*
else
{
*//如果是第一帧数据,则可以直接计算activeArea。因为这个时候,对机器人的位置是非常确定的,就是(0,0,0)*
for (ParticleVector::iterator it=m_particles.begin(); it!=m_particles.end(); it++)
{
m_matcher.invalidateActiveArea();
m_matcher.computeActiveArea(it->map, it->pose, plainReading);
m_matcher.registerScan(it->map, it->pose, plainReading);
*//m_matcher.registerScan(it->lowResolutionMap,it->pose,plainReading);*
*//为每个粒子创建路径的第一个节点。该节点的权重为0,父节点为it->node(这个时候为NULL)。*
*//因为第一个节点就是轨迹的根,所以没有父节点*
TNode* node=new TNode(it->pose, 0., it->node, 0);
node->reading = reading_copy;
it->node=node;
}
}
*//* *cerr* *<<* *"Tree:* *normalizing,* *resetting* *and* *propagating* *weights* *at* *the* *end..."* *;*
*//进行重采样之后,粒子的权重又会发生变化,因此需要再次更新粒子轨迹的累计权重*
*//GridSlamProcessor::updateTreeWeights(bool* *weightsAlreadyNormalized)* *函数在gridslamprocessor_tree.cpp里面实现*
updateTreeWeights(false);
*//* *cerr* *<<* *".done!"* *<
delete [] plainReading;
m_lastPartPose=m_odoPose; *//update* *the* *past* *pose* *for* *the* *next* *iteration*
*//机器人累计行走的多远的路程没有进行里程计的更新* *每次更新完毕之后都要把这个数值清零*
m_linearDistance=0;
m_angularDistance=0;
m_count++;
processed=true;
*//keep* *ready* *for* *the* *next* *step*
for (ParticleVector::iterator it=m_particles.begin(); it!=m_particles.end(); it++)
{
it->previousPose=it->pose;
}
}
m_readingCount++;
return processed;
}
中间有几个比较重要的函数,其余可以参考注释看懂,重要的函数包括一下几个小标题描述。
2.4.1、drawFromMotion()函数
*/**
*@desc* *里程计运动模型*
*@p* *表示粒子估计的最优位置(机器人上一个时刻的最优位置)*
*@pnew* *表示里程计算出来的新的位置*
*@pold* *表示里程计算出来的旧的位置(即上一个里程计的位置)*
**/*
OrientedPoint
MotionModel::drawFromMotion(const OrientedPoint& p, const OrientedPoint& pnew, const OrientedPoint& pold) const{*//不改变类其他成员的值*
double sxy=0.3*srr;*//srr为launch文件的设置好*
*/**
*** *计算出pnew* *相对于* *pold走了多少距离*
*** *这里的距离表达是相对于车身坐标系来说的。*
**/*
OrientedPoint delta=absoluteDifference(pnew, pold);*//计算两个的矢量差*
*/*初始化一个点*/*
OrientedPoint noisypoint(delta);
*/*走过的X轴方向的距离加入噪声*/*
*//这里的参数srr*fabs(delta.x)+str*fabs(delta.theta)+sxy*fabs(delta.y)是高斯分布的方差*
*/**
*** *这里的几个参数srr,str,sxy的作用会影响到相应小车的移动大小的噪声系数*
**/*
noisypoint.x+=sampleGaussian(srr*fabs(delta.x)+str*fabs(delta.theta)+sxy*fabs(delta.y));
*/*走过的Y轴方向的距离加入噪声*/*
noisypoint.y+=sampleGaussian(srr*fabs(delta.y)+str*fabs(delta.theta)+sxy*fabs(delta.x));
*/*走过的Z轴方向的距离加入噪声*/*
noisypoint.theta+=sampleGaussian(stt*fabs(delta.theta)+srt*sqrt(delta.x*delta.x+delta.y*delta.y));
*/*限制角度的范围*/*
noisypoint.theta=fmod(noisypoint.theta, 2*M_PI);
if (noisypoint.theta>M_PI)
noisypoint.theta-=2*M_PI;
*/*把加入了噪声的值* *加到粒子估计的最优的位置上* *即得到新的位置(根据运动模型推算出来的位置)*/*
return absoluteSum(p,noisypoint);
}
采样系数的大小即高斯分布的方差。
2.4.2、scanMatch()函数
这个函数在gridslamprocessor.hxx里面,它的作用是计算激光里程计,原理是模拟蒙特卡洛,即点图匹配:
inline void GridSlamProcessor::scanMatch(const double* plainReading)
{
*//* *sample* *a* *new* *pose* *from* *each* *scan* *in* *the* *reference*
*/*每个粒子都要进行scan-match*/*
double sumScore=0;
int particle_number = m_particles.size();
*//用openMP的方式来进行并行化,因此这里不能用迭代器* *只能用下标的方式进行访问*
*//并行话之后会把里面的循环均匀的分到各个不同的核里面去。*
*//#pragma* *omp* *parallel* *for*
for (int i = 0; i < particle_number;i++)
{
OrientedPoint corrected;
double score, l, s;
*/*进行scan-match* *计算粒子的最优位姿* *调用scanmatcher.cpp里面的函数* *--这是gmapping本来的做法*/*
score=m_matcher.optimize(corrected, m_particles[i].map, m_particles[i].pose, plainReading);
*/*矫正成功则更新位姿*/*
if (score>m_minimumScore)
{
m_particles[i].pose = corrected;
}
*/*扫描匹配不上* *则使用里程计的数据* *使用里程计数据不进行更新* *因为在进行扫描匹配之前* *里程计已经更新过了*/*
else
{
*//输出信息* *这个在并行模式下可以会出现错位*
if (m_infoStream)
{
m_infoStream << "Scan Matching Failed, using odometry. Likelihood=" << l <<std::endl;
m_infoStream << "lp:" << m_lastPartPose.x << " " << m_lastPartPose.y << " "<< m_lastPartPose.theta <<std::endl;
m_infoStream << "op:" << m_odoPose.x << " " << m_odoPose.y << " "<< m_odoPose.theta <<std::endl;
}
}
*//粒子的最优位姿计算了之后,重新计算粒子的权重(相当于粒子滤波器中的观测步骤,计算p(z|x,m)),粒子的权重由粒子的似然来表示。*
*/**
*** *计算粒子的得分和权重(似然)* *注意粒子的权重经过ScanMatch之后已经更新了*
*** *在论文中* *例子的权重不是用最有位姿的似然值来表示的。*
*** *是用所有的似然值的和来表示的。*
**/*
m_matcher.likelihoodAndScore(s, l, m_particles[i].map, m_particles[i].pose, plainReading);
sumScore+=score;
m_particles[i].weight+=l;
m_particles[i].weightSum+=l;
*//set* *up* *the* *selective* *copy* *of* *the* *active* *area*
*//by* *detaching* *the* *areas* *that* *will* *be* *updated*
*/*计算出来最优的位姿之后,进行地图的扩充* *这里不会进行内存分配*
**不进行内存分配的原因是这些粒子进行重采样之后有可能会消失掉,因此在后面进行冲采样的时候统一进行内存分配。*
**理论上来说,这里的操作是没有必要的,因为后面的重采样的时候还会进行一遍*
**/*
m_matcher.invalidateActiveArea();
m_matcher.computeActiveArea(m_particles[i].map, m_particles[i].pose, plainReading);
}
if (m_infoStream)
m_infoStream << "Average Scan Matching Score=" << sumScore/m_particles.size() << std::endl;
}
2.4.2.1、ScanMatcher::optimize()函数的原理
这个函数也是帧间匹配的核心函数,它的作用是计算最合适的位姿并返回其得分。向八个方向模拟移动粒子位姿,然后在八个移动位姿后的地方进行地图匹配计算找到最优的位姿。
*/**
*/* *zq* *commit*
*@desc* *根据地图、激光数据、位姿迭代求解一个最优的新的位姿出来*
*这个函数是真正被调用来进行scan-match的函数*
*@param* *pnew* *新的最优位置*
*@param* *map* *地图*
*@param* *init* *初始位置*
*@param* *readings* *激光数据*
**/*
double ScanMatcher::optimize(OrientedPoint& pnew, const ScanMatcherMap& map, const OrientedPoint& init, const double* readings) const
{
double bestScore=-1;
*/*计算当前位置的得分*/*
OrientedPoint currentPose=init;
double currentScore=score(map, currentPose, readings);
*/*所有时的步进增量*/*
double adelta=m_optAngularDelta, ldelta=m_optLinearDelta;
*/*精确搜索的次数*/*
unsigned int refinement=0;
*/*搜索的方向*/*
enum Move{*Front*, *Back*, *Left*, *Right*, *TurnLeft*, *TurnRight*, *Done*};
*//enum* *Move{Front,* *Back,* *Left,* *Right,* *TurnLeft,* *TurnRight,* *Done};*
int c_iterations=0;
do
{
*/*如果这一次(currentScore)算出来比上一次(bestScore)差,则有可能是走太多了,要减少搜索步长* *这个策略跟LM有点像*/*
if (bestScore>=currentScore)
{
refinement++;
adelta*=.5;
ldelta*=.5;
}
bestScore=currentScore;
OrientedPoint bestLocalPose=currentPose;
OrientedPoint localPose=currentPose;
*/*把8个方向都搜索一次* *得到这8个方向里面最好的一个位姿和对应的得分*/*
Move move=*Front*;
//模拟运动计算相应地图匹配得分
do
{
localPose=currentPose;
switch(move)
{
case *Front*:
localPose.x+=ldelta;
move=*Back*;
break;
case *Back*:
localPose.x-=ldelta;
move=*Left*;
break;
case *Left*:
localPose.y-=ldelta;
move=*Right*;
break;
case *Right*:
localPose.y+=ldelta;
move=*TurnLeft*;
break;
case *TurnLeft*:
localPose.theta+=adelta;
move=*TurnRight*;
break;
case *TurnRight*:
localPose.theta-=adelta;
move=*Done*;
break;
default:;
}
*//计算当前的位姿和初始位姿的区别* *区别越大增益越小*
double odo_gain=1;
*//计算当前位姿的角度和初始角度的区别* *如果里程计比较可靠的话*
*//那么进行匹配的时候就需要对离初始位姿比较远的位姿施加惩罚*
if (m_angularOdometryReliability>0.)
{
double dth=init.theta-localPose.theta; dth=atan2(sin(dth), cos(dth)); dth*=dth;
odo_gain*=exp(-m_angularOdometryReliability*dth);
}
*//计算线性距离的区别* *线性距离也是一样*
if (m_linearOdometryReliability>0.)
{
double dx=init.x-localPose.x;
double dy=init.y-localPose.y;
double drho=dx*dx+dy*dy;
odo_gain*=exp(-m_linearOdometryReliability*drho);
}
*/*计算得分=增益*score*/*
double localScore=odo_gain*score(map, localPose, readings);
*/*如果得分更好,则更新*/*
if (localScore>currentScore)
{
currentScore=localScore;
bestLocalPose=localPose;
}
c_iterations++;
} while(move!=*Done*);
*/** *把当前位置设置为目前最优的位置* *如果8个值都被差了的话,那么这个值不会更新*/*
currentPose=bestLocalPose;
}while (currentScore>bestScore || refinement<m_optRecursiveIterations);
*/*返回最优位置和得分*/*
pnew=currentPose;
return bestScore;
}
2.4.2.2、ScanMatcher::score()函数
这个函数原理是计算位姿的似然得分,出处是《概率机器人》的第六章,这一章专门开一章来介绍,即在第三章介绍。首先确定是否为障碍物,然后进行障碍物匹配计算高斯得分。
*/**
*@desc* *根据地图、机器人位置、激光雷达数据,计算出一个得分:原理为likelihood_field_range_finder_model*
*这个函数被scanmatcher.cpp里面的optimize(OrientedPoint&* *pnew,* *const* *ScanMatcherMap&* *map,* *const* *OrientedPoint&* *init,* *const* *double** *readings)*
*调用*
*@map* *对应的地图*
*@p* *机器人对应的初始位置*
*@readings* *激光雷达数据*
**/*
inline double ScanMatcher::score(const ScanMatcherMap& map, const OrientedPoint& p, const double* readings) const
{
double s=0;
const double * angle=m_laserAngles+m_initialBeamsSkip;
OrientedPoint lp=p;
*/**
*把激光雷达的坐标转换到世界坐标系*
*先旋转到机器人坐标系,然后再转换到世界坐标系*
*p表示base_link在map中的坐标*
*m_laserPose* *表示base_laser在base_link坐标系中的坐标*
**/*
lp.x+=cos(p.theta)*m_laserPose.x-sin(p.theta)*m_laserPose.y;
lp.y+=sin(p.theta)*m_laserPose.x+cos(p.theta)*m_laserPose.y;
lp.theta+=m_laserPose.theta;
*/**
*** *map.getDelta表示地图分辨率* *m_freeCellRatio* *=* *sqrt(2)*
*** *意思是如果激光hit了某个点* *那么沿着激光方向的freeDelta距离的地方要是空闲才可以*
**/*
unsigned int skip=0;
double freeDelta=map.getDelta()*m_freeCellRatio;
*//枚举所有的激光束*
for (const double* r=readings+m_initialBeamsSkip; r<readings+m_laserBeams; r++, angle++)
{
skip++;
skip=skip>m_likelihoodSkip?0:skip;
if (skip||*r>m_usableRange||*r==0.0) continue;
*/*被激光雷达击中的点* *在地图坐标系中的坐标*/*
Point phit=lp;
phit.x+=*r*cos(lp.theta+*angle);
phit.y+=*r*sin(lp.theta+*angle);
IntPoint iphit=map.world2map(phit);
*/*该束激光的最后一个空闲坐标,即紧贴hitCell的freeCell* *原理为:假设phit是被激光击中的点,这样的话沿着激光方向的前面一个点必定的空闲的*/*
Point pfree=lp;
*//理论上来说* *这个应该是一个bug。修改成下面的之后,改善不大。*
*//* *pfree.x+=(*r-map.getDelta()*freeDelta)*cos(lp.theta+*angle);*
*//* *pfree.y+=(*r-map.getDelta()*freeDelta)*sin(lp.theta+*angle);*
pfree.x+=(*r - freeDelta)*cos(lp.theta+*angle);
pfree.y+=(*r - freeDelta)*sin(lp.theta+*angle);
*/*phit* *和* *freeCell的距离*/*
pfree=pfree-phit;
IntPoint ipfree=map.world2map(pfree);
*/*在kernelSize大小的窗口中搜索出最优最可能被这个激光束击中的点* *这个kernelSize在大小为1*/*
bool found=false;
Point bestMu(0.,0.);
for (int xx=-m_kernelSize; xx<=m_kernelSize; xx++)
for (int yy=-m_kernelSize; yy<=m_kernelSize; yy++)
{
*/*根据已开始的关系* *搜索phit的时候,也计算出来pfree*/*
IntPoint pr=iphit+IntPoint(xx,yy);
IntPoint pf=pr+ipfree;
*/*得到各自对应的Cell*/*
const PointAccumulator& cell=map.cell(pr);
const PointAccumulator& fcell=map.cell(pf);
*/**
*(double)cell返回的是该cell被占用的概率*
*这束激光要合法必须要满足cell是被占用的,而fcell是空闲的*
*原理为:假设phit是被激光击中的点,这样的话沿着激光方向的前面一个点必定的空闲的*
**/*
if (((double)cell )> m_fullnessThreshold && ((double)fcell )<m_fullnessThreshold)
{
*/*计算出被击中的点与对应的cell的currentScore距离*/*
Point mu=phit-cell.mean();
if (!found)
{
bestMu=mu;
found=true;
}
else
{
bestMu=(mu*mu)<(bestMu*bestMu)?mu:bestMu;
}
}
}
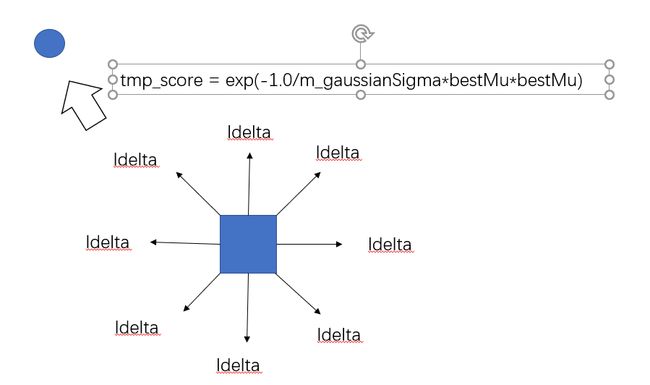
*/*socre的计算公式exp(-d^2* */* *sigma))* *这里的sigma表示方差* *不是标准差*/*
if (found)
{
double tmp_score = exp(-1.0/m_gaussianSigma*bestMu*bestMu);
s += tmp_score;
*//只在周围的9个栅格里面寻找,因此平方的意义不大。*
*//s* *+=* *tmp_score*tmp_score;*
}
}
return s;
}
2.4.3、onScanmatchUpdate()函数
void GridSlamProcessorThread::*onScanmatchUpdate*(){
pthread_mutex_lock(&hp_mutex);
hypotheses.clear();
weightSums.clear();
unsigned int bestIdx=0;
double bestWeight=-1e1000;
unsigned int idx=0;
for (GridSlamProcessor::ParticleVector::const_iterator part=getParticles().begin(); part!=getParticles().end(); part++ ){
hypotheses.push_back(part->pose);
weightSums.push_back(part->weightSum);
if(part->weightSum>bestWeight){
bestIdx=idx;
bestWeight=part->weightSum;
}
idx++;
}
ParticleMoveEvent* event=new ParticleMoveEvent;
event->scanmatched=true;
event->hypotheses=hypotheses;
event->weightSums=weightSums;
event->neff=m_neff;
addEvent(event);
if (! mapTimer){
MapEvent* event=new MapEvent;
event->index=bestIdx;
event->pmap=new ScanMatcherMap(getParticles()[bestIdx].map);
event->pose=getParticles()[bestIdx].pose;
addEvent(event);
}
mapTimer++;
mapTimer=mapTimer%mapUpdateTime;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&hp_mutex);
*syncOdometryUpdate*();
}
这个函数的作用是初始化全部粒子的权值。
2.4.4、updateTreeWeights()函数
void GridSlamProcessor::updateTreeWeights(bool weightsAlreadyNormalized)
{
if (!weightsAlreadyNormalized)
{
normalize();归一化权值
}
resetTree();//使树的每一个节点全部为0
propagateWeights();
}
2.4.4.1、resetTree()函数
*/*把所有粒子的所有的轨迹中各个节点的accWeight清零*/*
void GridSlamProcessor::resetTree()
{
*//* *don't* *calls* *this* *function* *directly,* *use* *updateTreeWeights(..)* *!*
for (ParticleVector::iterator it=m_particles.begin(); it!=m_particles.end(); it++)
{
TNode* n=it->node;
while (n)
{
n->accWeight=0;
n->visitCounter=0;
n=n->parent;
}
}
}
2.4.4.2、normalize()函数
*/**
*@desc* *把粒子的权重归一化*
*主要功能为归一化粒子的权重,同时计算出neff*
**/*
inline void GridSlamProcessor::normalize()
{
*//normalize* *the* *log* *m_weights*
double gain=1./(m_obsSigmaGain*m_particles.size());
*/*求所有粒子中的最大的权重*/*
double lmax= -std::numeric_limits<double>::max();
for (ParticleVector::iterator it=m_particles.begin(); it!=m_particles.end(); it++)
{
lmax=it->weight>lmax?it->weight:lmax;
}
*//cout* *<<* *"!!!!!!!!!!!* *maxwaight=* *"<<* *lmax* *<<* *endl;*
*/*权重以最大权重为中心的高斯分布*/*
m_weights.clear();
double wcum=0;
m_neff=0;
for (std::vector<Particle>::iterator it=m_particles.begin(); it!=m_particles.end(); it++)
{
m_weights.push_back(exp(gain*(it->weight-lmax)));
wcum+=m_weights.back();
*//cout* *<<* *"l="* *<<* *it->weight<<* *endl;*
}
*/**
*计算有效粒子数* *和* *归一化权重*
*权重=wi/w*
*neff* *=* *1/w*w*
**/*
m_neff=0;
for (std::vector<double>::iterator it=m_weights.begin(); it!=m_weights.end(); it++)
{
*it=*it/wcum;
double w=*it;
m_neff+=w*w;
}
m_neff=1./m_neff;*//这个变量的作用是判断是否进行重采样防止粒子耗散。*
}
2.4.5、resample函数
*/**
*@desc* *粒子滤波器重采样。*
*分为两步:*
*1.需要重采样,则所有保留下来的粒子的轨迹都加上一个新的节点,然后进行地图更新。*
*2.不需要冲采样,则所有的粒子的轨迹都加上一个新的节点,然后进行地图的更新*
*在重采样完毕之后,会调用registerScan函数来更新地图*
**/*
inline bool GridSlamProcessor::resample(const double* plainReading, int adaptSize, const RangeReading* reading)
{
bool hasResampled = false;
*/*备份老的粒子的轨迹* *即保留叶子节点* *在增加新节点的时候使用*/*
TNodeVector oldGeneration;
for (unsigned int i=0; i<m_particles.size(); i++)
{
oldGeneration.push_back(m_particles[i].node);
}
*/*如果需要进行重采样*/*
if (m_neff<m_resampleThreshold*m_particles.size())
{
if (m_infoStream)
m_infoStream << "*************RESAMPLE***************" << std::endl;
*//采取重采样方法决定,哪些粒子会保留* *保留的粒子会返回下标.里面的下标可能会重复,因为有些粒子会重复采样*
*//而另外的一些粒子会消失掉*
uniform_resampler<double, double> resampler;
m_indexes=resampler.resampleIndexes(m_weights, adaptSize);*//重采样第一个参数总共多少粒子,第二个保留多少粒子*
if (m_outputStream.is_open())
{
m_outputStream << "RESAMPLE "<< m_indexes.size() << " ";
for (std::vector<unsigned int>::const_iterator it=m_indexes.begin(); it!=m_indexes.end(); it++)
{
m_outputStream << *it << " ";
}
m_outputStream << std::endl;
}
onResampleUpdate();
*//BEGIN:* *BUILDING* *TREE*
*//重采样之后的粒子*
ParticleVector temp;
unsigned int j=0;
*//要删除的粒子下标*
std::vector<unsigned int> deletedParticles; *//this* *is* *for* *deleteing* *the* *particles* *which* *have* *been* *resampled* *away.*
*//枚举每一个要被保留的粒子*
for (unsigned int i=0; i<m_indexes.size(); i++)
{
*//统计要被删除的粒子*
while(j<m_indexes[i])
{
deletedParticles.push_back(j);
j++;
}
if (j==m_indexes[i])
j++;
*//得到当前的保留的粒子*
Particle & p=m_particles[m_indexes[i]];
*//每一个需要保留下来的粒子都需要在路径中增加一个新的节点*
TNode* node=0;
TNode* oldNode=oldGeneration[m_indexes[i]];
*//创建一个新的节点* *改节点的父节点为oldNode*
node=new TNode(p.pose, 0, oldNode, 0);
node->reading=reading;
*//这个要保留下来的粒子,要保留的粒子的下标为m_indexs*
temp.push_back(p);
temp.back().node=node;
temp.back().previousIndex=m_indexes[i];
}
while(j<m_indexes.size())
{
deletedParticles.push_back(j);
j++;
}
*//把要删除的粒子的Node都删除掉,Node表示轨迹的起点(最新的点)*
std::cerr << "Deleting Nodes:";
for (unsigned int i=0; i<deletedParticles.size(); i++)
{
std::cerr <<" " << deletedParticles[i];
delete m_particles[deletedParticles[i]].node;
m_particles[deletedParticles[i]].node=0;
}
std::cerr << " Done" <<std::endl;
std::cerr << "Deleting old particles..." ;
std::cerr << "Done" << std::endl;
*//清楚全部的粒子* *然后从tmp中读取保留下来的粒子*
m_particles.clear();
*//枚举要保留下来的所有的粒子* *每个粒子都需要更新地图*
std::cerr << "Copying Particles and Registering scans...";
*//对于保留下来的粒子进行更新* *这里是可以并行化操作的。*
*//在并行化操作里面* *m_particles.push_back()会报错* *因此并行化* *需要把push_back()提出来。*
*//在外面的的for循环进行*
int tmp_size = temp.size();
*//#pragma* *omp* *parallel* *for*
for(int i = 0; i<tmp_size;i++)
{
*//对保留下来的粒子数据进行更新*
*//每个粒子的权重都设置为相同的值*
temp[i].setWeight(0);
*//为每个粒子更新running_scans*
*//增加了一帧激光数据* *因此需要更新地图*
m_matcher.registerScan(temp[i].map,temp[i].pose,plainReading);
*//m_matcher.registerScan(temp[i].lowResolutionMap,temp[i].pose,plainReading);*
}
*//提取出来* *防止并行优化时报错*
for(int i = 0; i< tmp_size;i++)
m_particles.push_back(temp[i]);
std::cerr << " Done" <<std::endl;
hasResampled = true;
}
*/*否则的话,进行扫描匹配*/*
else
{
*//不进行重采样的话,权值不变。只为轨迹创建一个新的节点*
*//为每个粒子更新地图* *同样可以并行化*
int particle_size = m_particles.size();
*//#pragma* *omp* *parallel* *for*
for(int i = 0; i < particle_size;i++)
{
*//创建一个新的树节点*
TNode* node = 0;
node = new TNode(m_particles[i].pose,0.0,oldGeneration[i],0);
*//把这个节点接入到树中*
node->reading = reading;
m_particles[i].node = node;
*//更新各个例子的地图*
m_matcher.invalidateActiveArea();
m_matcher.registerScan(m_particles[i].map, m_particles[i].pose, plainReading);
m_particles[i].previousIndex = i;
}
std::cerr<<std::endl;
*//* *int* *index=0;*
*//* *TNodeVector::iterator* *node_it=oldGeneration.begin();*
*//* *for* *(ParticleVector::iterator* *it=m_particles.begin();* *it!=m_particles.end();* *it++)*
*//* *{*
*//* *//create* *a* *new* *node* *in* *the* *particle* *tree* *and* *add* *it* *to* *the* *old* *tree*
*//* *//新建一个树的节点。*
*//* *//BEGIN:* *BUILDING* *TREE*
*//* *TNode** *node=0;*
*//* *node=new* *TNode(it->pose,* *0.0,* **node_it,* *0);*
*//* *//node->reading=0;*
*//* *node->reading=reading;*
*//* *it->node=node;*
*//* *//END:* *BUILDING* *TREE*
*//* *//粒子的轨迹更新了之后,对应的地图也需要更新*
*//* *m_matcher.invalidateActiveArea();*
*//* *m_matcher.registerScan(it->map,* *it->pose,* *plainReading);*
*//* *it->previousIndex=index;*
*//* *index++;*
*//* *node_it++;*
*//* *}*
std::cerr << "Done" <<std::endl;
}
*//END:* *BUILDING* *TREE*
return hasResampled;
}
重采样原理操作,使用轮盘赌对权值进行选择。
2.5、占据栅格建图原理
由图可见,当雷达打到障碍物,会将障碍物点设置为hit点,中间的部分设置为miss点。每当被激光打到,则
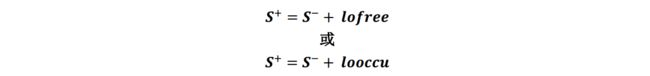
我们假设lofree为-0.4,looccu为0.8,则每当被打到则更新一次栅格概率,概率大于一定值时,则涂黑,中间部分用b氏算法画线。
代码:
//占据栅格地图构建算法
//输入激光雷达数据和机器人位姿数据
//目的:通过遍历所有帧数据,为pMap[]中的每个穿过的空闲栅格或者击中栅格赋新值,中间有个计算方法,也就是占用栅格地图构建的理论实现
void OccupanyMapping(std::vector<GeneralLaserScan>& scans,std::vector<Eigen::Vector3d>& robot_poses)
{
std::cout <<"Scans Size:"<<scans.size()<<std::endl;
std::cout <<"Poses Size:"<<robot_poses.size()<<std::endl;
//遍历所有帧激光雷达数据
for(int i = 0; i < scans.size();i++)
{
//获取每一帧的激光雷达、机器人位姿数据
GeneralLaserScan scan = scans[i];
Eigen::Vector3d robotPose = robot_poses[i];
//获取该帧机器人位姿的栅格序号
GridIndex robotIndex = ConvertWorld2GridIndex(robotPose(0),robotPose(1));
//判断该帧机器人位姿的栅格序号,是否在自己设定的栅格地图范围内
if(isValidGridIndex(robotIndex) == false) continue;
//遍历该帧激光雷达数据所有扫描点
for(int id = 0; id < scan.range_readings.size();id++)
{
//取出该激光雷达扫描点的距离和角度
double dist = scan.range_readings[id];
double angle = scan.angle_readings[id];
//剔除异常数据,跳过该次循环,不作处理
if(std::isinf(dist) || std::isnan(dist)) continue;
//机器人航向角,机器人x轴与世界坐标系x轴夹角
double theta = robotPose(2);
//在旋转过后(与世界坐标系(像素坐标系下)平行)的激光雷达坐标系下的坐标x,y
//该开始一直不理解这个为啥laser_y要加一个负号
//明确激光雷达数据的角度逆时针变化
//明确机器人航向角与世界坐标系x轴呈逆时针变化
//明确这里的世界坐标系world_x,不是真实的世界坐标系,而是像素坐标系,y轴与真实的世界坐标系相反,这样是laser_y加负号的原因
double laser_x = dist * cos(theta + angle);
double laser_y = -dist * sin(theta + angle);
//得到该激光扫描点,在世界坐标系下(像素坐标系下)的位置
double world_x = laser_x + robotPose(0);
double world_y = laser_y + robotPose(1);
//将该激光扫描点在世界坐标系下的位置,转化为栅格序号
GridIndex mapIndex = ConvertWorld2GridIndex(world_x,world_y);
//判断该激光扫描点的栅格序号,是否在自己设定的栅格地图900x900范围内,如果不在则跳过
if(isValidGridIndex(mapIndex) == false)continue;
//从机器人的栅格序号到该激光扫描点的栅格序号划线
//目的:找到两点之间途径的空闲栅格,将栅格序号存入std::vector中
std::vector<GridIndex> freeIndex = TraceLine(robotIndex.x,robotIndex.y,mapIndex.x,mapIndex.y);
//遍历该扫描激光点通过的所有空闲栅格
for(int k = 0; k < freeIndex.size();k++)
{
GridIndex tmpIndex = freeIndex[k];
//将空闲栅格的栅格序号,转化到数组序号,该数组用于存储每一个栅格的数据
int linearIndex = GridIndexToLinearIndex(tmpIndex);
//取出该栅格代表的数据
int data = pMap[linearIndex];
//根据栅格空闲规则,执行data += mapParams.log_free;
if(data > 0)//默认data=50
data += mapParams.log_free;//log_free=-1,data将变小
else
data = 0;
//给该空闲栅格赋新值,最小为0
pMap[linearIndex] = data;
}
//更新该激光扫描点集中的栅格,
int tmpIndex = GridIndexToLinearIndex(mapIndex);
int data = pMap[tmpIndex];
//根据栅格击中规则,执行data += mapParams.log_occ;
if(data < 100)//默认data=50
data += mapParams.log_occ;//log_occ=2,data将变大
else
data = 100;
//给击中的栅格赋新值,最大100
pMap[tmpIndex] = data;
//到这里,对一个位姿下的一个激光扫描数据经过的空闲栅格和击中栅格的pMap进行了重新赋值
}
//到这里,对一个位姿下的一帧激光扫描数据经过的空闲栅格和击中栅格进行了重新赋值
}
//到这里,对所有帧激光扫描数据经过的空闲栅格和击中栅格进行了重新赋值
}
第3章 传感器测量模型
3.1、测量仪的波术模型
测距仪是时下最流行的机器人传感器。因此本章第一个测量模型就是测距仪的近似物理模型。测距仪测量到附近物体的距离。可以沿着一个波束测量距离,或者可以在一个测量锥内测量距离。
3.1.1、基本测量算法
这里的模型采用四类测量误差,所有这些对使模型工作很重要。这四类误差包括小的测量噪声、意外对象引起的误差,以及由于未检测到对象引起的误差和随机庖外噪声。因此,期望模型 p(zIx,m) 是四个密度的混合,每一种密度都与一个特定类型的误差有关。
1.算法解析
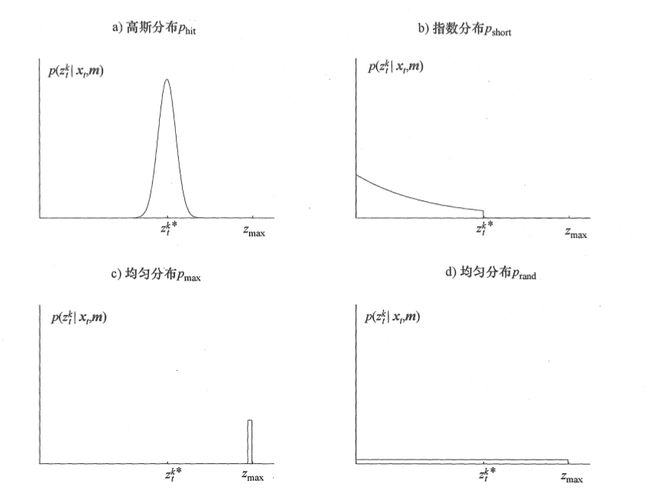
在理想的测量模型中,测量仪测量的物体总是位于离测量仪最近的物体上,但是因为一些误差因素,往往结果会与实际误差有一定的区别。实际上,测量仪的测量结果符合一个高斯模型(人造传感器多为此模型),均值为u,方差为o,u为最近物体的距离。
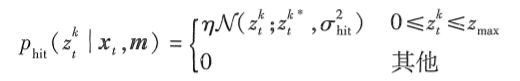
意外对象:移动机器人的环境是动态的,而地图 m 是静态的。因此,地图中不包含的对象可能引起测距仪产生惊人的短距离——至少与地图比较时。典型的移动对象就是与机器人共享操作空间的人。处理这类对象的一种方法是将它们作为状态向量的一部分来对待并估计它们的位置;另一种更简单的方法是将它们作为传感器噪声来处理。作为传感器噪声来处理,未建模对象具有这样的特性,即它们会导致比y原来更短而不是更长的距离。检测到意外对象的可能性随着距离而减少。想象有两个人,他们相互独立且在距离传感器的感知领域内出现的可能性是固定而且相同的。第一个人的距离是r1 第二个人的距离是 r2 。不失一般性的,进一步假定 rl < r2 。则更可能测量到r1 而不是 r2 。每当第一个人出现,传感器就会测量到 Tl 。而传感器要测量到r2则必须是在第二个人出现且第一个人不在的时候。这里我们常常用指数分布来模拟噪声模型。

检测失败。有时环境中障碍会被完全忽略。例如,在声呐传感器遇到了镜面反射时,会经常发生此情况。当用激光测距仪检测到黑色吸光的对象时,或者某些激光系统在明媚的阳光下测量物体时,也会发生检测失败。传感器检测失败 (sensor failure) 的典型结果是最大距离测量间题:传感器返回它的最大允许值 Zmax 。由于这样的事件经常发生,那么在测量模型中明确地建立最大测量范围的模型就很必要。这个噪声模型我们常常用一个均匀分布来表示。

随机测量。最后,测距仪偶尔会产生完全无法解释的测量。例如,当超声波被几面墙反弹或者它们受到不同传感器之间的串扰时,声呐常产生幻读。为了使之简单化,对千这样的测量,这里将使用一个分布在完整传感器测量范围[ 0; ZmaxJ 的均匀分布来建立模型:
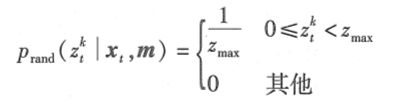
以上四种模型用以下图来表示:
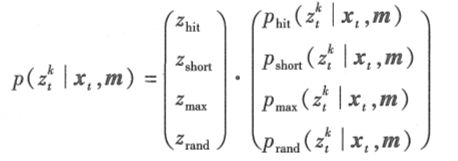
我们常常用到的测量算法即:
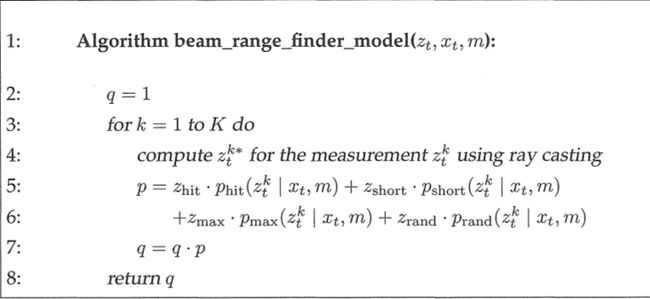
3.2、似然域模型
现在介绍另外一种模型,称为似然域,该模型缺乏一个合理的物理解释。事实上,它是一种“特设 (ad hoc)"算法,不必计算相对于任何有意义的传感器物理生成模型的条件概率。而且,这种方法在实践中运行效果良好。即使在混乱的空间,得到的后验也更光滑,同时计算更高效。主要思想就是首先将传感器扫描的终点Zhit, 映射到地图的全局坐标空间。这样做,必须了解相对于全局坐标系,机器人的局部坐标系位于何处?机器入传感器光束 Zk 起源千何处?传感器指向何处?照常,令 xt=(x,y,西塔)在时刻 t 的位姿。保持环境二维图,用 (xksense ,yksense)表示机器人Yksense表示与机器人固连的传感器的坐标位置。

当激光束发射出去,我们将重点Zhit以及传感器以及小车全部映射到地图上,这些坐标只有当传感器检测到一个障碍物时才是有意义的。如果测距传感器输出了最大值 Zt=Zmax 则这些坐标在物理世界没有任何意义(即使测量的确携带了信息)。似然域测量模型简单地将最大距离读数丢弃。因为只有测量到障碍物才可以有效的与地图进行障碍物匹配。Gmapping中的scanmather就是用的这个思路。
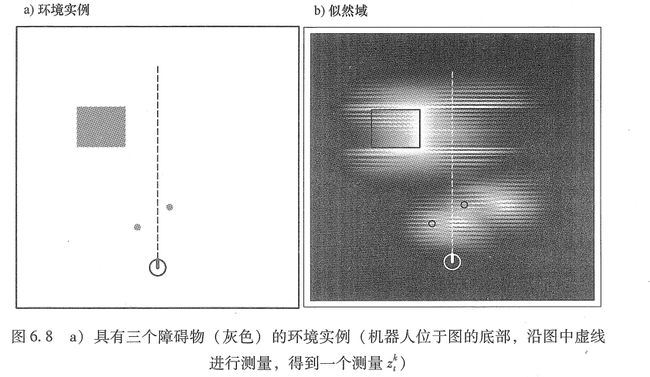
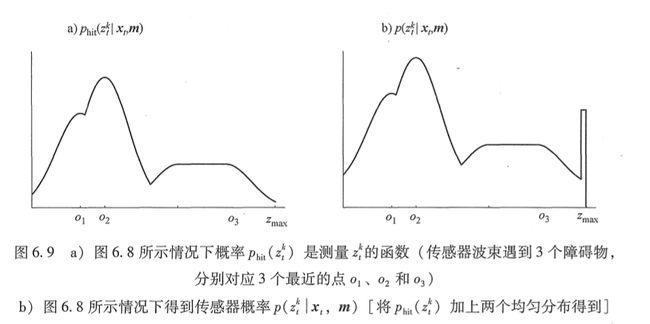
图中就是似然域的示意图。图中越亮的地方即为最有可能成为障碍物出现的地方。
测量模型与波束模型类似,式中,使用熟悉的混合权值 Zt、Zrand和Zmax。图 6.9b给出了一个测量波束与其结果分布 p(z| x, m) 的例子。很容易看到这个分布结合了图 6. 9a所示的 p,以及分布Pmax和 Prand。这里所说的调节混合参数大多转移到新模型上。它们可以通过手动调节或者利用极大似然估计得到。图 6.8b所示的表示法,将障碍物检测的似然描述成全局 x-y 坐标的函数,叫作似然域。
似然域算法为:

这个算法即为GMAPPING中score函数的原理。
第4章 launch文件
4.1、文件内容:
<launch>
<param name="use_sim_time" value="true"/>
<arg name="scan_topic" default="sick_scan" />
<node pkg="gmapping" type="slam_gmapping" name="slam_gmapping" output="screen">
<remap from="scan" to="$(arg scan_topic)"/>
*<!--* *GMapping* *Wrapper参数* *-->*
<param name="throttle_scans" value="1"/>
<param name="base_frame" value="base_link" />
<param name="odom_frame" value="odom"/>--
<param name="map_update_interval" value="5.0"/> *<!--* *地图更新速率* *-->*
*<!--* *Set* *maxUrange* *<* *actual* *maximum* *range* *of* *the* *Laser* *<=maxRange* *-->*
*<!--* *maxUrange* *<* *actual-->*
*<!--* *Laser* *Parameters(雷达相关参数)* *-->*
<param name="maxRange" value="5.51" /> *<!--* *激光最大范围* *-->*
<param name="maxUrange" value="5.5"/> *<!--* *激光最大使用范围* *maxUrange* *<* *真实范围* *<* *maxRange-->*
<param name="sigma" value="0.05"/> *<!--* *scan* *matching过程中的标准差(cell)* *-->*
<param name="kernelSize" value="1"/> *<!--* *scan* *matching过程中的搜索窗口大小* *-->*
<param name="lstep" value="0.05"/> *<!--* *scan* *matching过程中的位置增量* *-->*
<param name="astep" value="0.05"/> *<!--* *scan* *matching过程中的角度增量* *-->*
<param name="iterations" value="5"/> *<!--* *scan* *matching过程中的迭代优化次数* *-->*
<param name="lsigma" value="0.075"/> *<!--* *scan* *matching过程中的计算似然的标准差(single* *laser* *beam)* *-->*
<param name="ogain" value="3.0"/> *<!--* *平滑似然的增益* *-->*
<param name="lskip" value="0"/> *<!--* *取每第(n+1)个激光束来计算匹配(0表示取所有的激光束)* *-->*
<param name="minimumScore" value="50"/> *<!--* *scan* *matching被接受的最小阈值(不被接受,则使用里程计数据)* *-->*
*<!--* *小车运动模型参数* *-->*
<param name="srr" value="0.01"/> *<!--* *由平移造成的平移误差-->*
<param name="srt" value="0.005"/> *<!--* *由平移造成的角度误差-->*
<param name="str" value="0.01"/> *<!--* *由旋转造成的平移误差* *-->*
<param name="stt" value="0.005"/> *<!--* *由旋转造成的角度误差* *-->*
*<!--* *其他参数* *-->*
<param name="linearUpdate" value="0.2"/> *<!--* *小车每走过0.2m,处理一次激光数据* *-->*
<param name="angularUpdate" value="0.2"/> *<!--* *小车旋转0.2* */* *12度,处理一次激光数据* *-->*
**
**
**
**
**
**
**
**
**
**
**
**
**
**
第五章 参考帮助理解博客
博客内容:
https://blog.csdn.net/zhao_ke_xue/article/details/110702322
第六章 gmapping使用
近期为了更加熟练使用gmapping,开始做实验,但是做实验的路上,每一步都非常艰难,则在此写下gmapping使用以及研究过程中的各项问题,防止忘记。
因为小车电量有限,参数量庞大,且背电脑不方便,于是采取录bag包调试算法的方法研究。
6.1、bag包的录取
播放官方bag包时发现
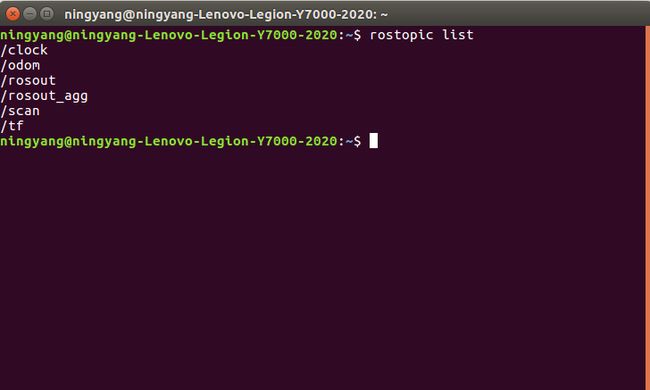
我们主要需要的几个话题,一个是/scan以及/tf,/odom可以在算法中计算,也可以使用imu以及其他方法得出,可以不录取。/clock是包的时钟,会自动录取。
故录取bag包时我们需要录取到雷达数据以及tf变换的过程包。
6.1.1、这里在tf变换上写点心得
因为录取后用网上的方法播放建图时候出现了很多问题,我将问题全部总结下来。

出现这个问题时候先分析
rosrun rqt_tf_tree rqt_tf_tree
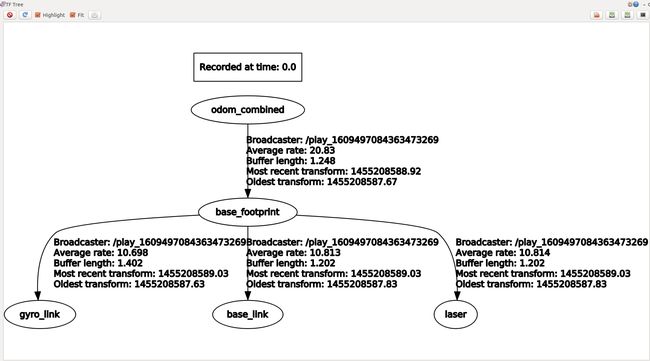
看tf树是否对齐,然后在分析如何更改launch文件中的tf包,
<launch>
<param name="use_sim_time" value="true"/>
<!-- we need a static tf transform from base to laser -->
<node pkg="tf" type="static_transform_publisher" name="base_to_link" args="0 0 0 0 0 0 base_footprint base_link 100" />
<node pkg="tf" type="static_transform_publisher" name="base_to_gyro" args="0 0 0 0 0 0 base_footprint gyro_link 100" />
<node pkg="tf" type="static_transform_publisher" name="base_to_laser" args="0.15 0 0.05 0 0 1.0 6.12323399574e-17 base_footprint laser 100" />
<!-- Gmapping -->
<include file="/home/ningyang//buildingpic/src/gmapping/launch/slam_gmapping_pr2.launch"/>
</launch>
对于任意一个tf变换来看,第一个是包的名字,第二个是变换类型,第三个是发布tf变换的节点名称,arg里面前三个是平移xyz变换,后面几个数字是旋转变换(三个是欧拉角,四个是四元数),后面两个是坐标系名称和子坐标系名称,最后一个是周期数,一般是100
这里出现上述问题的原因是bag包里面已经录了tf变换,比如base_link到base_footprint,但是launch里面又写了类似tf变换,launch文件中不需要对应坐标系变换。直接启用slam_gmapping_pr2.launch就好。只有当录取数据时没有用到的tf变换才需要在launch文件中加上。
还需要注意的问题,下面参数要改到对应bag包里面发布的tf变换
<remap from="scan" to="$(arg scan_topic)"/>
*<!--* *GMapping* *Wrapper参数* *-->*
<param name="throttle_scans" value="1"/>
<param name="base_frame" value="base_link" />
<param name="odom_frame" value="odom"/>--
由上面tf数可以看出odom坐标系用的odom_combined,base_frame可以是base_link,也可以是base_footprint。
从下面图片可以看出各个tf的发布者

和gmapping有关的就是map到odom_combined,所以gmapping文件中要写odom_combined。
[ WARN] [1584192934.752228918]: MessageFilter [target=odom ]: Dropped 100.00% of messages so far. Please turn the [ros.gmapping.message_notifier] rosconsole logger to DEBUG for more information.
同样是tf树没对齐的原因
6.1.2、地图保存
rosrun map_server map_saver -f {保存地址以及名称}
rosrun map_server map_server /home/ningyang/xxx.yaml
6.2、实验就绪
有包有代码就可以开始实验啦。
我们先试着改变粒子数然后看不同粒子数对建图的影响,在本场景中数量在200时效果最好
粒子数设置为8:
建图效果:
实验发现粒子数越大效果先上升后下降
地图更新速率:
地图更新速率同样先上升后下降,在本场景中数量在0.5时效果最好