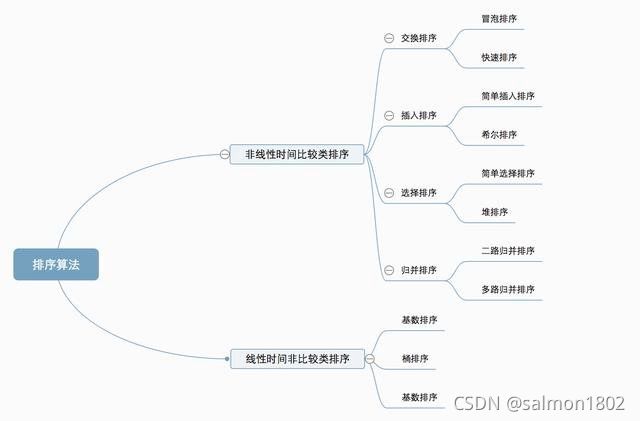
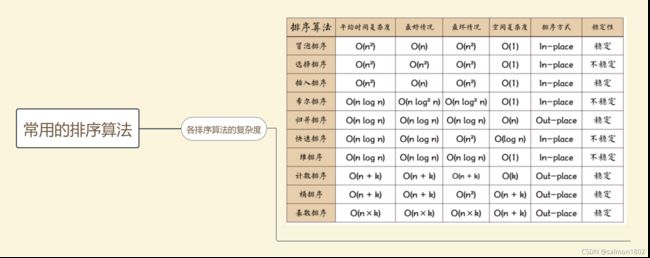
考研数据结构常考的代码题总结 C语言实现
PAT
leetcode
代码github备份
数据结构习题集
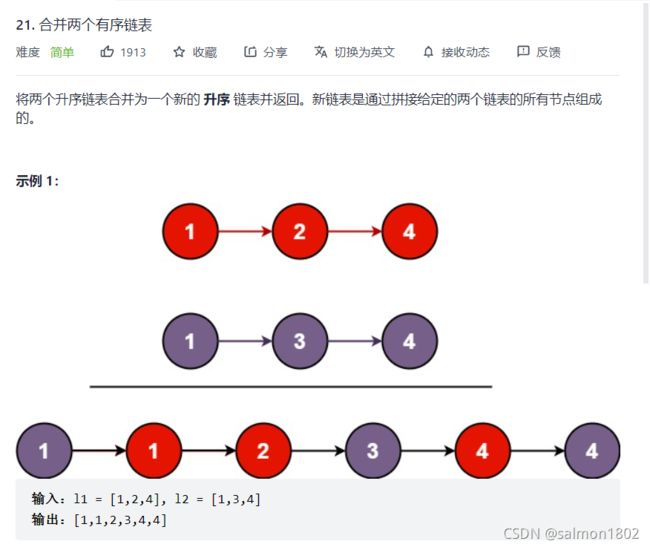
- leetcode 21. 合并两个有序链表
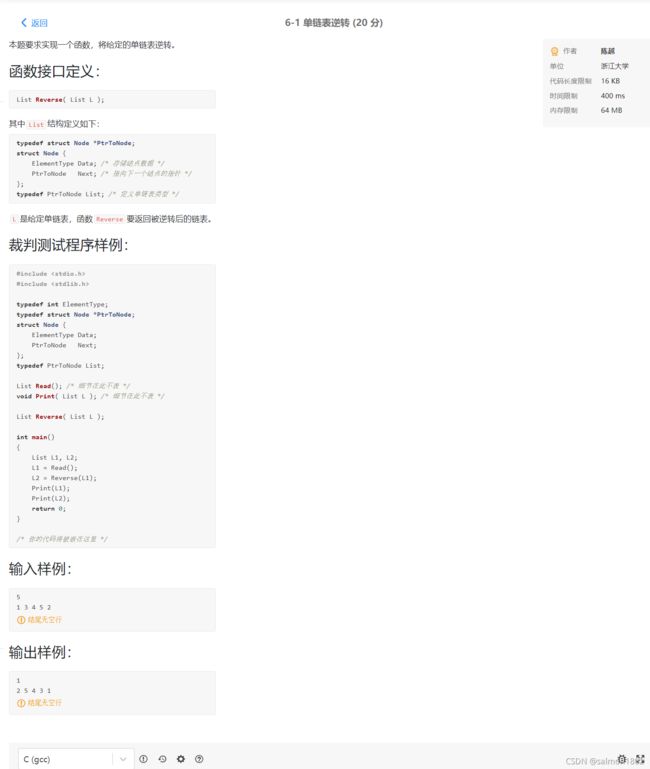
- PAT 6-1 单链表逆转 (20 分)
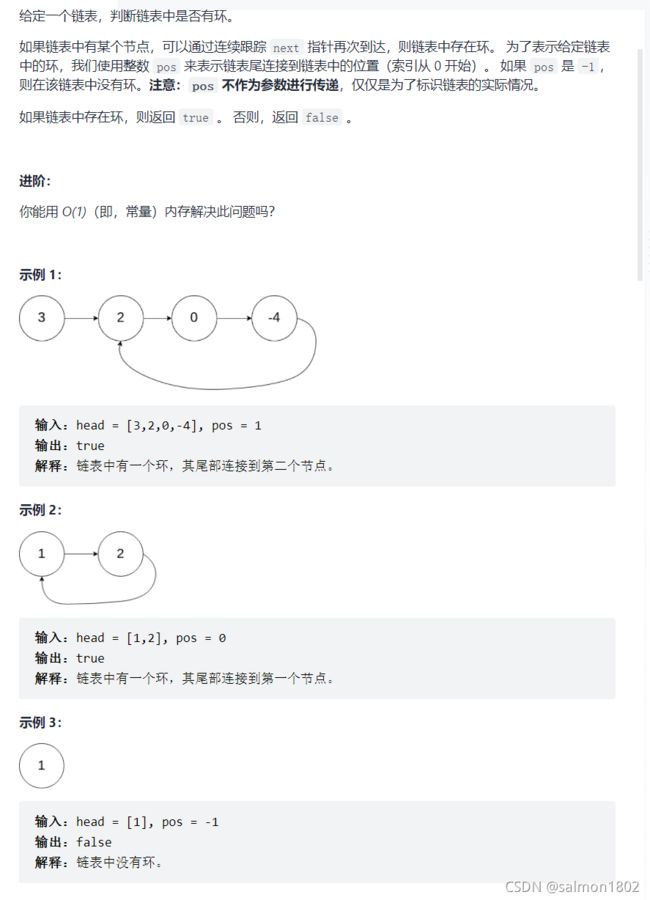
- leetcode 141. 环形链表
- PAT 6-2 顺序表操作集 (20 分)
- PAT 6-3 求链式表长(10 分)
- PAT 6-4 链式表的按序号查找 (10 分)
- leetcode 203. 移除链表元素
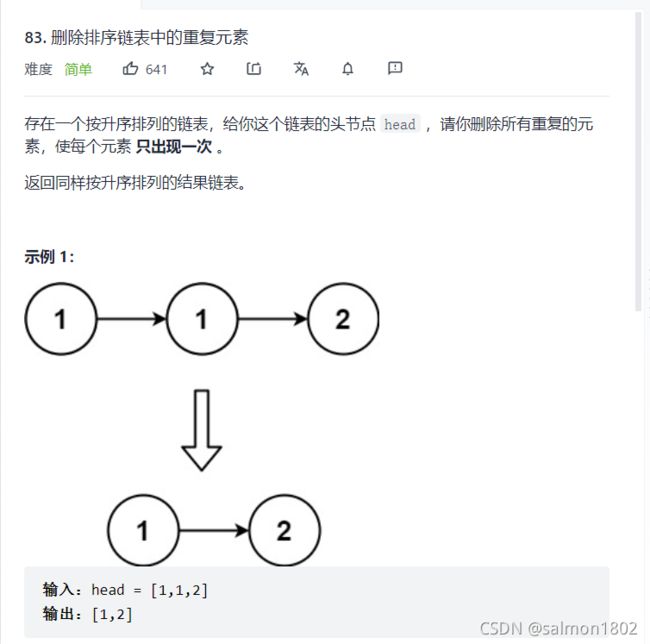
- leetcode 83. 删除排序链表中的重复元素
- PAT 6-5 链式表操作集 (20 分)
- PAT 6-6 带头结点的链式表操作集 (20 分)
- PAT 6-7 在一个数组中实现两个堆栈 (20 分)
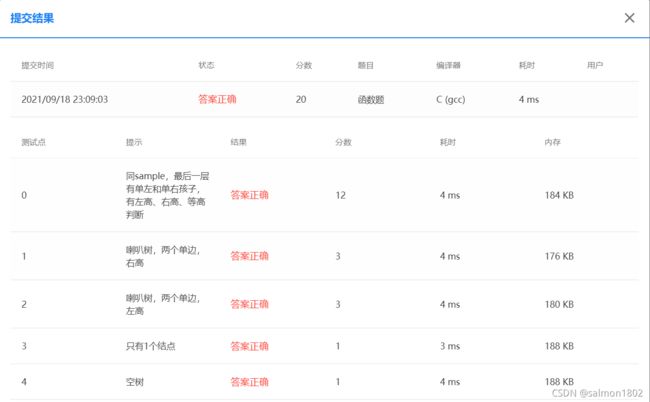
- PAT 6-8 求二叉树高度 (20 分) 递归与非递归方法
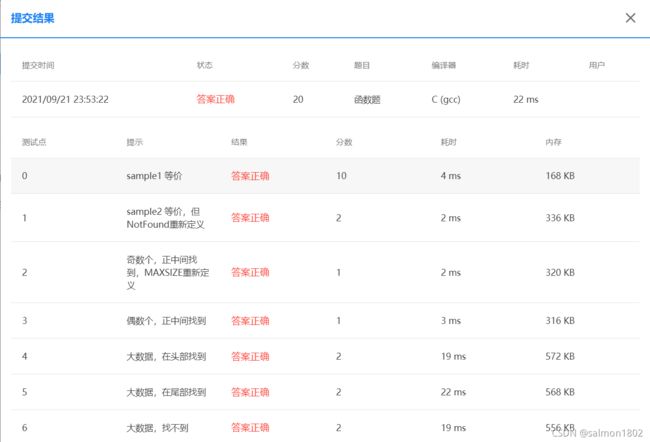
- PAT 6-10 二分查找 (20 分)(递归和迭代版本)
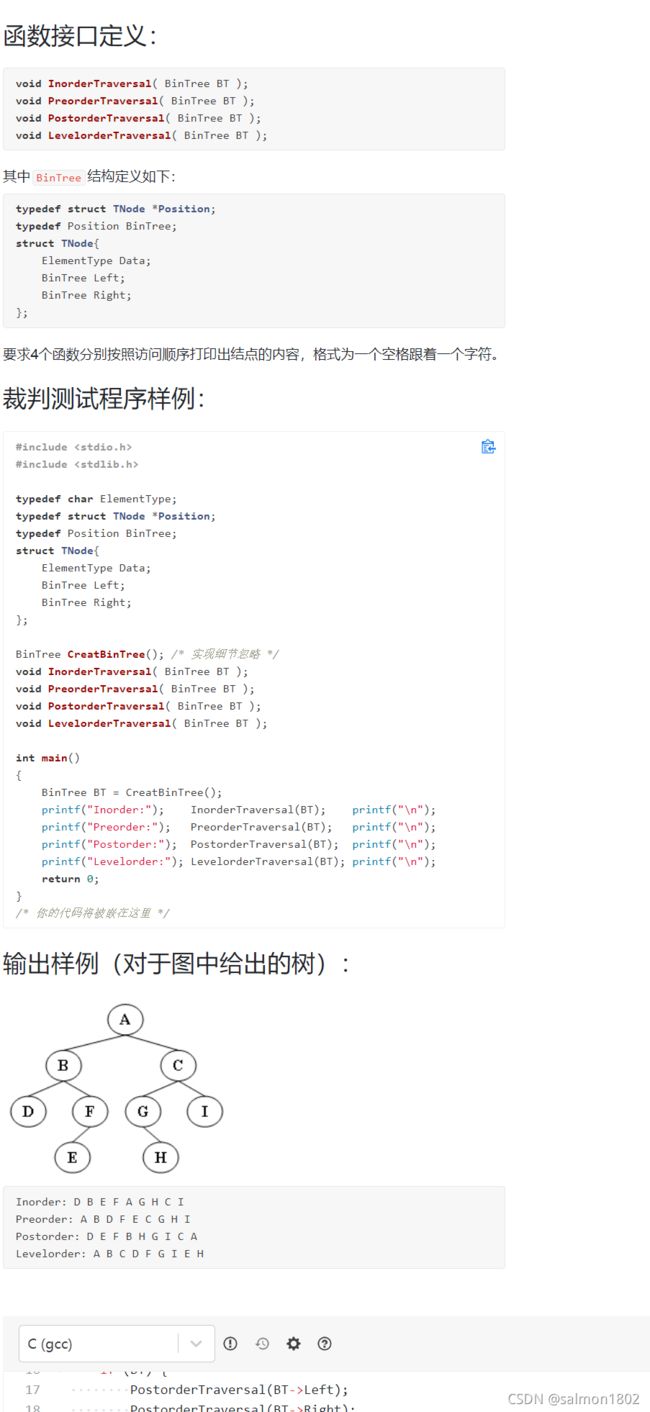
- PAT 6-9 二叉树的遍历 (25 分) 迭代和递归版本
- PAT 6-11 先序输出叶结点 (15 分)
- PAT 6-12 二叉搜索树的操作集 (30 分) 递归与非递归版本
- 求二叉树中度为0、1、2结点的个数
- ---------------以下只给出伪代码--------------------
- 二叉树自下而上,从右到左的层次遍历
- 判断二叉树是否为完全二叉树
- 将二叉树所有结点的左右子树交换
- 删除二叉树中所有值为X的节点,以及它的左右子树
- 在二叉树中查找值为X的结点,并输出其所有的祖先结点
- 求一个二叉树的宽度
- 求以孩子兄弟表示法存储的树的叶子节点数
- 求以孩子兄弟表示法存储的树的深度
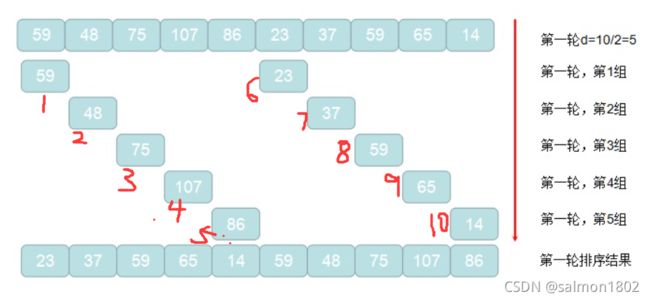
- 希尔排序
- 快速排序
- 冒泡排序
- 归并排序
- 简单选择排序
- 由二分查找优化的直接插入排序
- 带头结点链表,将小于第一个元素的结点放在其前面,大于放在后面
- 判断一颗树是否对称
- -------------------一些零碎的知识点-----------------------
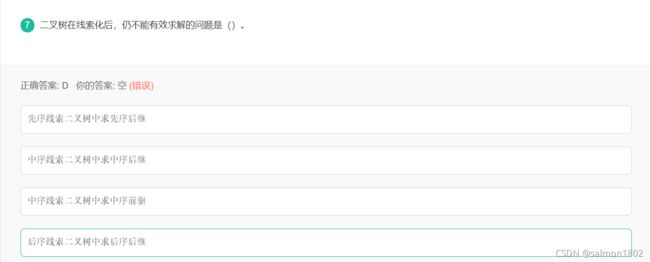
- 二叉树在线索化后,仍不能有效求解的问题
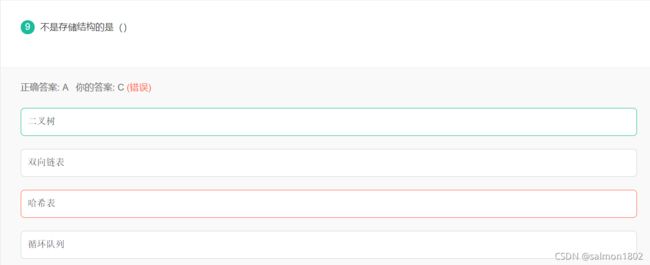
- 存储结构的相关问题
leetcode 21. 合并两个有序链表
/*
Created by salmon on 2021-9-14 21:27.
*/
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
struct ListNode* mergeTwoLists(struct ListNode* l1, struct ListNode* l2){
struct ListNode head;
struct ListNode* res = &head;
while (l1 != NULL && l2 != NULL) { //l2小于等于l1时插入l2,否则插入l1; 每次插入后指针后移一位;
if(l2 -> val <= l1 -> val){
res -> next = l2;
l2 = l2 -> next;
} else {
res -> next = l1;
l1 = l1 -> next;
}
res = res -> next;
}
//此时循环结束,必定至少有一个链表被循环到最后一个节点之后的空指针上
if(l1 == NULL){
res -> next = l2;
} else if (l2 == NULL){
res -> next = l1;
}
//返回头指针
//不能返回head->next,因为head不是指针是一个struct类型的变量
//参考文档:https://blog.csdn.net/faihung/article/details/79190039
return head.next;
}
PAT 6-1 单链表逆转 (20 分)
/*
Created by salmon on 2021-9-13 23:09.
单链表逆转
*/
typedef struct Node *PtrToNode;
struct Node {
ElementType Data; /* 存储结点数据 */
PtrToNode Next; /* 指向下一个结点的指针 */
};
typedef PtrToNode List; /* 定义单链表类型 */
#include leetcode 141. 环形链表
/**
*Created by salmon on 2021-9-14 22:25.
**/
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
bool hasCycle(struct ListNode *head) {
if(head == NULL){ //若为空必定不存在环
return false;
}
struct ListNode* fast = head -> next;
struct ListNode* slow = head;
//快慢指针,快的比慢的快一个位置
//如果快的追上慢的就表明有环
while (slow != fast) {
if(fast == NULL || fast -> next == NULL){
//因为fast一次移动两个元素,所以fast至少指向该链表倒数第二个节点
//否则会发生空指针访问空指针域的问题
return false;
}
fast = fast -> next -> next;
slow = slow -> next;
}
return true;
}
PAT 6-2 顺序表操作集 (20 分)
/**
*Created by salmon on 2021-9-14 23:32.
**/
/**
*Created by salmon on 2021-9-14 22:57.
**/
#include PAT 6-3 求链式表长(10 分)
/**
*Created by salmon on 2021-9-15 22:15.
**/
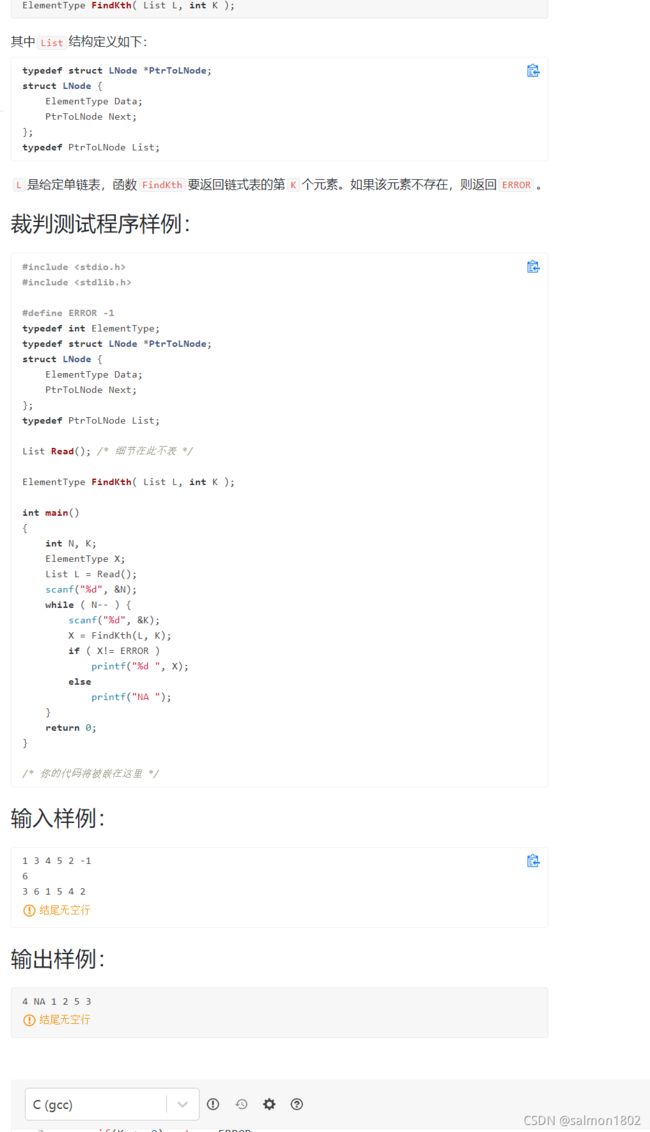
#include PAT 6-4 链式表的按序号查找 (10 分)
/**
*Created by salmon on 2021-9-15 22:21.
**/
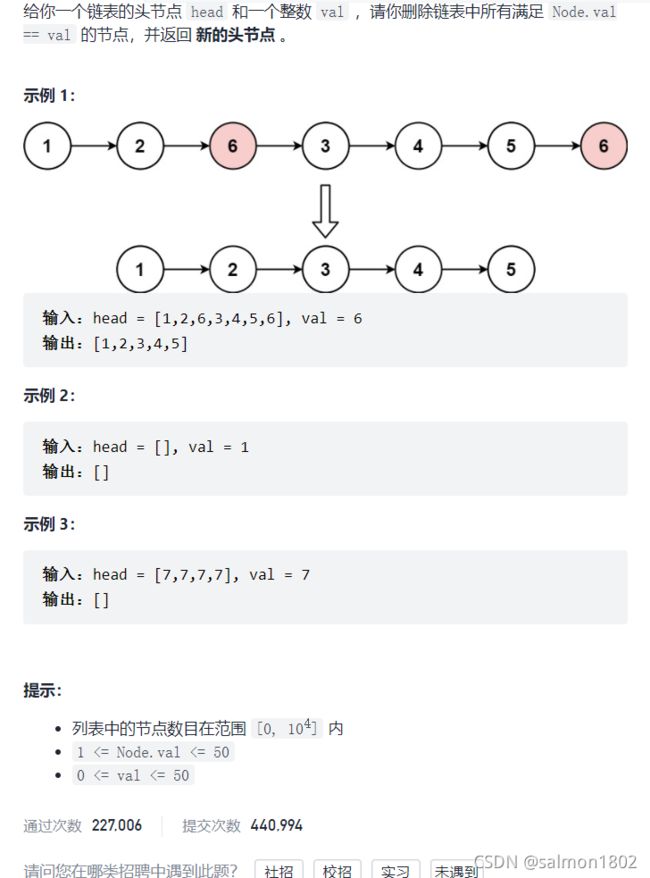
#include leetcode 203. 移除链表元素
struct ListNode* removeElements(struct ListNode* head, int val){
struct ListNode* res = malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
res -> next = head;//虚拟一个空的头结点出来
struct ListNode* p = res;//拷贝res,用p进行遍历,保证无论如何删除使res的下一个就是头结点,如果不拷贝res而是使用head返回,那么如果删除第一个元素就会出现问题
// while (p) { 这里如果不是下面这样写的话,会出现访问空指针空间的异常
while (p->next != NULL) {
if(p -> next -> val == val) {
p->next = p->next->next;
} else {
p = p -> next;
}
}
return res->next;
}
leetcode 83. 删除排序链表中的重复元素
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
struct ListNode* deleteDuplicates(struct ListNode* head){
if(head == NULL || head->next == NULL){
return head;
}
struct ListNode* p = head;
while (p->next != NULL) {
if(p->next->val == p->val){
p->next = p->next->next;
} else {
p = p->next;
}
}
return head;
}
PAT 6-5 链式表操作集 (20 分)
/**
*Created by salmon on 2021-9-16 22:07.
**/
#include PAT 6-6 带头结点的链式表操作集 (20 分)
/**
*Created by salmon on 2021-9-17 22:05.
**/
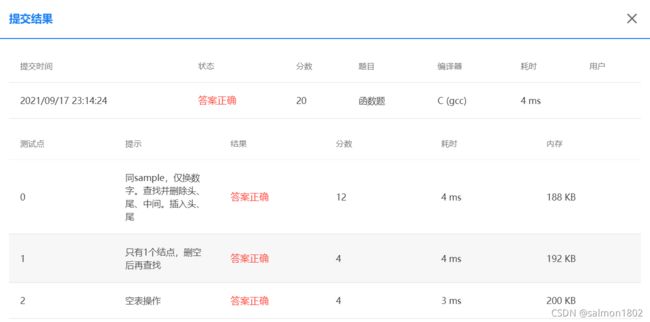
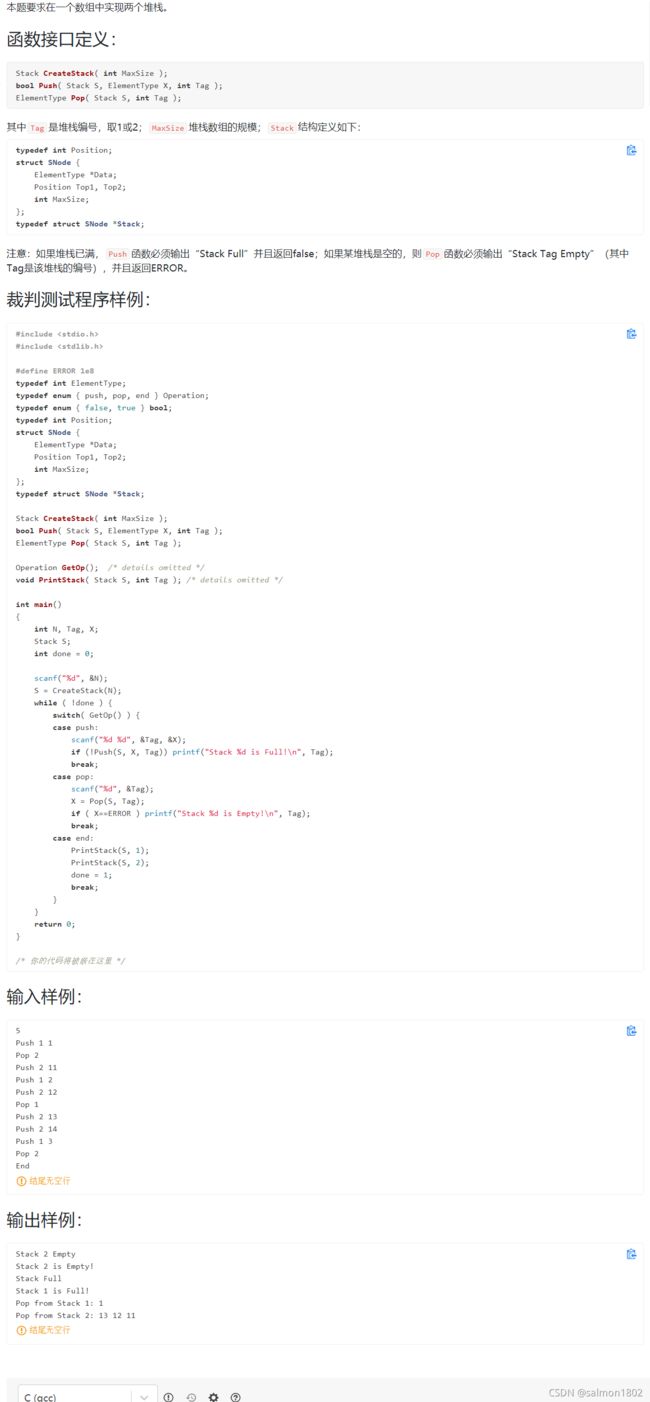
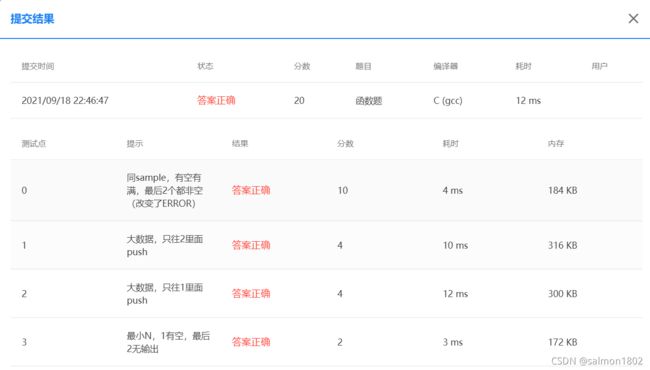
#include PAT 6-7 在一个数组中实现两个堆栈 (20 分)
/**
*Created by salmon on 2021-9-18 22:13.
**/
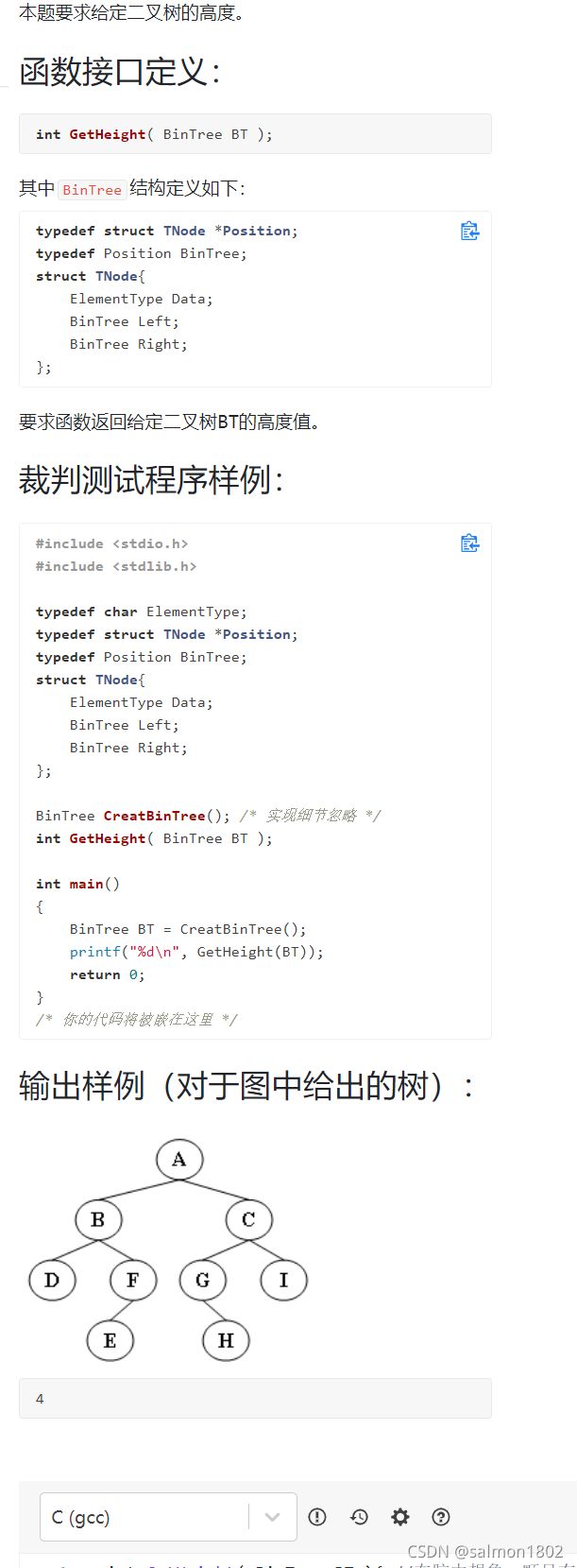
#include PAT 6-8 求二叉树高度 (20 分) 递归与非递归方法
int GetHeight( BinTree BT ){ //在脑中想象一颗只有2层的满二叉树可以更好地理解
int maxLeft = 0,maxRight = 0;
if(BT == NULL){ //第一次,一直递归到此树叶子结点的孩子结点时停止,此时该结点为NULL所以高度为0
return 0;
} else { //以当前BT为根节点判断左子树高度和右子树高度谁更大
maxLeft = GetHeight(BT->Left);
maxRight = GetHeight(BT->Right);
return (maxLeft > maxRight ? maxLeft + 1 : maxRight + 1); //此时已经计算完成一个叶结点,返回结点到它的双亲节点,显然高度要加1
}
}
非递归算法求二叉树的高度,一般利用层次遍历的方法,初始化一个队列,定义一个中间变量来保存每次循环一开始的rear,如果front追上了rear则二叉树高度加1
int GetHeight( BinTree BT ){ //在脑中想象一颗只有2层的满二叉树可以更好地理解
if (BT == NULL) return 0;
BinTree Queque[999];
//初始化队列
Queque[0] = BT;
int front = 0, rear = 1,last = rear;
int high = 0;
while (front < rear) {
if (Queque[front]->Left != NULL) {
Queque[rear] = Queque[front]->Left;
rear++;
}
if(Queque[front]->Right != NULL) {
Queque[rear] = Queque[front]->Right;
rear++;
}
front++;
if(front == last){
high++;
last = rear;
}
}
return high;
}
PAT 6-10 二分查找 (20 分)(递归和迭代版本)
Position trueBinarySearch( List L, ElementType X, Position low, Position high ){
if(low > high) return NotFound;
Position mid = (Position)((low + high) / 2);
if (X < L->Data[mid]) {
return trueBinarySearch(L,X,low,mid - 1);
} else if (X > L->Data[mid]) {
return trueBinarySearch(L,X,mid + 1,high);
} else {
return mid;
}
}
Position BinarySearch( List L, ElementType X ){
Position high = L->Last;
Position low = 0;
return trueBinarySearch(L,X,low,high);
}
Position BinarySearch( List L, ElementType X ){
ElementType tag;
Position low = 0;
Position high = L -> Last;
while (low <= high) {
Position mid = (ElementType)((low + high) / 2);
if (X < L->Data[mid]) {
high = mid - 1;
} else if (X > L->Data[mid]) {
low = mid + 1;
} else {
return mid;
}
}
return NotFound;
}
PAT 6-9 二叉树的遍历 (25 分) 迭代和递归版本
void InorderTraversal( BinTree BT ){//中序
if (BT) {
InorderTraversal(BT->Left);
printf(" %c",BT->Data);
InorderTraversal(BT->Right);
}
}
void PreorderTraversal( BinTree BT ){
if (BT) {
printf(" %c",BT->Data);
PreorderTraversal(BT->Left);
PreorderTraversal(BT->Right);
}
}
void PostorderTraversal( BinTree BT ){
if (BT) {
PostorderTraversal(BT->Left);
PostorderTraversal(BT->Right);
printf(" %c",BT->Data);
}
}
void LevelorderTraversal( BinTree BT ){//层次遍历
if (BT == NULL) return;
BinTree Queque[999];
//初始化队列
Queque[0] = BT;
int front = 0, rear = 1;
while (front < rear) {
if (Queque[front]->Left != NULL) {
Queque[rear] = Queque[front]->Left;
rear++;
}
if(Queque[front]->Right != NULL) {
Queque[rear] = Queque[front]->Right;
rear++;
}
printf(" %c",Queque[front]->Data);
front++;
}
}
BinTree assistStack[999];
int assistTop = -1;
void assistPush( BinTree BT ){
if(assistTop >= 999) return;
assistTop++;
assistStack[assistTop] = BT;
}
BinTree assistPop(){
if(assistTop <= -1) return NULL;
return assistStack[assistTop--];
}
int assistStackIsEmpty(){
if(assistTop <= -1) return -1; //-1为空
else return 1; //1为不空
}
BinTree Stack[999];
int top = -1;
void push( BinTree BT ){
if(top >= 999) return;
top++;
Stack[top] = BT;
}
BinTree pop(){
if(top <= -1) return NULL;
return Stack[top--];
}
int stackIsEmpty(){
if(top <= -1) return -1; //-1为空
else return 1; //1为不空
}
void InorderTraversal( BinTree BT ){//中序
while (BT != NULL || stackIsEmpty() == 1) {
while (BT != NULL) {
push(BT);
BT = BT->Left;
}
if (stackIsEmpty() == 1) {
BT = pop();
printf(" %c",BT->Data);
BT = BT->Right;
}
}
}
void PreorderTraversal( BinTree BT ){
if(BT == NULL) return;
push(BT);
while (stackIsEmpty() == 1) {
BT = pop();
printf(" %c",BT->Data);
if(BT->Right != NULL){
push(BT->Right);
}
if(BT->Left != NULL){
push(BT->Left);
}
}
}
void PostorderTraversal( BinTree BT ){
while (BT != NULL || assistStackIsEmpty() == 1) {
while (BT != NULL) {
assistPush(BT);
push(BT);
BT = BT->Right;
}
if(assistStackIsEmpty() == 1){
BT = assistPop();
BT = BT->Left;
}
}
while (stackIsEmpty() == 1) {
BinTree res = pop();
printf(" %c",res->Data);
}
}
void LevelorderTraversal( BinTree BT ){//层次遍历
if (BT == NULL) return;
BinTree Queque[999];
//初始化队列
Queque[0] = BT;
int front = 0, rear = 1;
while (front < rear) {
if (Queque[front]->Left != NULL) {
Queque[rear] = Queque[front]->Left;
rear++;
}
if(Queque[front]->Right != NULL) {
Queque[rear] = Queque[front]->Right;
rear++;
}
printf(" %c",Queque[front]->Data);
front++;
}
}
参考博客:https://blog.csdn.net/dabusiGin/article/details/102736180?spm=1001.2014.3001.5501

这里我们总结一下非递归版本的二叉树遍历:
- 先序遍历:没什么难的,先右后左,输出根
- 定义一个栈
- 把根节点入栈
- 建立一个以栈不空为条件的循环
- 出栈,当前指针指向出栈的元素,并输出当前元素的内容
- 将该节点按照先右后左的顺序入栈
- 循环往复直到退出循环
- 中序遍历:稍微有点东西,先访问到最左下角的结点,一边访问一遍入栈。到底后出栈,并输出当前结点的内容,如果当前有右节点那么接着访问该节点左孩子节点,否则出栈回到父节点
- 建立一个以当前指针不空或栈不空的循环
- 如果当前指针不为空,就入栈,并一直访问到最左节点的左孩子
- 如果栈不空就出栈并输出当前元素内容
- 访问右节点(这里比较巧妙的是,如果右节点为空,什么也不做,只是出栈回到父节点)
- 循环往复
- 后序遍历:有些难,需要两个栈配合,与中序反着来。先一直访问到最右结点,一边访问一边同时入两个栈。到底后出栈,如果出栈结点有左孩子结点就接着访问该节点的右孩子,否则出栈回到父节点
- 建立一个以当前指针不空或栈不空的循环
- 如果当前指针不为空,就入双栈,并一直访问到最右节点的右孩子
- 如果辅助栈不空就出辅助栈
- 访问左节点(这里比较巧妙的是,如果右节点为空,什么也不做,只是出栈回到父节点)
- 循环往复
- 输出非辅助栈内的元素
- 层序遍历:没啥好说的一个队列就完事
总的来说就是,前中后非递归遍历要利用好栈,用栈来代替递归中的回溯到父节点的功能。
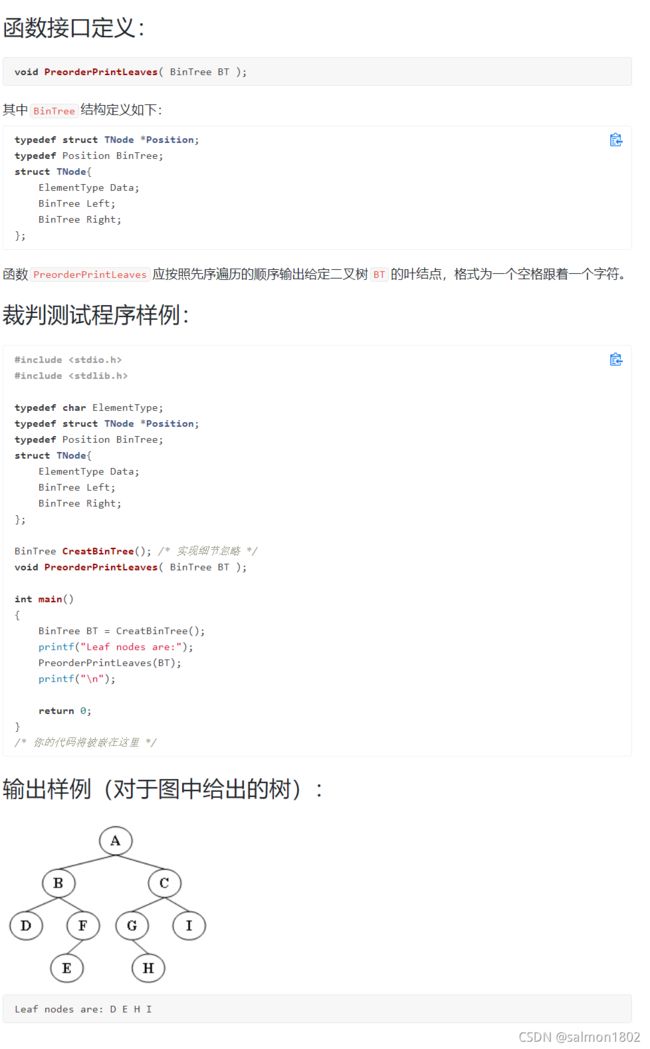
PAT 6-11 先序输出叶结点 (15 分)
/**
*Created by salmon on 2021-9-23 22:22.
**/
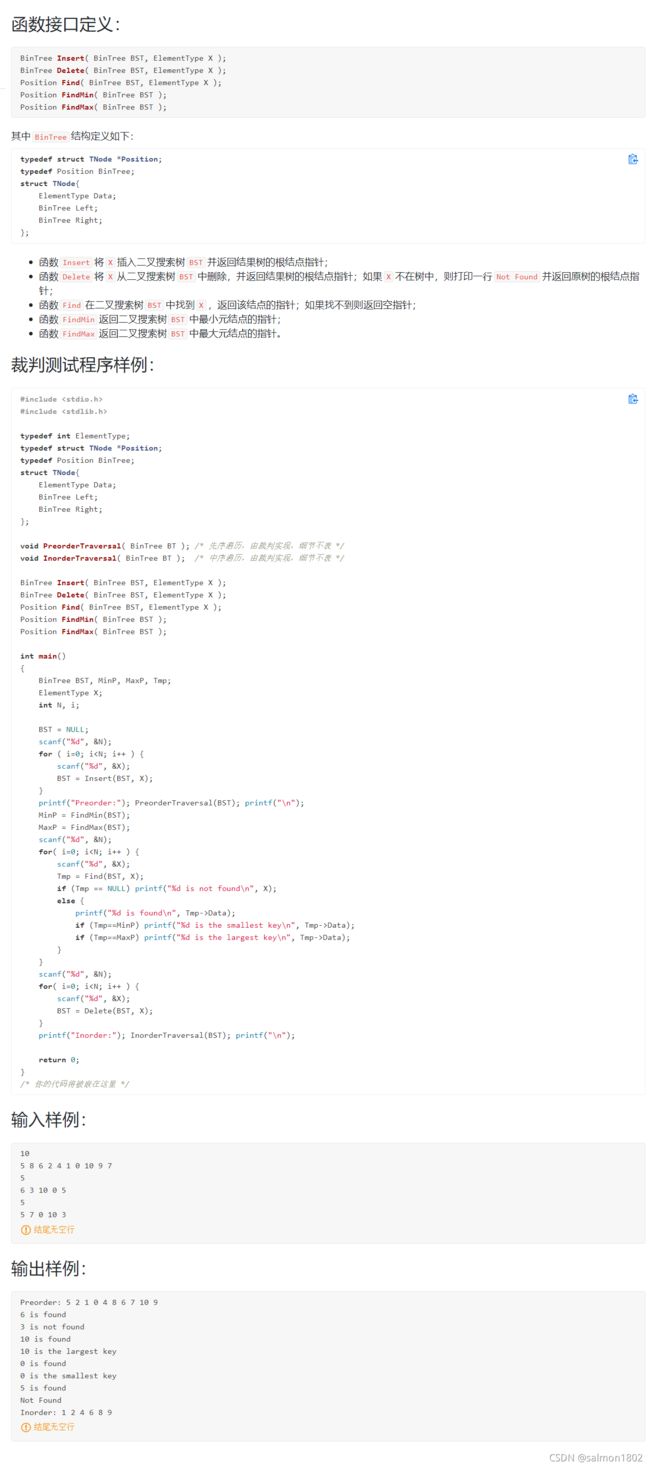
#include PAT 6-12 二叉搜索树的操作集 (30 分) 递归与非递归版本
BinTree Insert( BinTree BST, ElementType X ){
if (!BST) { //当递归到正确位置时创造结点
BST = (BinTree) malloc(sizeof(struct TNode));
BST->Right = NULL;
BST->Left = NULL;
BST->Data = X;
}
if(BST->Data > X) BST->Left = Insert(BST->Left,X); //根据二叉搜索树的特性,小了往左,大了往右,一直到叶节点为止
if(BST->Data < X) BST->Right = Insert(BST->Right,X);
return BST;
}
/**
* 二叉搜索树的删除有三种情况:
* 1.被删除节点为叶子结点,此时什么都不用做,直接删除
* 2.被删除节点只有左结点或右结点,用子结点代替即可
* 3.被删除节点有两个孩子,那么我们使用它的后继(或前驱)结点替换它,并且删除前驱结点
* @param BST
* @param X
* @return
*/
BinTree Delete( BinTree BST, ElementType X ){
if(!BST){
printf("Not Found\n");
return BST;
}
if(BST->Data < X) BST->Right = Delete(BST->Right,X);
if(BST->Data > X) BST->Left = Delete(BST->Left,X);
if(BST->Data == X){
if(BST->Left == NULL || BST->Right == NULL){
BST = BST->Left == NULL ? BST->Right : BST->Left;
} else {
Position temp = FindMin(BST->Right);
BST->Data = temp->Data; //注意只是把内容替换,务必不要整个替换节点
BST->Right = Delete(BST->Right,BST->Data);//删除结点
}
}
return BST;
}
Position Find( BinTree BST, ElementType X ){
if(!BST) return NULL;
if(BST->Data == X) return BST;
else if(BST->Data > X) return Find(BST->Left,X);
else return Find(BST->Right,X);
}
Position FindMin( BinTree BST ){
if(!BST) return NULL;
if (BST->Left) {
return FindMin(BST->Left);
}
return BST;
}
Position FindMax( BinTree BST ){
if(!BST) return NULL;
if (BST->Right) {
return FindMax(BST->Right);
}
return BST;
}
Position Find(BinTree BST, ElementType X){
while (BST){
if (X > BST->Data) BST = BST->Right;
else if (X < BST->Data) BST = BST->Left;//此处一定要加else,下同
else if(X==BST->Data) return BST;
}
return NULL;
}
Position FindMin( BinTree BST ){
if(!BST) return NULL;
while(BST->Left) BST = BST->Left;
return BST;
}
Position FindMax( BinTree BST ){
if(!BST) return NULL;
while(BST->Right) BST = BST->Right;
return BST;
}
BinTree Insert( BinTree BST, ElementType X ){
if(!BST){
BST = (BinTree)malloc(sizeof(struct TNode));
BST->Data = X;
BST->Left = NULL;
BST->Right = NULL;
}
if(X < BST->Data) BST->Left = Insert(BST->Left, X);
if(X > BST->Data) BST->Right = Insert(BST->Right, X);
return BST;
}
BinTree Delete( BinTree BST, ElementType X ){
Position temp;
if(!BST){
printf("Not Found\n");
return BST;
}
if(X < BST->Data) BST->Left = Delete(BST->Left, X);
if(X > BST->Data) BST->Right = Delete(BST->Right, X);
if(X==BST->Data){
if(BST->Left&&BST->Right){
temp = FindMin(BST->Right);
BST->Data = temp->Data;
BST->Right = Delete(BST->Right, BST->Data);
}
else{
if(BST->Left) BST = BST->Left;
else BST = BST->Right;
}
}
return BST;
}
求二叉树中度为0、1、2结点的个数
#include ---------------以下只给出伪代码--------------------
二叉树自下而上,从右到左的层次遍历
/**
*Created by salmon on 2021-9-29 22:50.
**/
#include 判断二叉树是否为完全二叉树
/**
*Created by salmon on 2021-9-29 23:12.
**/
#include 将二叉树所有结点的左右子树交换
/**
*Created by salmon on 2021-9-29 23:30.
**/
#include 删除二叉树中所有值为X的节点,以及它的左右子树
/**
*Created by salmon on 2021-10-1 00:23.
**/
#include 在二叉树中查找值为X的结点,并输出其所有的祖先结点
/**
*Created by salmon on 2021-10-3 23:48.
**/
#include 求一个二叉树的宽度
此题有些异议,一些题目中的宽度是树每层结点个数的最大值,另一些题目中先将一颗树转换为完全二叉树(一层中相隔的结点之间有空位的话补上结点),宽度指转换后的树每层结点个数的最大值
/**
*Created by salmon on 2021-10-5 00:33.
**/
#include 求以孩子兄弟表示法存储的树的叶子节点数
/**
*Created by salmon on 2021-10-10 23:29.
**/
#include 求以孩子兄弟表示法存储的树的深度
/**
*Created by salmon on 2021-10-10 23:40.
**/
#include 希尔排序
/**
*Created by salmon on 2021-10-8 23:41.
**/
#include 快速排序
/**
*Created by salmon on 2021-10-12 23:15.
**/
#include 冒泡排序
/**
*Created by salmon on 2021-10-13 23:42.
**/
#include 归并排序
/**
*Created by salmon on 2021-10-23 00:40.
**/
#include 简单选择排序
/**
*Created by salmon on 2021-10-15 23:58.
**/
#include 由二分查找优化的直接插入排序
/**
*Created by salmon on 2021-10-20 23:54.
**/
#include 带头结点链表,将小于第一个元素的结点放在其前面,大于放在后面
/**
*Created by salmon on 2021-10-24 23:24.
**/
#include 判断一颗树是否对称
/**
*Created by salmon on 2021-10-24 23:58.
**/
Definition for a binary tree node.
struct TreeNode {
int val;
struct TreeNode *left;
struct TreeNode *right;
};
bool traversal(struct TreeNode* left,struct TreeNode *right){
if(left == NULL && right == NULL){
return true;
}
if(left == NULL || right == NULL) {
return false;
}
if(left->val != right-> val) {
return false;
}
return traversal(left->left, right->right) && traversal(left->right, right->left);
}
bool isSymmetric(struct TreeNode* root){
if (root == NULL) {
return true;
}
return traversal(root->left, root->right);
}
-------------------一些零碎的知识点-----------------------
二叉树在线索化后,仍不能有效求解的问题
存储结构的相关问题
- 数据的逻辑结构包括:集合、线性结构、树形结构、图状结构或网状结构。
- 数据的存储结构(物理结构)包括:顺序存储、链式存储、索引存储和散列存储。