线索二叉树、中序线索二叉树的创建和遍历
线索二叉树
按照某种遍历次序对二叉树进行遍历,可以把二叉树中的所有结点排成一个线性序列。在具体应用中,有时需要访问二叉树中的结点在某种遍历序列中的前驱和后继,此时,在存储结构中应保存结点在某种遍历序列中的前驱和后继。这些指向前驱和后继结点的指针称为线索,加上线索的二叉树称为线索二叉树,相应地,加上线索的二叉链表叫做线索链表。线索链表结构如下:
字段:ltag, lchild, value, rchild, rtag
l t a g = { 0 , l c h i l d 指 向 该 结 点 的 左 孩 子 1 , l c h i l d 指 向 该 节 点 的 前 驱 r t a g = { 0 , r c h i l d 指 向 该 结 点 的 右 孩 子 1 , r c h i l d 指 向 该 节 点 的 后 继 ltag=\begin{cases}0,lchild指向该结点的左孩子 \\1,lchild指向该节点的前驱\end{cases}rtag=\begin{cases}0,rchild指向该结点的右孩子 \\1,rchild指向该节点的后继\end{cases} ltag={0,lchild指向该结点的左孩子1,lchild指向该节点的前驱rtag={0,rchild指向该结点的右孩子1,rchild指向该节点的后继
中序线索二叉树的创建
线索链表和线索链表的创建
// 线索二叉树结点
/*
ltag:0 lchild指向该节点的孩子;1 lchild指向该节点的前驱
rtag:0 rchild指向该节点的孩子;1 rchild指向该节点的后继
*/
typedef struct
{
int value;
struct ThrNode *lchild, *rchild;
int ltag, rtag;
}ThrNode;
// 创建线索树结点
/*
value:结点的值
*/
ThrNode* thrNode_createNode(int value)
{
ThrNode* node = (ThrNode* )malloc(sizeof(ThrNode));
// 初始化
node->ltag = 0;
node->rtag = 0;
node->lchild = NULL;
node->rchild = NULL;
node->value = value;
return node;
}
创建二叉树(此时没有线索)
// 递归用数组没带线索的树
// 用数组表示的二叉树,值为0表示没有这个节点
/*
arr:二叉树数组
len:数组长度
*/
ThrNode* thrNode_createTreeByArr(int* arr, int len)
{
ThrNode* root = thrNode_createNode(arr[0]);
thrNode_createTreeByArr_main(arr, len, 1, root ,'l');
thrNode_createTreeByArr_main(arr, len, 2, root ,'r');
return root;
}
// 递归创建二叉树
/*
arr:二叉树数组
len:数组长度
i:当前结点在arr中的索引
parent:当前结点的双亲
RorL:当前结点是左子树还是右子树
*/
void thrNode_createTreeByArr_main(int* arr,int len, int i, ThrNode* parent, char RorL)
{
if(i >= len || arr[i]==0)
{
// 越界了或没有结点
return;
}
ThrNode* node = thrNode_createNode(arr[i]);
if(RorL == 'r')
{
parent->rchild = node;
}
else
{
parent->lchild = node;
}
thrNode_createTreeByArr_main(arr, len, 2*(i+1)-1, node, 'l');
thrNode_createTreeByArr_main(arr, len, 2*(i+1), node, 'r');
}
生成中序线索
// 递归生成中序线索
void thrNode_thrTree(ThrNode* root)
{
thrNode_thrTree_main(root, NULL);
}
// 执行函数
/*
cur:需要用来建立线索的主要结点
pre:cur的双亲
*/
void thrNode_thrTree_main(ThrNode* cur, ThrNode* pre)
{
// 递归结束条件
if(cur == NULL) return;
// 左子树线索化
thrNode_thrTree_main(cur->lchild, pre);
// 当左子树为空,要指向前驱
if(cur->lchild == NULL)
{
// 如果有前驱
/*
中序线索二叉树中,
第一个输出的结点没有前驱,
最后一个输出的结点没有后继
*/
if(pre)
{
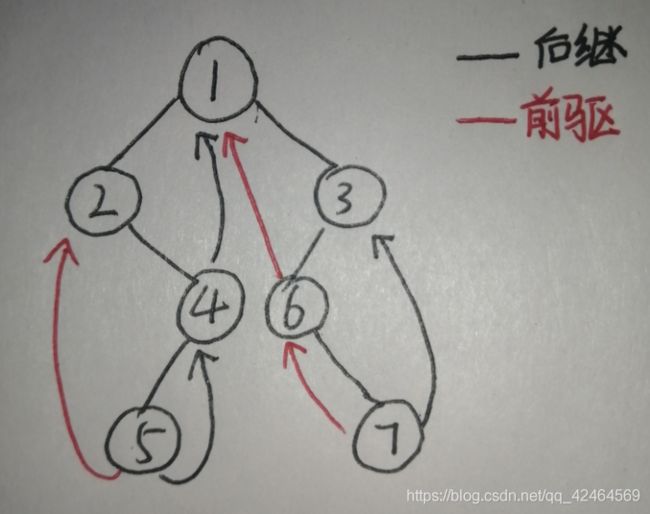
// 建立前驱线索
cur->lchild = pre;
cur->ltag = 1;
printf("建立前驱 %d -> %d\n", cur->value, pre->value, cur->ltag);
}
}
else
{
// 如果有左子树,那么cur结点就是左子树最右结点的后继
ThrNode* tmp = cur->lchild;
while(tmp->rchild)
{
tmp = tmp->rchild;
}
tmp->rchild = cur;
tmp->rtag = 1;
printf("建立后继 %d -> %d\n", tmp->value, cur->value, tmp->rtag);
}
// 右子树线索化
thrNode_thrTree_main(cur->rchild, cur);
}
中序线索二叉树的遍历
中序线索树的线索遍历
// 中序线索树的遍历
/*
root:要遍历的中序线索二叉树
printStr:输出结点值的格式
startStr:遍历前要输出的字符串
endStr:遍历结束后要输出的字符串
*/
void thrNode_thrTree_inOrder(ThrNode* root, char* printStr, char* startStr, char* endStr)
{
printf(startStr);
// 先找到中序遍历第一个结点,并输出
while(root->ltag == 0 && root->lchild)
{
root = root->lchild;
}
printf(printStr, root->value);
//当右子树不为空,循环
/*
因为是线索二叉树,所以只有最后一个输出的结点没有后继,
也就是右孩子,其他结点的右孩子是真右孩子或后继结点
*/
while(root->rchild != NULL)
{
// 右孩子是后继结点
if(root->rtag == 1)
{
// 可以直接得到下一个结点
root = root->rchild;
}
else
{
// 右孩子不是后继结点
// 找右子树的最左结点
root = root->rchild;
while(root->ltag == 0)
{
root = root->lchild;
}
}
// 输出
printf(printStr, root->value);
}
printf(endStr);
}
中序线索树的普通中序遍历
// 线索二叉树的普通中序遍历
/*
root:要遍历的二叉树
printStr:输出格式
*/
void thrNode_inOrder(ThrNode* root, char* printStr)
{
thrNode_inOrder_main(root, 0, printStr);
}
// 递归函数
/*
root:要遍历的二叉树
tag:当前结点是不是线索节点
printStr:输出格式
*/
void thrNode_inOrder_main(ThrNode* root, int tag, char* printStr)
{
// 如果当前节点为空或是线索节点,返回
if(root == NULL || tag == 1) return;
thrNode_inOrder_main(root->lchild, root->ltag, printStr);
printf(printStr, root->value);
thrNode_inOrder_main(root->rchild, root->rtag, printStr);
}
遍历测试
测试代码
#define N 15
int main()
{
int arr[N] = {1,2,3,0,4,6,0,0,0,5,0,0,7,0,0};
ThrNode* root = thrNode_createTreeByArr(arr, N);
thrNode_thrTree(root);
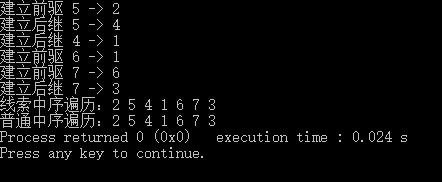
thrNode_thrTree_inOrder(root, "%d ", "线索中序遍历:", "\n");
printf("普通中序遍历:");
thrNode_inOrder(root, "%d ");
return 0;
}