Verilog全新语法认识--Xilinx language template
文章目录
- 0.背景
- 1、verilog语法篇
-
- 1.1、common constructs
- 1.2 、compiler directives(编译指令)
-
- define
- include
- timescale
- 1.3 operator
-
- arithmetric
- bitwise
- logic
- replicate/concatenate 复制和拼接操作
- shift移位操作
- unary reduction
- function and task 用法
0.背景
本篇blog将围绕官方提供的verilog模板以及仿真模板,来全新的认识verilog语法,这里面其实有很多你还不熟悉的语法,以及你没见过的语法,要不然我就不会打算写这么一篇文章了,当然,仅仅是逐步熟悉语法,以至于怎么将verilog和实际的数字电路对应起来,还需要更进一步的深刻认识,才能真正理解数字电路,这个在后续的日子中,我再好好理解理解,有空推出。另外关于VHDL和systemveriog这两个语法其实也很好懂,以后再来学一下,然后再推出文章。
1、verilog语法篇
1.1、common constructs
/* */ 对于多行的注释
// 对于单行的注释
1.2 、compiler directives(编译指令)
define
`define
`ifdef
;
`elsif
;
`else
;
`endif
`ifndef
;
`endif
例子:
// The `define, `ifdef, `elsif, `else, `ifndef and the `endif compiler directives
// ==============================================================================
//
// `define is a compiler directive that defines a value to a variable. That variable
// can then be called upon in the code by referencing the `name of the specified variable.
//
// `ifdef is a compiler directive that checks for the existence of a specified `define
// and then conditionally includes a section of code during compilation if it exists.
//
// `ifndef is the opposite of `ifdef in that if a `define was not declared, it includes
// a section of code.
//
// `elsif can be used in conjunction with a `ifdef to find the existence of another
// `define and conditionally compile a different section of code if the previous
// conditions were not met and this condition is met.
//
// `else also can be used in conjunction with a `ifdef where it will compile a section
// of code if all previous `ifdef and `elsif conditions were not met.
//
// `endif is used at the end of a `ifdef or `ifndef statement to signify the end of
// the included code.
//
// Example:
`define DATA_WIDTH 16
`define DATA_WIDTH16
reg [`DATA_WIDTH-1:0] data;
`ifdef DATA_WIDTH8
// If DATA_WIDTH8 was set, this would get compiled
`elsif DATA_WIDTH16
// Since DATA_WIDTH16 is set, this does get compiled
`else
// If DATA_WIDTH8 and DATA_WIDTH16 was not defined, this would be compiled
`endif
我的例子(以下例子是我个人在QUARTUS实验编译成功的模板结果):
`define datawidth 32
module CP_language_template_test
(
input clk,
output [`datawidth:0] result
);
endmodule
说明:宏定义可以在module的外面,也可以在module的里面,另外在引用宏定义的时候要记得前缀,在引用已定义的宏名时,必须在宏名的前面加上符号“`”,表示该名字是一个经过宏定义的名字。
module CP_language_template_test
`define datawidth 32
(
input clk,
output [`datawidth:0] result
);
endmodule
说明:以下是使用ifdef elsif else的例子
`ifdef datawidth1
`define datawidth1 3
`elsif datawidth2
`define datawidth2 3
`else
`define datawidth 32
`endif
module CP_language_template_test
(
input clk,
output [`datawidth-1:0] result
);
endmodule
说明:以下是ifndef endif的使用
module CP_language_template_test
`ifdef datawidth1
`define datawidth1 3
`elsif datawidth2
`define datawidth2 3
`else
`ifndef datawidth3
`define datawidth 32
`endif
`endif
(
input clk,
output [`datawidth-1:0] result
);
endmodule
include
`include ""
// The `include complier directive
// ===============================
//
// `include can be used to insert the contents of a separate file into a module.
// This is often used to communicate common functions, compiler directives, parameters
// and `defines to multiple files in a project. The file and path name must be
// specified in quotes and can consist of just the file name (looks in the current
// working directory for the file), a relative path to the file or an absolute path
// to the file. This directive can be specified both before the module declaration
// as well as within the module directive.
//
// Example:
// Include the contents of the parameters.vh file located in the current working directory.
// Many simulator and synthesis tools also offer a switch/option to allow specification
// of a search directory other than the working directory for files specified in this manner.
`include "parameters.vh"
// Include the contents of the ram_data.vh file in the relative directory ../data
`include "../data/ram_data.vh"
// Include the contents of master.vh in the absolute directory /export/vol1/sim_data
`include "/export/vol1/sim_data/master.vh"
我的例子(以下例子是我个人在QUARTUS实验编译成功的模板结果):
`include "define.v"
module CP_language_template_test
`ifdef datawidth1
`define datawidth 3
`elsif datawidth2
`define datawidth 4
`else
`ifndef datawidth
`define datawidth 32
`endif
`endif
(
input clk,
output [`datawidth-1:0] result
);
endmodule
另外,我再生成一个文件define.v的文件
`define datawidth 18
timescale
// The `timescale compile directive information
// ============================================
//
// `timescale is a compiler directive that indicates to the simulator the time units
// and precision to be used during simulation. The format is the following:
//
// `timescale /
//
// The units should be set to the base value in which time will be communicated to
// the simulator for that module.
// The precision is the minimum time units you wish the simulator to resolve. The
// smallest resolution value in all files and models compiled for simulation dictates
// the overall simulation resolution. In general for Xilinx FPGAs, a simulator
// resolution of 1ps is recommended since some components like the DCM require this
// resolution for proper operation and 1 ps is the resolution used for timing simulation.
//
// In general, this directive should appear at the top of the testbench, simulation models
// and all design files for a Verilog project.
//
// Example:
`timescale 1 ns / 1ps
#1; // Delays for 1 ns
#1.111; // Delays for 1111 ps
#1.111111111; // Delays for 1111 ps since the resolution is more course than
// what is specified, the delay amount is truncated
1.3 operator
arithmetric
// The following are the arithmetic operators as defined by the Verilog language.
//
// + .... Addition
// - .... Subtraction
// * .... Multiplication
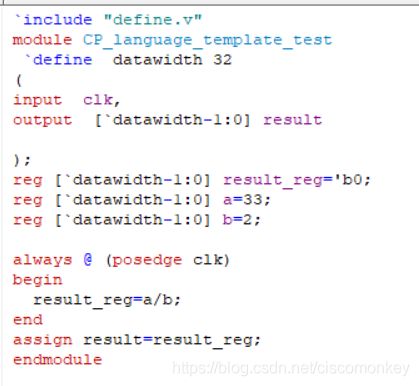
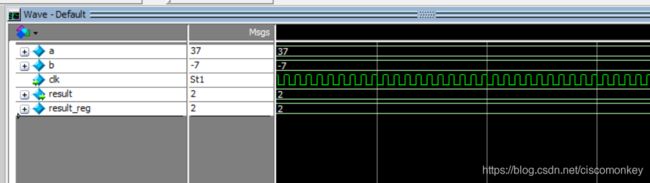
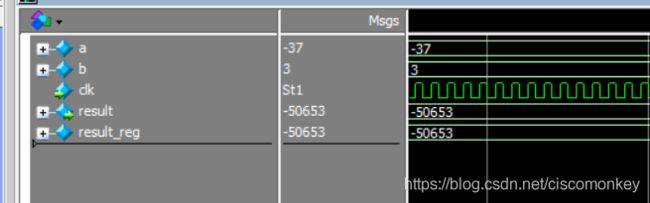
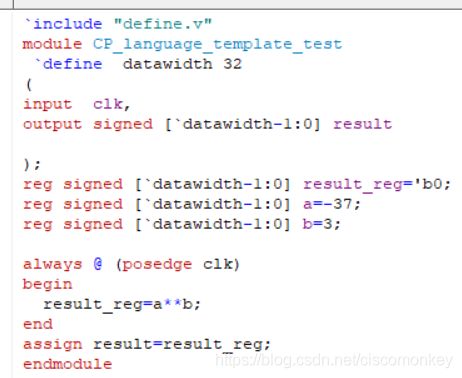
// / .... Divide
// % .... Modulus
// ** ... Power Operator (i.e. 2**8 returns 256)
bitwise
// The following operators can be used on two single bits to produce a single bit
// output or two equivalent sized bused signals where the operations are performed
// on each bit of the bus. In the case of the Invert, only one signal or bus is
// provided and the operation occurs on each bit of the signal.
//
// ~ .... Invert a single-bit signal or each bit in a bus
// & .... AND two single bits or each bit between two buses
// | .... OR two single bits or each bit between two buses
// ^ .... XOR two single bits or each bit between two buses
// ~^ ... XNOR two single bits or each bit between two buses
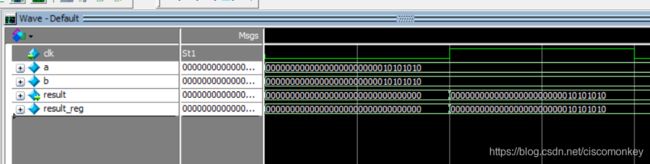
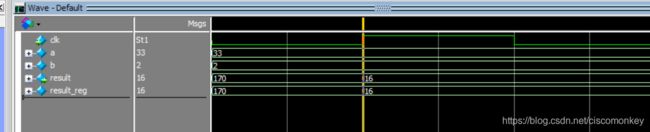
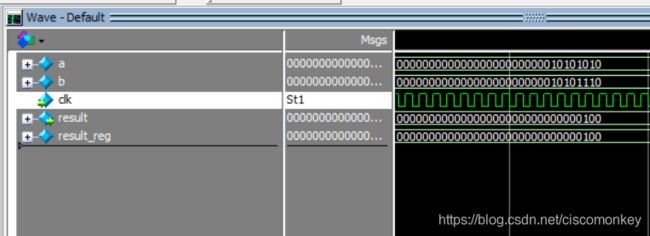
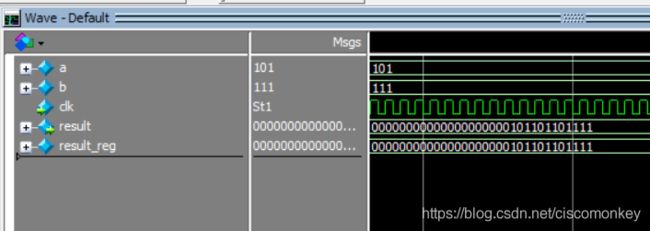
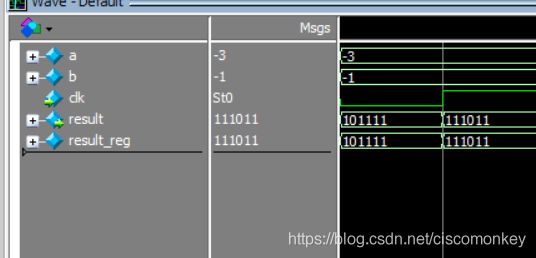
result_reg=a&b;如上图所示
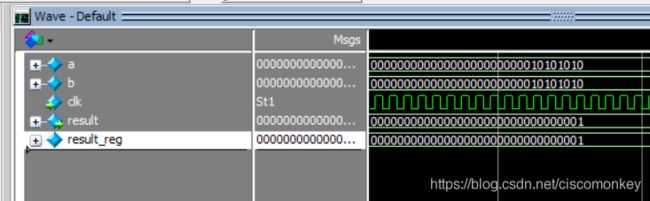
result_reg=a&&b;如上图所示
可以看出&是按照位进行操作的
logic
// The following logical operators are used in conditional TRUE/FALSE statements
// such as an if statement in order to specify the condition for the operation.
//
// ! .... Not True
// && ... Both Inputs True
// || ... Either Input True
// == ... Inputs Equal
// === .. Inputs Equal including X and Z (simulation only)
// != ... Inputs Not Equal
// !== .. Inputs Not Equal including X and Z (simulation only)
// < .... Less-than
// <= ... Less-than or Equal
// > .... Greater-than
// >= ... Greater-than or Equal
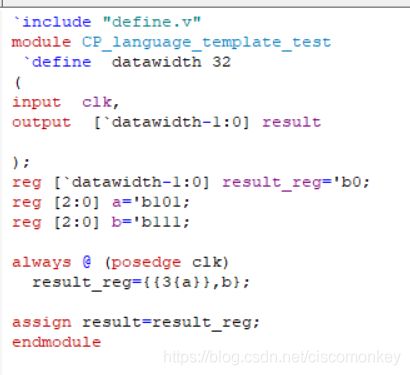
replicate/concatenate 复制和拼接操作
// The following operators either concatenates several bits into a bus or replicate
// a bit or combination of bits multiple times.
//
// {a, b, c} .... Concatenate a, b and c into a bus
// {3{a}} ....... Replicate a, 3 times
// {{5{a}}, b} .. Replicate a, 5 times and concatenate to b
//
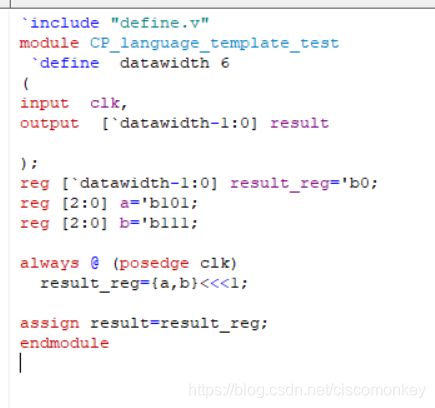
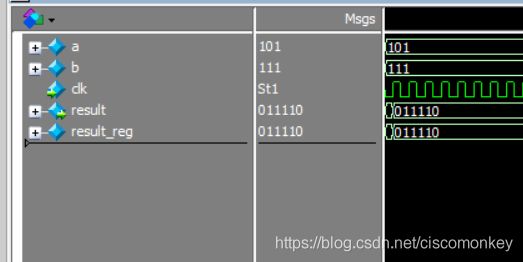
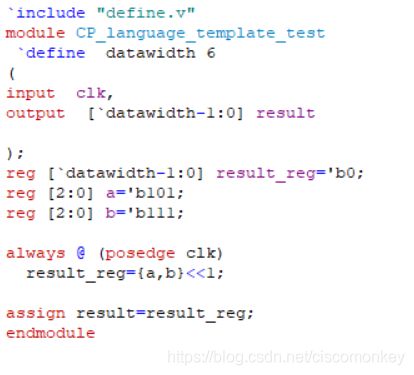
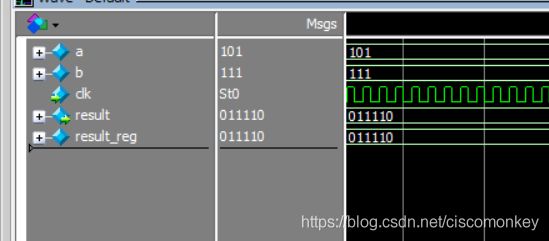
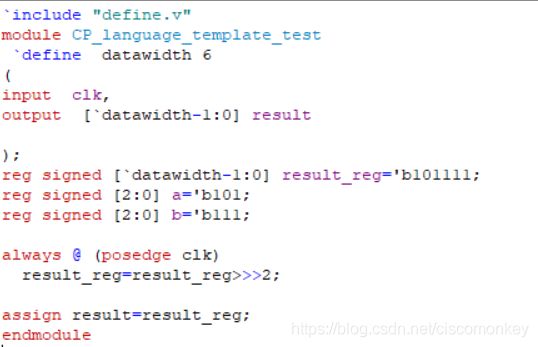
shift移位操作
// The following operators will shift a bus right or left a number of bits.
//
// << .... Left shift (i.e. a << 2 shifts a two bits to the left)
// <<< ... Left shift and fill with zeroes
// >> .... Right shift (i.e. b >> 1 shifts b one bits to the right)
// >>> ... Right shift and maintain sign bit
unary reduction
// The following operators can be used on a bussed signal where all bits in the bus
// are used to perform the operation and a single bit output is resolved.
//
// & .... AND all bits together to make single bit output
// ~& ... NAND all bits together to make single bit output
// | .... OR all bits together to make single bit output
// ~| ... NOR all bits together to make single bit output
// ^ .... XOR all bits together to make single bit output
// ~^ ... XNOR all bits together to make single bit output
function and task 用法
// User defined function and task information
// ==========================================
//
// A user defined function is a set of Verilog statements that
// can be called from elsewhere within the body of the code by
// an assignment. A function can have multiple inputs however
// can return only a single output. No timing information can
// be specified within a function.
//
// A user defined task is a subroutine that can be executed by
// a single call from elsewhere within the body of the code.
// A task can have any number of inputs, outputs and inouts as
// well as contain timing information.
//
// Example of a function declaration:
function [9:0] gray_encode;
input [9:0] binary_input;
begin
gray_encode[9] = binary_input[9];
for (k=8; k>=0; k=k-1) begin
gray_encode[k] = binary_input[k+1] ^ binary_input[k];
end
end
endfunction
// Example of calling a function:
// write_count is the binary input being passed to the function gray_encode.
// The output of the function gray_encode is then passed to the signal FIFO_ADDR
FIFO_ADDR = gray_encode(write_count);
// Example of a task declaration:
task error_action;
input read_write;
input correct_value;
input actual_value;
input [8*11:0] output_string;
begin
if (ERROR_CHECK) begin
if (read_write)
$display("Error: %s value incorrect during write %d at time %t\nExpecting %b, got %b",
output_string, write_attempt, $realtime, correct_value, actual_value);
else
$display("Error: %s value incorrect during read %d at time %t\nExpecting %b, got %b",
output_string, read_attempt, $realtime, correct_value, actual_value);
if (ON_ERROR=="FINISH")
$finish;
else if (ON_ERROR=="STOP")
$stop;
end
end
endtask
// Example of calling a task:
// The task error_action is called by name and passed the four input values
// in the order they are declared in the task
error_action(1'b1, wr_ready_value, WR_READY, "WR_READY");
function [:] ;
input ;
begin
end
endfunction
// A task is a subroutine with any number of input, output or inout
// arguments and may contain timing controls
task ;
input ;
output ;
begin
;
end
endtask
我的例子(以下例子是我个人在QUARTUS实验编译成功的模板结果):
function [:] ;
input ;
begin
end
endfunction
正如官方的语法说明所示,
function 语句标志着函数定义结构的开始; [:]参数代表了指定函数返回值的
位宽,是一个可选项,若没有指定,默认缺省值为 1 比特的寄存器数据;
量,函数调用的返回值就是通过函数名变量传递给调用语句。
//`include "define.v"
module CP_language_template_test
`define datawidth 7
(
input clk,
output [`datawidth-1:0] result
);
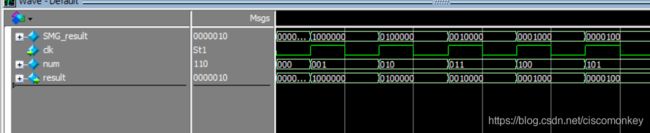
reg [6:0] SMG_result=7'd0;
reg [2:0] num=0;
always @ (posedge clk)
begin
num<=num+1'b1;
SMG_result<=SMG_translate(num);
end
assign result=SMG_result;
function [0:6] SMG_translate;
input [2:0] num;
reg [6:0] SMG_reg;
begin
case(num)
3'd0:SMG_reg=7'b1000000;
3'd1:SMG_reg=7'b0100000;
3'd2:SMG_reg=7'b0010000;
3'd3:SMG_reg=7'b0001000;
3'd4:SMG_reg=7'b0000100;
3'd5:SMG_reg=7'b0000010;
3'd6:SMG_reg=7'b0000001;
default: SMG_reg=7'b0000000;
endcase
SMG_translate=SMG_reg;
end
endfunction
endmodule
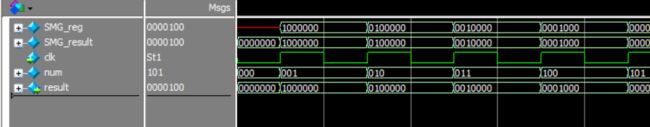
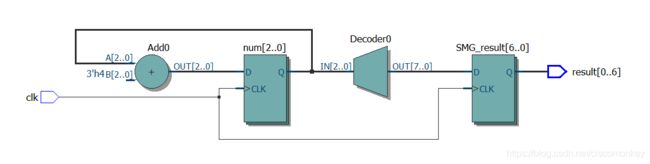
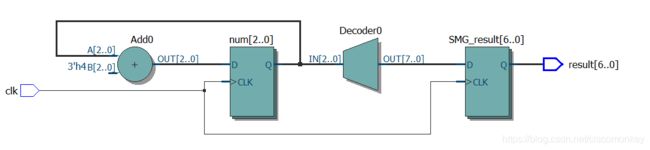
可以看出综合出来的RTL代码是一样的,说明使用functon函数可以简化我们的编程,而且是可综合的。
当然,这一眼看上去貌似都正确,细心的人有没有发现我们的RTL代码输出的result的数据表示呢?
其实,我发现,采用reg [高位:低位]和reg [低位:高位]两种定义的方法是一样的。
这里我的建议是【高位 低位】
此处例子参考:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_37147721/article/details/84889832
我的例子(以下例子是我个人在QUARTUS实验编译成功的模板结果):
下面我开始延时task的用法