玩转NVIDIA Jetson AGX Xavier
最近项目应用需要部署到边缘模块,所以就玩起了Xavier。感觉网上的资料不多,所以从头记录一下笔记,方便大家一起学习应用。
玩转NVIDIA Jetson AGX Xavier
- 1.刷机(安装sdkmanager)
-
- 1.1 NRU公司的工控机模组
- 1.2 英伟达(这个没有模组,所以没有usb驱动文件)
- 1.3 瑞泰新时代家的模组
- 2.配置yolov5环境并运行
-
- 2.1配置虚拟环境
- 2.2 yolo5进行tensorrt加速
- 3.CAN总线发送数据
- 4.拉出视频流
- 5.设备设置
- 6.win与xavier通信
- 7.references
1.刷机(安装sdkmanager)
这里刷机,我刷了三台,不一样的厂家,驱动文件不一样。所以文件会有差别。这里分别记录一下。
1.1 NRU公司的工控机模组
拿到这个首先是刷机,安装sdkmanager。这里需要用到一台装有ubuntu18.04版本的电脑,这里我是装的双系统,没有用虚拟机。
需要的材料:
一台装有ubuntu18.04的主机
xavier,这里我叫他工控机
usb线
两个网线
1.首先在主机上下载英伟达的sdkmanager,这里需要注册一个英伟达的账号。
2.用usb将主机和工控机链接,一条安卓线就可以,这里的工控机也要插上三孔电源。

开始设置工控机进入recovery模式:首先是关机状态,用笔尖按下1,两秒后按下2,pwr的灯亮后1秒,1和2都松开,此时pwr灯是亮的。

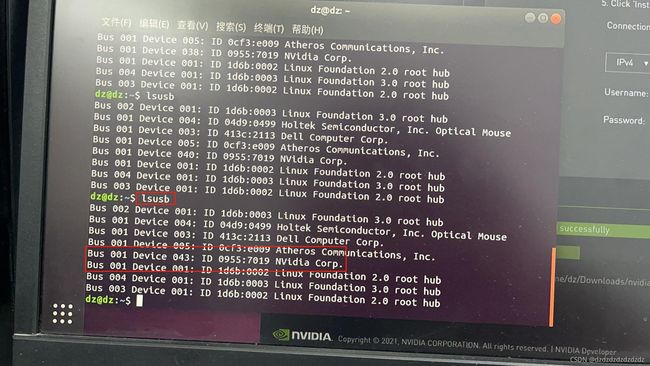
在terminal(ctrl+alt+t)中输入lsusb,可以看到NVIDIA corp说明此时工控机进入了recovery状态。
3.主机上下载好sdkmanager,工控机和主机连接并进入recovery之后进行安装启动
sudo dpkg -i [sdk名字.deb]
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install
sudo apt-get --fix-broken install
sdkmanager#启动
这里如果遇到问题就根据提示或者百度简单解决。启动sdk后选择AGX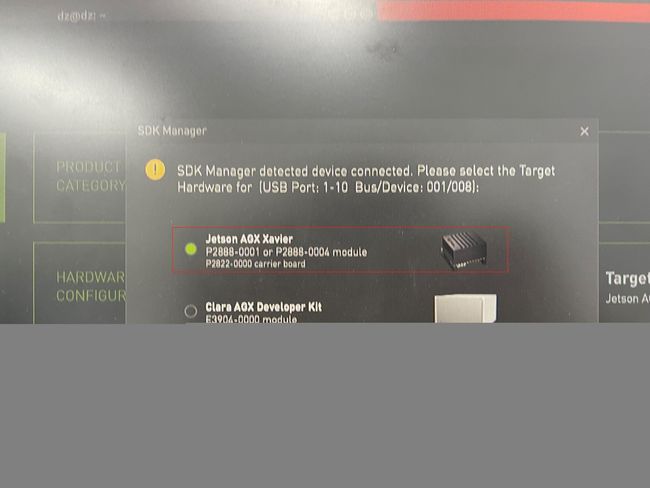
这里第二步host machine可以不选,第二步选择jetpack4.4,然后continue。
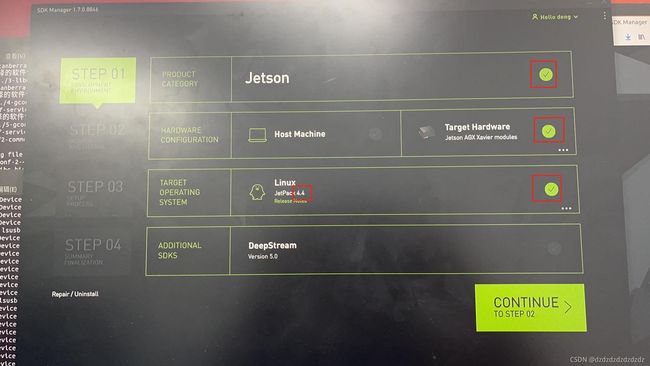
然后按步骤安装,安装目录可以自己选择,跳出选择框先skip,完成后会打开你的下载路径文件夹。下载dtb文件刷一下device tree,把下载的dtb文件放到jetpack的安装目录(nvidia_sdk/JetPack_4.4_Linux_JETSON_AGX_XAVIER/Linux_for_Tegra)下,在这个目录打开终端,输入sudo ./flash.sh -r -d NRU_JetPack4.4_v0.8.dtb jetson-xavier mmcblk0p1
这里按步骤应该没有问题,如果出现not existing,就看自己的工控机是否进入了recovery模式(lsusb有nvidia),成功后如下图。
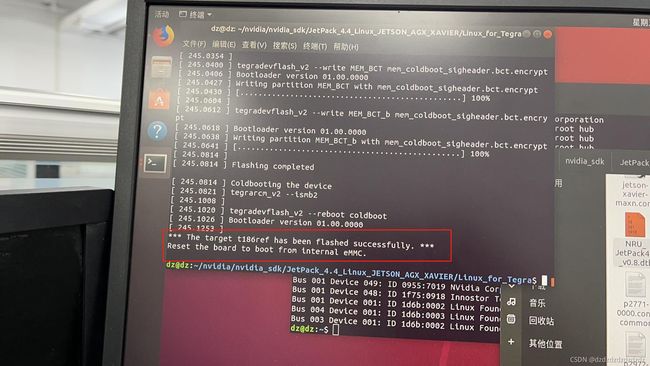
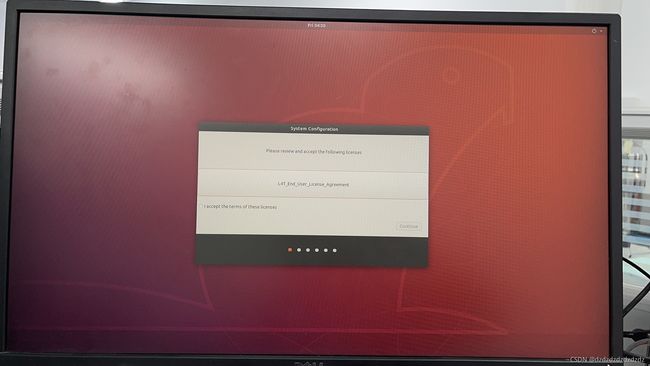
完成后给工控机插上网线(usb可以拔掉,我好像没拔,忘了),给工控机dp口插上显示屏,可以看到工控机开始安装ubuntu系统了,稍等一会儿。
选上accept,继续安装。安装好后查看自己工控机的ip。
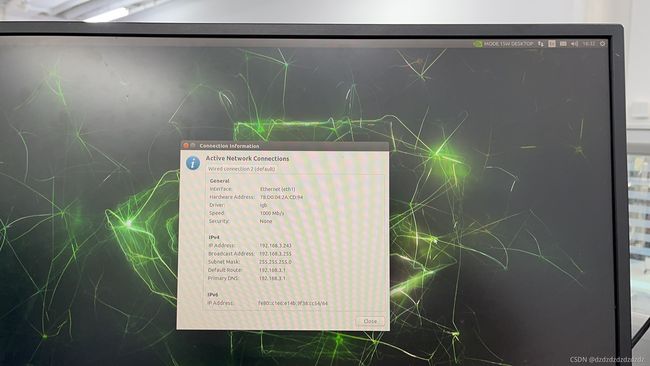
然后设置工控机的休眠,默认是5分钟,改成never。
然后回到主机的sdkmanager
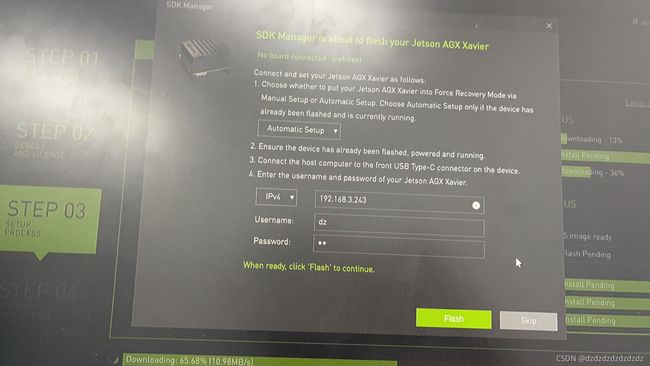
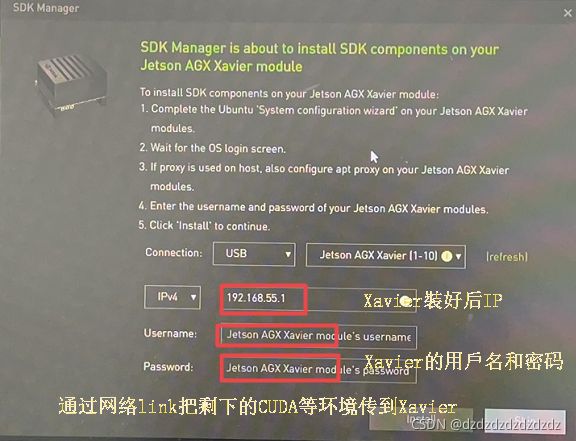
然后就会通过网络给工控机安装上CUDA环境。
安装完成后在工控机上可以查看cuda版本:sudo cat /usr/local/cuda/version.txt。
1.2 英伟达(这个没有模组,所以没有usb驱动文件)
这个工控机被我搞坏了,后来又拿了一个xavier模组,又进行了刷机,和这个过程类似,大家可以参考这个博主的:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_38679413/article/details/109398853,他写的很好,按步骤,没问题。
1.3 瑞泰新时代家的模组
1.下载文件:
首先下载 Jetson_Linux_R_aarch64.tbz2和Tegra-Linux-Sample-Root-Filesystem_R_aarch64.tbz2(这两个sdkmanager里面第二步就可以下载到自己的电脑上),还有驱动usb的bsp支持包Realtimes-L4T-.tar,这里我用的是32.4.3,具体可以找售后要文件,如果和我版本一样可以用我分享的realtimes_L4T_3243_Xavier.tar文件。
2.开始刷机:
2.1这三个文件下载好后开始,新建一个flash文件夹,首先将Linux Driver Package放入flash,然后打开终端,输入tar -vxf Jetson_Linux_R_aarch64.tbz2对它进行解压,
2.2然后进入他解压后的/Linux_for_Tegra/rootfs目录,把 the Root File System拷贝进来,解压到这个目录下 sudo tar -jxpf …/…/Tegra-Linux-Sample-Root-Filesystem_R_aarch64.tbz2,然后进入 Linux_for_Tegra目录,输入 sudo ./apply_binaries.sh(运行 apply_binaries.sh 脚本拷贝 NVIDIA 用户空间库进入目标文件系)。
2.3把Realtimes-L4T-.tar 包解压到与 Linux_for_Tegra 文件夹同级目录下面,使用命令: tar -xvf Realtimes-L4T-.tar,然后进入到 Realtimes-L4T 文件夹,运行sudo./install.sh
2.4然后开始进行烧录,同样把xavier开到recovery模式(关机状态下,中间件两秒钟然后中间件和右边建同时三秒钟一起松开,lsusb里面有了nvidia),在Linux_for_Tegra目录下输入sudo ./flash.sh rtso-1001 mmcblk0p1 //烧写系统
这个本来是打算烧录镜像文件的,但是感觉镜像文件并不好用,所以联系了售后进行了系统重装,并安装了cuda和opencv等(这个用sdkmanager刷一下就可以)这时候需要注意的几个点,首先在xavier上设置不睡眠,一直开机状态,查看xavier的ip地址,还要连上网,xavier不用更新源,用sdk刷的时候,不要os,usb线可以拔掉,他俩使用局域网传信息的。
1.Jetson 禁止指定软件及 L4T 系统升级:
sudo dpkg --get-selections | more //查看系统所有软件状态
sudo apt-mark hold nvidia-l4t-kernel //禁止 kernel 升级
sudo apt-mark hold nvidia-l4t-kernel-dtbs //禁止 kernel-dtb 升级
sudo dpkg --get-selections | grep hold //查看是否锁定成功
取消 L4T 系统升级
例如:Jetson L4T R32.4.x
System setting →softwore&Updates→other Software 取消勾选“…r32.4 main”
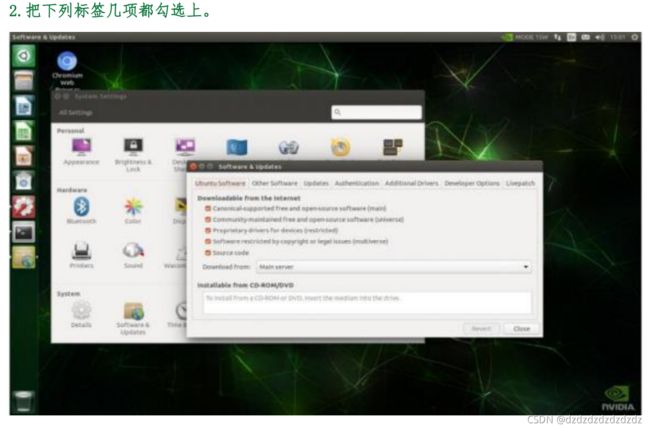

mount:https://blog.csdn.net/xingdou520/article/details/84309155
2.配置yolov5环境并运行
2.1配置虚拟环境
首先安装Archiconda3-0.2.3-Linux-aarch64.sh(类似于anconda),终端输入
sh Archiconda3-0.2.3-Linux-aarch64.sh
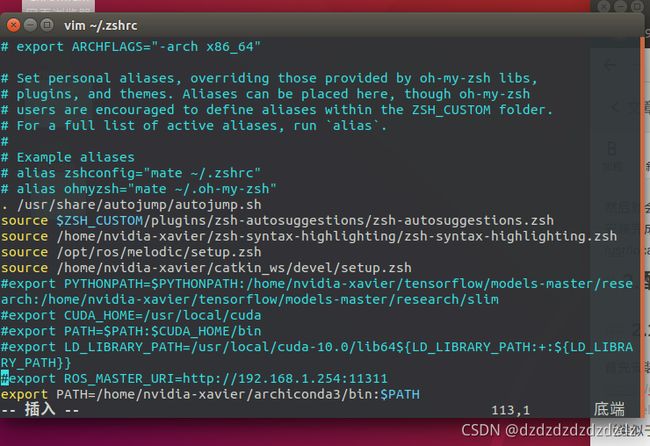
我是在zsh中(类似于bash),安装完毕后修改.zsh(或者.bash)文件,在终端中输入
vim ~/.zshrc
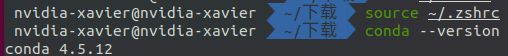
source ~/.zshrc
conda --version
conda create -n yolo python=3.6.9
source activate yolo
克隆yolo文件
git clone -b v5.0 https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5.git
git clone https://github.com/wang-xinyu/tensorrtx.git
在部署环境的时候走也一些弯路,其实直接用requirements文件就可以,下载不了的包单独领出来下载,用镜像路径。
pip install matplotlib==3.2.2
pip install -r requirements.txt -i http://mirrors.aliyun.com/pypi/simple/ --trusted-host mirrors.aliyun.com
python detect.py --source 0 --weights weights/yolov5s.pt --conf 0.25 #安装完后测试
这里是我的环境包,因为之后部署tensorrt的时候有些包版本不对,所以第一个是原始yolo5的环境,第二个是我的tensorrt环境下的yolo5的包。
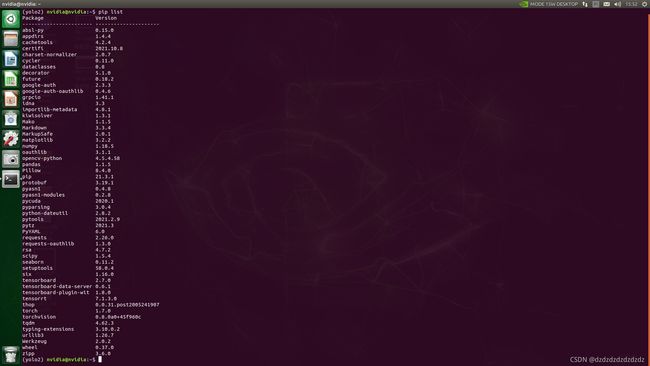

运行的时候总是出问题,这里大部分都是numpy的问题,可以试试更换numpy的版本。
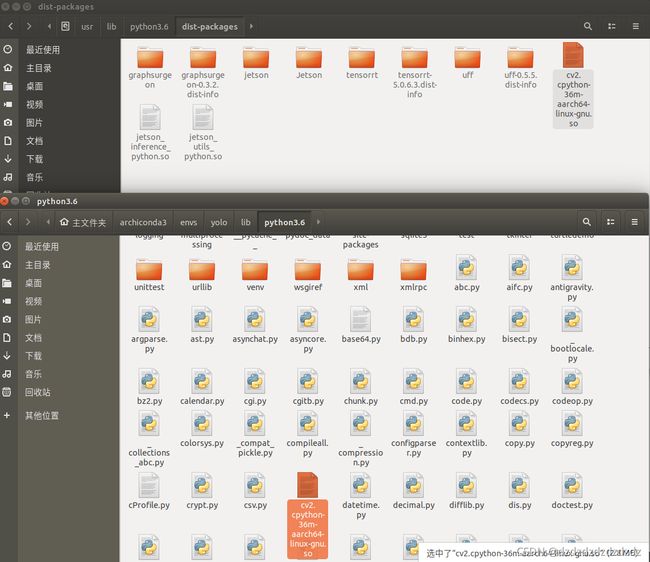
成功倒入cv:将cv2.cpython-36m-aarch64-linux-gnu.so复制到虚拟环境下:
cp -r cv2.cpython-36m-aarch64-linux-gnu.so /media/nvidia/ab1625d4-25fe-4be1-a9da-2198e4c13bb0/softwares/envs/yolo/lib/python3.6
pip install numpy==1.18.5
下载torch
pip install /home/nvidia/Desktop/torch-1.7.0-cp36-cp36m-linux_aarch64.whl
sudo apt-get install libopenblas-dev
下载torchvision
git clone -b v0.8.1 https://gitee.com/zero-one-game/vision vision-0.8.1
sudo /home/nvidia/archiconda3/envs/yolo/bin/python3.6 setup.py install
在yolo5的文件夹下打开虚拟环境,下载所需包
sudo apt install libfreetype6-dev -y
sudo apt install python3-matplotlib -y
pip install -r requirements.txt
pip install Cython matplotlib==3.2.2 numpy==1.18.5 Pillow PyYAML==5.4.1 scipy==1.5.4 tensorboard==1.15.0
pip install tqdm==4.58.0 seaborn==0.11.1 pandas thop pycocotools==2.0.2
下载不了matplotlib,然后就参考https://github.com/yqlbu/jetson-packages-family,还是不行,更换源https://www.it610.com/article/1280107338753130496.htm再
pip install matplotlib==3.2.2
pip install numpy==1.18.5 -i http://mirrors.aliyun.com/pypi/simple/ --trusted-host mirrors.aliyun.com
运行后需要在下载一个ttf文件。
arm64下载vscode参考:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_45321807/article/details/109428777
2.2 yolo5进行tensorrt加速
这里可以参考博文:
【1】https://blog.csdn.net/qq_40691868/article/details/117331162
【2】https://blog.csdn.net/xue_csdn/article/details/100748309
【3】https://github.com/wang-xinyu/tensorrtx.git
主要步骤是通过工程里的gen_wts.py将best.pt文件生成best.wts文件
python gen_wts.py -w weights/best.pt
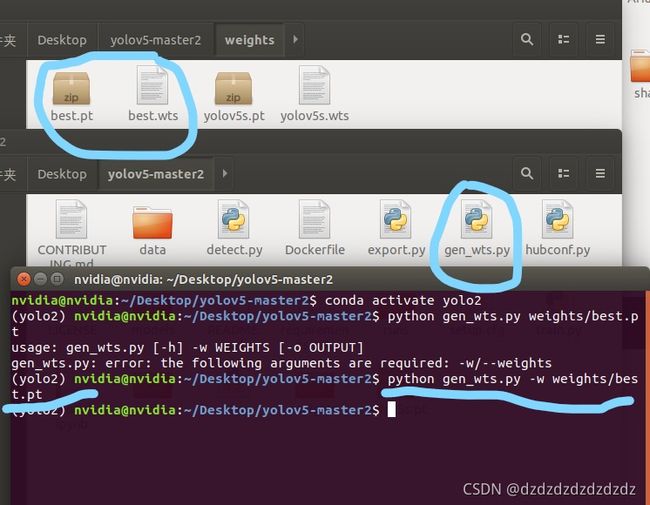
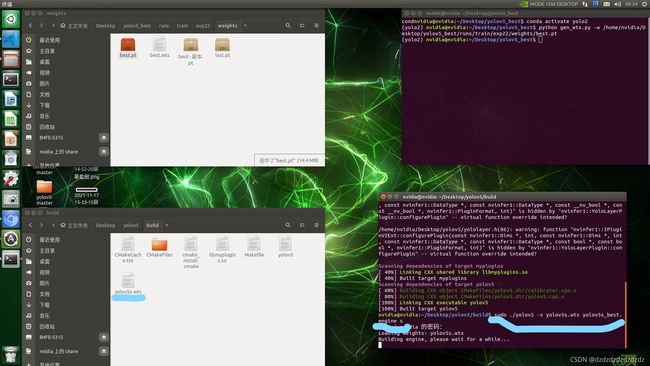
再将wts文件生成engine文件,首先在rt工程下新建build文件夹
mkdir build
cd build
cmake ..
make
sudo ./yolov5 -s yolov5s.wts yolov5s.engine s
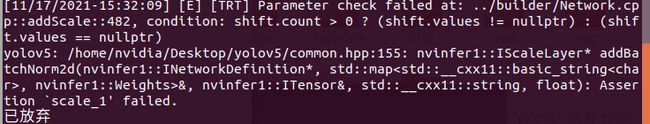
这里注意版本yolo和rt版本要一致,如果出现以下错误,就是版本不一样的问题
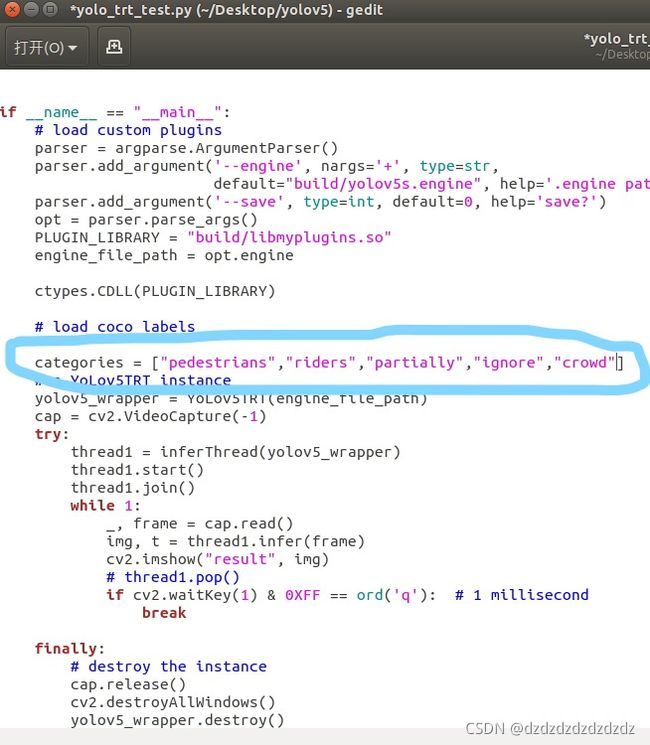
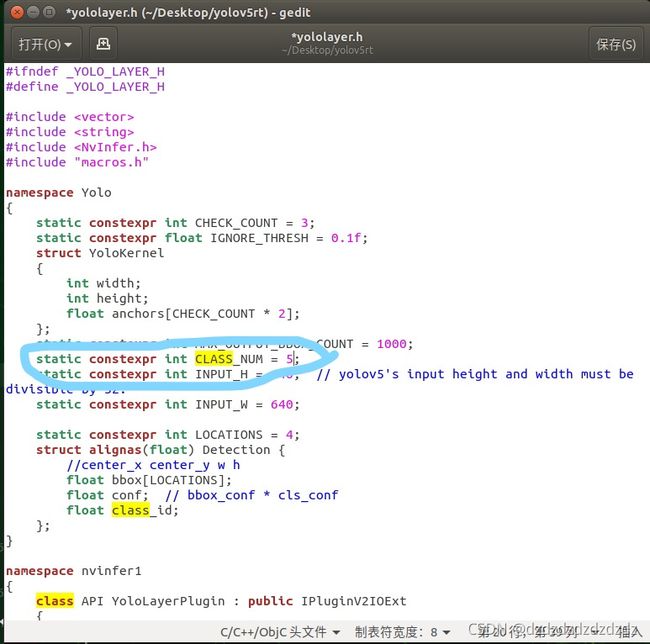
这里因为自己训练的数据和yolo本身的80类有区别,所以需要修改为自己的类别数和标签
3.CAN总线发送数据
这里我将框出来的坐标保存成了log文件,之后要通过can总线发送,所以运行文件做了修改。
这个是我的yolo_trt_test.py文件
"""
An example that uses TensorRT's Python api to make inferences.
"""
import sys
import ctypes
import os
import shutil
import random
import sys
import threading
import time
import cv2
import numpy as np
import pycuda.autoinit
import pycuda.driver as cuda
import tensorrt as trt
import torch
import torchvision
import argparse
CONF_THRESH = 0.5
IOU_THRESHOLD = 0.4
def get_img_path_batches(batch_size, img_dir):
ret = []
batch = []
for root, dirs, files in os.walk(img_dir):
for name in files:
if len(batch) == batch_size:
ret.append(batch)
batch = []
batch.append(os.path.join(root, name))
if len(batch) > 0:
ret.append(batch)
return ret
def plot_one_box(x, img, color=None, label=None, line_thickness=None):
"""
description: Plots one bounding box on image img,
this function comes from YoLov5 project.
param:
x: a box likes [x1,y1,x2,y2]
img: a opencv image object
color: color to draw rectangle, such as (0,255,0)
label: str
line_thickness: int
return:
no return
"""
tl = (
line_thickness or round(0.002 * (img.shape[0] + img.shape[1]) / 2) + 1
) # line/font thickness
color = color or [random.randint(0, 255) for _ in range(3)]
c1, c2 = (int(x[0]), int(x[1])), (int(x[2]), int(x[3]))
# 把框的坐标按照一定格式print
print('1F334455#'+hex(int(x[0]))[2:].zfill(4)+hex(int(x[1]))[2:].zfill(4) +
hex(int(x[2]))[2:].zfill(4)+hex(int(x[3]))[2:].zfill(4))
_console = sys.stdout # 获取print数据
fff = open("outfile.txt", "a+") # 打开这个文件
sys.stdout = fff # 将print数据写入这个文件
# with open("outfile.txt", "a+") as f:
# sys.stdout = f
cv2.rectangle(img, c1, c2, color, thickness=tl, lineType=cv2.LINE_AA)
if label:
tf = max(tl - 1, 1) # font thickness
t_size = cv2.getTextSize(label, 0, fontScale=tl / 3, thickness=tf)[0]
c2 = c1[0] + t_size[0], c1[1] - t_size[1] - 3
cv2.rectangle(img, c1, c2, color, -1, cv2.LINE_AA) # filled
cv2.putText(
img,
label,
(c1[0], c1[1] - 2),
0,
tl / 3,
[225, 255, 255],
thickness=tf,
lineType=cv2.LINE_AA,
)
class YoLov5TRT(object):
"""
description: A YOLOv5 class that warps TensorRT ops, preprocess and postprocess ops.
"""
def __init__(self, engine_file_path):
# Create a Context on this device,
self.ctx = cuda.Device(0).make_context()
stream = cuda.Stream()
TRT_LOGGER = trt.Logger(trt.Logger.INFO)
runtime = trt.Runtime(TRT_LOGGER)
# Deserialize the engine from file
with open(engine_file_path, "rb") as f:
engine = runtime.deserialize_cuda_engine(f.read())
context = engine.create_execution_context()
host_inputs = []
cuda_inputs = []
host_outputs = []
cuda_outputs = []
bindings = []
for binding in engine:
# print('bingding:', binding, engine.get_binding_shape(binding))
size = trt.volume(engine.get_binding_shape(
binding)) * engine.max_batch_size
dtype = trt.nptype(engine.get_binding_dtype(binding))
# Allocate host and device buffers
host_mem = cuda.pagelocked_empty(size, dtype)
cuda_mem = cuda.mem_alloc(host_mem.nbytes)
# Append the device buffer to device bindings.
bindings.append(int(cuda_mem))
# Append to the appropriate list.
if engine.binding_is_input(binding):
self.input_w = engine.get_binding_shape(binding)[-1]
self.input_h = engine.get_binding_shape(binding)[-2]
host_inputs.append(host_mem)
cuda_inputs.append(cuda_mem)
else:
host_outputs.append(host_mem)
cuda_outputs.append(cuda_mem)
# Store
self.stream = stream
self.context = context
self.engine = engine
self.host_inputs = host_inputs
self.cuda_inputs = cuda_inputs
self.host_outputs = host_outputs
self.cuda_outputs = cuda_outputs
self.bindings = bindings
self.batch_size = engine.max_batch_size
def infer(self, input_image_path):
threading.Thread.__init__(self)
# Make self the active context, pushing it on top of the context stack.
self.ctx.push()
self.input_image_path = input_image_path
# Restore
stream = self.stream
context = self.context
engine = self.engine
host_inputs = self.host_inputs
cuda_inputs = self.cuda_inputs
host_outputs = self.host_outputs
cuda_outputs = self.cuda_outputs
bindings = self.bindings
# Do image preprocess
batch_image_raw = []
batch_origin_h = []
batch_origin_w = []
batch_input_image = np.empty(
shape=[self.batch_size, 3, self.input_h, self.input_w])
input_image, image_raw, origin_h, origin_w = self.preprocess_image(input_image_path
)
batch_origin_h.append(origin_h)
batch_origin_w.append(origin_w)
np.copyto(batch_input_image, input_image)
batch_input_image = np.ascontiguousarray(batch_input_image)
# Copy input image to host buffer
np.copyto(host_inputs[0], batch_input_image.ravel())
start = time.time()
# Transfer input data to the GPU.
cuda.memcpy_htod_async(cuda_inputs[0], host_inputs[0], stream)
# Run inference.
context.execute_async(batch_size=self.batch_size,
bindings=bindings, stream_handle=stream.handle)
# Transfer predictions back from the GPU.
cuda.memcpy_dtoh_async(host_outputs[0], cuda_outputs[0], stream)
# Synchronize the stream
stream.synchronize()
end = time.time()
# Remove any context from the top of the context stack, deactivating it.
self.ctx.pop()
# Here we use the first row of output in that batch_size = 1
output = host_outputs[0]
# Do postprocess
result_boxes, result_scores, result_classid = self.post_process(
output, origin_h, origin_w)
# Draw rectangles and labels on the original image
for j in range(len(result_boxes)):
box = result_boxes[j]
plot_one_box(
box,
image_raw,
label="{}:{:.2f}".format(
categories[int(result_classid[j])], result_scores[j]
),
)
return image_raw, end - start
def destroy(self):
# Remove any context from the top of the context stack, deactivating it.
self.ctx.pop()
def get_raw_image(self, image_path_batch):
"""
description: Read an image from image path
"""
for img_path in image_path_batch:
yield cv2.imread(img_path)
def get_raw_image_zeros(self, image_path_batch=None):
"""
description: Ready data for warmup
"""
for _ in range(self.batch_size):
yield np.zeros([self.input_h, self.input_w, 3], dtype=np.uint8)
def preprocess_image(self, input_image_path):
"""
description: Convert BGR image to RGB,
resize and pad it to target size, normalize to [0,1],
transform to NCHW format.
param:
input_image_path: str, image path
return:
image: the processed image
image_raw: the original image
h: original height
w: original width
"""
image_raw = input_image_path
h, w, c = image_raw.shape
image = cv2.cvtColor(image_raw, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
# Calculate widht and height and paddings
r_w = self.input_w / w
r_h = self.input_h / h
if r_h > r_w:
tw = self.input_w
th = int(r_w * h)
tx1 = tx2 = 0
ty1 = int((self.input_h - th) / 2)
ty2 = self.input_h - th - ty1
else:
tw = int(r_h * w)
th = self.input_h
tx1 = int((self.input_w - tw) / 2)
tx2 = self.input_w - tw - tx1
ty1 = ty2 = 0
# Resize the image with long side while maintaining ratio
image = cv2.resize(image, (tw, th))
# Pad the short side with (128,128,128)
image = cv2.copyMakeBorder(
image, ty1, ty2, tx1, tx2, cv2.BORDER_CONSTANT, (128, 128, 128)
)
image = image.astype(np.float32)
# Normalize to [0,1]
image /= 255.0
# HWC to CHW format:
image = np.transpose(image, [2, 0, 1])
# CHW to NCHW format
image = np.expand_dims(image, axis=0)
# Convert the image to row-major order, also known as "C order":
image = np.ascontiguousarray(image)
return image, image_raw, h, w
def xywh2xyxy(self, origin_h, origin_w, x):
"""
description: Convert nx4 boxes from [x, y, w, h] to [x1, y1, x2, y2] where xy1=top-left, xy2=bottom-right
param:
origin_h: height of original image
origin_w: width of original image
x: A boxes tensor, each row is a box [center_x, center_y, w, h]
return:
y: A boxes tensor, each row is a box [x1, y1, x2, y2]
"""
y = torch.zeros_like(x) if isinstance(
x, torch.Tensor) else np.zeros_like(x)
r_w = self.input_w / origin_w
r_h = self.input_h / origin_h
if r_h > r_w:
y[:, 0] = x[:, 0] - x[:, 2] / 2
y[:, 2] = x[:, 0] + x[:, 2] / 2
y[:, 1] = x[:, 1] - x[:, 3] / 2 - \
(self.input_h - r_w * origin_h) / 2
y[:, 3] = x[:, 1] + x[:, 3] / 2 - \
(self.input_h - r_w * origin_h) / 2
y /= r_w
else:
y[:, 0] = x[:, 0] - x[:, 2] / 2 - \
(self.input_w - r_h * origin_w) / 2
y[:, 2] = x[:, 0] + x[:, 2] / 2 - \
(self.input_w - r_h * origin_w) / 2
y[:, 1] = x[:, 1] - x[:, 3] / 2
y[:, 3] = x[:, 1] + x[:, 3] / 2
y /= r_h
return y
def post_process(self, output, origin_h, origin_w):
"""
description: postprocess the prediction
param:
output: A tensor likes [num_boxes,cx,cy,w,h,conf,cls_id, cx,cy,w,h,conf,cls_id, ...]
origin_h: height of original image
origin_w: width of original image
return:
result_boxes: finally boxes, a boxes tensor, each row is a box [x1, y1, x2, y2]
result_scores: finally scores, a tensor, each element is the score correspoing to box
result_classid: finally classid, a tensor, each element is the classid correspoing to box
"""
# Get the num of boxes detected
num = int(output[0])
# Reshape to a two dimentional ndarray
pred = np.reshape(output[1:], (-1, 6))[:num, :]
# to a torch Tensor
pred = torch.Tensor(pred).cuda()
# Get the boxes
boxes = pred[:, :4]
# Get the scores
scores = pred[:, 4]
# Get the classid
classid = pred[:, 5]
# Choose those boxes that score > CONF_THRESH
si = scores > CONF_THRESH
boxes = boxes[si, :]
scores = scores[si]
classid = classid[si]
# Trandform bbox from [center_x, center_y, w, h] to [x1, y1, x2, y2]
boxes = self.xywh2xyxy(origin_h, origin_w, boxes)
# Do nms
indices = torchvision.ops.nms(
boxes, scores, iou_threshold=IOU_THRESHOLD).cpu()
result_boxes = boxes[indices, :].cpu()
result_scores = scores[indices].cpu()
result_classid = classid[indices].cpu()
return result_boxes, result_scores, result_classid
class inferThread(threading.Thread):
def __init__(self, yolov5_wrapper):
threading.Thread.__init__(self)
self.yolov5_wrapper = yolov5_wrapper
def infer(self, frame):
batch_image_raw, use_time = self.yolov5_wrapper.infer(frame)
# for i, img_path in enumerate(self.image_path_batch):
# parent, filename = os.path.split(img_path)
# save_name = os.path.join('output', filename)
# # Save image
# cv2.imwrite(save_name, batch_image_raw[i])
# print('input->{}, time->{:.2f}ms, saving into output/'.format(self.image_path_batch, use_time * 1000))
return batch_image_raw, use_time
class warmUpThread(threading.Thread):
def __init__(self, yolov5_wrapper):
threading.Thread.__init__(self)
self.yolov5_wrapper = yolov5_wrapper
def run(self):
batch_image_raw, use_time = self.yolov5_wrapper.infer(
self.yolov5_wrapper.get_raw_image_zeros())
# print(
# 'warm_up->{}, time->{:.2f}ms'.format(batch_image_raw[0].shape, use_time * 1000))
if __name__ == "__main__":
# load custom plugins
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument('--engine', nargs='+', type=str,
default="build/yolov5s.engine", help='.engine path(s)')
parser.add_argument('--save', type=int, default=0, help='save?')
opt = parser.parse_args()
PLUGIN_LIBRARY = "build/libmyplugins.so"
engine_file_path = opt.engine
ctypes.CDLL(PLUGIN_LIBRARY)
# load coco labels
categories = ["person", "bicycle", "car", "motorcycle", "airplane", "bus", "train", "truck", "boat", "traffic light",
"fire hydrant", "stop sign", "parking meter", "bench", "bird", "cat", "dog", "horse", "sheep", "cow",
"elephant", "bear", "zebra", "giraffe", "backpack", "umbrella", "handbag", "tie", "suitcase", "frisbee",
"skis", "snowboard", "sports ball", "kite", "baseball bat", "baseball glove", "skateboard", "surfboard",
"tennis racket", "bottle", "wine glass", "cup", "fork", "knife", "spoon", "bowl", "banana", "apple",
"sandwich", "orange", "broccoli", "carrot", "hot dog", "pizza", "donut", "cake", "chair", "couch",
"potted plant", "bed", "dining table", "toilet", "tv", "laptop", "mouse", "remote", "keyboard", "cell phone",
"microwave", "oven", "toaster", "sink", "refrigerator", "book", "clock", "vase", "scissors", "teddy bear",
"hair drier", "toothbrush"]
# a YoLov5TRT instance
yolov5_wrapper = YoLov5TRT(engine_file_path)
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(-1)
try:
thread1 = inferThread(yolov5_wrapper)
thread1.start()
thread1.join()
while 1:
_, frame = cap.read()
img, t = thread1.infer(frame)
cv2.imshow("result", img)
# thread1.pop()
if cv2.waitKey(1) & 0XFF == ord('q'): # 1 millisecond
break
finally:
# destroy the instance
cap.release()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
yolov5_wrapper.destroy()
这里我需要通过can1总线将坐标发出去,然后用自己的can0总线接受数据进行测试。这里我写了三个sh文件,如下:
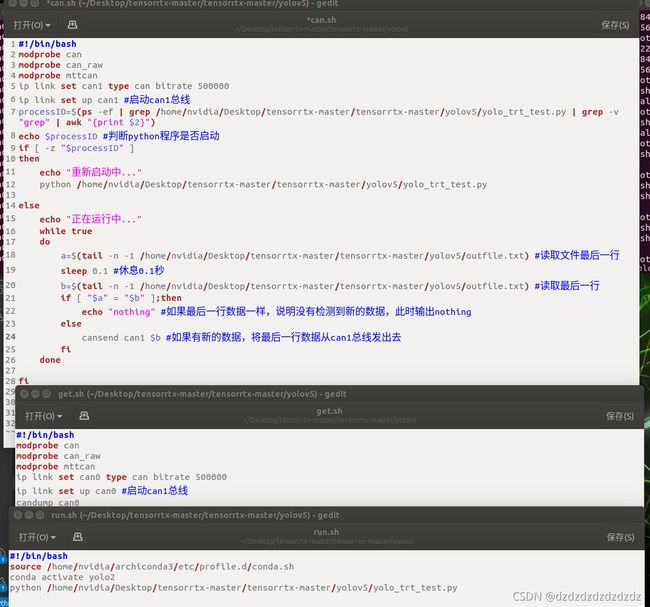
这里我有生成的v6.0版本的yolo.engine文件:
https://download.csdn.net/download/weixin_38226321/45462164
和我工程需要的行人检测的v5.0版本的engine文件:
https://download.csdn.net/download/weixin_38226321/45458756
4.拉出视频流
这里主要参考博文https://blog.csdn.net/u013033845/article/details/86765598
这个博主文件里运行_zhangwei文件夹即可。这里只需要修改自己的config文件即可。
这里我在linux上运行出现了cannot assign requested address错误,是因为linux客户端链接端口用尽,可以用本机的回环地址即消除错误。
[server]
host=192.168.3.105#接收视频的主机
;host=127.0.0.1
port=12340
;feed_host=127.0.0.1
feed_host=192.168.3.78#链接camera,发送视频的主机
feed_port=12341
[camera]
w=1280
h=720
d=3
pieces=10
[delay]
frame=0.01
piece=0.001
[header]
name=FIRE
data=4
index=1
time=7
data_size=60000
total_size=60016
[send]
queue_size=60
piece_limit=50
piece_min=15
fps=30
recv_fps=30
[receive]
queue_size=128
frame_limit=50
piece_limit=30
frame_delay=0.1
然后融合到yolo工程中。
在yolo融合中,我的第一次功能实现是传输原视频流,用can总线获取坐标再画到severse上。
主要用了yolo_trt_test3copy.py和client3.py文件
"""
An example that uses TensorRT's Python api to make inferences.
"""
import sys
import ctypes
import os
import shutil
import random
import sys
import threading
import time
import cv2
import numpy as np
import pycuda.autoinit
import pycuda.driver as cuda
import tensorrt as trt
import torch
import torchvision
import argparse
from client3 import SendVideo
from client3 import WebVideoStream
CONF_THRESH = 0.5
IOU_THRESHOLD = 0.4
def get_img_path_batches(batch_size, img_dir):
ret = []
batch = []
for root, dirs, files in os.walk(img_dir):
for name in files:
if len(batch) == batch_size:
ret.append(batch)
batch = []
batch.append(os.path.join(root, name))
if len(batch) > 0:
ret.append(batch)
return ret
def plot_one_box(x, img, color=None, label=None, line_thickness=None):
"""
description: Plots one bounding box on image img,
this function comes from YoLov5 project.
param:
x: a box likes [x1,y1,x2,y2]
img: a opencv image object
color: color to draw rectangle, such as (0,255,0)
label: str
line_thickness: int
return:
no return
"""
tl = (
line_thickness or round(0.002 * (img.shape[0] + img.shape[1]) / 2) + 1
) # line/font thickness
color = color or [random.randint(0, 255) for _ in range(3)]
c1, c2 = (int(x[0]), int(x[1])), (int(x[2]), int(x[3]))
# 把框的坐标按照一定格式print
print('1F334455#'+hex(int(x[0]))[2:].zfill(4)+hex(int(x[1]))[2:].zfill(4) +
hex(int(x[2]))[2:].zfill(4)+hex(int(x[3]))[2:].zfill(4))
_console = sys.stdout # 获取print数据
fff = open("outfile.txt", "a+") # 打开这个文件
sys.stdout = fff # 将print数据写入这个文件
# with open("outfile.txt", "a+") as f:
# sys.stdout = f
cv2.rectangle(img, c1, c2, color, thickness=tl, lineType=cv2.LINE_AA)
if label:
tf = max(tl - 1, 1) # font thickness
t_size = cv2.getTextSize(label, 0, fontScale=tl / 3, thickness=tf)[0]
c2 = c1[0] + t_size[0], c1[1] - t_size[1] - 3
cv2.rectangle(img, c1, c2, color, -1, cv2.LINE_AA) # filled
cv2.putText(
img,
label,
(c1[0], c1[1] - 2),
0,
tl / 3,
[225, 255, 255],
thickness=tf,
lineType=cv2.LINE_AA,
)
class YoLov5TRT(object):
"""
description: A YOLOv5 class that warps TensorRT ops, preprocess and postprocess ops.
"""
def __init__(self, engine_file_path):
# Create a Context on this device,
self.ctx = cuda.Device(0).make_context()
stream = cuda.Stream()
TRT_LOGGER = trt.Logger(trt.Logger.INFO)
runtime = trt.Runtime(TRT_LOGGER)
# Deserialize the engine from file
with open(engine_file_path, "rb") as f:
engine = runtime.deserialize_cuda_engine(f.read())
context = engine.create_execution_context()
host_inputs = []
cuda_inputs = []
host_outputs = []
cuda_outputs = []
bindings = []
for binding in engine:
# print('bingding:', binding, engine.get_binding_shape(binding))
size = trt.volume(engine.get_binding_shape(
binding)) * engine.max_batch_size
dtype = trt.nptype(engine.get_binding_dtype(binding))
# Allocate host and device buffers
host_mem = cuda.pagelocked_empty(size, dtype)
cuda_mem = cuda.mem_alloc(host_mem.nbytes)
# Append the device buffer to device bindings.
bindings.append(int(cuda_mem))
# Append to the appropriate list.
if engine.binding_is_input(binding):
self.input_w = engine.get_binding_shape(binding)[-1]
self.input_h = engine.get_binding_shape(binding)[-2]
host_inputs.append(host_mem)
cuda_inputs.append(cuda_mem)
else:
host_outputs.append(host_mem)
cuda_outputs.append(cuda_mem)
# Store
self.stream = stream
self.context = context
self.engine = engine
self.host_inputs = host_inputs
self.cuda_inputs = cuda_inputs
self.host_outputs = host_outputs
self.cuda_outputs = cuda_outputs
self.bindings = bindings
self.batch_size = engine.max_batch_size
def infer(self, input_image_path):
threading.Thread.__init__(self)
# Make self the active context, pushing it on top of the context stack.
self.ctx.push()
self.input_image_path = input_image_path
# Restore
stream = self.stream
context = self.context
engine = self.engine
host_inputs = self.host_inputs
cuda_inputs = self.cuda_inputs
host_outputs = self.host_outputs
cuda_outputs = self.cuda_outputs
bindings = self.bindings
# Do image preprocess
batch_image_raw = []
batch_origin_h = []
batch_origin_w = []
batch_input_image = np.empty(
shape=[self.batch_size, 3, self.input_h, self.input_w])
input_image, image_raw, origin_h, origin_w = self.preprocess_image(input_image_path
)
batch_origin_h.append(origin_h)
batch_origin_w.append(origin_w)
np.copyto(batch_input_image, input_image)
batch_input_image = np.ascontiguousarray(batch_input_image)
# Copy input image to host buffer
np.copyto(host_inputs[0], batch_input_image.ravel())
start = time.time()
# Transfer input data to the GPU.
cuda.memcpy_htod_async(cuda_inputs[0], host_inputs[0], stream)
# Run inference.
context.execute_async(batch_size=self.batch_size,
bindings=bindings, stream_handle=stream.handle)
# Transfer predictions back from the GPU.
cuda.memcpy_dtoh_async(host_outputs[0], cuda_outputs[0], stream)
# Synchronize the stream
stream.synchronize()
end = time.time()
# Remove any context from the top of the context stack, deactivating it.
self.ctx.pop()
# Here we use the first row of output in that batch_size = 1
output = host_outputs[0]
# Do postprocess
result_boxes, result_scores, result_classid = self.post_process(
output, origin_h, origin_w)
# Draw rectangles and labels on the original image
for j in range(len(result_boxes)):
box = result_boxes[j]
plot_one_box(
box,
image_raw,
label="{}:{:.2f}".format(
categories[int(result_classid[j])], result_scores[j]
),
)
return image_raw, end - start
def destroy(self):
# Remove any context from the top of the context stack, deactivating it.
self.ctx.pop()
def get_raw_image(self, image_path_batch):
"""
description: Read an image from image path
"""
for img_path in image_path_batch:
yield cv2.imread(img_path)
def get_raw_image_zeros(self, image_path_batch=None):
"""
description: Ready data for warmup
"""
for _ in range(self.batch_size):
yield np.zeros([self.input_h, self.input_w, 3], dtype=np.uint8)
def preprocess_image(self, input_image_path):
"""
description: Convert BGR image to RGB,
resize and pad it to target size, normalize to [0,1],
transform to NCHW format.
param:
input_image_path: str, image path
return:
image: the processed image
image_raw: the original image
h: original height
w: original width
"""
image_raw = input_image_path
h, w, c = image_raw.shape
image = cv2.cvtColor(image_raw, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
# Calculate widht and height and paddings
r_w = self.input_w / w
r_h = self.input_h / h
if r_h > r_w:
tw = self.input_w
th = int(r_w * h)
tx1 = tx2 = 0
ty1 = int((self.input_h - th) / 2)
ty2 = self.input_h - th - ty1
else:
tw = int(r_h * w)
th = self.input_h
tx1 = int((self.input_w - tw) / 2)
tx2 = self.input_w - tw - tx1
ty1 = ty2 = 0
# Resize the image with long side while maintaining ratio
image = cv2.resize(image, (tw, th))
# Pad the short side with (128,128,128)
image = cv2.copyMakeBorder(
image, ty1, ty2, tx1, tx2, cv2.BORDER_CONSTANT, (128, 128, 128)
)
image = image.astype(np.float32)
# Normalize to [0,1]
image /= 255.0
# HWC to CHW format:
image = np.transpose(image, [2, 0, 1])
# CHW to NCHW format
image = np.expand_dims(image, axis=0)
# Convert the image to row-major order, also known as "C order":
image = np.ascontiguousarray(image)
return image, image_raw, h, w
def xywh2xyxy(self, origin_h, origin_w, x):
"""
description: Convert nx4 boxes from [x, y, w, h] to [x1, y1, x2, y2] where xy1=top-left, xy2=bottom-right
param:
origin_h: height of original image
origin_w: width of original image
x: A boxes tensor, each row is a box [center_x, center_y, w, h]
return:
y: A boxes tensor, each row is a box [x1, y1, x2, y2]
"""
y = torch.zeros_like(x) if isinstance(
x, torch.Tensor) else np.zeros_like(x)
r_w = self.input_w / origin_w
r_h = self.input_h / origin_h
if r_h > r_w:
y[:, 0] = x[:, 0] - x[:, 2] / 2
y[:, 2] = x[:, 0] + x[:, 2] / 2
y[:, 1] = x[:, 1] - x[:, 3] / 2 - \
(self.input_h - r_w * origin_h) / 2
y[:, 3] = x[:, 1] + x[:, 3] / 2 - \
(self.input_h - r_w * origin_h) / 2
y /= r_w
else:
y[:, 0] = x[:, 0] - x[:, 2] / 2 - \
(self.input_w - r_h * origin_w) / 2
y[:, 2] = x[:, 0] + x[:, 2] / 2 - \
(self.input_w - r_h * origin_w) / 2
y[:, 1] = x[:, 1] - x[:, 3] / 2
y[:, 3] = x[:, 1] + x[:, 3] / 2
y /= r_h
return y
def post_process(self, output, origin_h, origin_w):
"""
description: postprocess the prediction
param:
output: A tensor likes [num_boxes,cx,cy,w,h,conf,cls_id, cx,cy,w,h,conf,cls_id, ...]
origin_h: height of original image
origin_w: width of original image
return:
result_boxes: finally boxes, a boxes tensor, each row is a box [x1, y1, x2, y2]
result_scores: finally scores, a tensor, each element is the score correspoing to box
result_classid: finally classid, a tensor, each element is the classid correspoing to box
"""
# Get the num of boxes detected
num = int(output[0])
# Reshape to a two dimentional ndarray
pred = np.reshape(output[1:], (-1, 6))[:num, :]
# to a torch Tensor
pred = torch.Tensor(pred).cuda()
# Get the boxes
boxes = pred[:, :4]
# Get the scores
scores = pred[:, 4]
# Get the classid
classid = pred[:, 5]
# Choose those boxes that score > CONF_THRESH
si = scores > CONF_THRESH
boxes = boxes[si, :]
scores = scores[si]
classid = classid[si]
# Trandform bbox from [center_x, center_y, w, h] to [x1, y1, x2, y2]
boxes = self.xywh2xyxy(origin_h, origin_w, boxes)
# Do nms
indices = torchvision.ops.nms(
boxes, scores, iou_threshold=IOU_THRESHOLD).cpu()
result_boxes = boxes[indices, :].cpu()
result_scores = scores[indices].cpu()
result_classid = classid[indices].cpu()
return result_boxes, result_scores, result_classid
class inferThread(threading.Thread):
def __init__(self, yolov5_wrapper):
threading.Thread.__init__(self)
self.yolov5_wrapper = yolov5_wrapper
def infer(self, frame):
batch_image_raw, use_time = self.yolov5_wrapper.infer(frame)
# for i, img_path in enumerate(self.image_path_batch):
# parent, filename = os.path.split(img_path)
# save_name = os.path.join('output', filename)
# # Save image
# cv2.imwrite(save_name, batch_image_raw[i])
# print('input->{}, time->{:.2f}ms, saving into output/'.format(self.image_path_batch, use_time * 1000))
return batch_image_raw, use_time
class warmUpThread(threading.Thread):
def __init__(self, yolov5_wrapper):
threading.Thread.__init__(self)
self.yolov5_wrapper = yolov5_wrapper
def run(self):
batch_image_raw, use_time = self.yolov5_wrapper.infer(
self.yolov5_wrapper.get_raw_image_zeros())
# print(
# 'warm_up->{}, time->{:.2f}ms'.format(batch_image_raw[0].shape, use_time * 1000))
if __name__ == "__main__":
# load custom plugins
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument('--engine', nargs='+', type=str,
default="build/yolov5s.engine", help='.engine path(s)')
parser.add_argument('--save', type=int, default=0, help='save?')
opt = parser.parse_args()
PLUGIN_LIBRARY = "build/libmyplugins.so"
engine_file_path = opt.engine
ctypes.CDLL(PLUGIN_LIBRARY)
# load coco labels
categories = ["pedestrians", "riders", "partially", "ignore", "crowd"]
# a YoLov5TRT instance
yolov5_wrapper = YoLov5TRT(engine_file_path)
wvs = WebVideoStream()
cap = wvs.stream
wvs.start()
try:
thread1 = inferThread(yolov5_wrapper)
thread1.start()
thread1.join()
while 1:
_, frame = cap.read()
# r_c(cap, _, frame)
img, t = thread1.infer(frame)
# wvs.frame_raw = img
cv2.imshow("result", img)
# thread1.pop()
if cv2.waitKey(1) & 0XFF == ord('q'): # 1 millisecond
break
SendVideo(wvs, img)
finally:
# destroy the instance
cap.release()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
yolov5_wrapper.destroy()
client3.py
from threading import Thread, Lock
# from queue import Queue
# from collections import deque as Queue
import socket
import cv2
import numpy
import time
import sys
import os
from fps import FPS
from config import Config
from packer import Packer
import logging
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.DEBUG,
filename='output.log',
format='%(asctime)s - %(name)s - %(levelname)s - %(message)s')
logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
class WebVideoStream:
def __init__(self, src="C:\\Tools\\titan_test.mp4"):
# 1080p D:\\kankan\\backup\\Automata.2014.1080p.BluRay.x264.YIFY.mp4
# 720p C:\\Tools\\titan_test.mp4
self.config = Config()
self.packer = Packer()
# initialize the file video stream along with the boolean
# used to indicate if the thread should be stopped or not
os.environ["OPENCV_VIDEOIO_DEBUG"] = "1"
os.environ["OPENCV_VIDEOIO_PRIORITY_MSMF"] = "0"
encode_param = [int(cv2.IMWRITE_JPEG_QUALITY), 15]
# self.stream = cv2.VideoCapture(src)
self.stream = cv2.VideoCapture(-1)
self.stream.set(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_WIDTH, self.packer.w) # float
self.stream.set(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_HEIGHT, self.packer.h) # float
# while True:
# if cv2.waitKey(1) & 0xFF == ord('q'):
# break
# ret, frame = self.stream.read()
# if ret:
# # print(frame.shape)
# frame = frame.reshape(self.packer.h, self.packer.w, self.packer.d)
# cv2.imshow('read video data.jpg', frame)
# self.stream.set(cv2.CAP_PROP_MODE, cv2.CAP_MODE_YUYV)
# print(self.stream.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FPS)) # 默认帧率30
# self.stream.set(cv2.CAP_PROP_FPS, 20) # cv version is 3.4.2
self.stopped = False
self.requesting = False
self.request = False
self.quit = False
self.fps = 40
self.recv_fps = 0
self.push_sleep = 0.01
self.push_sleep_min = 0.001
self.push_sleep_max = 0.2
self.send_sleep = 0.05
self.send_sleep_min = 0.01
self.send_sleep_max = 0.1
self.network_delay = 0
self.delay_timer = int(time.time()*1000)
self.piece_array = []
self.piece_time = int(time.time()*1000)
self.piece_fps = 40
for i in range(self.packer.frame_pieces):
self.piece_array.append(None)
self.frame = numpy.zeros(self.packer.frame_size_3d, dtype=numpy.uint8)
self.imshow = self.frame.reshape(
self.packer.h, self.packer.w, self.packer.d)
self.frame_size = 0
self.piece_size = 0
self.frame_pieces = 0
self.init_config()
self.init_connection()
# intialize thread and lock
self.thread = Thread(target=self.update, args=())
self.thread.daemon = True
def init_config(self):
config = self.config
# 初始化连接信息
host = config.get("server", "host")
port = config.get("server", "port")
feed_host = config.get("server", "feed_host")
feed_port = config.get("server", "feed_port")
self.address = (host, int(port))
self.feed_address = (feed_host, int(feed_port))
# 初始化delay信息
self.frame_delay = float(config.get("delay", "frame"))
self.piece_delay = float(config.get("delay", "piece"))
# 初始化队列大小信息
self.queue_size = int(config.get("receive", "queue_size"))
def init_connection(self):
try:
self.sock = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_DGRAM)
self.sock.setsockopt(socket.SOL_SOCKET, socket.SO_REUSEADDR, 1)
# self.sock.bind(self.address)
except socket.error as msg:
print(msg)
sys.exit(1)
def close_connection(self):
self.sock.close()
# def init_feedback_connection(self):
# try:
# feed_sock = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET,socket.SOCK_DGRAM)
# feed_sock.setsockopt(socket.SOL_SOCKET, socket.SO_REUSEADDR, 1)
# feed_sock.bind(self.feed_address)
# return feed_sock
# except socket.error as msg:
# print(msg)
# sys.exit(1)
def start(self):
# start a thread to read frames from the file video stream
self.thread.start()
recv_thread = Thread(target=self.recv_thread, args=())
recv_thread.daemon = True
recv_thread.start()
return self
def update(self):
piece_size = self.packer.piece_size
# keep looping infinitely until the thread is stopped
while True:
# if the thread indicator variable is set, stop the thread
if self.stopped:
return
# self.Q_stuck_control()
time.sleep(self.push_sleep)
# otherwise, read the next frame from the stream
(grabbed, frame_raw) = self.stream.read()
# print(frame_raw.shape)
now = int(time.time()*1000)
for i in range(self.packer.frame_pieces):
self.packer.pack_data(
i, now, frame_raw, self.piece_array, self.piece_time, self.piece_fps)
# print("pfps:", self.piece_fps)
# now2 = int(time.time()*1000)
# print("Time to get a frame:", (now2-now))
return
def Q_stuck_control(self):
if self.piece_fps == 0:
return False # 为零表示还没有变化
if self.piece_fps > self.packer.send_fps:
self.push_sleep = min(self.push_sleep + 0.01, self.push_sleep_max)
return True
if self.piece_fps < self.packer.send_fps:
self.push_sleep = max(self.push_sleep - 0.01, self.push_sleep_min)
return False
def send_stuck_control(self):
if self.recv_fps == 0:
return False
if self.recv_fps > self.packer.recv_fps_limit:
self.send_sleep = min(self.send_sleep + 0.01, self.send_sleep_max)
return True
if self.recv_fps < self.packer.recv_fps_limit:
self.send_sleep = max(self.send_sleep - 0.01, self.send_sleep_min)
return False
def get_request(self):
if self.requesting:
return
print("waiting...")
thread = Thread(target=self.get_request_thread, args=())
thread.daemon = True
thread.start()
self.requesting = True
def get_request_thread(self):
while True:
data = b''
try:
data, address = self.sock.recvfrom(4)
except:
pass
if(data == b"get"):
self.request = True
break
elif(data == b"quit"):
self.quit = True
break
def read(self, i):
return self.piece_array[i]
def read_send(self, i):
# while True:
# if cv2.waitKey(1) & 0xFF == ord('q'):
# break
# start threads to recieve
# for i in range(self.packer.frame_pieces):
# intialize thread
pack = self.piece_array[i]
if pack is None:
return
self.sock.sendto(pack, self.address)
# thread = Thread(target=self.send_thread, args=(i,))
# thread.daemon = True
# thread.start()
def send_thread(self, i):
pack = self.piece_array[i]
if pack is None:
return
self.sock.sendto(pack, self.address)
def recv_thread(self):
s = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
s.bind(self.feed_address)
s.listen(1)
conn, addr = s.accept()
while True:
data = conn.recv(self.packer.info_pack_len)
if len(data) > 0:
sname, server_fps, send_ctime = self.packer.unpack_info_data(
data)
now = int(time.time()*1000)
self.network_delay = int((now - send_ctime)/2.0)
self.recv_fps = server_fps
conn.close()
def stop(self):
# indicate that the thread should be stopped
self.stopped = True
def SendVideo(wvs, img):
t = 0
if t == 0:
sock = wvs.sock
address = wvs.address
# running = True
# while running:
now = time.time()
# camara_delay = 0.03
wvs.send_stuck_control()
time.sleep(wvs.send_sleep)
# time.sleep(0.03)
# print(wvs.send_sleep)
for i in range(wvs.packer.frame_pieces):
wvs.read_send(i)
now1 = time.time()
cnow = int(now1*1000)
ctime = now1 - now
# print("frame time", ctime)
if ctime > 0:
send_fps = str(int(1.0/ctime)).ljust(4)
recv_fps = str(wvs.recv_fps).ljust(4)
net_delay = str(wvs.network_delay).ljust(4)
if cnow - wvs.delay_timer > 300:
# if True:
wvs.delay_timer = cnow
# img = numpy.zeros((100, 900, 3), numpy.uint8)
font = cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX
bottomLeftCornerOfText = (10, 50)
fontScale = 0.7
fontColor = (255, 255, 255)
lineType = 2
# cv2.putText(img, 'Hello Fire! Send FPS:' + send_fps + ", Recv FPS:" + recv_fps + ", Net delay:" + net_delay,
# bottomLeftCornerOfText,
# font,
# fontScale,
# fontColor,
# lineType)
# cv2.imshow("Send clinet", img)
# 不断地从队列里面取数据尝试
# try:
# for i in range(wvs.packer.frame_pieces):
# pack = wvs.piece_array[i]
# line_data = cv2.imdecode(pack, 1).flatten()
# row_start = i*wvs.packer.piece_size
# row_end = (i+1)*wvs.packer.piece_size
# wvs.frame[row_start:row_end] = line_data
# frame = wvs.frame.reshape(wvs.packer.h, wvs.packer.w, wvs.packer.d)
# if frame is not None:
# cv2.imshow("FireStreamer", frame)
# except:
# pass
# now = time.time()
# frame = wvs.read(i)
# if frame:
# # print(len(frame))
# time.sleep(0.05)
# sock.sendto(frame, wvs.address)
# now1 = time.time()
# ctime += now1 - now
# print("frame time", ctime)
# if ctime>0:
# print("fps:", (1.0/(ctime)))
else:
con = Config()
host = con.get("server", "host")
port = con.get("server", "port")
address = (host, int(port))
sock = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_DGRAM)
capture = cv2.VideoCapture(0)
capture.set(cv2.CAP_PROP_MODE, cv2.CAP_MODE_YUYV)
# 读取一帧图像,读取成功:ret=1 frame=读取到的一帧图像;读取失败:ret=0
ret, frame = capture.read()
encode_param = [int(cv2.IMWRITE_JPEG_QUALITY), 60]
# 停止0.1S 防止发送过快服务的处理不过来,如果服务端的处理很多,那么应该加大这个值
time.sleep(0.01)
ret, frame = capture.read()
frame = cv2.flip(frame, 1) # 水平翻转
result, imgencode = cv2.imencode('.jpg', frame, encode_param)
print(len(imgencode))
s = frame.flatten().tostring()
for i in range(20):
time.sleep(0.001)
# print(i.to_bytes(1, byteorder='big'))
sock.sendto(s[i*46080:(i+1)*46080] +
i.to_bytes(1, byteorder='big'), address)
# result, imgencode = cv2.imencode('.jpg', frame, encode_param)
# data = numpy.array(imgencode)
# stringData = data.tostring()
# save data
# cv2.imwrite('read video data.jpg', frame, encode_param)
# show locally
# cv2.imshow('read video data.jpg', frame)
# 读取服务器返回值
# receive = sock.recvfrom(1024)
# if len(receive): print(str(receive,encoding='utf-8'))
# if cv2.waitKey(10) == 27: break
# exit(0)
# capture.release()
# cv2.destroyAllWindows()
# sock.close()
第二种方法直接传输有坐标框的视频流
5.设备设置
1.更改风扇转速
sudo vi /sys/devices/pwm-fan/target_pwm
更改,最大250,默认77
2.下载 vscode:https://code.visualstudio.com/Download
choose arm64 deb:
6.win与xavier通信
项目需要,需要win通过udp对xavier发送信息,xavier通过can给win发送数据。
首先通过一条网线将两者相连,设置两者的ip地址,xavier(192.168.1.124),win(192.168.3.123),xavier读取win通过udp发送的数据并写入udp_can.txt。
win发送:
import socket
def send_message(udp_socket,dest_ip,dest_port):
send_data = input("请输入你要发送的信息:")
udp_socket.sendto(send_data.encode("gbk"),(dest_ip,dest_port))
# def receive_message(udp_socket):
# udp_rece = udp_socket.recvfrom(1024)
# print(udp_rece[0].decode("gbk"),udp_rece[1])
def main():
#创建套接字
udp_socket = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET,socket.SOCK_DGRAM)
# dest_ip = input("请输入目标ip:")
# dest_port = int(input("请输入目标port:"))
dest_ip ="192.168.1.124"
dest_port =8000
#绑定ip和port
udp_socket.bind(("",8888))
#循环来处理事情
while True:
#发送
send_message(udp_socket,dest_ip,dest_port)
# #接受
# receive_message(udp_socket)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
xavier接受:
import socket
# def send_message(udp_socket, dest_ip, dest_port):
# send_data = input("请输入你要发送的信息:")
# udp_socket.sendto(send_data.encode("gbk"), (dest_ip, dest_port))
def receive_message(udp_socket):
udp_rece = udp_socket.recvfrom(1024)
print(udp_rece[0].decode("gbk"), udp_rece[1])
with open("udp_can.txt", 'a') as f:
f.write(udp_rece[0].decode("gbk")+"\n")
def main():
# 创建套接字
udp_socket = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_DGRAM)
# dest_ip = input("请输入目标ip:")
# dest_port = int(input("请输入目标port:"))
# 绑定ip和port
udp_socket.bind(("", 8000))
# 循环来处理事情
while True:
# 发送
# send_message(udp_socket,dest_ip,dest_port)
# 接受
receive_message(udp_socket)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
第二步通过查看udp_can.txt里又2新数据而通过can总线发送数据。
7.references
[1]https://blog.csdn.net/qq_40691868/article/details/114379061?spm=1001.2014.3001.5501
[2]https://blog.csdn.net/qq_40691868/article/details/114362278?spm=1001.2014.3001.5501
[3]https://blog.csdn.net/qq_40691868/article/details/117331162
[4]https://blog.csdn.net/xingdou520/article/details/84309155