基于AlexNet网络的CIFAR-10数据集识别(pytorch)
基于AlexNet网络的CIFAR-10数据集识别(pytorch)
- 目录
-
- AlexNet
-
-
- ILSVRC 2012的冠军模型
- AlexNet 网络结构
-
- CIFAR-10 数据集
- Pytorch代码实现
目录
AlexNet
ILSVRC 2012的冠军模型
ImageNet是一个由超过1500万张贴有标签的高分辨率图像组成的数据集,属于大约22000个类别。
这些图像是从网上收集的,并由人类标签员使用亚马逊的Mechanical Turk众包工具进行标注。从2010年开始,作为 Pascal Visual Object 挑战赛的一部分,一个被称为 "ILSVRC"的年度比赛开始了。
而今天应用的AlexNet就是2012年的冠军模型,这也是神经网络模型在图像识别上第一次打败传统机器学习方法!
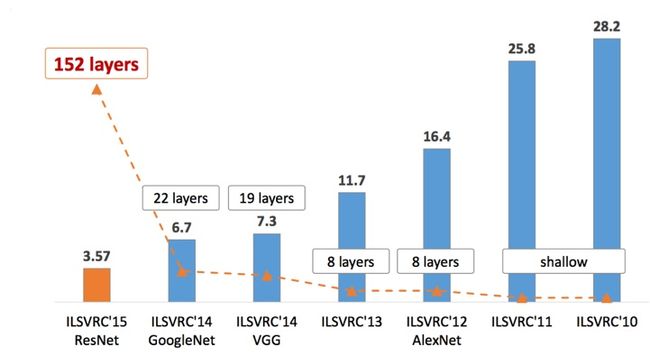
(历届冠军模型)
AlexNet 网络结构
该网络包含八个带权重的层;前五个是卷积层,其余三个是全连接层。最后一个全连接层的输出被送入一个1000路softmax,产生1000个类别标签的分布。
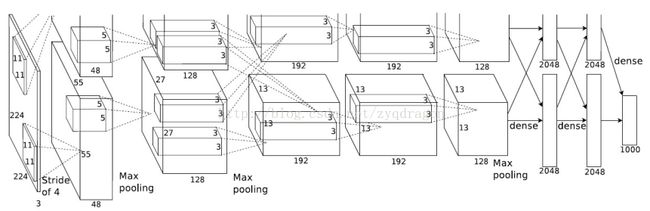
(AlexNet模型图)
作为当年的冠军模型,AlexNet还用到了很多little trick,有图像裁剪等预处理进行数据增强,以及LRN,Dropout等方法避免模型的过拟合,提高泛化能力,最终提高识别精度。
详情见当年的AlexNet论文
CIFAR-10 数据集
关于CIFAR-10数据集的介绍,详见我的上一篇博客
注:
为了应用AlexNet的原生超参数,在数据集图片导入的时候resize为当年ImageNet的数据集图片大小。(详见下面的代码)
Pytorch代码实现
import torch
from torch import nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
import torchvision
import numpy as np
import torch.utils.data as data
import torchvision.transforms as transforms
class AlexNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,input_channels):
super().__init__()
# 第1个卷积层
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(input_channels, 96, kernel_size=11, stride=4)
# 第1个池化层
self.pooling1 = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2)
# 第2个卷积层
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(96, 256, kernel_size=5, padding=2)
# 第2个池化层
self.pooling2 = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2)
# 第3个卷积层
self.conv3 = nn.Conv2d(256, 384, kernel_size=3, padding=1)
# 第4个卷积层
self.conv4 = nn.Conv2d(384, 384, kernel_size=3, padding=1)
# 第5个卷积层
self.conv5 = nn.Conv2d(384, 256, kernel_size=3, padding=1)
# 第3个池化层
self.pooling3 = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2)
##最后的三个FC
self.Flatten = nn.Flatten(start_dim=1,end_dim=-1)
# 计算得出的当前的前面处理过后的shape,当然也可print出来以后再确定
self.Linear1 = nn.Linear(6400, 4096)
self.drop1 = nn.Dropout(p = 0.5)
self.Linear2 = nn.Linear(4096, 4096)
self.drop2 = nn.Dropout(p = 0.5)
self.Linear3 = nn.Linear(4096, 10)
def forward(self,X):
X = self.pooling1(F.relu(self.conv1(X)))
X = self.pooling2(F.relu(self.conv2(X)))
X = F.relu(self.conv3(X))
X = F.relu(self.conv4(X))
X = F.relu(self.conv5(X))
X = self.pooling3(X)
X = X.view(X.size()[0], -1)
X = self.drop1(F.relu(self.Linear1(X)))
X = self.drop2(F.relu(self.Linear2(X)))
X = F.relu(self.Linear3(X))
return X
def load_CIFAR10(batch_size, resize=224):
""" 加载数据集到内存 ,迎合Alex改变大小 """
trans = [transforms.ToTensor(),transforms.Normalize((0.5, 0.5, 0.5), (0.5, 0.5, 0.5))]
if resize:
trans.insert(0, transforms.Resize(resize))
trans = transforms.Compose(trans)
mnist_train = torchvision.datasets.CIFAR10(root=r"dataset",
train=True,
transform=trans,
download=True)
mnist_test = torchvision.datasets.CIFAR10(root=r"dataset",
train=False,
transform=trans,
download=True)
return (data.DataLoader(mnist_train, batch_size, shuffle=True,
num_workers=2),
data.DataLoader(mnist_test, batch_size, shuffle=False,
num_workers=2))
def get_labels(labels):
''' 标签转换 '''
text_labels = ['plane', 'car', 'bird', 'cat', 'deer', 'dog', 'frog', 'horse', 'ship', 'truck']
return [text_labels[int(i)] for i in labels]
def train(loss,updater,train_iter,net,epoches):
''' 训练模型 '''
for epoch in range(epoches):
run_loss = 0
for step,(X,y) in enumerate(train_iter):
if torch.cuda.is_available():
X = X.cuda()
y = y.cuda()
y_hat = net.forward(X) #前向推导,用了自定义的forward
ls = loss(y_hat,y).sum() #计算误差
updater.zero_grad() #梯度清零
ls.backward() #计算新的梯度
run_loss += ls.item()
updater.step() #更新权值
see_yh = y_hat.argmax(axis=1)
print( f'true:{y[0:6]} preds:{see_yh[0:6]} epoch:{epoch:02d}\t epoch_loss {run_loss/390}\t ')
print('finished training\n')
def predict(net,test_iter,batch_size,n=6):
''' 测试集预测 '''
acc_loss = 0
for index,(X, y) in enumerate(test_iter):
if torch.cuda.is_available():
X = X.cuda()
y = y.cuda()
trues = get_labels(y)
preds = get_labels(net(X).argmax(axis=1))
for true,pred in zip(trues,preds):
if true == pred:
acc_loss += 1
print('totals: ',index*batch_size)
print('total accuracy: ',acc_loss/(index*batch_size))
if __name__ == '__main__':
#设置超参数
batch_size, learning_rate, epoches = 128, 0.05, 20 # 超参数初始化
trainSet,testSet = load_CIFAR10(batch_size) #加载数据
net = AlexNet(3) #加载模型
if torch.cuda.is_available():
net.cuda()
loss = nn.CrossEntropyLoss() # 选择损失函数
updater = torch.optim.SGD(net.parameters(), lr=learning_rate) # 优化器
train(loss,updater,trainSet,net,epoches) #训练
predict(net,testSet,batch_size)