matlab期末大作业(基础功能、人脸识别、特殊风格等)
提示:文章写完后,目录可以自动生成,如何生成可参考右边的帮助文档
文章目录
- 1.导入图片和从摄像头端加载图片。
-
- 1.1算法原理
- 1.2代码
- 1.3结果及分析
- 2.将一张彩色图像进行不同角度的旋转,各种程度的对比度,彩色图像灰度化,裁剪图片。
-
- 2.1算法原理
- 2.2代码
- 2.3结果及分析
- 3.不同阈值的二值化处理
-
- 3.1算法原理
- 3.2代码
- 3.3结果及分析
- 4.两幅图像相加
-
- 4.1算法原理
- 4.2代码
- 4.3结果及分析
- 5.两幅图像相减
-
- 5.1算法原理
- 5.2代码
- 5.3结果及分析
- 6.对数2 、5 、15不同程度的变化,指数2 、4 、0.5的不同程度的变换图片。将图片镜像和反色
-
- 6.1算法原理
- 6.2代码
- 6.3结果及分析
- 7.直方图和直方图均衡化
-
- 7.1算法原理
- 7.2代码
- 7.3结果及分析
- 8.添加高斯和椒盐噪声并分别用不同3*3和5*5模板进行均值、中值、高斯滤波器处理
-
- 8.1算法原理
- 8.2代码
- 8.3结果及分析
- 9.分别采用roberts、sobel、拉普拉斯、log、prewitt算子进行边缘提取
-
- 9.1算法原理
- 9.2代码
- 9.3结果及分析
- 10.对图像进行巴斯沃特高通、理想高通、高斯高通、巴斯沃特低通、理想低通、高斯低通频域处理,可以设置各种不同的D0处理
-
- 10.1算法原理
- 10.2代码
- 10.3结果及分析
- 11.运动模糊再复原,维也纳滤波复原
-
- 11.1算法原理
- 11.2代码
- 11.3结果及分析
- 12.傅里叶正变换、腐蚀膨胀开运算和闭运算,形态学滤波
-
- 12.1算法原理
- 12.2代码
- 12.3结果及分析
- 13.提取红苹果
-
- 13.1算法原理
- 13.2代码
- 13.3结果及分析
- 14.硬币检测
-
- 14.1算法原理
- 14.2代码
- 14.3结果及分析
- 15.圆和矩形检测
-
- 15.1算法原理
- 15.2代码
- 15.3结果及分析
- 16人脸识别,眼睛识别,嘴巴识别
-
- 16 1算法原理
- 16.2 代码
- 16.3结果及分析
- 17浮雕、复古风、倒影、羽化、马赛克、素描
-
- 17.1算法原理
- 17.2代码
- 17.3结果及分析
1.导入图片和从摄像头端加载图片。
1.1算法原理
1.2代码
[fp,pn,fg]=uigetfile('*.*','选择图片');
I = imread([pn fp]);
axes(handles.axes1);%创建坐标轴图形对象
imshow(I);%显示图像
handles.image = I;
guidata(hObject,handles);%设置为全局图片
%从摄像头端加载图片
vid = videoinput('winvideo', 1, 'YUY2_640x480')
set(vid,'ReturnedColorSpace','rgb');
vidRes=get(vid,'VideoResolution');
width=vidRes(1);
height=vidRes(2);
nBands=get(vid,'NumberOfBands');
hImage=image(zeros(vidRes(2),vidRes(1),nBands));
preview(vid,hImage);
start(vid);
img = getsnapshot(vid);
axes(handles.axes1);
imshow(img);
delete(vid);
handles.image = img;
guidata(hObject,handles);%设置为全局图片
1.3结果及分析
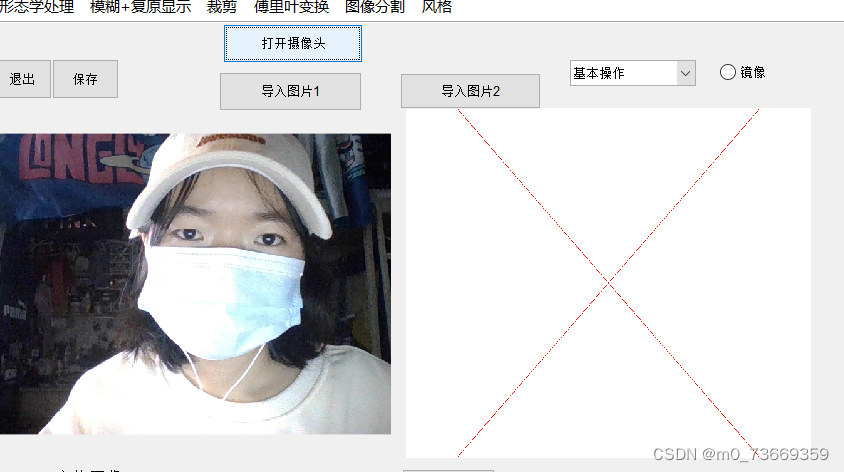
用完之后清除对象
clear
2.将一张彩色图像进行不同角度的旋转,各种程度的对比度,彩色图像灰度化,裁剪图片。
2.1算法原理
rgb2gray 函数通过消除色调和饱和度信息,同时保留亮度,来将 RGB 图像转换为灰度图
真彩色图像,指定为 m×n×3 数值数组
灰度图像,以 m×n 数值数组形式返回
2.2代码
%图像的对比度
I=handles.image;
num=get(handles.slider2,'value');
I1 = imadjust(I,[0 num],[]);
set(handles.axes2,'HandleVisibility','ON');
axes(handles.axes2);
imshow(I1)
%旋转
set(hObject,'Min',0,'Max',360);
I=handles.image;
a=get(handles.slider3,'value');
L=imrotate(I,a);
set(handles.axes2,'HandleVisibility','ON');
axes(handles.axes2);
imshow(L);
%做图像裁剪
im = handles.image;
%figure,imshow(im);
imcroped = imcrop; % 直接将figure前置并使鼠标显示十字架让你画框,画完双击就截取了矩形图像
axes(handles.axes2);
imshow(imcroped); %截取后的图像存在imcroped中
2.3结果及分析


 分析:B=imrotate(A,angle),将图像A围绕其中心点进行angle角度的逆时针旋转 imadjust函数实现对比度 图像裁剪 imcroped = imcrop; % 直接将figure前置并使鼠标显示十字架让你画框,画完双击就截取了矩形图像
分析:B=imrotate(A,angle),将图像A围绕其中心点进行angle角度的逆时针旋转 imadjust函数实现对比度 图像裁剪 imcroped = imcrop; % 直接将figure前置并使鼠标显示十字架让你画框,画完双击就截取了矩形图像
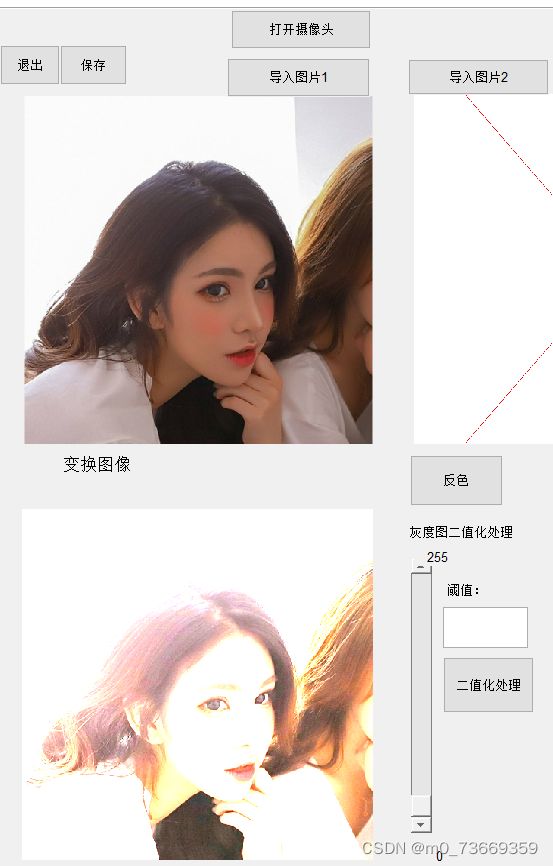
3.不同阈值的二值化处理
3.1算法原理
将灰度图像 I 转换为二进制图像
3.2代码
I=handles.image;
mysize = size(I);
%把图像转换成灰度图
if numel(mysize) > 2
I = rgb2gray(I);
end
a=im2double(I);
%全局变量设置的二值化阈值
binary_img = im2bw(a,handles.binary_thresh);
%显示二值化后的图片
axes(handles.axes2)
imshow(binary_img)
3.3结果及分析

 分析: 阈值越高,黑色部分越高。
分析: 阈值越高,黑色部分越高。
4.两幅图像相加
4.1算法原理
存储当做一个二维的矩阵、进一步地,视为二维数组来进行处理。可以想到:如果我们的目的是完成对两张图片的融合,最简单的方法就是把每一个像素点加起来
4.2代码
I = handles.image;%得到第一张全局图像
J=handles.image2;%得到第二张全局图像
H1=imadd(I,J);%两张图像相加
4.3结果及分析
5.两幅图像相减
5.1算法原理
图像减法也称为差分方法,进行代数运算
5.2代码
I = handles.image;%得到第一张全局图像
J=handles.image2;%得到第二张全局图像
%图像相减,要求图像矩阵相同大小
H2=imsubtract(I,J);
imshow(H2);
5.3结果及分析
6.对数2 、5 、15不同程度的变化,指数2 、4 、0.5的不同程度的变换图片。将图片镜像和反色
6.1算法原理
对数函数会扩张低灰度区域压缩高灰度区域,因此低灰度区域细节会增强,图像整体会变亮,而指数函数则相反
反色的实际含义是将R、G、B值反转,若颜色的量化级别是256,则新图的R、G、B值为255减去原图的R、G、B值。
flipdim函数实现图片镜像翻转
6.2代码
%对数变换
I=handles.image;%获取全局图像
set(handles.axes2,'HandleVisibility','ON');
axes(handles.axes2);
I=double(rgb2gray(I))/255;
I=log2(1+I)/log2(5);
imshow(I);
% Hint: get(hObject,'Value') returns toggle state of radiobutton4
%指数变换
I=handles.image;%获取全局图像
set(handles.axes2,'HandleVisibility','ON');
axes(handles.axes2);
I=double(rgb2gray(I))/255;
c=255;
I = c/255*(I.^2);
imshow(I);
%镜像处理
%图形的几何变换—垂直镜像
set(handles.axes2,'HandleVisibility','ON');
axes(handles.axes2);
I = handles.image;
J = flipdim(I,2);%原图像的垂直镜像
imshow(J);
%反色
I=handles.image;
[rows , cols , colors] = size(I);%得到原来图像的矩阵的参数
Res = zeros(rows , cols);%创建一个空矩阵用来存储新的灰度图
Res = uint8(Res);
Res(:,:,1)=255-I(:,:,1);
Res(:,:,2)=255-I(:,:,2);
Res(:,:,3)=255-I(:,:,3);
set(handles.axes2,'HandleVisibility','ON');
axes(handles.axes2);
imshow(Res);
6.3结果及分析


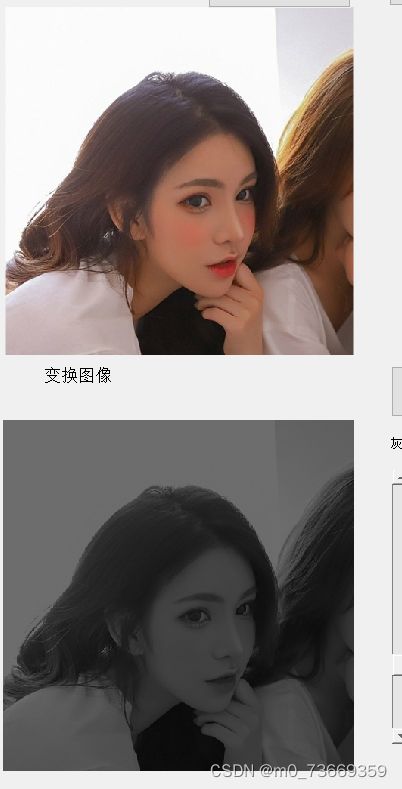

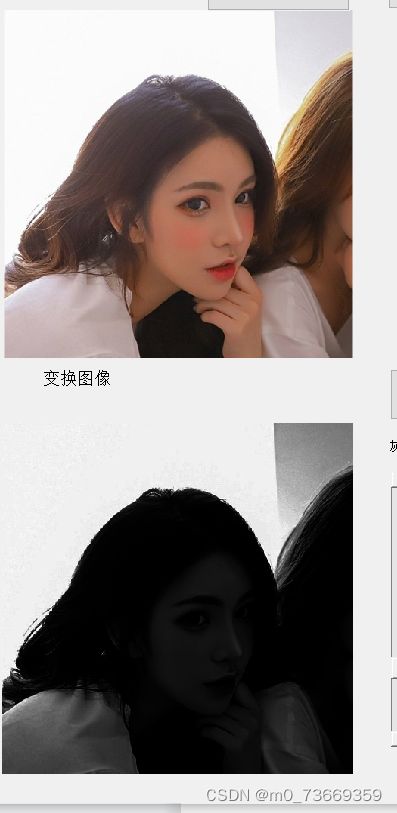



分析:彩图是每像素占3个字节,而变化成灰度图后每像素占一个字节,彩图在转化为灰度图的同时,抛弃了颜色信息,只保留了图像亮度信息。指数越大,图像灰度程度就越大,看不清物品。
7.直方图和直方图均衡化
7.1算法原理
直方图均值化,将低灰度值归并,高灰度值拉伸,当一个图像灰度分布均匀时,图像的整体细节与质量会提升很多
7.2代码
%绘制灰度直方图
set(handles.axes4,'HandleVisibility','ON');
axes(handles.axes4);
I = rgb2gray(handles.image);%转换为灰度图
imhist(I);%显示直方图
%直方图均衡化
set(handles.axes4,'HandleVisibility','ON');
axes(handles.axes4);
I = rgb2gray(handles.image);
I = histeq(I);%直方图均衡化
imhist(I);
7.3结果及分析


8.添加高斯和椒盐噪声并分别用不同33和55模板进行均值、中值、高斯滤波器处理
8.1算法原理
均值滤波和中值滤波是都属于空间滤波(对于某一像素点,以该点为中心,通过对该像素点邻域部分的像素进行处理,得到中心替代像素点的滤波方法
如果噪声为高斯噪声,测量值在真实值周围波动,取得平均之后会得到相对准确的值。
如果噪声为椒盐噪声,像素会出现剧烈跳动,而中值对极大值和极小值不敏感,取中值后可以很好过滤掉此类噪声。
8.2代码
%添加椒盐噪声
I = handles.image;
var=get(handles.popupmenu2,'value');
set(handles.axes2,'HandleVisibility','ON');
axes(handles.axes2);
J=imnoise(I,'salt & pepper',0.2); %添加椒盐噪声,密度为0.2
imshow(J);
I = handles.image;
%空域滤波去除椒盐噪声实例
I=rgb2gray(I);
J=imnoise(I,'salt & pepper',0.2); %添加椒盐噪声,密度为0.2
var =get(handles.popupmenu3,'value');
switch var
case 1
K1 = filter2(fspecial('average',3),J)/255;%均值滤波器
K2 = medfilt2(J,[3,3]);%中值滤波器
figure('NumberTitle', 'off', 'Name', '空域滤波去除椒盐噪声');
subplot(2,2,1);
imshow(J);
title('含椒盐噪声的图像');
subplot(2,2,2);
imshow(K1);
title('均值滤波器');
subplot(2,2,3);
imshow(K2);
title('中值滤波器');
case 2
K1 = filter2(fspecial('average',5),J)/255;%均值滤波器
K2 = medfilt2(J,[5,5]);%中值滤波器
figure('NumberTitle', 'off', 'Name', '空域滤波去除椒盐噪声');
subplot(2,2,1);
imshow(J);
title('含椒盐噪声的图像');
subplot(2,2,2);
imshow(K1);
title('均值滤波器');
subplot(2,2,3);
imshow(K2);
title('中值滤波器');
end
%添加高斯噪声
I = handles.image;
var=get(handles.popupmenu2,'value');
set(handles.axes2,'HandleVisibility','ON');
axes(handles.axes2);
G=imnoise(I,'gaussian',0,0.2);
imshow(G);%添加高斯噪声,
%做高斯噪声3*3和5*5
I = handles.image;
%空域滤波去除高斯噪声实例
I=rgb2gray(I);
J=imnoise(I,'gaussian',0,0.02); %添加高斯噪声
var =get(handles.popupmenu4,'value');
switch var
case 1
K1 = filter2(fspecial('average',3),J)/255;%均值滤波器
K2 = medfilt2(J,[3,3]);%中值滤波器
figure('NumberTitle', 'off', 'Name', '空域滤波去除高斯噪声');
subplot(2,2,1);
imshow(J);
title('含高斯噪声的灰度图像');
subplot(2,2,2);
imshow(K1);
title('33均值滤波器');
subplot(2,2,3);
imshow(K2);
title('33中值滤波器');
case 2
K1 = filter2(fspecial('average',5),J)/255;%均值滤波器
K2 = medfilt2(J,[5,5]);%中值滤波器
figure('NumberTitle', 'off', 'Name', '空域滤波去除高斯噪声');
subplot(2,2,1);
imshow(J);
title('含高斯噪声的图像');
subplot(2,2,2);
imshow(K1);
title('5*5均值滤波器');
subplot(2,2,3);
imshow(K2);
title('5*5中值滤波器');
end
%高斯平滑滤波器
Image=handles.image;
mysize=size(handles.image);
if numel(mysize)>2
Image=rgb2gray(handles.image);
end
sigma1=0.6; sigma2=10; r=3; % 高斯模板的参数
NoiseI= imnoise(Image,'gaussian'); %加噪
gausFilter1=fspecial('gaussian',[2*r+1 2*r+1],sigma1);
gausFilter2=fspecial('gaussian',[2*r+1 2*r+1],sigma2);
result1=imfilter(NoiseI,gausFilter1,'conv');
result2=imfilter(NoiseI,gausFilter2,'conv');
figure('NumberTitle', 'off', 'Name', '高斯平滑滤波器');
subplot(2,2,1),title('原图'),imshow(Image);
subplot(2,2,2),title('高斯噪声'),imshow(NoiseI);
subplot(2,2,3),title('sigma1'),imshow(result1);
subplot(2,2,4),title('sigmal2'),imshow(result2);
8.3结果及分析



 分析:模板5*5比3*去除噪声结果更好,高斯噪声在每个像素上都会出现,赋值服从高斯分布。椒盐噪声出现位置随机,所以可以控制椒盐噪声的密度,椒盐噪声的幅度确定,椒噪声偏暗,盐噪声偏亮
分析:模板5*5比3*去除噪声结果更好,高斯噪声在每个像素上都会出现,赋值服从高斯分布。椒盐噪声出现位置随机,所以可以控制椒盐噪声的密度,椒盐噪声的幅度确定,椒噪声偏暗,盐噪声偏亮
9.分别采用roberts、sobel、拉普拉斯、log、prewitt算子进行边缘提取
9.1算法原理
图像边缘是图像最基本的特征,所谓边缘(Edge) 是指图像局部特性的不连续性。灰度或结构等信息的突变处称之为边缘。例如,灰度级的突变、颜色的突变,、纹理结构的突变等。边缘是一个区域的结束,也是另一个区域的开始,利用该特征可以分割图像。
图像的边缘有方向和幅度两种属性。边缘通常可以通过一阶导数或二阶导数检测得到。一阶导数是以最大值作为对应的边缘的位置,而二阶导数则以过零点作为对应边缘的位置
9.2代码
I=rgb2gray(handles.image);
BW1 = edge(I,'Roberts');%Roberts算子
set(handles.axes2,'HandleVisibility','ON');
axes(handles.axes2);
imshow(BW1);
I=rgb2gray(handles.image);
BW2 = edge(I,'Prewitt');%Prewitt算子
set(handles.axes2,'HandleVisibility','ON');
axes(handles.axes2);
imshow(BW2);
I=rgb2gray(handles.image);
BW3 = edge(I,'Sobel');%Sobel算子
set(handles.axes2,'HandleVisibility','ON');
axes(handles.axes2);
imshow(BW3);
I=rgb2gray(handles.image);
[M,N] = size(I);%拉普拉斯算子
BW4 = zeros(size(I));
for x = 2:M-1
for y = 2:N-1
BW4(x,y) = I(x+1,y) + I(x-1,y) + I(x,y+1) + I(x,y-1) - 4*I(x,y);
end;
end
set(handles.axes2,'HandleVisibility','ON');
axes(handles.axes2);
imshow(BW4);
mysize=size(handles.image);
if numel(mysize)>2
handles.img=rgb2gray(handles.image);
end
L=edge(handles.img,'log');
set(handles.axes2,'HandleVisibility','ON');
axes(handles.axes2);
imshow(L);
9.3结果及分析


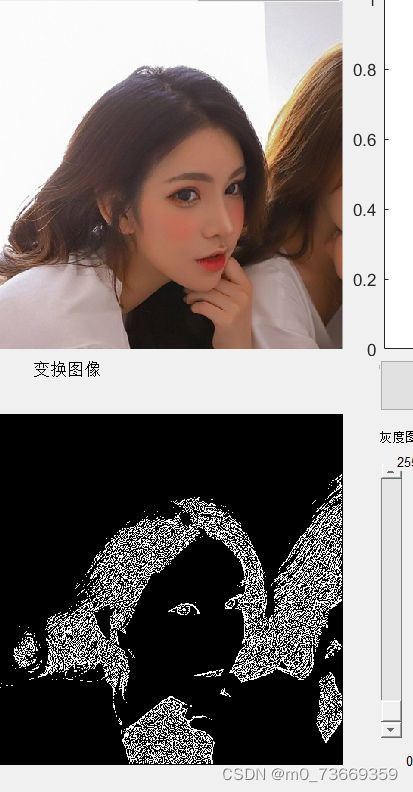
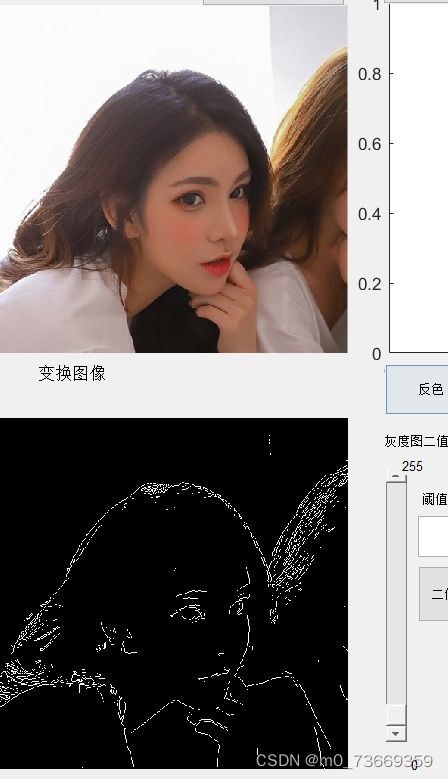

分析:
Roberts算子检测方法对具有陡峭的低噪声的图像处理效果较好,但是利用roberts算子提取边缘的结果是边缘比较粗,因此边缘的定位不是很准确。
Sobel算子检测方法对灰度渐变和噪声较多的图像处理效果较好,sobel算子对边缘定位不是很准确,图像的边缘不止一个像素。
Prewitt算子检测方法对灰度渐变和噪声较多的图像处理效果较好。但边缘较宽,而且间断点多。
Laplacian算子法对噪声比较敏感,所以很少用该算子检测边缘,而是用来判断边缘像素视为与图像的明区还是暗区。
Canny方法不容易受噪声干扰,能够检测到真正的弱边缘。优点在于,使用两种不同的阈值分别检测强边缘和弱边缘,并且当弱边缘和强边缘相连时,才将弱边缘包含在输出图像中
10.对图像进行巴斯沃特高通、理想高通、高斯高通、巴斯沃特低通、理想低通、高斯低通频域处理,可以设置各种不同的D0处理
10.1算法原理
函数fft2()用于计算二维傅立叶变换,函数fftshift()是对函数fft2()作傅里叶变换后得到的频谱进行平移,将变换后的图像频谱中心从矩阵的原点移到矩阵的中心.最后通过傅里叶反变换转换到时域图像。
通过低通滤波后,去除了图像的高频部分,图像的边缘变得模糊。
高通滤波器而言,由于直流分量被衰减,所以,所得到的图像的动态范围是非常狭窄的,也就造成了图像偏灰
10.2代码
% --- Executes on button press in radiobutton16.
function radiobutton16_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
%巴特沃斯
prompt={'请设置巴斯沃特低通滤波器的半径' };
name='理想低通滤波器的半径';
numlines=1;
defaultanswer={'80'};
anss=inputdlg(prompt,name,numlines,defaultanswer);
D0=str2num(anss{1});
I=handles.image;
I=rgb2gray(I);
I=im2double(I);
M=2*size(I,1); %滤波器行数 读入图像宽度的2倍 请解释为什么是两倍?
N=2*size(I,2); %滤波器列数
u=-M/2:(M/2-1);
v=-N/2:(N/2-1);
[U,V]=meshgrid(u,v);
D=sqrt(U.^2+V.^2);
n=6;
H=1./(1+(D./D0).^(2*n)); %构造巴特沃斯滤波器
J=fftshift(fft2(I,size(H,1),size(H,2))); %转换到频域
K=J.*H;
L=ifft2(ifftshift(K)); %傅立叶反变换
L=L(1:size(I,1),1:size(I,2)); %改变图像大小
set(handles.axes2,'HandleVisibility','ON');
axes(handles.axes2);
imshow(L);
% --- Executes on button press in radiobutton17.
function radiobutton17_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% Hint: get(hObject,'Value') returns toggle state of radiobutton17
prompt={'请设置理想低通滤波器的半径' };
name='理想低通滤波器的半径';
numlines=1;
defaultanswer={'80'};
anss=inputdlg(prompt,name,numlines,defaultanswer);
d=str2num(anss{1});
I=handles.image;
I=rgb2gray(I);
I=im2double(I);
s=fftshift(fft2(I));
[a,b]=size(s);
a0=round(a/2);
b0=round(b/2);
for i=1:a
for j=1:b
distance=sqrt((i-a0)^2+(j-b0)^2);
if distance<=d
h=1;
else
h=0;
end
s(i,j)=h*s(i,j);
end
end
L=real(ifft2(ifftshift(s)));
set(handles.axes2,'HandleVisibility','ON');
axes(handles.axes2);
imshow(L);
% --- Executes on button press in radiobutton18.
function radiobutton18_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% Hint: get(hObject,'Value') returns toggle state of radiobutton18
%高斯低通
prompt={'请设置高斯低通滤波器的半径' };
name='理想低通滤波器的半径';
numlines=1;
defaultanswer={'80'};
anss=inputdlg(prompt,name,numlines,defaultanswer);
d0=str2num(anss{1});
%高斯低通
image=handles.image;
image=rgb2gray(image);
[M ,N]=size(image);
img_f = fft2(double(image));%傅里叶变换得到频谱
img_f=fftshift(img_f); %移到中间
m_mid=floor(M/2);%中心点坐标
n_mid=floor(N/2);
h = zeros(M,N);%高斯低通滤波器构造
for i = 1:M
for j = 1:N
d = ((i-m_mid)^2+(j-n_mid)^2);
h(i,j) = exp(-(d)/(2*(d0^2)));
end
end
img_lpf = h.*img_f;
img_lpf=ifftshift(img_lpf); %中心平移回原来状态
img_lpf=uint8(real(ifft2(img_lpf))); %反傅里叶变换,取实数部分
set(handles.axes2,'HandleVisibility','ON');
axes(handles.axes2);
imshow(img_lpf);
% --- Executes on button press in radiobutton21.
function radiobutton21_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% Hint: get(hObject,'Value') returns toggle state of radiobutton21
%高斯高通
prompt={'请设置高斯高通滤波器的半径' };
name='高斯低通滤波器的半径';
numlines=1;
defaultanswer={'80'};
anss=inputdlg(prompt,name,numlines,defaultanswer);
D0=str2num(anss{1});
I=handles.image;
mysize=size(handles.image);
if numel(mysize)>2
I=rgb2gray(handles.image);
end
I2=im2double(I);
%计算滤波器的行数
M=2*size(I,1);
N=2*size(I,2);
u=-M/2:(M/2-1);
v=-N/2:(N/2-1);
[U,V]=meshgrid(u,v);
D=sqrt(U.^2+V.^2);
H2=1-exp(-(D.^2)./(2*(D0^2)));%设计高斯高通滤波器
J2=fftshift(fft2(I2,size(H2,1),size(H2,2)));
K2=J2.*H2;
L2=ifft2(ifftshift(K2));
L2=L2(1:size(I2,1),1:size(I2,2));
set(handles.axes2,'HandleVisibility','ON');
axes(handles.axes2);
imshow(L2);
% --- Executes on button press in radiobutton19.
function radiobutton19_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
%巴斯沃特
prompt={'请设置巴斯沃特高通滤波器的半径' };
name='高斯低通滤波器的半径';
numlines=1;
defaultanswer={'80'};
anss=inputdlg(prompt,name,numlines,defaultanswer);
D0=str2num(anss{1});
I=handles.image;
mysize=size(handles.image);
if numel(mysize)>2
I=rgb2gray(handles.image);
end
I=im2double(I);
M=2*size(I,1);%滤波器行数
N=2*size(I,2);%滤波器列数
u=-M/2:(M/2-1);
v=-N/2:(N/2-1);
[U,V]=meshgrid(u, v);
D=sqrt(U.^2+V.^2);
n=6;
H=1./(1+(D0./D).^(2*n)); %设置巴特沃斯高通滤波器
J=fftshift(fft2(I, size(H, 1), size(H, 2))); %转化到频域
K=J.*H;
L=ifft2(ifftshift(K));%傅里叶翻转
L=L(1:size(I,1), 1:size(I, 2));%改变图像大小
set(handles.axes2,'HandleVisibility','ON');
axes(handles.axes2);
imshow(L);
% --- Executes on button press in radiobutton20.
function radiobutton20_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
%理想高通
prompt={'请设置理想高通滤波器的半径' };
name='高斯低通滤波器的半径';
numlines=1;
defaultanswer={'80'};
anss=inputdlg(prompt,name,numlines,defaultanswer);
d=str2num(anss{1});
I=handles.image;
mysize=size(handles.image);
if numel(mysize)>2
I=rgb2gray(handles.image);
end
I=im2double(I);
s=fftshift(fft2(I));
[a,b]=size(s);
a0=round(a/2);
b0=round(b/2);
for i=1:a
for j=1:b
distance=sqrt((i-a0)^2+(j-b0)^2);
if distance<=d % 根据理想高通滤波器产生公式,当D(i,j)<=D0,置为0
h=0;
else
h=1; % 根据理想高通滤波器产生公式,当D(i,j)>D0,置为1
end
s(i,j)=h*s(i,j);% 频域图像乘以滤波器的系数
end
end
L=real(ifft2(ifftshift(s)));
set(handles.axes2,'HandleVisibility','ON');
axes(handles.axes2);
imshow(L);
10.3结果及分析
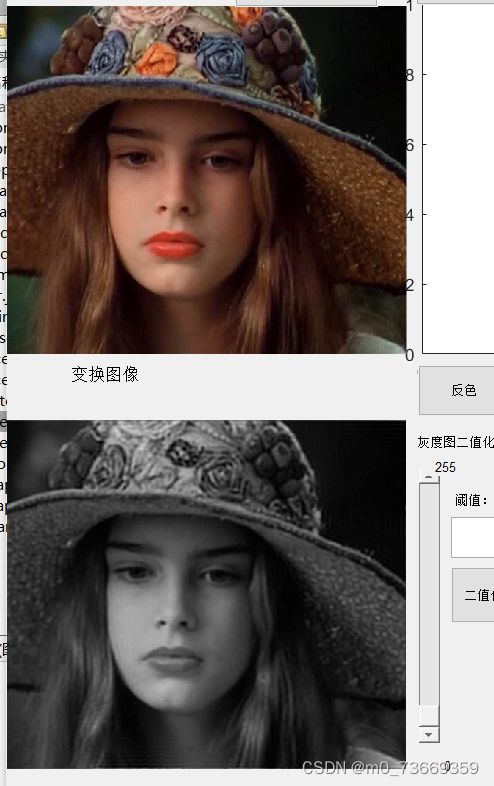
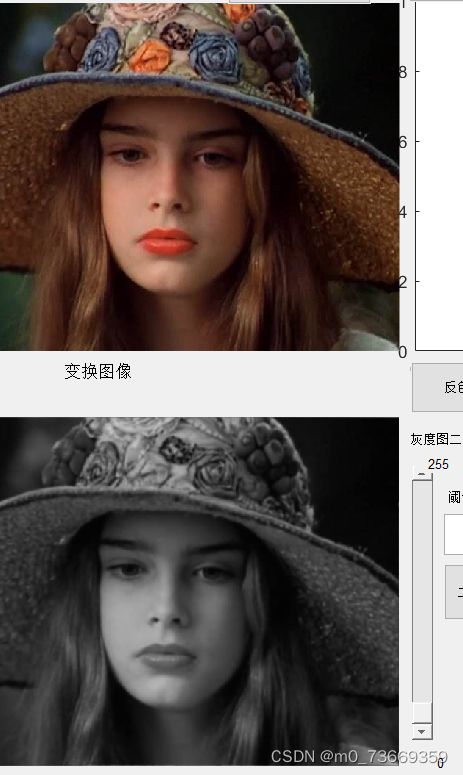

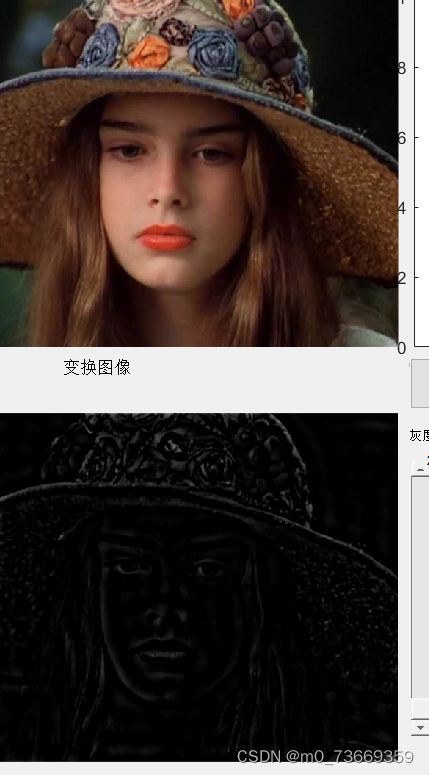
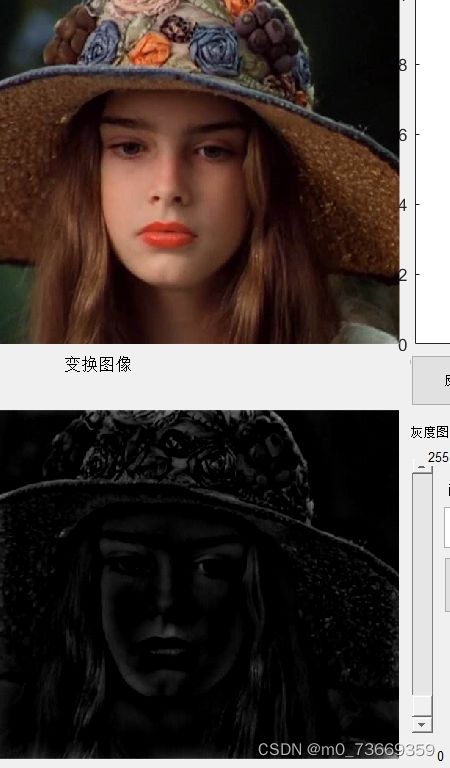

理想低通滤波器可以在一定程度上去除图像噪声,但由此带来的图像边缘和细节的模糊效应也比较明显,其滤波之后的处理效果比较类似于平均模板的平均平滑,实际上,理想低通滤波器是一个与频谱图像同样尺寸的二维矩阵
D0为巴特沃斯低通滤波器的截止频率,参数n为巴特沃斯滤波器的阶数,n越大则滤波器的形状越陡峭。通过高通滤波后,抑制了图像中的低频信息,很好地保留了图像的边缘信息。
11.运动模糊再复原,维也纳滤波复原
11.1算法原理
设运动图像为f(x,y),其傅里叶变换为F(u,v)
设模糊后的图像为g(x,y),其傅里叶变换为G(u,v)
通过F(u,v)和H(u,v)频域相乘得到G(u,v),即
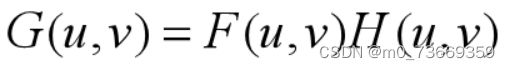
将G(u,v)反变换,就可以得到运动模糊后的图像g(x,y)。
11.2代码
I=handles.image;
Len=30;
Theta=45;
PSF=fspecial('motion',Len,Theta);
BlurredA=imfilter(I,PSF,'circular','conv');
Wnrl=deconvwnr(BlurredA,PSF);
BlurredD=imfilter(I,PSF,'circ','conv');
INITPSF=ones(size(PSF));
[K DePSF]=deconvblind(BlurredD,INITPSF,30);
BlurredB=imfilter(I,PSF,'conv');
V=0.02;
Blurred_I_Noisy=imnoise(BlurredB,'gaussian',0,V);
NP=V*prod(size(I));
J=deconvreg(Blurred_I_Noisy,PSF,NP);
BlurredC=imfilter(I,PSF,'symmetric','conv');
V=0.002;
BlurredNoisy=imnoise(BlurredC,'gaussian',0,V);
Luc=deconvlucy(BlurredNoisy,PSF,5);
figure('NumberTitle', 'off', 'Name', '图像模糊及复原');
subplot(2,3,1);imshow(I);title('原图像');
subplot(2,3,6);imshow(PSF);title('运动模糊后图像');
subplot(2,3,2);imshow(Wnrl);title('维纳滤波修复图像');
subplot(2,3,3);imshow(J);title('最小二乘方修复图像');
subplot(2,3,4);imshow(Luc);title('Lucy-Richardson修复图像');
subplot(2,3,5);imshow(K);title('盲去卷积修复图像');
11.3结果及分析
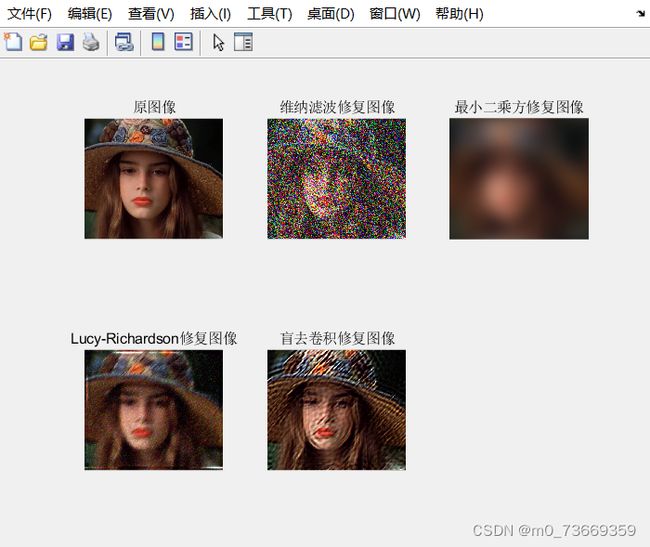 分析:
分析:
可以由fspecial函数创建一个确定类型的PSF(点扩散函数),然后使用这个PSF与原始图像进行卷积,从而得到退化(模糊)的图像 在没有噪声的情况下,维纳滤波器退化成理想的逆滤波器
12.傅里叶正变换、腐蚀膨胀开运算和闭运算,形态学滤波
12.1算法原理
使用 fftshift 函数对变换执行以零为中心的循环平移。
腐蚀的作用是标记原图像中结构元素出现的位置,标记的位置为参考点所在的位置
膨胀,具有让二值图像视觉加粗的效果,膨胀的方向,取决于结构元素
开运算是用同一个结构元素对原图像先腐蚀后膨胀 闭运算是用同一个结构元素对原图像先膨胀后腐蚀,形态学滤波 从图像中提取固定形状的原图像内容
12.2代码
function Untitled_13_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
%正
f=handles.image;
mysize=size(handles.image);
if numel(mysize)>2
f=rgb2gray(handles.image);
end
[M,N]=size(f);
y=fft2(f);
g=log(abs(fftshift(y))+1);
axes(handles.axes2);
imshow(g,[8,12]);
% --------------------------------------------------------------------
function Untitled_4_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to Untitled_4 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
%开运算
I=handles.image;
BW=im2bw(I);
SE=strel('square',3);
L=imdilate(imerode(BW,SE),SE);%先腐蚀再膨胀
%用3×3结构元素进行开运算
set(handles.axes2,'HandleVisibility','ON');
axes(handles.axes2);
imshow(L);
% --------------------------------------------------------------------
function Untitled_5_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to Untitled_5 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
%闭运算
I=handles.image;
BW=im2bw(I);
SE=strel('square',3);
L=imerode(imdilate(BW,SE),SE);%先膨胀在腐蚀
%用3×3结构元素进行闭运算
set(handles.axes2,'HandleVisibility','ON');
axes(handles.axes2);
imshow(L);
% --------------------------------------------------------------------
function Untitled_8_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to Untitled_8 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
%膨胀33
%膨胀
I=handles.image;
se=strel('ball',3,3);%选取球形结构元素
L=imdilate(I,se)%膨胀灰度图像
set(handles.axes2,'HandleVisibility','ON');
axes(handles.axes2);
imshow(L);
% --------------------------------------------------------------------
function Untitled_9_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to Untitled_9 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
%膨胀55
%膨胀
I=handles.image;
se=strel('ball',5,5);%选取球形结构元素
L=imdilate(I,se)%膨胀灰度图像
set(handles.axes2,'HandleVisibility','ON');
axes(handles.axes2);
imshow(L);
% --------------------------------------------------------------------
function Untitled_6_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to Untitled_6 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
%33模板
%腐蚀
I=handles.image;
se=strel('ball',3,3);%选取球形结构元素
L=imerode(I,se)%膨胀灰度图像
set(handles.axes2,'HandleVisibility','ON');
axes(handles.axes2);
imshow(L);
% --------------------------------------------------------------------
function Untitled_7_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to Untitled_7 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
I=handles.image;
se=strel('ball',5,5);%选取球形结构元素
L=imerode(I,se)%膨胀灰度图像
set(handles.axes2,'HandleVisibility','ON');
axes(handles.axes2);
imshow(L);
12.3结果及分析
13.提取红苹果
13.1算法原理
将已知图像进行消噪处理
对彩色图像进行目标和背景分析
通过颜色将图像进行分割
进行形态学处理,提取目标
13.2代码
function Untitled_16_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to Untitled_16 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
%苹果监测
% Image=handles.image;
% hsv=rgb2hsv(Image);
% h=hsv(:,:,1);
% h(h>330/360)=0;
% [N,M]=size(h);
% training=h(:);
% startdata = [0;60/360;120/360;180/360;240/360;300/360];
% [IDX,C]= kmeans(training,6,'Start',startdata);
% idbw = (IDX == 1);
% template = reshape(idbw, size(h));
% axes(handles.axes2);
% imshow(template);
pic1=(handles.image);
%分别提取RGB三个通道(也就是三个二维矩阵)
R=pic1(:,:,1);
G=pic1(:,:,2);
B=pic1(:,:,3);
%获取图像的矩阵
[y,x,z]=size(pic1);
%使用灰度整合二值化方法
%循环每个像素
for i=1:x
for j=1:y
%改变灰度值,系数可以自己调整
pic2(j,i)=(1*R(j,i)-0.3*G(j,i)-0.3*B(j,i));
end
end
t=graythresh(pic2); %确定二值化阈值
pic3=im2bw(pic2,t); %二值化
pic3=imfill(pic3,'holes'); %填充洞
pic3=bwareaopen(pic3,10); %删掉一些小块噪点
%由于二值图元素的类型都是 logical型(逻辑型),在进行运算处理时不符合要求,所以转为 uint8
a1=im2uint8(pic3)/255;
R1=R.*a1; %各个通道的矩阵乘以二值图,中心的蝴蝶矩阵数值不变,背景变为0
G1=G.*a1;
B1=B.*a1;
b1(:,:,1)=R1; %三个通道叠加,组成一个三维的RGB图
b1(:,:,2)=G1;
b1(:,:,3)=B1;
%显示结果环节
axes(handles.axes2);
imshow(b1);
13.3结果及分析
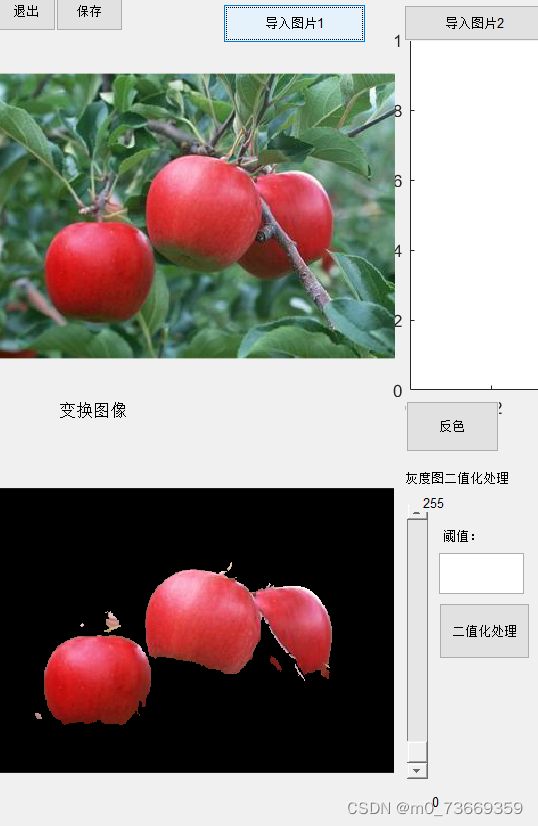 分析:
分析:
%分别提取RGB三个通道
二值化填充洞,删除噪点、二值图像分别和原图提取出来的RGB分量相乘。
14.硬币检测
14.1算法原理
分割硬币 去除噪声 连通区域判断硬币个数
14.2代码
% --------------------------------------------------------------------
function Untitled_17_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to Untitled_17 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
%硬币个数检测
Image=handles.image;
BW=im2bw(Image);
SE=strel('square',6);
result1=imopen(imclose(BW,SE),SE);%先闭后开;
[L,NUM]=bwlabel(result1,4);%检测二值图像中连通域的个数
%N可以取值4或者8表示连接四联通和八联通区域
% NUM 为找到的连通区域数目;
S=sprintf('检测到的硬币个数为:%d',NUM);msgbox(S);%弹窗显示运行结果
14.3结果及分析
 分析:
分析:
[L,num] = bwlabel(BW,n)这里num返回的就是BW中连通区域的个数。L = bwlabel(BW,n) 返回一个和BW大小相同的L矩阵,包含了标记了BW中每个连通区域的类别标签,这些标签的值为1、2、num(连通区域的个数)。n的值为4或8,表示是按4连通寻找区域,还是8连通寻找,默认为8。
15.圆和矩形检测
15.1算法原理
矩形连通区域与其最小边界矩形的像素比是1,所以可自定义设置阈值大于0.95判断 设圆形半径为R,最小边界矩形即正方形边长为2R,圆形连通区域与其最小边界矩形的面积比为 π R 2 ( 2 R ) 2 = π 4 ≈ 0.7854 \dfrac{\pi R2}{(2R)2}=\dfrac{\pi}{4}\approx0.7854 (2R)2πR2=4π≈0.7854,所以可自定义设置阈值介于 [ 0.76 , 0.80 ] [0.76,0.80] [0.76,0.80]判断。
15.2代码
% --------------------------------------------------------------------
function Untitled_28_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to Untitled_28 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% image=handles.image;
% mysize=size(handles.image);
% if numel(mysize)>2
% image=rgb2gray(handles.image);
% end
%
%
%
% BW=edge(image,'canny');
%
% % imwrite(BW,'shapeedge.jpg');
% SE=strel('disk',5);
% Morph=imclose(BW,SE);
%
% % imwrite(Morph,'shapemorph.jpg');
% Morph=imfill(Morph,'holes');
%
% imwrite(Morph,'shapefill.jpg');
% [B,L]=bwboundaries(Morph);
% STATS = regionprops(L,'Area', 'Centroid','BoundingBox');
% len=length(STATS);
% hold on
% for i=1:len
% R=STATS(i).Area/(STATS(i).BoundingBox(3)*STATS(i).BoundingBox(4));
% boundary=fliplr(B{i});
% everylen=length(boundary);
% F=4*pi*STATS(i).Area/(everylen^2);
% dis=pdist2(STATS(i).Centroid,boundary,'euclidean');
% miu=sum(dis)/everylen;
% sigma=sum((dis-miu).^2)/everylen;
% C=miu/sigma;
% if R>0.9 && F<1
% rectangle('Position',STATS(i).BoundingBox,'edgecolor','g','linewidth',2);
% plot(STATS(i).Centroid(1),STATS(i).Centroid(2),'g*');
% end
% if R>pi/4-0.1 && R<pi/4+0.1 && F>0.9 && C>10
% rectangle('Position',[STATS(i).Centroid(1)-miu,STATS(i).Centroid(2)-miu,2*miu,2*miu],...
% 'Curvature',[1,1],'edgecolor','r','linewidth',2);
% plot(STATS(i).Centroid(1),STATS(i).Centroid(2),'r*');
% end
% end
% hold off
% axes(handles.axes2);
% imshow(L);
pic=handles.image;
binary_img=1-im2bw(pic,0.73); %灰度图转换成二值图像,直接进行灰度反转,让图形区域置1
for i=202:265
binary_img(188,i)=1;
end
fill_hole=imfill(binary_img,'holes');
fill_hole=bwareaopen(fill_hole,10);
[B,L]=bwboundaries(fill_hole,'noholes');
out_result=regionprops(fill_hole,'Extent','Centroid','boundingbox'); %Extent:各连通区域像素点与最小边界像素点比值
centroids = cat(1, out_result.Centroid); %各连通区域质心
draw_rect=cat(1,out_result.BoundingBox); %各连通区域最小边界矩形
figure('NumberTitle', 'off', 'Name', '苹果检测');
subplot(2,2,1);imshow(pic,[]);title('原图');
subplot(2,2,2);imshow(binary_img,[]);title('二值化');
subplot(2,2,3);imshow(fill_hole,[]);title('区域填充');
subplot(2,2,4);imshow(fill_hole,[]);title('圆和矩形检测');
hold on;
for i=1:size(out_result)
rectangle('position',draw_rect(i,:),'EdgeColor','y','LineWidth',2); %绘出各连通区域最小边界矩形
if out_result(i).Extent>0.95
text(centroids(i,1)-20, centroids(i,2)-10,'矩形','Color','b','FontSize',9);
text(centroids(i,1)-32, centroids(i,2)+10,num2str(out_result(i).Extent),'Color','b','FontSize',8);
elseif out_result(i).Extent>0.76&&out_result(i).Extent<0.80
text(centroids(i,1)-20, centroids(i,2)-10,'圆形','Color','b','FontSize',9);
text(centroids(i,1)-32, centroids(i,2)+10,num2str(out_result(i).Extent/(pi/4)),'Color','b','FontSize',8);
end
end
hold on;
for j=1:length(B)
boundary=B{j};
plot(boundary(:,2),boundary(:,1),'r','LineWidth',2);
end
15.3结果及分析
 分析:
分析:
二值化处理,进行区域填充
Regionprops:用途是get the properties of region,即用来度量图像区域属性的函数。
%Extent:各连通区域像素点与最小边界像素点比值
‘BoundingBox’:是1行ndims(L)*2列的向量,即包含相应区域的最小矩形
根据extent的大小来判断圆和矩形
16人脸识别,眼睛识别,嘴巴识别
16 1算法原理
使用matlab自带的函数detector = vision.CascadeObjectDetector;
16.2 代码
% --------------------------------------------------------------------
function Untitled_31_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to Untitled_31 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
%人脸识别
img=handles.image
detector = vision.CascadeObjectDetector;
bboxes=detector(img);
FrontalFaceCART=insertObjectAnnotation(img,'rectangle',bboxes,'Face');
axes(handles.axes2);
imshow(FrontalFaceCART);
% --------------------------------------------------------------------
function Untitled_32_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to Untitled_32 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
%眼睛识别
img=handles.image
detector = vision.CascadeObjectDetector;
release(detector);
detector.ClassificationModel='EyePairBig';
bboxes=detector(img);
EyePairBig=insertObjectAnnotation(img,'rectangle',bboxes,'Eyes');
axes(handles.axes2);
imshow(EyePairBig);
release(detector);
detector.ClassificationModel='EyePairSmall';
bboxes=detector(img);
EyePairSmall=insertObjectAnnotation(img,'rectangle',bboxes,'Eyes');
axes(handles.axes2);
imshow(EyePairSmall);
% --------------------------------------------------------------------
function Untitled_33_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to Untitled_33 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
%嘴巴识别
img=handles.image
detector = vision.CascadeObjectDetector;
release(detector);
detector.ClassificationModel='Mouth';
detector.MergeThreshold=100;%增加合并阈值
bboxes=detector(img);
Mouth=insertObjectAnnotation(img,'rectangle',bboxes,'Mouth');
axes(handles.axes2);
imshow(Mouth);
分析:发现matlab自带的detector在人脸照片将这些特征体现出来、较为清晰地图片,才能准确识别嘴巴、眼睛、人脸
16.3结果及分析


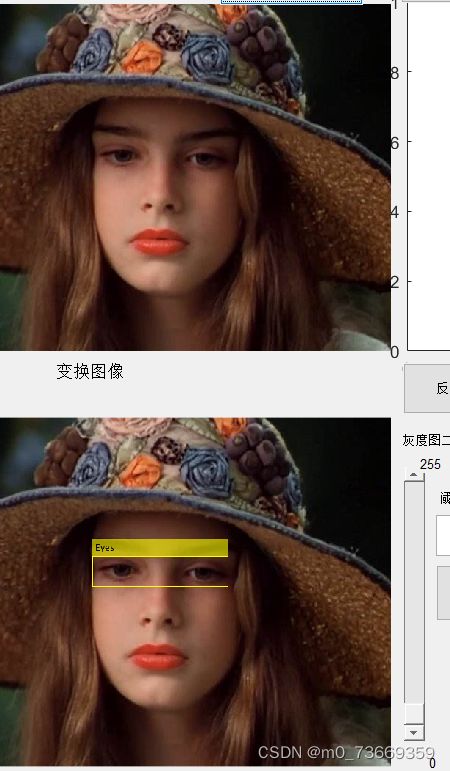
17浮雕、复古风、倒影、羽化、马赛克、素描
17.1算法原理
借鉴于一个厉害的博主
1.浮雕效果
浮雕的算法是对图像的每一个点进行卷积处理,采用的矩阵如下:
[1 0 0; 0 0 0; 0 0 -1];
假设原图像为X,处理后的图像为Y。对于坐标为(i,j)点,其浮雕效果图的算法为Y(i,j)=X(i+1,j+1)-X(i-1,j-1)+128;X,Y的取值均在0~255之间。
2.怀旧色效果
怀旧风格滤镜是一种使图像颜色发黄的颜色风格。该滤镜模拟久置的相片发生褪色老化的效果。怀旧风格滤镜算法可以用一种点运算来表示,R、G、B分量的点运算映射函数分别如下所示:
R = 0.393r+0.769g+0.189b (2-1)
G = 0.349r+0.686g+0.168b (2-2)
B = 0.272r+0.534g+0.131b (2-3)
3.扩散(毛玻璃)效果
PhotoShop里的扩散,就相当于毛玻璃的感觉。扩散原理:用当前点四周一定范围内任意一点的颜色来替代当前点颜色,最常用的是随机的采用相邻点进行替代。
4.羽化效果
在PhotoShop里,羽化就是使你选定范围的图边缘达到朦胧的效果。羽化值越大,朦胧范围越宽,羽化值越小,朦胧范围越窄。可根据你想留下图的大小来调节。算法如下:
1.通过对rgb值增加额外的V值实现朦胧效果;
2.通过控制V值的大小实现范围控制;
3.V = 255 × (当前点Point距中点距离的平方)s1 / (顶点距中点的距离平方 × mSize)s2;
5.素描效果
PhotoShop里面把彩色图片打造成素描的效果仅仅需要几步操作:
1.去色(转为灰度图);
2.复制去色图层,并且反色(反色相当于Y(i,j) = 255 - X(i,j));
3.对反色图像进行高斯模糊;
4.模糊后的图像叠加模式选择颜色减淡效果。减淡公式:C = MIN( A +(A×B)/(255-B, 255),其中C为混合结果,A为去色后的像素点,B为高斯模糊后的像素点。
17.2代码
% --------------------------------------------------------------------
function Untitled_22_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to Untitled_22 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
%浮雕
img=handles.image;
I=rgb2gray(img);
f1=imnoise(I,'speckle',0.01);%加高斯噪声
f1=im2double(f1);
h3=1/9*[1 1 1;1 1 1;1 1 1];
f4=conv2(f1,h3,'same');%f1 h3做卷积,创建,返回与f1相同的中间部分
h2=fspecial('sobel');%用于边缘提取
g3=filter2(h2,f4,'same');%返回与h2同样大小的卷积中间部分
k=mat2gray(g3);%mat2gray将矩阵转换为灰度图像
axes(handles.axes2);
imshow(k);
% --------------------------------------------------------------------
function Untitled_24_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to Untitled_24 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
%素描
axes(handles.axes2);
I = handles.image;
info_size=size(I);
height=info_size(1);
width=info_size(2);
N=zeros(height,width);
g=zeros(height,width);
imggray=rgb2gray(I);
out=zeros(height,width);
spec=zeros(height,width,3);
for i=1:height
for j=1:width
N(i,j)=255-imggray(i,j);
end
end
for i=2:height-1
for j=2:width-1
sum=0;
sum=1*double(N(i-1,j-1))+2*double(N(i-1,j))+1*double(N(i-1,j+1));
sum=sum+2*double(N(i,j-1))+4*double(N(i,j))+2*double(N(i,j+1));
sum=sum+1*double(N(i+1,j-1))+2*double(N(i+1,j))+1*double(N(i+1,j+1));
sum=sum/16;
g(i,j)=sum;
end
end
for i=1:height
for j=1:width
b=double(g(i,j));
a=double(imggray(i,j));
temp=a+a*b/(256-b);
out(i,j)=uint8(min(temp,255));
end
end
imshow(out/255);
% --------------------------------------------------------------------
function Untitled_25_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to Untitled_25 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
%复古风
img=handles.image;
[h w k]=size(img);%二维矩阵当作第三维为1的三维矩阵,这也如同我们把n维列向量当作n×1的矩阵一样
imshow(img);
R=double(img(:,:,1));%一维和二维的所有数据,三维的第一个
G=double(img(:,:,2));
B=double(img(:,:,3));
rR=R*0.393+G*0.769+B*0.198;
rG=R*0.349+G*0.686+B*0.168;
rB=R*0.272+G*0.534+B*0.131;
randR=rand()*0.5+0.5;
randG=rand()*0.5+0.5;
randB=rand()*0.5+0.5;
imgn=zeros(h,w,k);%创建三维矩阵
imgn(:,:,1)=randR*rR+(1-randR)*R;
imgn(:,:,2)=randG*rG+(1-randG)*G;
imgn(:,:,3)=randB*rB+(1-randB)*B;
axes(handles.axes2);
imshow(uint8(imgn));
% --------------------------------------------------------------------
function Untitled_26_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to Untitled_26 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
%倒影
axes(handles.axes2);
img_src = handles.image;
m=size(img_src,1);
n=size(img_src,2);
img_up=imresize(img_src,[floor(m*0.5),n]); %将原图像压缩为原来大小的一半
img_down=imrotate(img_src,180);%压缩后的图像旋转180度
r=img_down(:,:,1);
g=img_down(:,:,2);
b=img_down(:,:,3);
for i=1:m
for j=1:n %下半部分图像做左右镜像
rr(i,n-j+1)=r(i,j);
gg(i,n-j+1)=g(i,j);
bb(i,n-j+1)=b(i,j);
end
end
A(:,:,1)=rr;
A(:,:,2)=gg;
A(:,:,3)=bb; %A是镜像以后的图像
img_down=A;
%*************倒影部分进行雾化,实现更好的倒影效果***********
m1=size(img_down,1);
n1=size(img_down,2);
r1=img_down(:,:,1);
g1=img_down(:,:,2);
b1=img_down(:,:,3);
for i=2:m1-10
for j=2:n1-10
k=rand(1)*10;
di=i+round(mod(k,33));
dj=j+round(mod(k,33));
rr1(i,j)=r1(di,dj);
gg1(i,j)=g1(di,dj);
bb1(i,j)=b1(di,dj);
end
end
A1(:,:,1)=rr1;
A1(:,:,2)=gg1;
A1(:,:,3)=bb1;
%****************雾化完成*******************************
img_down=imresize(A1,[floor(m*0.5),n]);
A=[img_up;img_down];
imshow(A);
% --------------------------------------------------------------------
function Untitled_27_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to Untitled_27 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
%羽化边缘
src=handles.image;
srcgray=rgb2gray(src);%首先进行灰度变换
[height,width] = size(srcgray);%获得图像的高度和宽度
centery=width/2;
centerx=height/2;
maxv=centerx*centerx+centery*centery;
msize=0.5;%改变这个值,可以改变羽化效果,羽化明显或者不明显
minv=(maxv*(1-msize));
diff=maxv-minv;
%ratio=width>height? height/width : width/height;
if width>height
ratio=(height/width);
else
ratio=(width/height);
end
height=height-1;
width=width-1;
for x=1:height
for y=1:width
r=src(x,y,1);
g=src(x,y,2);
b=src(x,y,3);
dy=centery-y;
dx=centerx-x;
dstsq=(dx*dx+dy*dy);
v=((dstsq/diff)*128); %原文这个地方是255,我们实际测试的时候
%发现这个地方应该改成128,否则效果会过于明显
r=r+v;
g=g+v;
b=b+v;
if r>255
r=255;
elseif r<0
r=0;
end
if g>255
g=255;
elseif g<0
g=0;
end
if b>255
b=255;
elseif b<0
b=0;
end
dst(x,y,1)=uint8(r);
dst(x,y,2)=uint8(g);
dst(x,y,3)=uint8(b);
end
end
axes(handles.axes2);
imshow(dst);
17.3结果及分析

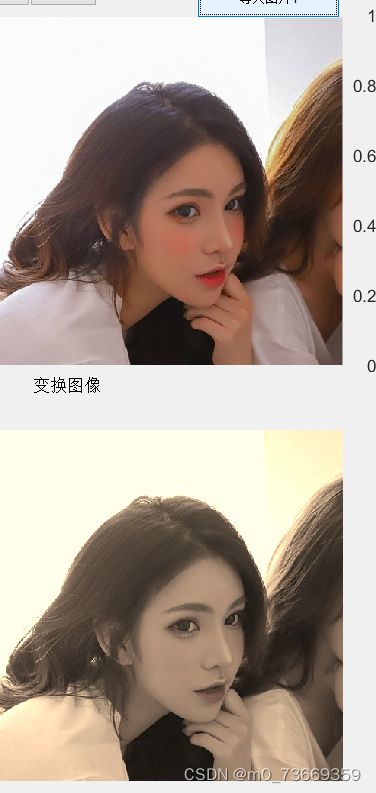



 大作业心得体会: 为了写基础版,学习了gui的使用,输入框的使用、怎么得到点击控件去获得value值,怎么设置回调函数等.....遇到很多不会的问题,但学习起来很迅速,很快就掌握了gui的使用。灰度图像的指数变换和对数变换、红苹果检测等、圆和矩形检测等.....基本上都能在csdn上和平时做的实验找到模板,然后根据上面的内容加上自己的理解和看法,做出让人满意的小工具。看到上面有人脸检测的博文,本以为很难,结果是借助matlab自带的函数detector =vision.CascadeObjectDetector、insertObjectAnnotation等结合使用、底层算法肯定实现不来。从摄像头加载图片,刚开始没有一点头绪,后来通过看老师的代码,才把这个功能实现。图片裁剪,镜像翻转,放大、反色等...都有相关的函数,然后学为己用。
大作业心得体会: 为了写基础版,学习了gui的使用,输入框的使用、怎么得到点击控件去获得value值,怎么设置回调函数等.....遇到很多不会的问题,但学习起来很迅速,很快就掌握了gui的使用。灰度图像的指数变换和对数变换、红苹果检测等、圆和矩形检测等.....基本上都能在csdn上和平时做的实验找到模板,然后根据上面的内容加上自己的理解和看法,做出让人满意的小工具。看到上面有人脸检测的博文,本以为很难,结果是借助matlab自带的函数detector =vision.CascadeObjectDetector、insertObjectAnnotation等结合使用、底层算法肯定实现不来。从摄像头加载图片,刚开始没有一点头绪,后来通过看老师的代码,才把这个功能实现。图片裁剪,镜像翻转,放大、反色等...都有相关的函数,然后学为己用。

