Eigen——线性代数运算的C++模板库
前几天,帮着师兄改写程序,需要将Mathematica编写的程序用C语言翻译出来并运行出结果。这几天下来也算对Eigen有了初步的了解。写一下,希望对大家有所帮助。
在最初选择C++矩阵运算库是,主要参考了如下两篇文,
http://blog.csdn.net/chenbang110/article/details/12304123
http://blog.csdn.net/houston11235/article/details/8501135
目前比较主流的矩阵运行库有Armadillo,Eigen ,OpenCV,在选择C++矩阵库时,主要看大家实际情况,这里就对Eigen做初步介绍。深入学习请参考 http://eigen.tuxfamily.org/dox/,也可以下载它的离线下载包学习 http://eigen.tuxfamily.org/dox/index.html。
Eigen——线性代数运算的C++模板库,面向矩阵,向量,数值运算以及相关的 运算。
使用Eigen准备工作
Eigen官网上下载Eigen源码库函数包 http://eigen.tuxfamily.org/index.php?title=Main_Page,将它解压到一个不含中文的目录下。
下面就是安装Eigen,我是基于Visual Studio 2010的Windows开发,运行VS2010,创建一个基于Win32控制台应用程序的空项目,在解决方案资源管理器中右击源文件,添加C++文件,粘贴如下代码:
#include
#include
using Eigen::MatrixXd;
int main()
{
MatrixXd m(2,2);
m(0,0) = 3;
m(1,0) = 2.5;
m(0,1) = -1;
m(1,1) = m(1,0) + m(0,1);
std::cout << m << std::endl;
}
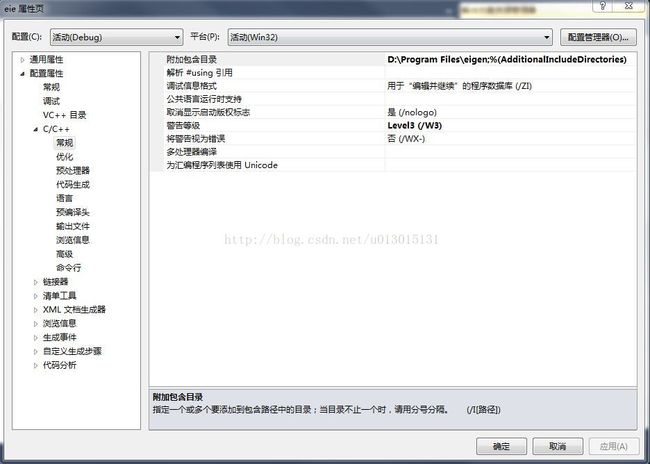
右击项目->属性->C/C++->常规->附加包含目录,添加解压后的Eigen库函数包。
输出3 -1
2.5 1.5 输出成功!
Eigen矩阵运算的简单介绍
Eigen provides two kinds of dense objects: mathematical matrices andvectors which are both represented by the template class Matrix, and general 1D and 2D arrays represented by the template class Array:
这两种类型的变量主要区别:1、Matrix类型变量加减法若行列数不相等,不能做加减。Array类型的变量是可以加减一个常数,作用是各个元素分别加减该常数;2、Matrix与Array类型变量做乘法也会不同,Matrix是矩阵相乘,Array对应元素相乘;
Matrix 与Array可以相互转换,方法 .array()和.matrix()。如下:
|
#include
#include
using namespaceEigen;
using namespacestd;
int main()
{
MatrixXf m(2,2);
MatrixXf n(2,2);
MatrixXf result(2,2);
m << 1,2,
3,4;
n << 5,6,
7,8;
result = m * n;
cout << "-- Matrix m*n: --" << endl << result << endl << endl;
result = m.array() * n.array();
cout << "-- Array m*n: --" << endl << result << endl << endl;
result = m.cwiseProduct(n);
cout << "-- With cwiseProduct: --" << endl << result << endl << endl;
result = m.array() + 4;
cout << "-- Array m + 4: --" << endl << result << endl << endl;
}
|
-- Matrix m*n: -- 19 22 43 50 -- Array m*n: -- 5 12 21 32 -- With cwiseProduct: -- 5 12 21 32 -- Array m + 4: -- 5 6 7 8 |
如下是Eigen关于Matrix与Array类型的运算操作(详细参见官网):
Basic matrix manipulation
Basic matrix manipulation
| 1D objects | 2D objects | Notes | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Constructors |
Vector4d v4;
Vector2f v1(x, y);
Array3i v2(x, y, z);
Vector4d v3(x, y, z, w);
VectorXf v5; // empty object
ArrayXf v6(size);
|
Matrix4f m1;
MatrixXf m5; // empty object
MatrixXf m6(nb_rows, nb_columns);
|
By default, the coefficients are left uninitialized |
| Comma initializer |
Vector3f v1; v1 << x, y, z;
ArrayXf v2(4); v2 << 1, 2, 3, 4;
|
Matrix3f m1; m1 << 1, 2, 3,
4, 5, 6,
7, 8, 9;
|
|
| Comma initializer (bis) |
int rows=5, cols=5;
MatrixXf m(rows,cols);
m << ( Matrix3f() << 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9).finished(),
MatrixXf::Zero(3,cols-3),
MatrixXf::Zero(rows-3,3),
MatrixXf::Identity(rows-3,cols-3);
cout << m;
|
output: 1 2 3 0 0 4 5 6 0 0 7 8 9 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1
|
|
| Runtime info |
vector.size();
vector.innerStride();
vector.data();
|
matrix.rows(); matrix.cols();
matrix.innerSize(); matrix.outerSize();
matrix.innerStride(); matrix.outerStride();
matrix.data();
|
Inner/Outer* are storage order dependent |
| Compile-time info |
ObjectType::Scalar ObjectType::RowsAtCompileTime
ObjectType::RealScalar ObjectType::ColsAtCompileTime
ObjectType::Index ObjectType::SizeAtCompileTime
|
||
| Resizing |
vector.resize(size);
vector.resizeLike(other_vector);
vector.conservativeResize(size);
|
matrix.resize(nb_rows, nb_cols);
matrix.resize(Eigen::NoChange, nb_cols);
matrix.resize(nb_rows, Eigen::NoChange);
matrix.resizeLike(other_matrix);
matrix.conservativeResize(nb_rows, nb_cols);
|
no-op if the new sizes match,
|
| Coeff access with range checking |
vector(i) vector.x()
vector[i] vector.y()
vector.z()
vector.w()
|
matrix(i,j)
|
Range checking is disabled if
|
| Coeff access without range checking |
vector.coeff(i)
vector.coeffRef(i)
|
matrix.coeff(i,j)
matrix.coeffRef(i,j)
|
|
| Assignment/copy |
object = expression;
object_of_float = expression_of_double.cast< float>();
|
the destination is automatically resized (if possible)
|
|
Array operators:
| Arithmetic operators |
array1 * array2 array1 / array2 array1 *= array2 array1 /= array2
array1 + scalar array1 - scalar array1 += scalar array1 -= scalar
|
| Comparisons |
array1 < array2 array1 > array2 array1 < scalar array1 > scalar
array1 <= array2 array1 >= array2 array1 <= scalar array1 >= scalar
array1 == array2 array1 != array2 array1 == scalar array1 != scalar
|
| Trigo, power, and misc functions and the STL variants |
array1.min(array2)
array1.max(array2)
array1.abs2()
array1.abs() abs(array1)
array1.sqrt() sqrt(array1)
array1.log() log(array1)
array1.exp() exp(array1)
array1.pow(exponent) pow(array1,exponent)
array1.square()
array1.cube()
array1.inverse()
array1.sin() sin(array1)
array1.cos() cos(array1)
array1.tan() tan(array1)
array1.asin() asin(array1)
array1.acos() acos(array1)
|
Arithmetic Operators
| add subtract |
mat3 = mat1 + mat2; mat3 += mat1;
mat3 = mat1 - mat2; mat3 -= mat1;
|
| scalar product |
mat3 = mat1 * s1; mat3 *= s1; mat3 = s1 * mat1;
mat3 = mat1 / s1; mat3 /= s1;
|
| matrix/vector products * |
col2 = mat1 * col1;
row2 = row1 * mat1; row1 *= mat1;
mat3 = mat1 * mat2; mat3 *= mat1;
|
| transposition adjoint * |
mat1 = mat2.transpose(); mat1.transposeInPlace();
mat1 = mat2.adjoint(); mat1.adjointInPlace();
|
| dot product inner product * |
scalar = vec1.dot(vec2);
scalar = col1.adjoint() * col2;
scalar = (col1.adjoint() * col2).value();
|
| outer product * |
mat = col1 * col2.transpose();
|
| norm normalization * |
scalar = vec1.norm(); scalar = vec1.squaredNorm()
vec2 = vec1.normalized(); vec1.normalize(); // inplace
|
| cross product * |
#include
vec3 = vec1.cross(vec2);
|
使用Eigen矩阵库运算结果与Mathematica运算结果丝毫不差!