pytorch常用函数总结(更新中)
目录
一、 初始化张量
1. torch.arange()和range()
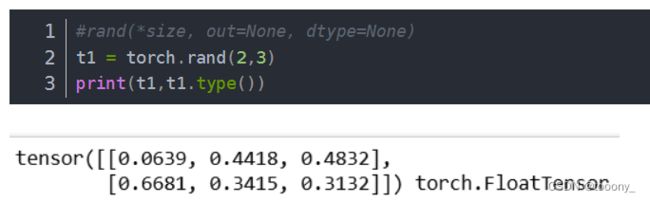
2. torch.rand()、torch.randn()、torch.randint()、torch.randperm()、torch.normal()
二、 运算
1.张量比较
2. torch.eq
3. torch.sum
4. torch.mean
5. torch.mm
6. torch.matmul
7. torch.clamp
8. torch.max
9. torch.norm
10. torch.argmax
三、维度操作
1. torch.cat
2. torch.chunk
3. torch.squeeze和unqueeze
一、 初始化张量
1. torch.arange()和range()
torch.arange(start=0, end, step=1, *, out=None, dtype=None, layout=torch.strided, device=None, requires_grad=False) → Tensor
>>> torch.arange(5) # 默认以 0 为起点
tensor([ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4])
>>> torch.arange(1, 4) # 默认间隔为 1
tensor([ 1, 2, 3])
>>> torch.arange(1, 2.5, 0.5) # 指定间隔 0.5
tensor([ 1.0000, 1.5000, 2.0000])
torch.range(start=0, end, step=1, *, out=None, dtype=None, layout=torch.strided, device=None, requires_grad=False) → Tensor
>>> y=torch.range(1,6)
>>> y
tensor([1., 2., 3., 4., 5., 6.])2. torch.rand()、torch.randn()、torch.randint()、torch.randperm()、torch.normal()
torch.randint()同rand,生成int(均匀分布)
torch.randperm
torch.randperm(n, generator=None, out=None, dtype=torch.int64, layout=torch.strided, device=None, requires_grad=False, pin_memory=False) → Tensor
torch.normal()
返回一个张量,包含了从指定均值mean和标准差std的离散正态分布中抽取的一组随机数。
torch.normal(mean, std, generator=None, out=None) → Tensor
torch.normal(mean=torch.arange(1., 11.), std=torch.arange(1, 0, -0.1))
返回:
tensor([ 1.0425, 3.5672, 2.7969, 4.2925, 4.7229, 6.2134,
8.0505, 8.1408, 9.0563, 10.0566])
torch.normal(mean=torch.arange(1., 6.))
返回:
tensor([ 1.1552, 2.6148, 2.6535, 5.8318, 4.2361])
torch.normal(2, 3, size=(1, 4))
返回:
tensor([[-1.3987, -1.9544, 3.6048, 0.7909]])二、 运算
1.张量比较
对于x=Tensor([0,1,2,3,4]),返回满足的则为1(True),否为0(False)
torch.gt(x, 1) 大于 -> [0,0,1,1,1]
torch.ne(x, 1) 不等于 -> [1,0,1,1,1]
torch.lt(x, 3) 小于 -> [1,1,1,0,0]
torch.eq(x, 3) 等于 -> [0,0,0,1,0]2. torch.eq
torch.pow(input, exponent, *, out=None) → Tensor
计算两个张量或者一个张量与一个标量的指数计算结果,返回一个张量。
input和exponent都可以是张量或者标量,
1)若input和exponent都为张量,则必须维度一致;
2)若input和exponent其中一个为标量,一个为张量,标量以广播的形式进行计算
>>> a = torch.randn(4)
>>> a
tensor([ 0.4331, 1.2475, 0.6834, -0.2791])
>>> torch.pow(a, 2)
tensor([ 0.1875, 1.5561, 0.4670, 0.0779])
>>> exp = torch.arange(1., 5.)
>>> a = torch.arange(1., 5.)
>>> a
tensor([ 1., 2., 3., 4.])
>>> exp
tensor([ 1., 2., 3., 4.])
>>> torch.pow(a, exp)
tensor([ 1., 4., 27., 256.])
>>> torch.pow(2, a)
tensor([ 2., 4., 8., 16.])
>>> torch.pow(a, 2)
tensor([ 1., 4., 9., 16.])3. torch.sum
1.torch.sum(input, dtype=None)
2.torch.sum(input, list: dim, bool: keepdim=False, dtype=None) → Tensor
import torch
a = torch.ones((2, 3))
a1 = torch.sum(a)
a2 = torch.sum(a, dim=0)
a3 = torch.sum(a, dim=1)
print(a)
print(a1)
print(a2)
print(a3)
4. torch.mean
求平均数。
mean()函数的参数:dim=0,按列求平均值,返回的形状是(1,列数);dim=1,按行求平均值,返回的形状是(行数,1),默认不设置dim的时候,返回的是所有元素的平均值。
x=torch.arange(12).view(4,3)
'''
注意:在这里使用的时候转一下类型,否则会报RuntimeError: Can only calculate the mean of floating types. Got Long instead.的错误。
查看了一下x元素类型是torch.int64,根据提示添加一句x=x.float()转为tensor.float32就行
'''
x=x.float()
x_mean=torch.mean(x)
x_mean0=torch.mean(x,dim=0,keepdim=True)
x_mean1=torch.mean(x,dim=1,keepdim=True)
print('x:')
print(x)
print('x_mean0:')
print(x_mean0)
print('x_mean1:')
print(x_mean1)
print('x_mean:')
print(x_mean)
x:
tensor([[ 0., 1., 2.],
[ 3., 4., 5.],
[ 6., 7., 8.],
[ 9., 10., 11.]])
x_mean0:
tensor([[4.5000, 5.5000, 6.5000]])
x_mean1:
tensor([[ 1.],
[ 4.],
[ 7.],
[10.]])
x_mean:
tensor(5.5000)
5. torch.mm
torch.mm(mat1, mat2, *, out=None) → Tensor
注意:mat1和mat1只能是矩阵matrix, 并且无法只用广播机制
6. torch.matmul
该方法支持张量乘法,可以实现广播机制
torch.matmul(input, other, *, out=None) → Tensor7. torch.clamp
将输入input张量每个元素的夹紧到区间 [min,max]内,并返回结果到一个新张量。
torch.clamp(input, min, max, out=None) → Tensor
| min, if input < min
output = | input, if min <= input <= max
| max, if input > maxa=torch.randint(low=0,high=10,size=(10,1))
print(a)
a=torch.clamp(a,3,9)
print(a)
tensor([[9.],
[3.],
[0.],
[4.],
[4.],
[2.],
[4.],
[1.],
[2.],
[9.]])
tensor([[9.],
[3.],
[3.],
[4.],
[4.],
[3.],
[4.],
[3.],
[3.],
[9.]])
8. torch.max
torch.max(input, dim, max=None, max_indices=None) -> (Tensor, LongTensor)
返回输入张量给定维度上每行的最大值,并同时返回每个最大值的位置索引。
(返回的是最大值和索引!)
torch.max(input, other, out=None) → Tensor
返回输入张量给定维度上每行的最大值,并同时返回每个最大值的位置索引。
即,( out_i=max(input_i,other_i) \)
9. torch.norm
torch.norm(input, p, dim, out=None,keepdim=False) → Tensor
返回输入张量给定维dim 上每行的p 范数。
参数:
input (Tensor) – 输入张量
p (float) – 范数计算中的幂指数值
dim (int) – 缩减的维度
out (Tensor, optional) – 结果张量
keepdim(bool)– 保持输出的维度 (此参数官方文档中未给出,但是很常用)10. torch.argmax
得到指定维度最大值的索引值。
1. torch.argmax(input, dim=None, keepdim=False)
import torch
a=torch.tensor(
[
[1, 5, 5, 2],
[9, -6, 2, 8],
[-3, 7, -9, 1]
])
b=torch.argmax(a,dim=0)
print(b)
print(a.shape)
#tensor([1, 2, 0, 1])
#torch.Size([3, 4])
2. a.argmax(dim)三、维度操作
1. torch.cat
即concatnate,将张量组合,拼接。
outputs = torch.cat(inputs, dim=?) → Tensor
>>> import torch
>>> A=torch.ones(2,3) #2x3的张量(矩阵)
>>> A
tensor([[ 1., 1., 1.],
[ 1., 1., 1.]])
>>> B=2*torch.ones(4,3)#4x3的张量(矩阵)
>>> B
tensor([[ 2., 2., 2.],
[ 2., 2., 2.],
[ 2., 2., 2.],
[ 2., 2., 2.]])
>>> C=torch.cat((A,B),0)#按维数0(行)拼接
>>> C
tensor([[ 1., 1., 1.],
[ 1., 1., 1.],
[ 2., 2., 2.],
[ 2., 2., 2.],
[ 2., 2., 2.],
[ 2., 2., 2.]])
>>> C.size()
torch.Size([6, 3])
>>> D=2*torch.ones(2,4) #2x4的张量(矩阵)
>>> C=torch.cat((A,D),1)#按维数1(列)拼接
>>> C
tensor([[ 1., 1., 1., 2., 2., 2., 2.],
[ 1., 1., 1., 2., 2., 2., 2.]])
>>> C.size()
torch.Size([2, 7])
2. torch.chunk
与cat相反,将张量拆分
torch.chunk(tensor, chunk_num, dim)
将tensor按dim(行或列)分割成chunk_num个tensor块,返回的是一个元组。
c = torch.tensor([[1., 2., 4.],
[4., 5., 7.],
[3., 9., 8.],
[9., 6., 7.]])
#在dim=1这一个维度进行拆分, chunk_num是拆分的块数,当其大于等于dim=1中元
#素的个数n, 则拆成n块,小于则平分。
torch.chunk(c,4,dim = 1)
结果:
(tensor([[1.],
[4.],
[3.],
[9.]]),
tensor([[2.],
[5.],
[9.],
[6.]]),
tensor([[4.],
[7.],
[8.],
[7.]]))
torch.chunk(c,3,dim = 1)
结果:
(tensor([[1.],
[4.],
[3.],
[9.]]),
tensor([[2.],
[5.],
[9.],
[6.]]),
tensor([[4.],
[7.],
[8.],
[7.]]))
torch.chunk(c,2,dim = 1)
结果:
(tensor([[1., 2.],
[4., 5.],
[3., 9.],
[9., 6.]]),
tensor([[4.],
[7.],
[8.],
[7.]]))
3. torch.squeeze和unqueeze
对维度进行压缩与扩充。
1)a.squeeze(N) 就是在a中指定位置N加上一个维数为1的维度。
2)b=torch.squeeze(a,N) a就是在a中指定位置N加上一个维数为1的维度
c = torch.tensor([[[1., 2., 4.],
[4., 5., 7.],
[3., 9., 8.],
[9., 6., 7.]]])
c.shape
#torch.Size([1, 4, 3])
b = c.squeeze(0)
print(b, b.shape)
tensor([[1., 2., 4.],
[4., 5., 7.],
[3., 9., 8.],
[9., 6., 7.]]) torch.Size([4, 3])