【分别使用OpenCV、ONNXRuntime部署YOLOV6目标检测,包含C++和Python两个版本的程序】
最近美团视觉团队研发了一款致力于工业应用的目标检测框架YOLOv6,看到他们在昨天发布公布了训练模型。 于是我在今天编写了一套使用opencv的dnn模块做YOLOv6目标检测推理的程序,包含C++和Python两个版本的程序。
接着编写了使用ONNXRuntime做YOLOv6目标检测推理的程序,依然是包含C++和Python两个版本的程序。
onnx文件在百度云盘,下载链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1XqnZaG_0AswxnsYv4sCk6A 提取码:1hii
YOLOV6目标检测
分别使用OpenCV、ONNXRuntime部署YOLOV6目标检测,包含C++和Python两个版本的程序
参考:https://tech.meituan.com/2022/06/23/yolov6-a-fast-and-accurate-target-detection-framework-is-opening-source.html
yolov6传送门
YOLOv6 是美团视觉智能部研发的一款目标检测框架,致力于工业应用。本框架同时专注于检测的精度和推理效率,在工业界常用的尺寸模型中:YOLOv6-nano 在 COCO 上精度可达 35.0% AP,在 T4 上推理速度可达 1242 FPS;YOLOv6-s 在 COCO 上精度可达 43.1% AP,在 T4 上推理速度可达 520 FPS。在部署方面,YOLOv6 支持 GPU(TensorRT)、CPU(OPENVINO)、ARM(MNN、TNN、NCNN)等不同平台的部署,极大地简化工程部署时的适配工作。
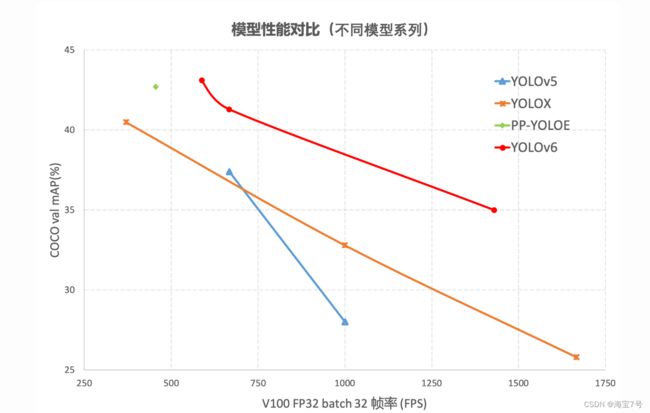
通过研究并借鉴了业界已有的先进技术,开发了一套新的目标检测框架——YOLOv6。该框架支持模型训练、推理及多平台部署等全链条的工业应用需求,并在网络结构、训练策略等算法层面进行了多项改进和优化,在 COCO 数据集上,YOLOv6 在精度和速度方面均超越其他同体量算法,相关结果分析对比如图所示,
github源码地址是:
https://github.com/hpc203/yolov6-opencv-onnxruntime
github源码地址是:
https://github.com/hpc203/yolov6-opencv-onnxruntime
C++程序
main.cpp
#include <fstream>
#include <sstream>
#include <iostream>
#include <opencv2/dnn.hpp>
#include <opencv2/imgproc.hpp>
#include <opencv2/highgui.hpp>
using namespace cv;
using namespace dnn;
using namespace std;
struct Net_config
{
float confThreshold; // Confidence threshold
float nmsThreshold; // Non-maximum suppression threshold
string modelpath;
};
class YOLOV6
{
public:
YOLOV6(Net_config config);
void detect(Mat& frame);
private:
const int inpWidth = 640;
const int inpHeight = 640;
vector<string> class_names;
int num_class;
float confThreshold;
float nmsThreshold;
const bool keep_ratio = true;
Net net;
void drawPred(float conf, int left, int top, int right, int bottom, Mat& frame, int classid);
Mat resize_image(Mat srcimg, int *newh, int *neww, int *top, int *left);
};
YOLOV6::YOLOV6(Net_config config)
{
this->confThreshold = config.confThreshold;
this->nmsThreshold = config.nmsThreshold;
this->net = readNet(config.modelpath);
ifstream ifs("coco.names");
string line;
while (getline(ifs, line)) this->class_names.push_back(line);
this->num_class = class_names.size();
}
Mat YOLOV6::resize_image(Mat srcimg, int *newh, int *neww, int *top, int *left)
{
int srch = srcimg.rows, srcw = srcimg.cols;
*newh = this->inpHeight;
*neww = this->inpWidth;
Mat dstimg;
if (this->keep_ratio && srch != srcw) {
float hw_scale = (float)srch / srcw;
if (hw_scale > 1) {
*newh = this->inpHeight;
*neww = int(this->inpWidth / hw_scale);
resize(srcimg, dstimg, Size(*neww, *newh), INTER_AREA);
*left = int((this->inpWidth - *neww) * 0.5);
copyMakeBorder(dstimg, dstimg, 0, 0, *left, this->inpWidth - *neww - *left, BORDER_CONSTANT, 114);
}
else {
*newh = (int)this->inpHeight * hw_scale;
*neww = this->inpWidth;
resize(srcimg, dstimg, Size(*neww, *newh), INTER_AREA);
*top = (int)(this->inpHeight - *newh) * 0.5;
copyMakeBorder(dstimg, dstimg, *top, this->inpHeight - *newh - *top, 0, 0, BORDER_CONSTANT, 114);
}
}
else {
resize(srcimg, dstimg, Size(*neww, *newh), INTER_AREA);
}
return dstimg;
}
void YOLOV6::drawPred(float conf, int left, int top, int right, int bottom, Mat& frame, int classid) // Draw the predicted bounding box
{
//Draw a rectangle displaying the bounding box
rectangle(frame, Point(left, top), Point(right, bottom), Scalar(0, 0, 255), 2);
//Get the label for the class name and its confidence
string label = format("%.2f", conf);
label = this->class_names[classid] + ":" + label;
//Display the label at the top of the bounding box
int baseLine;
Size labelSize = getTextSize(label, FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, 1, &baseLine);
top = max(top, labelSize.height);
//rectangle(frame, Point(left, top - int(1.5 * labelSize.height)), Point(left + int(1.5 * labelSize.width), top + baseLine), Scalar(0, 255, 0), FILLED);
putText(frame, label, Point(left, top), FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.75, Scalar(0, 255, 0), 1);
}
void YOLOV6::detect(Mat& frame)
{
int newh = 0, neww = 0, padh = 0, padw = 0;
Mat dstimg = this->resize_image(frame, &newh, &neww, &padh, &padw);
Mat blob = blobFromImage(dstimg, 1 / 255.0, Size(this->inpWidth, this->inpHeight), Scalar(0, 0, 0), true, false);
this->net.setInput(blob);
vector<Mat> outs;
this->net.forward(outs, this->net.getUnconnectedOutLayersNames());
int num_proposal = outs[0].size[0];
int nout = outs[0].size[1];
if (outs[0].dims > 2)
{
num_proposal = outs[0].size[1];
nout = outs[0].size[2];
outs[0] = outs[0].reshape(0, num_proposal);
}
/generate proposals
vector<float> confidences;
vector<Rect> boxes;
vector<int> classIds;
float ratioh = (float)frame.rows / newh, ratiow = (float)frame.cols / neww;
int n = 0, row_ind = 0; ///cx,cy,w,h,box_score,class_score
float* pdata = (float*)outs[0].data;
for (n = 0; n < num_proposal; n++) ///ÌØÕ÷ͼ³ß¶È
{
float box_score = pdata[4];
if (box_score > this->confThreshold)
{
Mat scores = outs[0].row(row_ind).colRange(5, nout);
Point classIdPoint;
double max_class_socre;
// Get the value and location of the maximum score
minMaxLoc(scores, 0, &max_class_socre, 0, &classIdPoint);
max_class_socre *= box_score;
if (max_class_socre > this->confThreshold)
{
const int class_idx = classIdPoint.x;
float cx = (pdata[0] - padw) * ratiow; ///cx
float cy = (pdata[1] - padh) * ratioh; ///cy
float w = pdata[2] * ratiow; ///w
float h = pdata[3] * ratioh; ///h
int left = int(cx - 0.5 * w);
int top = int(cy - 0.5 * h);
confidences.push_back((float)max_class_socre);
boxes.push_back(Rect(left, top, (int)(w), (int)(h)));
classIds.push_back(class_idx);
}
}
row_ind++;
pdata += nout;
}
// Perform non maximum suppression to eliminate redundant overlapping boxes with
// lower confidences
vector<int> indices;
dnn::NMSBoxes(boxes, confidences, this->confThreshold, this->nmsThreshold, indices);
for (size_t i = 0; i < indices.size(); ++i)
{
int idx = indices[i];
Rect box = boxes[idx];
this->drawPred(confidences[idx], box.x, box.y,
box.x + box.width, box.y + box.height, frame, classIds[idx]);
}
}
int main()
{
Net_config YOLOV6_nets = { 0.3, 0.5, "onnxmodel/yolov6s.onnx" };
YOLOV6 YOLOV6_model(YOLOV6_nets);
string imgpath = "images/image1.jpg";
Mat srcimg = imread(imgpath);
YOLOV6_model.detect(srcimg);
static const string kWinName = "Deep learning object detection in OpenCV";
namedWindow(kWinName, WINDOW_NORMAL);
imshow(kWinName, srcimg);
waitKey(0);
destroyAllWindows();
}
python程序
main.py
import cv2
import argparse
import numpy as np
class yolov6():
def __init__(self, modelpath, confThreshold=0.5, nmsThreshold=0.5):
self.classes = list(map(lambda x:x.strip(), open('coco.names', 'r').readlines()))
# self.num_classes = len(self.classes)
self.inpHeight, self.inpWidth = 640, 640
self.net = cv2.dnn.readNet(modelpath)
self.confThreshold = confThreshold
self.nmsThreshold = nmsThreshold
self.keep_ratio=True
def resize_image(self, srcimg):
top, left, newh, neww = 0, 0, self.inpWidth, self.inpHeight
if self.keep_ratio and srcimg.shape[0] != srcimg.shape[1]:
hw_scale = srcimg.shape[0] / srcimg.shape[1]
if hw_scale > 1:
newh, neww = self.inpHeight, int(self.inpWidth / hw_scale)
img = cv2.resize(srcimg, (neww, newh), interpolation=cv2.INTER_AREA)
left = int((self.inpWidth - neww) * 0.5)
img = cv2.copyMakeBorder(img, 0, 0, left, self.inpWidth - neww - left, cv2.BORDER_CONSTANT,
value=(114, 114, 114)) # add border
else:
newh, neww = int(self.inpHeight * hw_scale), self.inpWidth
img = cv2.resize(srcimg, (neww, newh), interpolation=cv2.INTER_AREA)
top = int((self.inpHeight - newh) * 0.5)
img = cv2.copyMakeBorder(img, top, self.inpHeight - newh - top, 0, 0, cv2.BORDER_CONSTANT,
value=(114, 114, 114))
else:
img = cv2.resize(srcimg, (self.inpWidth, self.inpHeight), interpolation=cv2.INTER_AREA)
return img, newh, neww, top, left
def preprocess(self, img):
img = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
img = img.astype(np.float32) / 255.0
return img
def postprocess(self, frame, outs, padsize=None):
frameHeight = frame.shape[0]
frameWidth = frame.shape[1]
newh, neww, padh, padw = padsize
ratioh, ratiow = frameHeight / newh, frameWidth / neww
# Scan through all the bounding boxes output from the network and keep only the
# ones with high confidence scores. Assign the box's class label as the class with the highest score.
confidences = []
boxes = []
classIds = []
for detection in outs:
if detection[4] > self.confThreshold:
scores = detection[5:]
classId = np.argmax(scores)
confidence = scores[classId] * detection[4]
if confidence > self.confThreshold:
center_x = int((detection[0] - padw) * ratiow)
center_y = int((detection[1] - padh) * ratioh)
width = int(detection[2] * ratiow)
height = int(detection[3] * ratioh)
left = int(center_x - width * 0.5)
top = int(center_y - height * 0.5)
confidences.append(float(confidence))
boxes.append([left, top, width, height])
classIds.append(classId)
# Perform non maximum suppression to eliminate redundant overlapping boxes with
# lower confidences.
indices = cv2.dnn.NMSBoxes(boxes, confidences, self.confThreshold, self.nmsThreshold).flatten()
for i in indices:
box = boxes[i]
left = box[0]
top = box[1]
width = box[2]
height = box[3]
frame = self.drawPred(frame, classIds[i], confidences[i], left, top, left + width, top + height)
return frame
def drawPred(self, frame, classId, conf, left, top, right, bottom):
# Draw a bounding box.
cv2.rectangle(frame, (left, top), (right, bottom), (0, 0, 255), thickness=2)
label = '%.2f' % conf
label = '%s:%s' % (self.classes[classId], label)
# Display the label at the top of the bounding box
labelSize, baseLine = cv2.getTextSize(label, cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, 1)
top = max(top, labelSize[1])
# cv.rectangle(frame, (left, top - round(1.5 * labelSize[1])), (left + round(1.5 * labelSize[0]), top + baseLine), (255,255,255), cv.FILLED)
cv2.putText(frame, label, (left, top - 10), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 1, (0, 255, 0), thickness=1)
return frame
def detect(self, srcimg):
img, newh, neww, padh, padw = self.resize_image(srcimg)
blob = cv2.dnn.blobFromImage(img, scalefactor=1 / 255.0, swapRB=True)
# blob = cv2.dnn.blobFromImage(self.preprocess(img))
# Sets the input to the network
self.net.setInput(blob)
# Runs the forward pass to get output of the output layers
outs = self.net.forward(self.net.getUnconnectedOutLayersNames())[0].squeeze(axis=0)
srcimg = self.postprocess(srcimg, outs, padsize=(newh, neww, padh, padw))
return srcimg
if __name__ == "__main__":
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument('--imgpath', type=str, default='images/image1.jpg', help="image path")
parser.add_argument('--modelpath', type=str, default='onnxmodel/yolov6s.onnx')
parser.add_argument('--confThreshold', default=0.3, type=float, help='class confidence')
parser.add_argument('--nmsThreshold', default=0.5, type=float, help='nms iou thresh')
args = parser.parse_args()
yolonet = yolov6(args.modelpath, confThreshold=args.confThreshold, nmsThreshold=args.nmsThreshold)
srcimg = cv2.imread(args.imgpath)
srcimg = yolonet.detect(srcimg)
winName = 'Deep learning object detection in OpenCV'
cv2.namedWindow(winName, 0)
cv2.imshow(winName, srcimg)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
原文来源:https://github.com/hpc203/yolov6-opencv-onnxruntime/blob/main/opencv/main.py
实验结果:
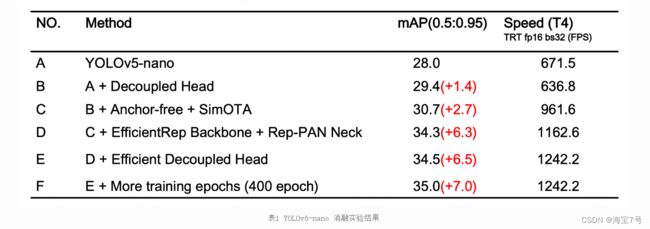
经过以上优化策略和改进,YOLOv6 在多个不同尺寸下的模型均取得了卓越的表现。下表 1 展示了 YOLOv6-nano 的消融实验结果,从实验结果可以看出,我们自主设计的检测网络在精度和速度上都带来了很大的增益。

结果分析:
YOLOv6-nano 在 COCO val 上 取得了 35.0% AP 的精度,同时在 T4 上使用 TRT FP16 batchsize=32 进行推理,可达到 1242FPS 的性能,相较于 YOLOv5-nano 精度提升 7% AP,速度提升 85%。
YOLOv6-tiny 在 COCO val 上 取得了 41.3% AP 的精度, 同时在 T4 上使用 TRT FP16 batchsize=32 进行推理,可达到 602FPS 的性能,相较于 YOLOv5-s 精度提升 3.9% AP,速度提升 29.4%。
YOLOv6-s 在 COCO val 上 取得了 43.1% AP 的精度, 同时在 T4 上使用 TRT FP16 batchsize=32 进行推理,可达到 520FPS 的性能,相较于 YOLOX-s 精度提升 2.6% AP,速度提升 38.6%;相较于 PP-YOLOE-s 精度提升 0.4% AP的条件下,在T4上使用 TRT FP16 进行单 batch 推理,速度提升 71.3%。
参考来源:
https://tech.meituan.com/2022/06/23/yolov6-a-fast-and-accurate-target-detection-framework-is-opening-source.html