计算机视觉(CV)中的注意力Attention机制
记录看到的一些不错的attention的文章,持续更新。。。
目录
1.Squeeze-and-Excitation Networks
2.CBAM: Convolutional Block Attention Module
3.Selective Kernel Networks
4.Non-local Neural Networks
5.GCNet: Non-local Networks Meet Squeeze-Excitation Networks and Beyond
6.Improving Convolutional Networks with Self-Calibrated Convolutions
1.Squeeze-and-Excitation Networks
论文链接:https://arxiv.org/pdf/1709.01507.pdf
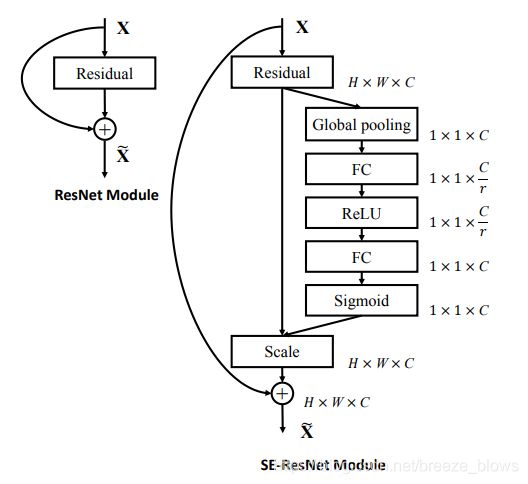
主要思想:该方法是winners of ILSVRC 2017 classification competition。主要思想就是下面这幅图。
通道数为C’的feature在经过一系列卷积变换Ftr之后变成通道数为C的feature,之后便分为三个步骤,首先是Squeeze即Fsq,用一个全局池化层将通道数为C的feature变为1*1*C,顺着空间维度来进行特征压缩,将每个二维的特征通道变成一个实数,这个实数某种程度上具有全局的感受野,并且输出的维度和输入的特征通道数相匹配。它表征着在特征通道上响应的全局分布,第二步是Excitation即Fex,按照作者的说法是类似于一个类似于循环神经网络中门的机制,通过改操作为每个通道学习新的权重,对通道之间的关系进行建模,在代码的实现中其实就是对应着两个fc与一个sigmoid,最后一步就是Reweight,将Fex之后的到的1*1*C 直接乘以原来的通道数为C的feature中。
代码很简单:来自https://github.com/moskomule/senet.pytorch/blob/master/senet/se_module.py
from torch import nn
class SELayer(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, channel, reduction=16):
super(SELayer, self).__init__()
self.avg_pool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d(1) #Squeeze
self.fc = nn.Sequential( #Excitation
nn.Linear(channel, channel // reduction, bias=False),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Linear(channel // reduction, channel, bias=False),
nn.Sigmoid()
)
def forward(self, x):
b, c, _, _ = x.size()
y = self.avg_pool(x).view(b, c)
y = self.fc(y).view(b, c, 1, 1)
return x * y.expand_as(x) #scale这是将SENET用于resnet中得奖结构图,对于Squeeze操作文中对比了max与avg,发现max更好一点,在excitation中对比了Relu,Tanh,sigmoid,发现sigmoid更好。
- 为什么是使用两个fc而不是一个,作者认为主要是为了增加非线性复杂性还有就是减少参数量,作者原话:我们首先将特征维度降低到输入的1/16,然后经过ReLu激活后再通过一个Fully Connected 层升回到原来的维度。这样做比直接用一个Fully Connected层的好处在于:1)具有更多的非线性,可以更好地拟合通道间复杂的相关性;2)极大地减少了参数量和计算量。
- 为什么在resnet中在addition前面进行scale而不是后面,在Addition前对分支上Residual的特征进行了特征重标定。如果对Addition后主支上的特征进行重标定,由于在主干上存在0~1的scale操作,在网络较深BP优化时就会在靠近输入层容易出现梯度消散的情况,导致模型难以优化。
参考:https://www.zhihu.com/question/63460684/answer/300021819
2.CBAM: Convolutional Block Attention Module
ECCV2018的一篇文章
论文链接:http://openaccess.thecvf.com/content_ECCV_2018/papers/Sanghyun_Woo_Convolutional_Block_Attention_ECCV_2018_paper.pdf
主要思想:主要就是将通道注意力和空间注意力作为模块加入到了网络中,框架图如下图
首先是Channel Attention module,其实和SENET很像,只不过是并行的采用了Avg和Max两种池化层,那个加号表示相加,之后在经过一个sigmoid。
对应公式描述
对于Spatial Attention module,是将F’分别经过Max与Avg pool之后的feature cat起来,结果经过一个conv,在用sigmoid得到最后的Ms。
对应公式描述
在resnet中用CBAM的结构
作者通过实验发现在channel attention,用max,avg pool并行的方式比单一的池化效果要好,channel attention在spatial attention之前效果更好。
代码:https://github.com/luuuyi/CBAM.PyTorch/blob/master/model/resnet_cbam.py
class ChannelAttention(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_planes, ratio=16):
super(ChannelAttention, self).__init__()
self.avg_pool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d(1)
self.max_pool = nn.AdaptiveMaxPool2d(1)
self.fc1 = nn.Conv2d(in_planes, in_planes // 16, 1, bias=False)
self.relu1 = nn.ReLU()
self.fc2 = nn.Conv2d(in_planes // 16, in_planes, 1, bias=False)
self.sigmoid = nn.Sigmoid()
def forward(self, x):
avg_out = self.fc2(self.relu1(self.fc1(self.avg_pool(x))))
max_out = self.fc2(self.relu1(self.fc1(self.max_pool(x))))
out = avg_out + max_out
return self.sigmoid(out)
class SpatialAttention(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, kernel_size=7):
super(SpatialAttention, self).__init__()
assert kernel_size in (3, 7), 'kernel size must be 3 or 7'
padding = 3 if kernel_size == 7 else 1
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(2, 1, kernel_size, padding=padding, bias=False)
self.sigmoid = nn.Sigmoid()
def forward(self, x):
avg_out = torch.mean(x, dim=1, keepdim=True)
max_out, _ = torch.max(x, dim=1, keepdim=True)
x = torch.cat([avg_out, max_out], dim=1)
x = self.conv1(x)
return self.sigmoid(x)
3.Selective Kernel Networks
SKnet CVPR2019的一篇文章
论文链接:https://arxiv.org/pdf/1903.06586.pdf
代码:https://github.com/implus/SKNet
主要思想:对SENET的改进,受inceptionnets多分支的影响,设计出一个Multi-branch convolutional networks,多个分支采用不同的卷积核,使该模块可以自适应的调节感受野。
整个模块分为三步split,fuse,select。
Split表示用不同卷积核对X进行卷积,为了平衡准备率与速度,默认采用两个kernel 3*3与5*5(也可以都是3*3,dilation分别为1和2也可以达到同样的效果)
Fuse是将Split之后的feature相加得到U,接着用全局池化层Fgp,全连接层Ffc(其实也可以用conv),这里的操作其实跟SENET的很像,
Select很像一种门的操作,将Fuse之后经过softmax,接着与Split之后的相乘,最后相加得到融合后的feature V
附上torch源码https://github.com/pprp/SimpleCVReproduction/blob/master/attention/SK/sknet.py,实现的跟作者公布的caffe版本有点不一样,但是大概思想一样
import torch.nn as nn
import torch
class SKConv(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, features, WH, M, G, r, stride=1, L=32):
super(SKConv, self).__init__()
d = max(int(features / r), L)
self.M = M
self.features = features
self.convs = nn.ModuleList([])
for i in range(M):
# 使用不同kernel size的卷积
self.convs.append(
nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(features,
features,
kernel_size=3 + i * 2,
stride=stride,
padding=1 + i,
groups=G), nn.BatchNorm2d(features),
nn.ReLU(inplace=False)))
self.fc = nn.Linear(features, d)
self.fcs = nn.ModuleList([])
for i in range(M):
self.fcs.append(nn.Linear(d, features))
self.softmax = nn.Softmax(dim=1)
def forward(self, x):
for i, conv in enumerate(self.convs):
fea = conv(x).unsqueeze_(dim=1) #split
if i == 0:
feas = fea
else:
feas = torch.cat([feas, fea], dim=1)
fea_U = torch.sum(feas, dim=1) #fuse
fea_s = fea_U.mean(-1).mean(-1)
fea_z = self.fc(fea_s)
for i, fc in enumerate(self.fcs):
print(i, fea_z.shape)
vector = fc(fea_z).unsqueeze_(dim=1)
print(i, vector.shape)
if i == 0:
attention_vectors = vector
else:
attention_vectors = torch.cat([attention_vectors, vector],
dim=1)
attention_vectors = self.softmax(attention_vectors) #select
attention_vectors = attention_vectors.unsqueeze(-1).unsqueeze(-1)
fea_v = (feas * attention_vectors).sum(dim=1)
return fea_v
if __name__ == "__main__":
t = torch.ones((1, 256, 24, 24))
sk = SKConv(256, WH=1, M=2, G=1, r=2)
out = sk(t)
print(out.shape)在作者写的文章以及评论中,SKNET对超分辨率还有分割都是有效的,但是对于目标检测似乎没有大的效果,需要尝试着看看
4.Non-local Neural Networks
https://blog.csdn.net/breeze_blows/article/details/104715120
5.GCNet: Non-local Networks Meet Squeeze-Excitation Networks and Beyond
https://blog.csdn.net/breeze_blows/article/details/104878928
6.Improving Convolutional Networks with Self-Calibrated Convolutions
https://blog.csdn.net/breeze_blows/article/details/105878853