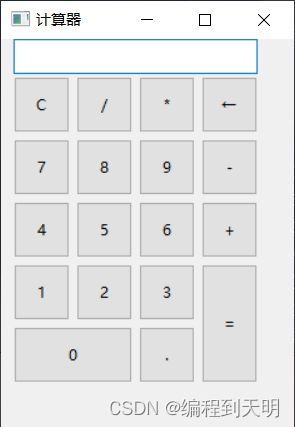
Python大作业——两种方法设计计算器(使用wx库)。
python大作业
本次设计用Pycharm开发工具,Python语言进行主要功能是基于图形用户面的多功能。该计算器的主要功能是加、减、乘、除等常规运算以及指数,对数,三角函数等科学运算功能。该计算器分为数据输入模块和运算规则选择模块以及过程和结果显示模块三个模块。
第一种方法
该方法较简单。
代码如下:
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
import wx
class MyFrame(wx.Frame):
def __init__(self, parent):
wx.Frame.__init__(self, parent, id=100, title='计算器', size=(250, 350)) #初始化界面窗口
panel = wx.Panel(self)
# 创建文本框
self.entry = wx.TextCtrl(panel, id=15, pos=(10, 0), size=(195, 28), style=wx.TE_RIGHT) #定义文本框的属性
#创建按钮
self.b_clear = wx.Button(parent=panel, id=10, label='C', pos=(10, 30), size=(45, 45)) #定义计算器的各个按钮,label是名称,pos是位置,size是按钮的大小
self.b_divide = wx.Button(parent=panel, id=11, label='/', pos=(60, 30), size=(45, 45))
self.b_multiply = wx.Button(parent=panel, id=12, label='*', pos=(110, 30), size=(45, 45))
self.b_backspace = wx.Button(parent=panel, id=13, label='←', pos=(160, 30), size=(45, 45))
self.b_sub = wx.Button(parent=panel, id=14, label='-', pos=(160, 80), size=(45, 45))
self.b_add = wx.Button(parent=panel, id=15, label='+', pos=(160, 130), size=(45, 45))
self.b_point = wx.Button(parent=panel, id=16, label='.', pos=(110, 230), size=(45, 45))
self.b_equal = wx.Button(parent=panel, id=17, label='=', pos=(160, 180), size=(45, 95))
self.b_zero = wx.Button(parent=panel, id=0, label='0', pos=(10, 230), size=(95, 45))
self.b_seven = wx.Button(parent=panel, id=7, label='7', pos=(10, 80), size=(45, 45))
self.b_eight = wx.Button(parent=panel, id=8, label='8', pos=(60, 80), size=(45, 45))
self.b_nine = wx.Button(parent=panel, id=9, label='9', pos=(110, 80), size=(45, 45))
self.b_six = wx.Button(parent=panel, id=6, label='6', pos=(110, 130), size=(45, 45))
self.b_five = wx.Button(parent=panel, id=5, label='5', pos=(60, 130), size=(45, 45))
self.b_four = wx.Button(parent=panel, id=4, label='4', pos=(10, 130), size=(45, 45))
self.b_three = wx.Button(parent=panel, id=3, label='3', pos=(110, 180), size=(45, 45))
self.b_two = wx.Button(parent=panel, id=2, label='2', pos=(60, 180), size=(45, 45))
self.b_one = wx.Button(parent=panel, id=1, label='1', pos=(10, 180), size=(45, 45))
#创建捆绑事件
self.b_one.Bind(wx.EVT_BUTTON, self.B_one, self.b_one) #使用wx.Bind将按钮和事件捆绑起来
self.b_two.Bind(wx.EVT_BUTTON, self.B_two, self.b_two)
self.b_three.Bind(wx.EVT_BUTTON, self.B_three, self.b_three)
self.b_four.Bind(wx.EVT_BUTTON, self.B_four, self.b_four)
self.b_five.Bind(wx.EVT_BUTTON, self.B_five, self.b_five)
self.b_six.Bind(wx.EVT_BUTTON, self.B_six, self.b_six)
self.b_seven.Bind(wx.EVT_BUTTON, self.B_seven, self.b_seven)
self.b_eight.Bind(wx.EVT_BUTTON, self.B_eight, self.b_eight)
self.b_nine.Bind(wx.EVT_BUTTON, self.B_nine, self.b_nine)
self.b_zero.Bind(wx.EVT_BUTTON, self.B_zero, self.b_zero)
self.b_divide.Bind(wx.EVT_BUTTON, self.B_divide, self.b_divide)
self.b_clear.Bind(wx.EVT_BUTTON, self.B_clear, self.b_clear)
self.b_multiply.Bind(wx.EVT_BUTTON, self.B_multiply, self.b_multiply)
self.b_backspace.Bind(wx.EVT_BUTTON, self.B_backspace, self.b_backspace)
self.b_sub.Bind(wx.EVT_BUTTON, self.B_sub, self.b_sub)
self.b_add.Bind(wx.EVT_BUTTON, self.B_add, self.b_add)
self.b_equal.Bind(wx.EVT_BUTTON, self.B_equal, self.b_equal)
self.b_point.Bind(wx.EVT_BUTTON, self.B_point, self.b_point)
#创建按钮点击事件
def B_one(self,event): #创建捆绑的事件
self.entry.AppendText("1")
def B_two(self, event):
self.entry.AppendText("2")
def B_three(self, event):
self.entry.AppendText("3")
def B_four(self, event):
self.entry.AppendText("4")
def B_five(self, event):
self.entry.AppendText("5")
def B_six(self, event):
self.entry.AppendText("6")
def B_seven(self, event):
self.entry.AppendText("7")
def B_eight(self, event):
self.entry.AppendText("8")
def B_nine(self, event):
self.entry.AppendText("9")
def B_zero(self, event):
self.entry.AppendText("0")
def B_point(self, event):
self.entry.AppendText(".")
def B_add(self, event):
self.entry.AppendText("+")
def B_sub(self, event):
self.entry.AppendText("-")
def B_multiply(self, event):
self.entry.AppendText("*")
def B_divide(self, event):
self.entry.AppendText("/")
def B_clear(self, event):
self.entry.Clear()
def B_backspace(self, event):
input_len = len(self.entry.GetValue())
self.entry.Remove(input_len - 1, input_len)
def B_equal(self,event):
try:
pre_result = str(self.entry.GetValue())
result = eval(pre_result)
self.entry.SetValue(str(result))
except:
self.entry.SetValue("Error")
if __name__ == '__main__':
app = wx.App()
MyFrame(None).Show()
app.MainLoop()
第二种方法
该方法较第一种复杂,但是实现的功能更多。
代码如下:
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
import wx
from math import *
class Calculator(wx.Frame):
def __init__(self):
wx.Frame.__init__(self, None, -1, "计算器", size=(350, 480),
style=wx.DEFAULT_FRAME_STYLE ^ (wx.RESIZE_BORDER |wx.MINIMIZE_BOX | wx.MAXIMIZE_BOX))
panel = wx.Panel(self)
boxsize = wx.BoxSizer(wx.VERTICAL)
gridBox = wx.GridSizer(rows=6, cols=5, hgap=5, vgap=5)
self.equation = "" # 记录等式
self.textprint = wx.TextCtrl(panel, -1, '', style=wx.TE_MULTILINE | wx.TE_READONLY)
# 按钮数据
self.buttonData = "% pi e ← C sqrt ^ ln log tan 7 8 9 cos sin 4 5 6 + - 1 2 3 * / 0 ( ) . =".split()
buttonLength = len(self.buttonData) #使用循环来定义按钮的属性,简化代码
for i in range(buttonLength):
labels = "%s" % self.buttonData[i]
buttonIterm = wx.Button(panel, i, labels, size=(63, 52))
self.bangding(buttonIterm, labels) #调用绑定方法,减少重复性工作
gridBox.Add(buttonIterm, 0, 0)
boxsize.Add(self.textprint, 1, wx.EXPAND)
boxsize.Add(gridBox, 5, wx.EXPAND)
panel.SetSizerAndFit(boxsize)
# 创建绑定方法
def bangding(self, button, labels):
item = "← C ="
if labels not in item:
self.Bind(wx.EVT_BUTTON, self.OnAppend, button)
elif labels == '←':
self.Bind(wx.EVT_BUTTON, self.OnDel, button)
elif labels == 'C':
self.Bind(wx.EVT_BUTTON, self.OnAc, button)
elif labels == '=':
self.Bind(wx.EVT_BUTTON, self.OnTarget, button)
# 添加运算符与数字
def OnAppend(self, event):
eventbutton = event.GetEventObject()
label = eventbutton.GetLabel()
self.equation += label
self.textprint.SetValue(self.equation)
def OnDel(self, event):
self.equation = self.equation[:-1]
self.textprint.SetValue(self.equation)
def OnAc(self, event):
self.textprint.Clear()
self.equation = "" #将文本框的内容清空,实现归零
def OnTarget(self, event):
string = self.equation
if '^' in string:
string = string.replace('^', '**') #将指数符号进行转换,便于eval()函数进行识别
try:
target = eval(string)
self.equation += '=' + str(target)
self.textprint.SetValue(self.equation)
except SyntaxError:
dlg = wx.MessageDialog(self, '请输入正确的等式!', '请注意',
wx.OK | wx.ICON_INFORMATION)
dlg.ShowModal()
dlg.Destroy()
if __name__ == '__main__':
app = wx.App()
frame = Calculator()
frame.Show()
app.MainLoop()