Pytorch实战 |Y2 yolov5训练自己的数据集
一、我的环境
● 语言环境:Python3.8
● 编译器:pycharm
● 深度学习环境:Pytorch
● 数据来源:水果链接
二、准备数据
1、在yolov5的主目录下,新建自己的文件夹data-test, 新建文件夹annotations、images、ImageSets三个文件夹。

2、将下载的水果数据集中的xml文件放到annotations文件夹下,如下图。xml文件都是图片中水果标注的位置、分类等信息。

3、将水果数据集中的图片放到images文件夹下,如下图,为水果的原始图片。

三、定制代码编写
1、编写并运行split_train_val.py文件
在data-test文件夹下编写并运行split_train_val.py文件,运行后会在ImageSets文件夹的Main文件夹下,生成train.txt,val.txt.test.txt.tranval.txt四个文件。
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import os
import random
import argparse
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
# xml文件地址
parser.add_argument('--xml_path', default='Annotations', type=str, help='input xml label path')
# 划分数据集存放位置
parser.add_argument('--txt_path', default='ImageSets/Main', type=str, help='output txt label path')
opt = parser.parse_args()
trainval_percent = 0.9
train_percent = 8/9
xmlfilepath = opt.xml_path
txtsavepath = opt.txt_path
total_xml = os.listdir(xmlfilepath)
if not os.path.exists(txtsavepath):
os.makedirs(txtsavepath)
num = len(total_xml)
list_index = range(num)
train_val_num = int(num * trainval_percent)
train_num = int(train_val_num * train_percent)
trainval = random.sample(list_index, train_val_num)
train = random.sample(trainval, train_num)
file_trainval = open(txtsavepath + '/trainval.txt', 'w')
file_test = open(txtsavepath + '/test.txt', 'w')
file_train = open(txtsavepath + '/train.txt', 'w')
file_val = open(txtsavepath + '/val.txt', 'w')
for i in list_index:
name = total_xml[i][:-4] + '\n'
if i in trainval:
file_trainval.write(name)
if i in train:
file_train.write(name)
else:
file_val.write(name)
else:
file_test.write(name)
file_trainval.close()
file_train.close()
file_val.close()
file_test.close()
运行之后生成如下图文件

训练数据量和验证数据量可自行调整,如下图

2、编写并运行voc_label.py文件
在data-test文件夹下,编写voc_label.py文件,代码如下
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
import os
from os import getcwd
sets = ['train', 'val', 'test']
classes = ['banana', 'snake fruit', 'dragon fruit', 'pineapple']
abs_path = os.getcwd()
print(abs_path)
def convert(size, box):
dw = 1. / (size[0])
dh = 1. / (size[1])
x = (box[0] + box[1]) / 2.0 - 1
y = (box[2] + box[3]) / 2.0 - 1
w = box[1] - box[0]
h = box[3] - box[1]
x = x * dw
w = w * dh
y = y * dh
h = h * dh
return x, y, w, h
def convert_annotation(image_id):
in_file = open('./annotations/%s.xml' % (image_id), encoding='UTF-8')
out_file = open('./labels/%s.txt' % (image_id), 'w')
tree = ET.parse(in_file)
root = tree.getroot()
size = root.find('size')
w = int(size.find('width').text)
h = int(size.find('height').text)
for obj in root.iter('object'):
difficult = obj.find('difficult').text
cls = obj.find('name').text
if cls not in classes or int(difficult) == 1:
continue
cls_id = classes.index(cls)
xmlbox = obj.find('bndbox')
b = (float(xmlbox.find('xmin').text), float(xmlbox.find('xmax').text), float(xmlbox.find('ymin').text),
float(xmlbox.find('ymax').text))
b1, b2, b3, b4 = b
# 标注越界修正
if b2 > w:
b2 = w
if b4 > h:
b4 = h
b = (b1, b2, b3, b4)
bb = convert((w, h), b)
out_file.write(str(cls_id) + " " + " ".join([str(a) for a in bb]) + '\n')
wd = getcwd()
for image_set in sets:
if not os.path.exists('./labels/'):
os.makedirs('./labels/')
image_ids = open('./ImageSets/Main/%s.txt' % (image_set)).read().strip().split()
list_file = open('./%s.txt' % (image_set), 'w')
for image_id in image_ids:
list_file.write(abs_path + '/images/%s.png\n' % (image_id))
convert_annotation(image_id)
list_file.close()
运行如上代码,生成train.txt, test.txt, val.txt三个文件,文件中放着图片的地址

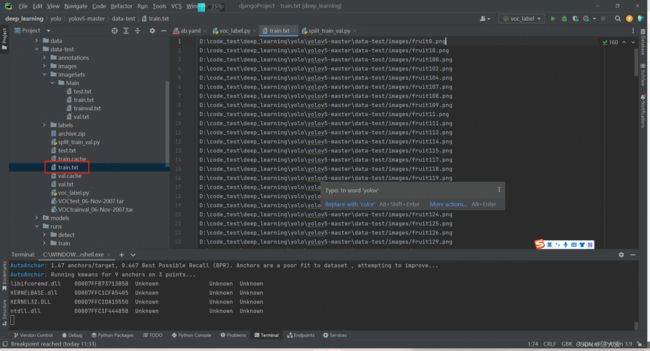
3、创建ab.yaml文件
在data文件夹下,创建ab.yaml文件,代码如下
train: ./data-test/train.txt
val: ./data-test/val.txt
nc: 1
names: ['banana', 'snake fruit', 'dragon fruit', 'pineapple']
三、训练模型
在yolov5-master文件夹下,cmd运行命令
python train.py --img 900 --batch 2 --epoch 100 --data ./data/ab.yaml --cfg ./models/yolov5s.yaml --weights weights/yolov5s.pt --device '0'
