OpenCV-Camshift算法解析
Camshift算法简述
Camshift它是MeanShift算法的改进,称为连续自适应的MeanShift算法,CamShift算法英文全称是"Continuously Adaptive Mean-SHIFT",它的基本思想是视频图像的所有帧作MeanShift运算,并将上一帧的结果(即Search Window的中心和大小)作为下一帧MeanShift算法的Search Window的初始值,如此迭代下去。(百度百科)
一.预备知识
(1)HSV(Hue, Saturation, Value)是根据颜色的直观特性由A. R. Smith在1978年创建的一种颜色空间, 也称六角锥体模型(Hexcone Model)。、这个模型中颜色的参数分别是:色调(H),饱和度(S),亮度(V)。
为什么要在HSV空间进行?HSV在用于指定颜色分割时,有比较大的作用.其中,H和S分量代表了色彩信息。HSV是对RGB 色彩空间中点的两种有关系的表示,它们尝试描述比 RGB 更准确的感知颜色联系,并仍保持在计算上简单。
(2)HSV颜色分量上的范围:H: 0— 180
S: 0— 255
V: 0— 255
黑
灰
白
红
橙
黄
绿
青
蓝
紫
hmin
0
0
0
0
156
11
26
35
78
100
125
hmax
180
180
180
10
180
25
34;
77
99
124
155
smin
0
0
0
43
43
43
43
43
43
43
smax
255
43
30
255
255
255
255
255
255
255
vmin
0
46
221
46
46
46
46
46
46
46
vmax
46
220
255
255
255
255
255
255
255
255
(3)图像通道:简单的讲,对于一个灰度像素点,只需要一个数值来进行描述,即为单通道。如果一个像素点用RGB三种颜色来进行描述,那么就是三通道。OpenCV中可以通过滑动条阈值分割多通道图像。(4)颜色直方图:在运行官网的demo时会出现一个直方图。颜色直方图是在许多图像检索系统中被广泛采用的颜色特征。它所描述的是不同色彩在整幅图像中所占的比例,而并不关心每种色彩所处的空间位置,即无法描述图像中的对象或物体。颜色直方图特别适于描述那些难以进行自动分割的图像。(来源百度百科))
(5)反向投影图:反向投影用于在输入图像(通常较大)中查找特定图像(通常较小或者仅1个像素,以下将其称为模板图像)最匹配的点或者区域,也就是定位模板图像出现在输入图像的位置。
(6)程序在具体执行时分解为以下几个具体步骤:
一 选择画面中要进行跟踪的目标
二 求出视频中物体的反向投影图
三 根据反向投影图和输入的方框进行meanshift迭代,由于它向反向投影图概率大的地方移动,
四 下一帧图像用上一帧输出的方框进行迭代
具体代码如下
#include
#include "opencv2/video/tracking.hpp"
#include "opencv2/imgproc.hpp"
#include "opencv2/videoio.hpp"
#include "opencv2/highgui.hpp"
#include
#include
using namespace cv;
using namespace std;
Mat image;
bool backprojMode = false;
bool selectObject = false;
int trackObject = 0;
bool showHist = true;
Point origin;
Rect selection;
int vmin = 10, vmax = 256, smin = 30;
// User draws box around object to track. This triggers CAMShift to start tracking
static void onMouse( int event, int x, int y, int, void* )
{
if( selectObject )
{
selection.x = MIN(x, origin.x);
selection.y = MIN(y, origin.y);
selection.width = std::abs(x - origin.x);
selection.height = std::abs(y - origin.y);
selection &= Rect(0, 0, image.cols, image.rows);
}
switch( event )
{
case EVENT_LBUTTONDOWN:
origin = Point(x,y);
selection = Rect(x,y,0,0);
selectObject = true;
break;
case EVENT_LBUTTONUP:
selectObject = false;
if( selection.width > 0 && selection.height > 0 )
trackObject = -1; // Set up CAMShift properties in main() loop
break;
}
}
string hot_keys =
"\n\nHot keys: \n"
"\tESC - quit the program\n"
"\tc - stop the tracking\n"
"\tb - switch to/from backprojection view\n"
"\th - show/hide object histogram\n"
"\tp - pause video\n"
"To initialize tracking, select the object with mouse\n";
static void help()
{
cout << "\nThis is a demo that shows mean-shift based tracking\n"
"You select a color objects such as your face and it tracks it.\n"
"This reads from video camera (0 by default, or the camera number the user enters\n"
"Usage: \n"
" ./camshiftdemo [camera number]\n";
cout << hot_keys;
}
const char* keys =
{
"{help h | | show help message}{@camera_number| 0 | camera number}"
};
int main( int argc, const char** argv )
{
VideoCapture cap;
Rect trackWindow;
int hsize = 16;
float hranges[] = {0,180};
const float* phranges = hranges;
CommandLineParser parser(argc, argv, keys);
if (parser.has("help"))
{
help();
return 0;
}
int camNum = parser.get(0);
cap.open(camNum);
if( !cap.isOpened() )
{
help();
cout << "***Could not initialize capturing...***\n";
cout << "Current parameter's value: \n";
parser.printMessage();
return -1;
}
cout << hot_keys;
namedWindow( "Histogram", 0 );
namedWindow( "CamShift Demo", 0 );
setMouseCallback( "CamShift Demo", onMouse, 0 );
createTrackbar( "Vmin", "CamShift Demo", &vmin, 256, 0 );
createTrackbar( "Vmax", "CamShift Demo", &vmax, 256, 0 );
createTrackbar( "Smin", "CamShift Demo", &smin, 256, 0 );
Mat frame, hsv, hue, mask, hist, histimg = Mat::zeros(200, 320, CV_8UC3), backproj;
bool paused = false;
for(;;)
{
if( !paused )
{
cap >> frame;
if( frame.empty() )
break;
}
frame.copyTo(image);
if( !paused )
{
cvtColor(image, hsv, COLOR_BGR2HSV);
if( trackObject )
{
int _vmin = vmin, _vmax = vmax;
inRange(hsv, Scalar(0, smin, MIN(_vmin,_vmax)),
Scalar(180, 256, MAX(_vmin, _vmax)), mask);
int ch[] = {0, 0};
hue.create(hsv.size(), hsv.depth());
mixChannels(&hsv, 1, &hue, 1, ch, 1);
if( trackObject < 0 )
{
// Object has been selected by user, set up CAMShift search properties once
Mat roi(hue, selection), maskroi(mask, selection);
calcHist(&roi, 1, 0, maskroi, hist, 1, &hsize, &phranges);
normalize(hist, hist, 0, 255, NORM_MINMAX);
trackWindow = selection;
trackObject = 1; // Don't set up again, unless user selects new ROI
histimg = Scalar::all(0);
int binW = histimg.cols / hsize;
Mat buf(1, hsize, CV_8UC3);
for( int i = 0; i < hsize; i++ )
buf.at(i) = Vec3b(saturate_cast(i*180./hsize), 255, 255);
cvtColor(buf, buf, COLOR_HSV2BGR);
for( int i = 0; i < hsize; i++ )
{
int val = saturate_cast(hist.at(i)*histimg.rows/255);
rectangle( histimg, Point(i*binW,histimg.rows),
Point((i+1)*binW,histimg.rows - val),
Scalar(buf.at(i)), -1, 8 );
}
}
// Perform CAMShift
calcBackProject(&hue, 1, 0, hist, backproj, &phranges);
backproj &= mask;
RotatedRect trackBox = CamShift(backproj, trackWindow,
TermCriteria( TermCriteria::EPS | TermCriteria::COUNT, 10, 1 ));
if( trackWindow.area() <= 1 )
{
int cols = backproj.cols, rows = backproj.rows, r = (MIN(cols, rows) + 5)/6;
trackWindow = Rect(trackWindow.x - r, trackWindow.y - r,
trackWindow.x + r, trackWindow.y + r) &
Rect(0, 0, cols, rows);
}
if( backprojMode )
cvtColor( backproj, image, COLOR_GRAY2BGR );
ellipse( image, trackBox, Scalar(0,0,255), 3, LINE_AA );
}
}
else if( trackObject < 0 )
paused = false;
if( selectObject && selection.width > 0 && selection.height > 0 )
{
Mat roi(image, selection);
bitwise_not(roi, roi);
}
imshow( "CamShift Demo", image );
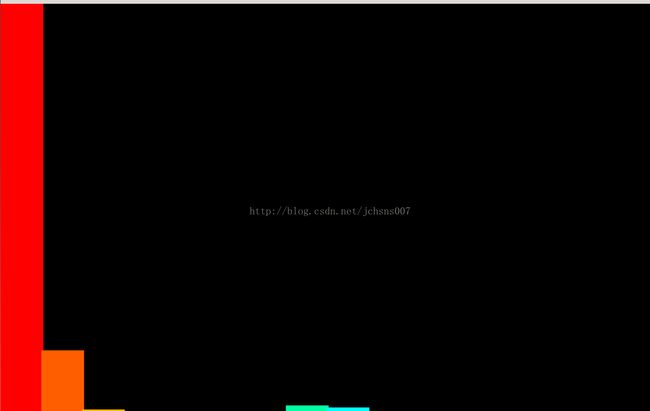
imshow( "Histogram", histimg );
char c = (char)waitKey(10);
if( c == 27 )
break;
switch(c)
{
case 'b':
backprojMode = !backprojMode;
break;
case 'c':
trackObject = 0;
histimg = Scalar::all(0);
break;
case 'h':
showHist = !showHist;
if( !showHist )
destroyWindow( "Histogram" );
else
namedWindow( "Histogram", 1 );
break;
case 'p':
paused = !paused;
break;
default:
;
}
}
return 0;
} 下面附上运行程序后的截图(追踪一个红色瓶盖)
总结:Camshift是一种半自动追踪算法,需要手动选定追踪目标这个算法对于纯色物体在黑白背景下的跟踪效果是很好的,但是如果背景的颜色与目标相近,或者目标附近有与目标的色调相近的算法比较物体,则CAMSHIFT会自动将其包括在内,导致跟踪窗口扩大,甚至有时会将跟踪窗口扩大到整个视频框架。