C# 常用算法 递归
一 递归
逻辑上:一个问题化为同样的问题;
形式上:自己调用自己
示例:
求阶乘;
菲波那契数列;
Celay数
其他,Koch分形集;
求阶乘
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace 求阶乘
{
public class Fac
{
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("Fac of 5 is" + fac(5));
Console.ReadKey();
}
static long fac(int n)
{
if (n == 0 || n == 1) return 1;
else
return fac(n - 1) * n;
}
}
}
走台阶
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace 走台阶
{
public class Fibonacci
{
public static void Main(string[]args)
{
Console.WriteLine("Fibonacci(10)is" + fib(10));
Console.ReadKey();
}
static long fib(int n)
{
if (n == 0 || n == 1) return 1;
else return fib(n - 1) + fib(n - 2);
}
}
}
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Data;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace 画树
{
public partial class Form1 : Form
{
private Graphics graphics;
const double PI = Math.PI;
double th1 = 40 * Math.PI / 180;
double th2 = 30 * Math.PI / 180;
double per1 = 0.6;
double per2 = 0.7;
public Form1()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void Form1_Paint(object sender, PaintEventArgs e)
{
graphics = e.Graphics;
drawTree(10, 200, 310, 100, -PI / 2);
}
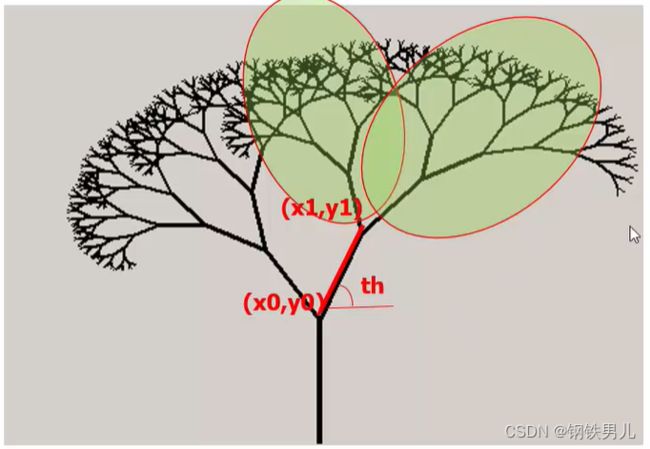
void drawTree(int n,double x0,double y0,double leng,double th)
{
if (n == 0)
return;
double x1 = x0 + leng * Math.Cos(th);
double y1 = y0 + leng * Math.Sin(th);
drawLine(x0, y0, x1, y1, n / 2);
drawTree(n - 1, x1, y1, per1 * leng, th + th1);
drawTree(n - 1, x1, y1, per2 * leng, th - th2);
}
void drawLine(double x0,double y0,double x1,double y1,int width)
{
graphics.DrawLine(new Pen(Color.Blue, width), (int)x0, (int)y0,
(int)x1, (int)y1);
}
}
}
画出不同的树
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Data;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace 画出不同的树
{
public partial class Form1 : Form
{
private Graphics graphics;
const double PI = Math.PI;
double th1 = 35 * Math.PI / 180;
double th2 = 25 * Math.PI / 180;
double per1 = 0.6;
double per2 = 0.7;
Random rnd = new Random();
public Form1()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void Form1_Paint(object sender, PaintEventArgs e)
{
graphics = e.Graphics;
drawTree(10, 200, 380, 100, -PI / 2);
}
double rand()
{
return rnd.NextDouble();
}
void drawTree(int n,double x0,double y0,double leng,double th)
{
if (n == 0)
return;
double x1 = x0 + leng * Math.Cos(th);
double y1 = y0 + leng * Math.Sin(th);
drawLine(x0, y0, x1, y1);
drawTree(n - 1, x1, y1, per1 * leng * (0.5 + rand()), th + th1 * (0.5 + rand()));
drawTree(n - 1, x1, y1, per2 * leng * (0.4 + rand()), th - th2 * (0.5 + rand()));
if (rand() > 0.6)
drawTree(n - 1, x1, y1, per2 * leng * (0.4 + rand()), th - th2 * (0.5 + rand()));
}
void drawLine(double x0,double y0,double x1,double y1)
{
graphics.DrawLine(Pens.BlueViolet, (int)x0, (int)y0, (int)x1, (int)y1);
}
}
}