PCL - 3D点云配准(registration)介绍
前面多篇博客都提到过,要善于从官网去熟悉一样东西。API部分详细介绍见
Point Cloud Library (PCL): Module registration
这里博主主要借鉴Tutorial里内容(博主整体都有看完)
Introduction — Point Cloud Library 0.0 documentation
接下来主要跑下Registration中的sample例子
一.直接运行下How to use iterative closet point中的代码(稍微做了变化,打印输出了Final点云)
#include
#include
#include
#include
int main()
{
pcl::PointCloud::Ptr cloud_in(new pcl::PointCloud(5, 1));
pcl::PointCloud::Ptr cloud_out(new pcl::PointCloud);
// source->CloudIn data
for (auto& point : *cloud_in)
{
point.x = 1024 * rand() / (RAND_MAX + 1.0f);
point.y = 1024 * rand() / (RAND_MAX + 1.0f);
point.z = 1024 * rand() / (RAND_MAX + 1.0f);
}
std::cout << "source->cloud_in:" << std::endl;
for (auto& point : *cloud_in)
std::cout << point << std::endl;
std::cout << std::endl;
//target->CloudOut data
* cloud_out = *cloud_in;
for (auto& point : *cloud_out)
{
point.x += 1.6f;
point.y += 2.4f;
point.z += 3.2f;
}
std::cout << "target->cloud_out:" << std::endl;
for (auto& point : *cloud_out)
std::cout << point << std::endl;
std::cout << std::endl;
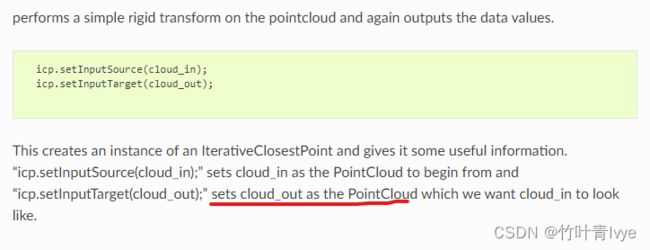
pcl::IterativeClosestPoint icp;
icp.setInputSource(cloud_in);
icp.setInputTarget(cloud_out);
//final->
pcl::PointCloud Final;
icp.align(Final);
std::cout << "Final data points:" << std::endl;
for (auto& point : Final)
std::cout << point << std::endl;
std::cout << std::endl;
//transform info
std::cout << "has converged:" << icp.hasConverged() << " score: " <<
icp.getFitnessScore() << std::endl;
std::cout << icp.getFinalTransformation() << std::endl;
return (0);
}
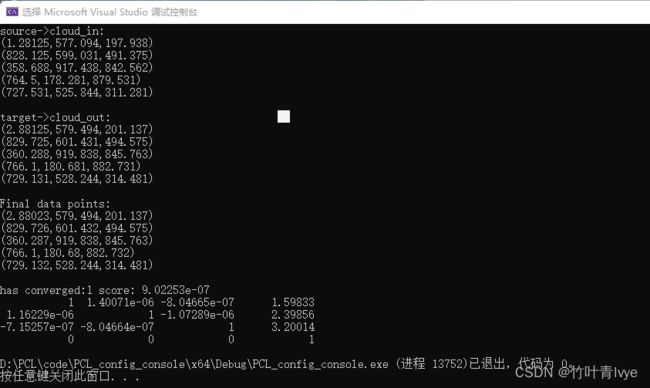
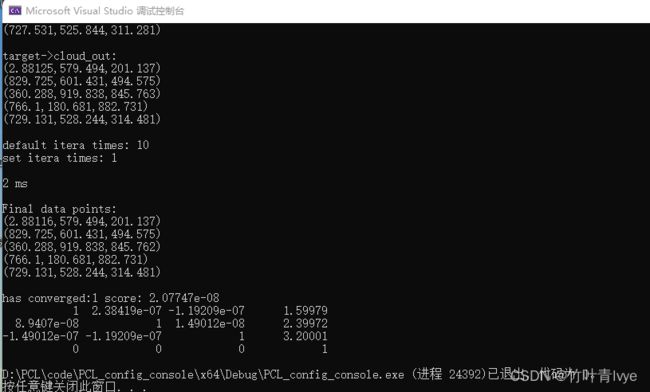
输出结果如下:
这里需要清楚的一点,是将源点云向目标点云对齐,让其变换到目标点云的样子。
从上面结果中也能够看出,输出的final点云数据是和target是非常近似的,也验证了上面的表述。同时也能够看到transform的信息也是对的。
这边在上面代码基础上增加设置迭代次数,部分代码如下
//target->CloudOut data
*cloud_out = *cloud_in;
for (auto& point : *cloud_out)
{
point.x += 1.6f;
point.y += 2.4f;
point.z += 3.2f;
}
std::cout << "target->cloud_out:" << std::endl;
for (auto& point : *cloud_out)
std::cout << point << std::endl;
std::cout << std::endl;
pcl::IterativeClosestPoint icp;
icp.setInputSource(cloud_in);
icp.setInputTarget(cloud_out);
std::cout << "default itera times: " << icp.getMaximumIterations() << std::endl;
icp.setMaximumIterations(1);
std::cout << "set itera times: " << icp.getMaximumIterations() << std::endl;
std::cout << std::endl;
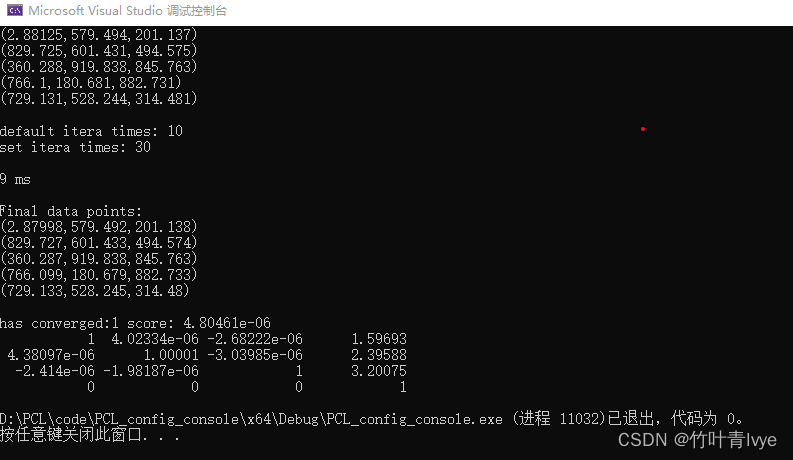
//final-> 可看到设为1时精度并没有迭代次数默认值为10高。
这边可以统计下对齐函数运行的时间,还是在上面代码的基础上
//final->
pcl::PointCloud Final;
clock_t start = clock();
icp.align(Final);
clock_t end = clock();
std::cout << end - start << " ms" << std::endl;
std::cout << std::endl; 当迭代次数设为30时,耗时9ms.
当迭代次数设为1时,耗时2ms
二. 这里改写下How to use iterative closest point中的代码,如下:
// test_vtk63.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点。
//
#include
#include
#include "vtkAutoInit.h"
//VTK_MODULE_INIT(vtkRenderingOpenGL2);
//VTK_MODULE_INIT(vtkInteractionStyle);
//#define vtkRenderingCore_AUTOINIT 2(vtkRenderingOpenGL2, vtkInteractionStyle)
#include
#include
#include
#include //pcd 读写类相关的头文件。
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace pcl;
using namespace pcl::io;
using namespace std;
int testpointcloudToPcd()
{
vtkObject::GlobalWarningDisplayOff();
pcl::PointCloud::Ptr cloud_in(new pcl::PointCloud);
char strfilepath[256] = "D:\\PCL\\rabbit.pcd";
//第一种读入方法较多场合如此
if (-1 == pcl::io::loadPCDFile(strfilepath, *cloud_in)) {
cout << "error input!" << endl;
return -1;
}
//输出源点云点坐标
std::cout << "Saved " << cloud_in->size() << " data points to input:" << std::endl;
//for (auto& point : *cloud_in)
//std::cout << point << std::endl;
//目标点云由输入点云来构造
pcl::PointCloud::Ptr cloud_out(new pcl::PointCloud);
*cloud_out = *cloud_in;
std::cout << "size:" << cloud_out->size() << std::endl;
for (auto& point : *cloud_out)
{
point.x += 0.7f;
point.y += 0.7f;
point.z += 1.0f;
}
//输出目标点云
std::cout << "Transformed " << cloud_in->size() << " data points:" << std::endl;
//for (auto& point : *cloud_out)
//std::cout << point << std::endl;
pcl::io::savePCDFileASCII("D:\\PCL\\rabbit_trans.pcd", *cloud_out);
pcl::IterativeClosestPoint icp;
icp.setInputSource(cloud_in);
icp.setInputTarget(cloud_out);
pcl::PointCloud Final;
icp.align(Final);
std::cout << "has converged:" << icp.hasConverged() << " score: " <<
icp.getFitnessScore() << std::endl;
std::cout << "Final data points size: " << Final.size() << std::endl;
pcl::io::savePCDFileASCII("D:\\PCL\\Final.pcd", Final);
//输出变换矩阵
std::cout << icp.getFinalTransformation() << std::endl;
}
int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
testpointcloudToPcd();
return 0;
}
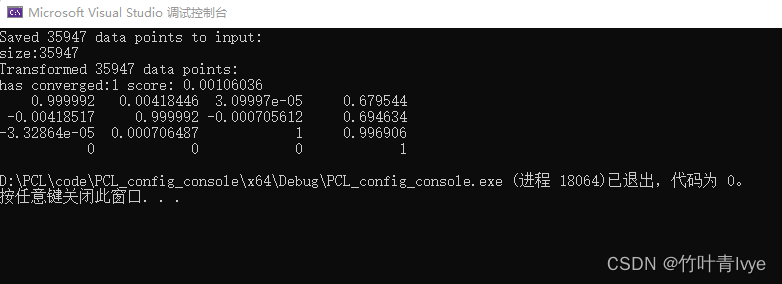
目标点云由输入点云变换得到,同时也保存到了本地,方便下次直接加载。运行结果如下:
理论上目标点云是由源点云x平移0.7,y平移0.7,z平移1获得。实际计算结果是如下矩阵的最后一列。和理论变换值还是有一些差距的。
输入源点云,目标点云,Final点云的部分点坐标做了一个比较。可以看到源点云经过变换后,已经和目标点云很对齐了。
这里上传下上面的三份点云文件。
链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1LUB9jLOG1eIq8JT4wheqHw
提取码:pfsy
三. 小实验1
读取两份点云,在窗口中拆分显示, 测试点云来自于mirrors / pointcloudlibrary / data · GitCode
#include // for pcl::make_shared
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using pcl::visualization::PointCloudColorHandlerGenericField;
using pcl::visualization::PointCloudColorHandlerCustom;
//convenient typedefs
typedef pcl::PointXYZ PointT;
typedef pcl::PointCloud PointCloud;
typedef pcl::PointNormal PointNormalT;
typedef pcl::PointCloud PointCloudWithNormals;
int main()
{
PointCloud::Ptr cloud_src(new PointCloud);
PointCloud::Ptr cloud_tgt(new PointCloud);
pcl::io::loadPCDFile("D://PCL//data-master//tutorials//pairwise//capture0001.pcd", *cloud_src);
pcl::io::loadPCDFile("D://PCL//data-master//tutorials//pairwise//capture0005.pcd", *cloud_tgt);
std::cout << "cloud_src size: " << cloud_src->size() << std::endl;
std::cout << "cloud_target size: " << cloud_tgt->size() << std::endl;
pcl::VoxelGrid grid;
PointCloud::Ptr src(new PointCloud);
PointCloud::Ptr tgt(new PointCloud);
grid.setLeafSize(0.05, 0.05, 0.05);
grid.setInputCloud(cloud_src);
grid.filter(*src);
std::cout << "src size: " << src->size() << std::endl;
grid.setInputCloud(cloud_tgt);
grid.filter(*tgt);
std::cout << "target size: " << tgt->size() << std::endl;
pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer* p;
int vp_1, vp_2;
p = new pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer("view");
p->createViewPort(0.0, 0, 0.5, 1.0, vp_1);
p->createViewPort(0.5, 0, 1.0, 1.0, vp_2);
PointCloudColorHandlerCustom src_h(cloud_src, 255, 0, 0);
PointCloudColorHandlerCustom tgt_h(cloud_tgt, 0, 255, 0);
p->addPointCloud(cloud_src, src_h, "vp1_src", vp_1);
p->addPointCloud(cloud_tgt, tgt_h, "vp1_target", vp_1);
p->addPointCloud(cloud_tgt, tgt_h, "vp2_target", vp_2);
p->spin();
return (0);
}
运行结果如下:
四. 小实验2
上面main函数中的代码修改为如下:
PointCloud::Ptr cloud_src(new PointCloud);
PointCloud::Ptr cloud_tgt(new PointCloud);
pcl::io::loadPCDFile("D://PCL//data-master//tutorials//pairwise//capture0001.pcd", *cloud_src);
pcl::io::loadPCDFile("D://PCL//data-master//tutorials//pairwise//capture0005.pcd", *cloud_tgt);
std::cout << "cloud_src size: " << cloud_src->size() << std::endl;
std::cout << "cloud_target size: " << cloud_tgt->size() << std::endl;
pcl::VoxelGrid grid;
PointCloud::Ptr src(new PointCloud);
PointCloud::Ptr tgt(new PointCloud);
grid.setLeafSize(0.05, 0.05, 0.05);
grid.setInputCloud(cloud_src);
grid.filter(*src);
std::cout << "src size: " << src->size() << std::endl;
grid.setInputCloud(cloud_tgt);
grid.filter(*tgt);
std::cout << "target size: " << tgt->size() << std::endl;
// Compute surface normals and curvature
PointCloudWithNormals::Ptr points_with_normals_src(new PointCloudWithNormals);
PointCloudWithNormals::Ptr points_with_normals_tgt(new PointCloudWithNormals);
pcl::NormalEstimation norm_est;
pcl::search::KdTree::Ptr tree(new pcl::search::KdTree());
norm_est.setSearchMethod(tree);
norm_est.setKSearch(30);
norm_est.setInputCloud(src);
norm_est.compute(*points_with_normals_src);
pcl::copyPointCloud(*src, *points_with_normals_src);
norm_est.setInputCloud(tgt);
norm_est.compute(*points_with_normals_tgt);
pcl::copyPointCloud(*tgt, *points_with_normals_tgt);
pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer* p;
int vp_1, vp_2;
p = new pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer("view");
p->createViewPort(0.0, 0, 0.5, 1.0, vp_1);
p->createViewPort(0.5, 0, 1.0, 1.0, vp_2);
PointCloudColorHandlerCustom src_h(points_with_normals_src, 255, 0, 0);
PointCloudColorHandlerCustom tgt_h(points_with_normals_tgt, 0, 255, 0);
p->addPointCloud(points_with_normals_src, src_h, "vp1_src", vp_1);
p->addPointCloud(points_with_normals_tgt, tgt_h, "vp1_target", vp_1);
p->addPointCloud(points_with_normals_tgt, tgt_h, "vp2_target", vp_2);
p->spin();
return (0); 运行结果如下:
若注释掉上面代码中copyPointCloud部分两句
//pcl::copyPointCloud(*src, *points_with_normals_src);
norm_est.setInputCloud(tgt);
norm_est.compute(*points_with_normals_tgt);
//pcl::copyPointCloud(*tgt, *points_with_normals_tgt);运行结果如下:
五. 小实验3
对上面两个点云进行配准,迭代次数设为30。
#include // for pcl::make_shared
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using pcl::visualization::PointCloudColorHandlerGenericField;
using pcl::visualization::PointCloudColorHandlerCustom;
//convenient typedefs
typedef pcl::PointXYZ PointT;
typedef pcl::PointCloud PointCloud;
typedef pcl::PointNormal PointNormalT;
typedef pcl::PointCloud PointCloudWithNormals;
// Define a new point representation for < x, y, z, curvature >
class MyPointRepresentation : public pcl::PointRepresentation < PointNormalT>
{
using pcl::PointRepresentation::nr_dimensions_;
public:
MyPointRepresentation()
{
// Define the number of dimensions
nr_dimensions_ = 4;
}
// Override the copyToFloatArray method to define our feature vector
virtual void copyToFloatArray(const PointNormalT & p, float* out) const
{
// < x, y, z, curvature >
out[0] = p.x;
out[1] = p.y;
out[2] = p.z;
out[3] = p.curvature;
}
};
int main()
{
PointCloud::Ptr cloud_src(new PointCloud);
PointCloud::Ptr cloud_tgt(new PointCloud);
pcl::io::loadPCDFile("D://PCL//data-master//tutorials//pairwise//capture0001.pcd", *cloud_src);
pcl::io::loadPCDFile("D://PCL//data-master//tutorials//pairwise//capture0005.pcd", *cloud_tgt);
std::cout << "cloud_src size: " << cloud_src->size() << std::endl;
std::cout << "cloud_target size: " << cloud_tgt->size() << std::endl;
pcl::VoxelGrid grid;
PointCloud::Ptr src(new PointCloud);
PointCloud::Ptr tgt(new PointCloud);
grid.setLeafSize(0.05, 0.05, 0.05);
grid.setInputCloud(cloud_src);
grid.filter(*src);
std::cout << "src size: " << src->size() << std::endl;
grid.setInputCloud(cloud_tgt);
grid.filter(*tgt);
std::cout << "target size: " << tgt->size() << std::endl;
// Compute surface normals and curvature
PointCloudWithNormals::Ptr points_with_normals_src(new PointCloudWithNormals);
PointCloudWithNormals::Ptr points_with_normals_tgt(new PointCloudWithNormals);
pcl::NormalEstimation norm_est;
pcl::search::KdTree::Ptr tree(new pcl::search::KdTree());
norm_est.setSearchMethod(tree);
norm_est.setKSearch(30);
norm_est.setInputCloud(src);
norm_est.compute(*points_with_normals_src);
pcl::copyPointCloud(*src, *points_with_normals_src);
norm_est.setInputCloud(tgt);
norm_est.compute(*points_with_normals_tgt);
pcl::copyPointCloud(*tgt, *points_with_normals_tgt);
//
// Instantiate our custom point representation (defined above) ...
MyPointRepresentation point_representation;
// ... and weight the 'curvature' dimension so that it is balanced against x, y, and z
float alpha[4] = { 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0 };
point_representation.setRescaleValues(alpha);
// Align
pcl::IterativeClosestPointNonLinear reg;
reg.setTransformationEpsilon(1e-6);
// Set the maximum distance between two correspondences (src<->tgt) to 10cm
// Note: adjust this based on the size of your datasets
reg.setMaxCorrespondenceDistance(0.1);
// Set the point representation
reg.setPointRepresentation(pcl::make_shared(point_representation));
reg.setInputSource(points_with_normals_src);
reg.setInputTarget(points_with_normals_tgt);
PointCloudWithNormals::Ptr reg_result(new PointCloudWithNormals);
reg.setMaximumIterations(30);
reg.align(*reg_result);
Eigen::Matrix4f transform = reg.getFinalTransformation();
std::cout << "has converaged: " << reg.hasConverged() << " score: " << reg.getFitnessScore() << std::endl;
std::cout << "transform: " << std::endl;
std::cout << transform << std::endl;
std::cout << std::endl;
pcl::io::savePCDFileASCII("D:\\PCL\\trans_method1_final.pcd", *reg_result);
pcl::io::savePCDFileASCII("D:\\PCL\\trans_method1_out.pcd", *points_with_normals_tgt);
PointCloudWithNormals::Ptr transform_src(new PointCloudWithNormals);
pcl::transformPointCloud(*points_with_normals_src, *transform_src, transform);
pcl::io::savePCDFileASCII("D:\\PCL\\trans_method1_tranform_src.pcd", *transform_src);
//
pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer* p;
int vp_1, vp_2;
p = new pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer("view");
p->createViewPort(0.0, 0, 0.5, 1.0, vp_1);
p->createViewPort(0.5, 0, 1.0, 1.0, vp_2);
PointCloudColorHandlerCustom src_h(points_with_normals_src, 255, 0, 0);
PointCloudColorHandlerCustom tgt_h(points_with_normals_tgt, 0, 255, 0);
PointCloudColorHandlerCustom final_h(reg_result, 0, 0, 255);
p->addPointCloud(points_with_normals_src, src_h, "vp1_src", vp_1);
p->addPointCloud(reg_result, final_h, "reg_result", vp_1);
p->addPointCloud(points_with_normals_src, src_h, "vp1_src_copy", vp_2);
p->addPointCloud(points_with_normals_tgt, tgt_h, "vp2_target", vp_2);
p->spin();
return (0);
}
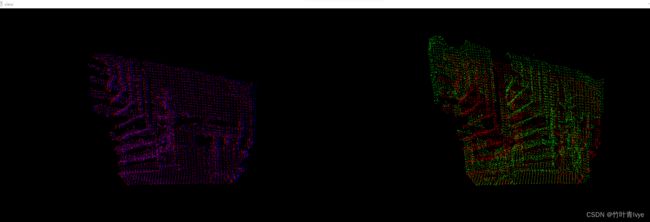
运行效果如下(左边显示的是对齐后的点云和目标点云,右边是源点云和目标点云),左边两组点云的一致性很好,而右边两组由于未对齐,可看到是错乱分布的。
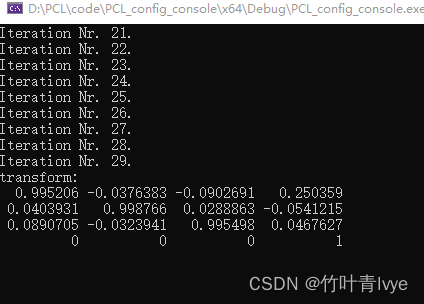
源点云到目标点云迭代30次配准的变换矩阵如下:
由变换矩阵将源点云映射得到的点云和直接通过配准函数获得的对齐后点云,部分数据如下,很接近。
六. 小实验4
将ICP的最小迭代次数设为1,外面加一个循环执行此过程30次。
#include // for pcl::make_shared
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using pcl::visualization::PointCloudColorHandlerGenericField;
using pcl::visualization::PointCloudColorHandlerCustom;
//convenient typedefs
typedef pcl::PointXYZ PointT;
typedef pcl::PointCloud PointCloud;
typedef pcl::PointNormal PointNormalT;
typedef pcl::PointCloud PointCloudWithNormals;
// Define a new point representation for < x, y, z, curvature >
class MyPointRepresentation : public pcl::PointRepresentation < PointNormalT>
{
using pcl::PointRepresentation::nr_dimensions_;
public:
MyPointRepresentation()
{
// Define the number of dimensions
nr_dimensions_ = 4;
}
// Override the copyToFloatArray method to define our feature vector
virtual void copyToFloatArray(const PointNormalT & p, float* out) const
{
// < x, y, z, curvature >
out[0] = p.x;
out[1] = p.y;
out[2] = p.z;
out[3] = p.curvature;
}
};
int main()
{
PointCloud::Ptr cloud_src(new PointCloud);
PointCloud::Ptr cloud_tgt(new PointCloud);
pcl::io::loadPCDFile("D://PCL//data-master//tutorials//pairwise//capture0001.pcd", *cloud_src);
pcl::io::loadPCDFile("D://PCL//data-master//tutorials//pairwise//capture0005.pcd", *cloud_tgt);
std::cout << "cloud_src size: " << cloud_src->size() << std::endl;
std::cout << "cloud_target size: " << cloud_tgt->size() << std::endl;
pcl::VoxelGrid grid;
PointCloud::Ptr src(new PointCloud);
PointCloud::Ptr tgt(new PointCloud);
grid.setLeafSize(0.05, 0.05, 0.05);
grid.setInputCloud(cloud_src);
grid.filter(*src);
std::cout << "src size: " << src->size() << std::endl;
grid.setInputCloud(cloud_tgt);
grid.filter(*tgt);
std::cout << "target size: " << tgt->size() << std::endl;
// Compute surface normals and curvature
PointCloudWithNormals::Ptr points_with_normals_src(new PointCloudWithNormals);
PointCloudWithNormals::Ptr points_with_normals_tgt(new PointCloudWithNormals);
pcl::NormalEstimation norm_est;
pcl::search::KdTree::Ptr tree(new pcl::search::KdTree());
norm_est.setSearchMethod(tree);
norm_est.setKSearch(30);
norm_est.setInputCloud(src);
norm_est.compute(*points_with_normals_src);
pcl::copyPointCloud(*src, *points_with_normals_src);
norm_est.setInputCloud(tgt);
norm_est.compute(*points_with_normals_tgt);
pcl::copyPointCloud(*tgt, *points_with_normals_tgt);
//
// Instantiate our custom point representation (defined above) ...
MyPointRepresentation point_representation;
// ... and weight the 'curvature' dimension so that it is balanced against x, y, and z
float alpha[4] = { 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0 };
point_representation.setRescaleValues(alpha);
// Align
pcl::IterativeClosestPointNonLinear reg;
reg.setTransformationEpsilon(1e-6);
// Set the maximum distance between two correspondences (src<->tgt) to 10cm
// Note: adjust this based on the size of your datasets
reg.setMaxCorrespondenceDistance(0.1);
// Set the point representation
reg.setPointRepresentation(pcl::make_shared(point_representation));
reg.setInputSource(points_with_normals_src);
reg.setInputTarget(points_with_normals_tgt);
//
// Run the same optimization in a loop and visualize the results
Eigen::Matrix4f Ti = Eigen::Matrix4f::Identity(), prev, targetToSource;
PointCloudWithNormals::Ptr reg_result = points_with_normals_src;
reg.setMaximumIterations(1);
pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer* p;
p = new pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer("view");
for (int i = 0; i < 30; ++i)
{
PCL_INFO("Iteration Nr. %d.\n", i);
// save cloud for visualization purpose
points_with_normals_src = reg_result;
// Estimate
reg.setInputSource(points_with_normals_src);
reg.align(*reg_result);
//accumulate transformation between each Iteration
Ti = reg.getFinalTransformation() * Ti;
//if the difference between this transformation and the previous one
//is smaller than the threshold, refine the process by reducing
//the maximal correspondence distance
if (std::abs((reg.getLastIncrementalTransformation() - prev).sum()) < reg.getTransformationEpsilon())
reg.setMaxCorrespondenceDistance(reg.getMaxCorrespondenceDistance() - 0.001);
prev = reg.getLastIncrementalTransformation();
// visualize current state
p->removePointCloud("source");
p->removePointCloud("target");
PointCloudColorHandlerGenericField src_color_handler(points_with_normals_src, "curvature");
if (!src_color_handler.isCapable())
PCL_WARN("Cannot create curvature color handler!\n");
PointCloudColorHandlerGenericField tgt_color_handler(points_with_normals_tgt, "curvature");
if (!tgt_color_handler.isCapable())
PCL_WARN("Cannot create curvature color handler!\n");
p->addPointCloud(points_with_normals_src, src_color_handler, "source");
p->addPointCloud(points_with_normals_tgt, tgt_color_handler, "target");
p->spinOnce();
}
std::cout << "transform: " << std::endl;
std::cout << Ti << std::endl;
std::cout << std::endl;
pcl::io::savePCDFileASCII("D:\\PCL\\trans_method2_final.pcd", *reg_result);
return (0);
}
运行结果如下(可看到和上面一次迭代次数设为30的方法对比,结果是一致的,只是这样做的一个好处是可以对齐过程可视化,不像上面黑盒子一样):
七. 两个点云的融合(相加)
#include // for pcl::make_shared
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using pcl::visualization::PointCloudColorHandlerGenericField;
using pcl::visualization::PointCloudColorHandlerCustom;
//convenient typedefs
typedef pcl::PointXYZ PointT;
typedef pcl::PointCloud PointCloud;
typedef pcl::PointNormal PointNormalT;
typedef pcl::PointCloud PointCloudWithNormals;
int main()
{
PointCloud::Ptr cloud_src(new PointCloud);
PointCloud::Ptr cloud_tgt(new PointCloud);
pcl::io::loadPCDFile("D://PCL//data-master//tutorials//pairwise//capture0001.pcd", *cloud_src);
pcl::io::loadPCDFile("D://PCL//data-master//tutorials//pairwise//capture0005.pcd", *cloud_tgt);
std::cout << "cloud_src size: " << cloud_src->size() << std::endl;
std::cout << "cloud_target size: " << cloud_tgt->size() << std::endl;
pcl::VoxelGrid grid;
PointCloud::Ptr src(new PointCloud);
PointCloud::Ptr tgt(new PointCloud);
grid.setLeafSize(0.05, 0.05, 0.05);
grid.setInputCloud(cloud_src);
grid.filter(*src);
std::cout << "src size: " << src->size() << std::endl;
grid.setInputCloud(cloud_tgt);
grid.filter(*tgt);
std::cout << "target size: " << tgt->size() << std::endl;
pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer* p;
int vp_1, vp_2;
p = new pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer("view");
p->createViewPort(0.0, 0, 0.5, 1.0, vp_1);
p->createViewPort(0.5, 0, 1.0, 1.0, vp_2);
PointCloudColorHandlerCustom src_h(cloud_src, 255, 0, 0);
PointCloudColorHandlerCustom tgt_h(cloud_tgt, 0, 255, 0);
p->addPointCloud(cloud_src, src_h, "vp1_src", vp_1);
p->addPointCloud(cloud_tgt, tgt_h, "vp1_target", vp_1);
PointCloud::Ptr total(new PointCloud);
total = cloud_src;
*total += *cloud_tgt;
PointCloudColorHandlerCustom total_h(total, 0, 0, 255);
p->addPointCloud(total, total_h, "vp2_target", vp_2);
p->spin();
return (0);
}
运行效果如下:
八. How to incrementally register pairs of clouds
有了上面的例子后,再去看官网上的这段代码就很容易了
How to incrementally register pairs of clouds — Point Cloud Library 0.0 documentation
代码会加载5张点云数据,A,B,C,D,E分别代表这5个点云,然后AB,BC,CD,DE分别两两配准,这样就可以把B,C,D,E都变换到A空间中去, 向A对齐,完毕后将这5个点云数据做融合(相加),这样就可以实现一个拼接或者融合的功能,后续任务就可以基于这份包含更细致信息的点云做文章。