点云配准5:4pcs算法在pcl上的实现
目录
- 配准结果
- 点云配准系列
- 准备
- 完整项目文件
- 参数设定及说明
-
- 数据
- 参数
- 代码
- 结果
-
- Bunny
- hippo
- 算法缺点
- 参考及感谢
- 完
配准结果
偶尔效果比较好,白色是目标点云0°的Bunny,紫红色是配准后的45°Bunny点云

点云配准系列
点云配准1:配准基础及icp算法
点云配准2:icp算法在PCL1.10.0上的实现+源码解析
点云配准3:3d-ndt算法在pcl上的实现以及参数设置
点云配准4:cloudcompare的使用以及点云配准功能
点云配准5:4pcs算法在pcl上的实现
点云配准6:tricp算法在pcl上的实现
点云配准论文阅读笔记–Efficient Variants of the ICP Algorithm
点云配准论文阅读笔记–Comparing ICP variants on real-world data sets
点云配准论文阅读笔记–(4PCS)4-Points Congruent Sets for Robust Pairwise Surface Registration
点云配准论文阅读笔记–3d-dnt博士论文
准备
本实例是在visual studio2019+pcl1.10.0上进行,环境配置方法在之前的博客已进行详细说明:
vs2019配置pcl1.10.0+点云可视化示例
完整项目文件
免费下载地址:share_noel/PCL/4pcs/4pcs_registration_carlos202012.zip
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_41102371/article/details/125646840
愿意用c币支持的朋友也可在此下载:
4pcs_registration_carlos202012.zip
(上述下载链接中csdn与网盘的文件完全相同,只不过网盘免费下载)
参数设定及说明
数据
配准点云来自斯坦福的兔子点云,本文使用其中0度及45度扫描点云,但经过放大处理,xyz都放大了100倍。原因是原点云太小,导致阈值不好控制。比如对于原点云来说,点间距离本来就特别小,即使是非正确对应点。
本文将45度点云配准至0度点云。
参数
delta的可通过以下方式调节:
delta太小,结果是输出的是单位矩阵,应该增大delta;
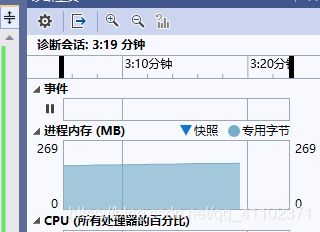
delta太大,结果是运行很久,内存一直增加,可能还会占满电脑所有内存然后程序崩掉,应该减小delta
vs2019可以直接查看内存情况,若非vs2019则可打开任务管理器
代码
#include 结果
Bunny
原始位置:
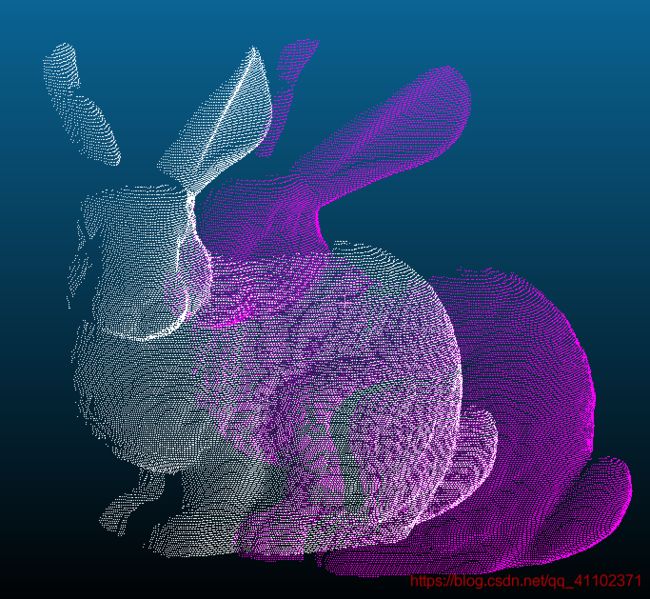

配准后:
偶尔效果比较好

效果不是很好情况,必须进行进一步精配准
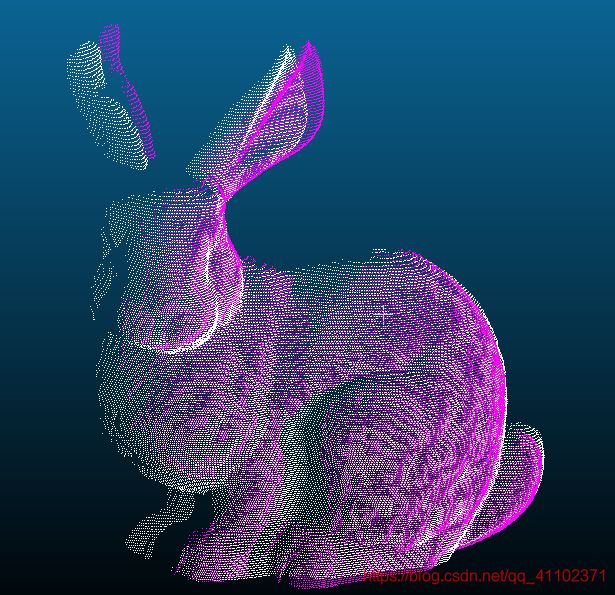

有时候直接跑偏
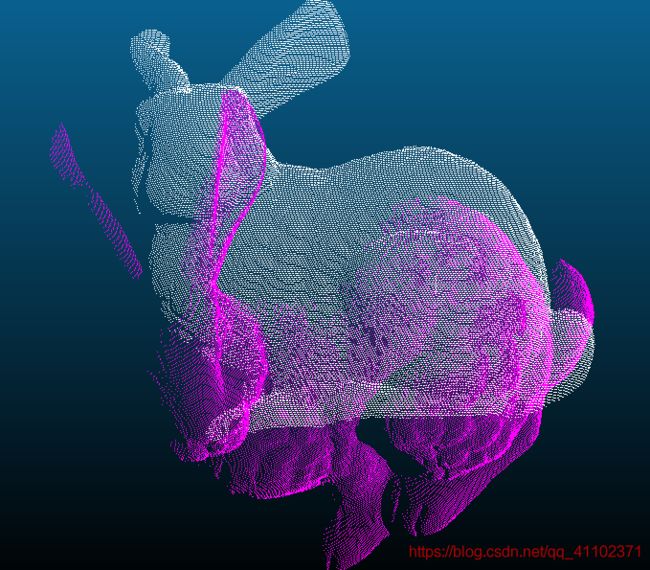

上述三种结果都是在同一参数下获得,可见每次的结果不一样,而且不稳定
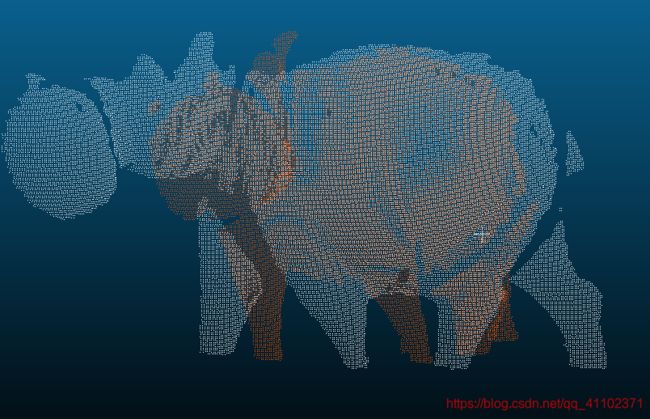
hippo
配准后:
相对较好情况
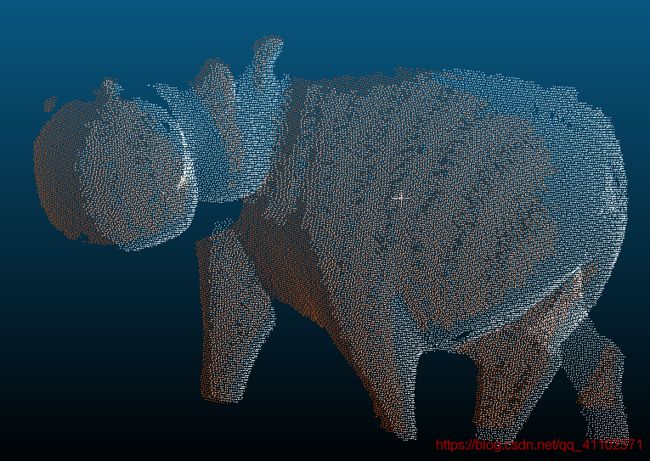

不是太好

跑偏
实验的时候可以将代码中被注释掉的for循环部分放开,每次得到一个矩阵,然后复制矩阵,使用cloudcompare查看变换结果,就不用每次通过代码可视化然后又重新运行来记录结果了。
cloudcompare直接使用矩阵来对点云进行空间变换方法:
点云配准4:cloudcompare的使用以及点云配准功能
算法缺点
从使用角度来看,4pcs算法与3d-ndt一样,参数设定要根据不同的模型有不同的设定。所以针对某一待配准点云模型来说,最优的参数设定得慢慢找。
从原理角度,4pcs每次都是随机地采样,所以出来的结果每次是不一样的,而icp与3d-ndt在同样参数的情况下出来的结果是一样的,相对更好调参数;即使在最优的参数下,经过多次重复实验,发现会出现配准效果差或者直接跑偏的情况,这就感觉算法不稳定。
参考及感谢
paper:
Aiger D , Mitra N J , Cohen-Or D . 4-points congruent sets for robust pairwise surface registration[J]. Acm Transactions on Graphics, 2008, 27(3):1-10.
blog:
点云配准——(2)四点法
其余文中已列出
完
边学边用,如有错漏,敬请指正
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------诺有缸的高飞鸟20201226
