损失函数:交叉熵、KLDivLoss、标签平滑(LabelSmoothing)
写在前面的话:input或x表示模型预测结果,target表示标签
1. torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss()是交叉熵计算,输入的预测值不需要进行softmax,也不需要进行log运算!!!!直接用原始的预测输出,标签用整数序列。
官网说明:
The `input` is expected to contain raw, unnormalized scores for each class. `input` size: (minibatch, C)
`target` : 1D tensor of size `minibatch`
2. torch.nn KLDivLoss()是计算KL散度的损失函数,要将模型输出的原始预测值要先进行softmax,然后进行log运算(torch.nn.functional.log_softmax可以直接实现),得到结果作为input输入到KLDivLoss中。target是二维的,形状与input一样
Shape:
- Input: :math:`(N, *)` where :math:`*` means, any number of additional
dimensions
- Target: :math:`(N, *)`, same shape as the input
- Output: scalar by default. If :attr:``reduction`` is ``'none'``, then :math:`(N, *)`,
the same shape as the input
size_average=False
nn.KLDivLoss_咕噜咕噜day的博客-CSDN博客_kldivloss pytorch
KLDivLoss
作用:
用于连续分布的距离度量;并且对离散采用的连续输出空间分布进行回归通常很有用;用label_smoothing就采用这个;
公式:
![]()
![]()
![]()
所以这里 xn=log(q(xi)),所以预测值要进行log运算之后再传入到kldivloss函数中
![]()
公式理解:
p(x)是真实分布,q(x)是拟合分布;实际计算时;通常p(x)作为target,只是概率分布;而xn则是把输出做了LogSoftmax计算;即把概率分布映射到log空间;所以
K-L散度值实际是看log(p(x))-log(q(x))的差值,差值越小,说明拟合越相近。
pytorch使用:
![]()
当前版本torch(1.3.1)要想获得真正的KL散度;设置:
reduce=False;size_average=False
(reduce默认也是True,返回所有元素loss的和;size_average=默认是True,是对batch中每个元素进行求平均,当为False时,返回各样本各维度的loss之和;
因为reduce为False会忽略size_average参数,所以其实只需要把reduce=False即可)
二、Label Smoothing
Pytorch:交叉熵损失(CrossEntropyLoss)以及标签平滑(LabelSmoothing)的实现_我是大黄同学呀的博客-CSDN博客_标签平滑交叉熵
Label Smoothing也称之为标签平滑,其实是一种防止过拟合的正则化方法。传统的分类loss采用softmax loss,先对全连接层的输出计算softmax,视为各类别的置信度概率,再利用交叉熵计算损失。
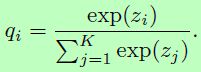 |
(1) |
 |
(2) |
三、CrossEntropyLoss
Pytorch:交叉熵损失(CrossEntropyLoss)以及标签平滑(LabelSmoothing)的实现_我是大黄同学呀的博客-CSDN博客_标签平滑交叉熵
实现 pytorch 中 torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss_Agwave的博客-CSDN博客
相信大家对于如何计算交叉熵已经非常熟悉,常规步骤是①计算softmax得到各类别置信度;②计算交叉熵损失。但其实从Pytorch的官方文档可以看出,还有更一步到位的方法,如下:
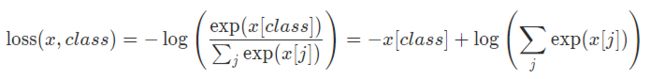 |
(3) |
x 的维度是 (batch_size, C)
class 的维度是 (batch_size)
(这里的 C 是分类的个数)
所以交叉熵最通俗的理解:目标标签值(class)对应的预测概率(softmax)取对数(-log,注意负号),即为交叉熵。交叉熵之所以可以(2)式写成(3)式,是因为在(2)式中,pi是真实标签值,在遍历i的过程中,除了正确的标签值为1,其余的标签值都为0。所以用(2)式时,标签要用one-hot进行编码,用(3)式时,只需要标签的整数形式即可。
综合示例:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Created on 2021/8/9 16:52
@author: Janben
参考链接:
1. 交叉熵:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_41805511/article/details/99438838
2. KLDivLoss: https://blog.csdn.net/qq_36533552/article/details/104034759
3. LabelSmoothing: https://blog.csdn.net/qq_36560894/article/details/118424356
"""
import numpy as np
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as Function
from torch.autograd import Variable
import warnings
warnings.simplefilter('ignore')
class MyCrossEntropyLoss():
def __init__(self, weight=None, size_average=True):
"""
初始化参数,因为要实现 torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss 的两个比较重要的参数
:param weight: 给予每个类别不同的权重
:param size_average: 是否要对 loss 求平均
"""
self.weight = weight
self.size_average = size_average
def __call__(self, input, target):
"""
计算损失
这个方法让类的实例表现的像函数一样,像函数一样可以调用
:param input: (batch_size, C),C是类别的总数
:param target: (batch_size, 1)
:return: 损失
"""
batch_loss = 0.
for i in range(input.shape[0]):
# print('***',input[i, target[i]],i,target[i],np.exp(input[i, :]))
numerator = torch.exp(input[i, target[i]]) # 分子
denominator = torch.sum(torch.exp(input[i, :])) # 分母
# 计算单个损失
loss = -torch.log(numerator / denominator)
if self.weight:
loss = self.weight[target[i]] * loss
print("单个损失: ",loss)
# 损失累加
batch_loss += loss
# 整个 batch 的总损失是否要求平均
if self.size_average == True:
batch_loss /= input.shape[0]
return batch_loss
class MyKLDivLossFunc(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,reduce = True):
super(MyKLDivLossFunc,self).__init__()
self.reduce = reduce
def forward(self,x,target):
logtarget = torch.log(target+0.00001) #加一个非常小的数,防止当target中有0时log得到-inf
loss = target*(logtarget-x)
if self.reduce == False:
return loss
else:
return torch.sum(loss)
class LabelSmoothingLoss(nn.Module):
"Implement label smoothing."
def __init__(self, class_num, smoothing):
'''
:param class_num: 有5个类别,那么class_num=5
:param smoothing: 标签平滑的程度,为0时表示不进行标签平滑
'''
super(LabelSmoothingLoss, self).__init__()
self.confidence = 1.0 - smoothing
self.smoothing = smoothing
self.class_num = class_num
# self.criterion = nn.KLDivLoss(size_average=True)
# self.criterion = nn.KLDivLoss(size_average=False)
def forward(self, x, target):
'''
:param x: 预测结果,形状为(batchsize,classnum)
:param target: 真实标签,形状为(batchsize,)
:return:
'''
# print(x.shape)
assert x.size(1) == self.class_num
# if self.smoothing <=0.0 or self.smoothing == None:
if self.smoothing == None:
return nn.CrossEntropyLoss()(x,target)
true_dist = x.data.clone()
true_dist.fill_(self.smoothing / (self.class_num-1))
true_dist.scatter_(1, target.data.unsqueeze(1), self.confidence) #此行代码实现了标签平滑
#计算交叉熵,与nn.CrossEntropyLoss()公式一样,所以当smoothing=0.0时,输出的损失值与nn.CrossEntropyLoss()的一样的
logprobs = Function.log_softmax(x,dim=1) #softmax+log
mean_loss = -torch.sum(true_dist*logprobs)/x.size(-2) #平均损失,所以要除以样本数量
return mean_loss,true_dist
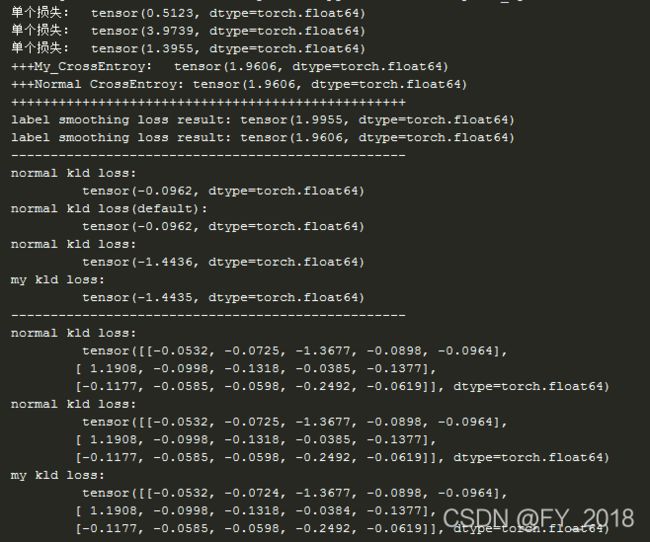
if __name__ == "__main__":
input = np.array([[-1.5616, -0.7906, 1.4143, -0.0957, 0.1657],
[-1.4285, 0.3045, 1.5844, -2.1508, 1.8181],
[ 1.0205, -1.3493, -1.2965, 0.1715, -1.2118]])
target = np.array([2, 0, 3])
test_input = torch.from_numpy(input)
test_target = torch.from_numpy(target).long()
#自定义的交叉熵函数
criterion = MyCrossEntropyLoss()
# 类中实现了 __call__,所以类实例可以像函数一样可以调用
loss = criterion(test_input, test_target)
print("+++My_CrossEntroy: ", loss) #输出: tensor(1.9606, dtype=torch.float64)
#torch.nn中库函数
#The `input` is expected to contain raw, unnormalized scores for each class.
#Input: 形状为(N, C)` where `C = number of classes`,N是batchsize
#交叉熵的input不需要进行任何标准化(不需要softmax,不需要log),用原始的数据
#Target: :math:`(N)`
test_loss = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
test_out = test_loss(test_input,test_target)
print('+++Normal CrossEntroy:',test_out) #test loss: tensor(1.9606, dtype=torch.float64)
print('+'*50)
lloss = LabelSmoothingLoss(5,smoothing=0.1)
loss_result, true_dist = lloss.forward(test_input,test_target)
print('label smoothing loss result:',loss_result) #label smoothing loss result: tensor(2.2265, dtype=torch.float64)
lloss = LabelSmoothingLoss(5,smoothing=0.)
loss_result,_ = lloss.forward(test_input,test_target)
print('label smoothing loss result:',loss_result)
print('-' * 50) #以下是验证自定义的KLDivLoss的正确性
#以下的test_input要理解为已经完成log运算之后的数据
print('normal kld loss:\n\t\t', nn.KLDivLoss(size_average=True, reduce=True)(test_input, Variable(true_dist, requires_grad=False)))
print('normal kld loss(default):\n\t\t',nn.KLDivLoss()(test_input,Variable(true_dist,requires_grad=False))) #默认size_average=True, reduce=True
print('normal kld loss:\n\t\t', nn.KLDivLoss(size_average=False, reduce=True)(test_input, Variable(true_dist, requires_grad=False)))
print('my kld loss:\n\t\t', MyKLDivLossFunc(reduce=True)(test_input, true_dist)) #自己实现的不进行size_average,size_average是指除以元素个数,本例中元素个数为15
print('-'*50)
print('normal kld loss:\n\t\t', nn.KLDivLoss(size_average=True, reduce=False)(test_input, Variable(true_dist, requires_grad=False)))
print('normal kld loss:\n\t\t', nn.KLDivLoss(size_average=False, reduce=False)(test_input, Variable(true_dist, requires_grad=False)))
print('my kld loss:\n\t\t', MyKLDivLossFunc(reduce=False)(test_input, true_dist))
p = torch.Tensor([[0,0.1,0.3],[0.1,0.9,0.3],[0,0.1,0.]])
t = torch.Tensor([[0,0,1.],[0,1.,0],[1.,0,0]])
c = nn.KLDivLoss(size_average=False)
print(c(p,t))
print(MyKLDivLossFunc()(p,t))
print(torch.log(t+0.00001))运行结果: