Matplotlib可视化练习
Matplotlib 官网
Matplotlib的设计理念是能够用轻松简单的方式生成强大的可视化效果,是Python学习过程中核心库之一。
用在python中绘制数组的2D图形库
matplotlib代码在概念上分为3个部分:
1.pylab接口是由matplotlib.pylab提供的函数集,允许用户使用非常类似于MATLAB图生成代码的代码创建绘图
2.matplotlib前端或API是一组重要的类,可创建和管理图形,文本,线条,图表等(艺术家教程),是一个对输出无所了解的抽象接口
3.后端是设备相关的绘图设备,也称为渲染器,将前端表示转换为打印件或显示设备;后端示例:PS 创建 PostScript® 打印件,SVG 创建可缩放矢量图形打印件,Agg 使用 Matplotlib 附带的高质量反颗粒几何库创建 PNG 输出,GTK 在 Gtk+ 应用程序中嵌入 Matplotlib,GTKAgg 使用反颗粒渲染器创建图形并将其嵌入到 Gtk+ 应用程序中,以及用于 PDF,WxWidgets,Tkinter 等
第一步 引入库
import numpy as np
import matplotlib
import matplotlib.mlab as mlab
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
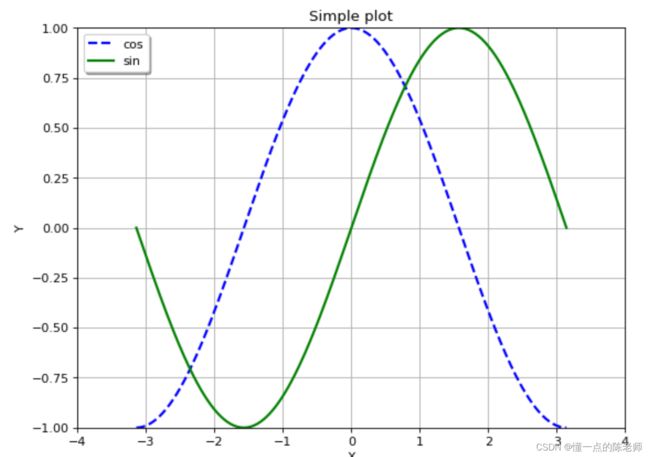
例子1:正弦函数
# 例子1
def simple_plot():
# 生成测试数据
x = np.linspace(-np.pi, np.pi, 256, endpoint=True)
y_cos, y_sin = np.cos(x), np.sin(x)
# 生成画布,并设定标题
# 画布大小,dpi=清晰度
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 6), dpi=80)
plt.title("Simple plot")
plt.grid(True) # 带网格
# 设置X轴
plt.xlabel("X")
plt.xlim(-4.0, 4.0)
plt.xticks(np.linspace(-4, 4, 9, endpoint=True))
# 设置Y轴
plt.ylabel("Y")
plt.ylim(-1.0, 1.0)
plt.yticks(np.linspace(-1, 1, 9, endpoint=True))
# 画两条曲线
plt.plot(x, y_cos, "b--", linewidth=2.0, label="cos")
plt.plot(x, y_sin, "g-", linewidth=2.0, label="sin")
# 设置图例位置,loc可以为[upper, lower, left, right, center]
plt.legend(loc="upper left",shadow=True)
# 图形显示
plt.show()
return
# 运行
simple_plot()
更复杂一点
# 更复杂一点
def simple_advanced_plot():
"""
simple advanced plot
"""
# 生成测试数据
x = np.linspace(-np.pi, np.pi, 256, endpoint=True)
y_cos, y_sin = np.cos(x), np.sin(x)
# 生成画布, 并设定标题
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 6), dpi=80)
plt.title("simple advanced plot")
plt.grid(True)
# 画图的另外一种方式
ax_1 = plt.subplot(111) # 也可以写成plt.subplot(1,1,1)
ax_1.plot(x, y_cos, color="blue", linewidth=2.0, linestyle="--", label="left cos")
ax_1.legend(loc="upper left", shadow=True)
# 设置Y轴(左边)
ax_1.set_ylabel("left cos y")
ax_1.set_ylim(-1.0, 1.0)
ax_1.set_yticks(np.linspace(-1, 1, 9, endpoint=True))
# 画图的另外一种方式
ax_2 = ax_1.twinx()
ax_2.plot(x, y_sin, color="green", linewidth=2.0, linestyle="-", label="right sin")
ax_2.legend(loc="upper right", shadow=True)
# 设置Y轴(右边)
ax_2.set_ylabel("right sin y")
ax_2.set_ylim(-2.0, 2.0)
ax_2.set_yticks(np.linspace(-2, 2, 9, endpoint=True))
# 设置X轴(共同)
ax_1.set_xlabel("x")
ax_1.set_xlim(-4.0, 4.0)
ax_1.set_xticks(np.linspace(-4, 4, 9, endpoint=True))
# 图形显示
plt.show()
return
# 运行
simple_advanced_plot()
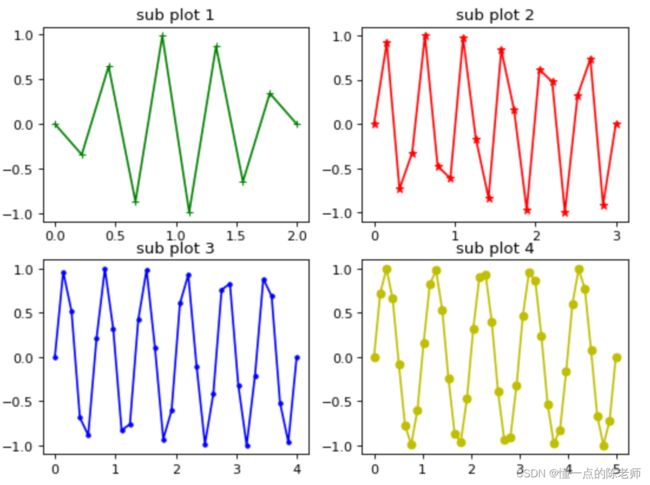
一次画多个图
# 一次画多个图
def subplot_plot():
"""
subplot plot
"""
# 子图的style列表
style_list = ["g+-", "r*-", "b.-", "yo-"]
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 6), dpi=80)
# 依次画图
for num in range(4):
# 生成测试数据
x = np.linspace(0.0, 2+num, num=10*(num+1))
y = np.sin((5-num) * np.pi * x)
# 子图的生成方式
plt.subplot(2, 2, num+1)
plt.title("sub plot %d" % (num+1))
plt.plot(x, y, style_list[num])
# 图形显示
plt.show()
return
# 运行
subplot_plot()
柱状图
# 柱状图
def bar_plot():
"""
bar plot
"""
# 生成测试数据
means_men = (20, 35, 30, 35, 27)
means_women = (25, 32, 34, 20, 25)
# 设置标题
plt.title("bar plot")
# 设置相关参数
index = np.arange(len(means_men))
bar_width = 0.35
# 画柱状图
plt.bar(index, means_men, width=bar_width, alpha=0.2, color="b", label="boy")
plt.bar(index+bar_width, means_women, width=bar_width, alpha=0.8, color="r", label="lady")
plt.legend(loc="upper right",shadow=True)
# 设置柱状图标示
for x, y in zip(index, means_men):
plt.text(x, y+0.3, y, ha="center", va="bottom")
for x, y in zip(index, means_women):
plt.text(x+bar_width, y+0.3, y, ha="center", va="bottom")
# 设置刻度范围/坐标轴名称等
plt.ylim(0, 45)
plt.xlabel("Group")
plt.ylabel("Scores")
plt.xticks(index+(bar_width/2), ("A", "B", "C", "D", "E"))
# 图形显示
plt.show()
return
# 横向柱状图
def barh_plot():
"""
barh plot
"""
# 生成测试数据
means_men = (20, 35, 30, 35, 27)
means_women = (25, 32, 34, 20, 25)
# 设置标题
plt.title("barh plot")
# 设置相关参数
index = np.arange(len(means_men))
bar_height = 0.35
# 画柱状图(水平方向)
plt.barh(index, means_men, height=bar_height, alpha=0.2, color="b", label="Men")
plt.barh(index+bar_height, means_women, height=bar_height, alpha=0.8, color="r", label="Women")
plt.legend(loc="upper right", shadow=True)
# 设置柱状图标示
for x, y in zip(index, means_men):
plt.text(y+0.3, x, y, ha="left", va="center")
for x, y in zip(index, means_women):
plt.text(y+0.3, x+bar_height, y, ha="left", va="center")
# 设置刻度范围/坐标轴名称等
plt.xlim(0, 45)
plt.xlabel("Scores")
plt.ylabel("Group")
plt.yticks(index+(bar_height/2), ("A", "B", "C", "D", "E"))
# 图形显示
plt.show()
return
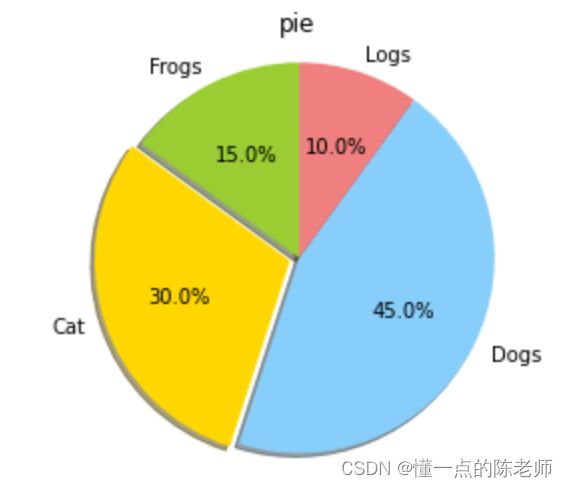
饼状图
# 饼图
def pie_plot():
"""
pie plot
"""
# 生成测试数据
sizes = [15, 30, 45, 10]
labels = ["Frogs", "Cat", "Dogs", "Logs"]
colors = ["yellowgreen", "gold", "lightskyblue", "lightcoral"]
# 设置标题
plt.title("pie")
# 设置突出参数
explode = [0, 0.05, 0, 0]
# 画饼状图
patches, l_text, p_text = plt.pie(sizes, explode=explode, labels=labels, colors=colors, autopct="%1.1f%%", shadow=True, startangle=90)
plt.axis("equal")
# 图形显示
plt.show()
return
# 运行
pie_plot()
散点图
# 散点图
def scatter_plot():
"""
scatter plot
"""
# 生成测试数据
point_count = 1000
x_index = np.random.random(point_count)
y_index = np.random.random(point_count)
# 设置标题
plt.title("scatter")
# 设置相关参数
color_list = np.random.random(point_count)
scale_list = np.random.random(point_count) * 100
# 画散点图
plt.scatter(x_index, y_index, s=scale_list, c=color_list, marker="o")
# 图形显示
plt.show()
return
# 运行
scatter_plot()