pytorch深度学习实战lesson36
第三十六课 锚框
因为我们在目标检测里面需要预测边缘框,所以给我们的预测带来了很大的问题。我们在卷积神经网络里面做图片分类的时候,整个代码写起来看上去非常简单,就是一个 soft Max 出去就完事了。但是因为有边框的加入,使得我们在预测的时候麻烦特别多。今天这里讲的一个技术是锚框。锚框就是计算机视觉算法里生成的一些用于预测的边缘框。叫anchor box。
目录
第三十六课 锚框
理论部分
实践部分
理论部分
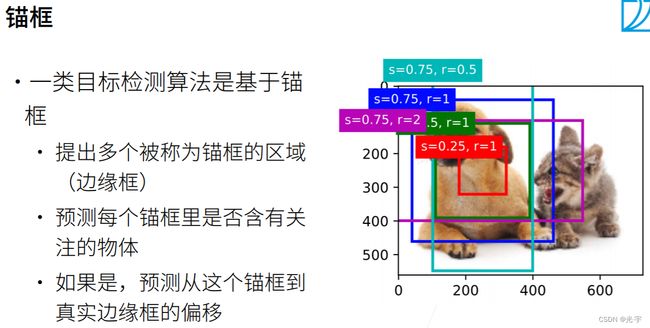
锚框就是说先对物体边框的位置进行猜测,因为我并不知道边框到底在什么地方。所以一般来讲先提出多个锚框,比如上面这张图片,提出了5 个框,我先画算法给你画出 5 个框,然后要去看这 5 个框里面有没有我要的物体。如果有,比如蓝色的框基本上跟真实边框经很近了。那么如果一个锚框里面含有我要关注的物体,接下来会基于锚框去预测锚框到正好的边框是怎么样调整过去的。所以可以看到要做两次预测,一次是锚框里面是不是含了哪一类物体,另外一个是对位置的预测。
处理毛框首先要比较两个框之间的相似度。一般来说,它用的是一个叫做 i o u 的计算标准,叫做交并比。它是一个 0 到 1 之间的数值。如果它是0,表示你两个框间没有重叠,1表示它是完全重合。越接近1,它的重合度就越高。算法是两个框的交集比上两个框的并集。基本上并集大于等于交集,所以一定是 0 和 1 之间的一个数字。
在训练集中,每个锚框视为一个训练样本,为了训练目标检测模型,需要每个锚框的类别(class,与锚框相关的对象的类别)和偏移量(offset,真实边缘框相对于锚框的偏移量)标签。在预测的时候,首先为每个图像生成多个锚框,预测所有锚框的类别和偏移量,根据预测的偏移量调整它们的位置以获得预测的边缘框,最后只输出符合特定条件的预测边缘框。
基于锚框的目标检测是首先提出多个锚框,然后对锚框是否包含所感兴趣的物体以及锚框相对于边缘框的偏移进行预测,所以在训练的时候,每一个锚框是一个训练样本
对于每一个锚框来说,要么被标注成背景(不包含所感兴趣的物体,只包含背景),要么关联上一个真实的边缘框(锚框所框住的物体的标号与所关联的边缘框所包含的物体的标号相同;锚框相对于边缘框的偏移就是相对于它所关联的边缘框的偏移,这个偏移量根据锚框和真实边缘框中心坐标的相对位置以及这两个框的相对大小进行标记)
鉴于数据集内不同的框的位置和大小不同,可以对那些相对位置和大小应用变换,使其获得分布更均匀且易于拟合的偏移量
一般来讲算法会生成大量的锚框,而只有少量的边缘框,绝大部分锚框都是背景,背景类别的锚框通常被称为“负类”锚框,其余的被称为“正类”锚框
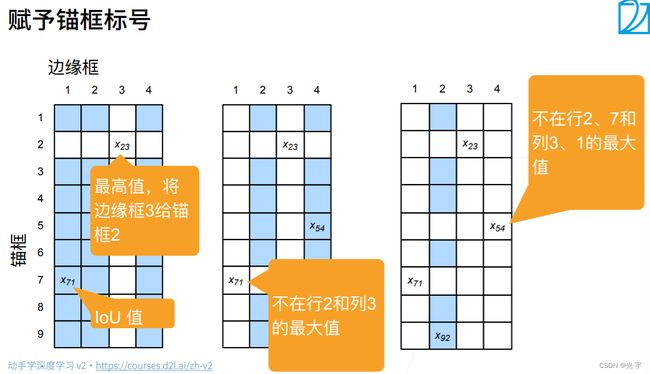
首先假设一张图片中有标注好的4个边缘框(即图片中有四个物体),而我们生成了9个锚框(实际上的锚框要比这个多很多)。
如上图所示:列表示标注的边框,行表示生成的锚框,我们将锚框和边框求IoU就得到了这个9*4矩阵。
算法思想:
每次找出矩阵中最大的那个值,这个值对应的行和列即为边框和其对应的锚框,然后将两者关联起来,之后再删除其所在的行和列。比如第一次找到的是X23,那么边框3对应的最大交并比的锚框就是2,那么两者就关联起来。
然后重复这个步骤4次即可找出所有边框对应的锚框。
这里有两点需要注意:1、付以锚框标号的操作是每次把图片读进来之后都要做的操作,假设有 9 个锚框,我就会生成一 9 个训练样本出来;2、付以锚框标号的算法各有千秋,不唯一。
在预测时会为图像生成多个锚框,然后再为这些锚框逐个预测类别和偏移量,一个预测好的边界框是根据其中某个带有预测偏移量的锚框而生成的。所以最终会得到很多相似的具有明显重叠的预测边缘框,而且都是围绕着同一个目标,因此需要对这些相似的框进行剔除,最终保留下来比较干净的预测输出结果。
NMS也是剔除方法之一,首先选中所有预测框中非背景类的最大预测值(对类的预测的softmax值,越接近于1置信度越高),然后去掉所有其它和它IoU值大于θ的预测值(也就是去掉和最大预测值相似度比较高的其它锚框),重复这个过程,直到所有的预测框要么被选中,要么被去掉,最终得到一个比较干净的输出(NMS的输出)。
在NMS前,可以将置信度较低的预测边缘框移除,从而减少算法中的计算量;也可以对非极大抑制的输出结果进行后处理,比如只保留置信度更高的结果作为最终输出。
实践部分
代码:
#锚框
import torch
from d2l import torch as d2l
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
torch.set_printoptions(2)
#锚框的宽度和高度分别是 ws√r和 hs/√r。 我们只考虑组合:(s1,r1),(s1,r2),…,(s1,rm),(s2,r1),(s3,r1),…,(sn,r1)
def multibox_prior(data, sizes, ratios):
"""生成以每个像素为中心具有不同形状的锚框。"""
in_height, in_width = data.shape[-2:]
device, num_sizes, num_ratios = data.device, len(sizes), len(ratios)
boxes_per_pixel = (num_sizes + num_ratios - 1)
size_tensor = torch.tensor(sizes, device=device)
ratio_tensor = torch.tensor(ratios, device=device)
offset_h, offset_w = 0.5, 0.5
steps_h = 1.0 / in_height
steps_w = 1.0 / in_width
center_h = (torch.arange(in_height, device=device) + offset_h) * steps_h
center_w = (torch.arange(in_width, device=device) + offset_w) * steps_w
shift_y, shift_x = torch.meshgrid(center_h, center_w)
shift_y, shift_x = shift_y.reshape(-1), shift_x.reshape(-1)
w = torch.cat((size_tensor * torch.sqrt(ratio_tensor[0]),
sizes[0] * torch.sqrt(ratio_tensor[1:])))\
* in_height / in_width
h = torch.cat((size_tensor / torch.sqrt(ratio_tensor[0]),
sizes[0] / torch.sqrt(ratio_tensor[1:])))
anchor_manipulations = torch.stack(
(-w, -h, w, h)).T.repeat(in_height * in_width, 1) / 2
out_grid = torch.stack([shift_x, shift_y, shift_x, shift_y],
dim=1).repeat_interleave(boxes_per_pixel, dim=0)
output = out_grid + anchor_manipulations
return output.unsqueeze(0)
#返回的锚框变量 Y 的形状
img = d2l.plt.imread('../img/catdog.jpg')
h, w = img.shape[:2]
print(h, w)
X = torch.rand(size=(1, 3, h, w))
Y = multibox_prior(X, sizes=[0.75, 0.5, 0.25], ratios=[1, 2, 0.5])
print(Y.shape)
#访问以 (250, 250) 为中心的第一个锚框
boxes = Y.reshape(h, w, 5, 4)
print(boxes[250, 250, 0, :])
#显示以图像中一个像素为中心的所有锚框
def show_bboxes(axes, bboxes, labels=None, colors=None):
"""显示所有边界框。"""
def _make_list(obj, default_values=None):
if obj is None:
obj = default_values
elif not isinstance(obj, (list, tuple)):
obj = [obj]
return obj
labels = _make_list(labels)
colors = _make_list(colors, ['b', 'g', 'r', 'm', 'c'])
for i, bbox in enumerate(bboxes):
color = colors[i % len(colors)]
rect = d2l.bbox_to_rect(bbox.detach().numpy(), color)
axes.add_patch(rect)
if labels and len(labels) > i:
text_color = 'k' if color == 'w' else 'w'
axes.text(rect.xy[0], rect.xy[1], labels[i], va='center',
ha='center', fontsize=9, color=text_color,
bbox=dict(facecolor=color, lw=0))
d2l.set_figsize()
bbox_scale = torch.tensor((w, h, w, h))
fig = d2l.plt.imshow(img)
plt.show()
show_bboxes(fig.axes, boxes[250, 250, :, :] * bbox_scale, [
's=0.75, r=1', 's=0.5, r=1', 's=0.25, r=1', 's=0.75, r=2', 's=0.75, r=0.5'
])
#交并比(IoU)
def box_iou(boxes1, boxes2):
"""计算两个锚框或边界框列表中成对的交并比。"""
box_area = lambda boxes: ((boxes[:, 2] - boxes[:, 0]) *
(boxes[:, 3] - boxes[:, 1]))
areas1 = box_area(boxes1)
areas2 = box_area(boxes2)
inter_upperlefts = torch.max(boxes1[:, None, :2], boxes2[:, :2])
inter_lowerrights = torch.min(boxes1[:, None, 2:], boxes2[:, 2:])
inters = (inter_lowerrights - inter_upperlefts).clamp(min=0)
inter_areas = inters[:, :, 0] * inters[:, :, 1]
union_areas = areas1[:, None] + areas2 - inter_areas
return inter_areas / union_areas
#将真实边界框分配给锚框
def assign_anchor_to_bbox(ground_truth, anchors, device, iou_threshold=0.5):
"""将最接近的真实边界框分配给锚框。"""
num_anchors, num_gt_boxes = anchors.shape[0], ground_truth.shape[0]
jaccard = box_iou(anchors, ground_truth)
anchors_bbox_map = torch.full((num_anchors,), -1, dtype=torch.long,
device=device)
max_ious, indices = torch.max(jaccard, dim=1)
anc_i = torch.nonzero(max_ious >= 0.5).reshape(-1)
box_j = indices[max_ious >= 0.5]
anchors_bbox_map[anc_i] = box_j
col_discard = torch.full((num_anchors,), -1)
row_discard = torch.full((num_gt_boxes,), -1)
for _ in range(num_gt_boxes):
max_idx = torch.argmax(jaccard)
box_idx = (max_idx % num_gt_boxes).long()
anc_idx = (max_idx / num_gt_boxes).long()
anchors_bbox_map[anc_idx] = box_idx
jaccard[:, box_idx] = col_discard
jaccard[anc_idx, :] = row_discard
return anchors_bbox_map
#给定框 A 和 B,中心坐标分别为 (xa,ya) 和 (xb,yb),宽度分别为 wa 和 wb,高度分别为 ha 和 hb。 我们可以将 A 的偏移量标记为⎛⎝xb−xawa−μxσx,yb−yaha−μyσy,logwbwa−μwσw,loghbha−μhσh⎞⎠
def offset_boxes(anchors, assigned_bb, eps=1e-6):
"""对锚框偏移量的转换。"""
c_anc = d2l.box_corner_to_center(anchors)
c_assigned_bb = d2l.box_corner_to_center(assigned_bb)
offset_xy = 10 * (c_assigned_bb[:, :2] - c_anc[:, :2]) / c_anc[:, 2:]
offset_wh = 5 * torch.log(eps + c_assigned_bb[:, 2:] / c_anc[:, 2:])
offset = torch.cat([offset_xy, offset_wh], axis=1)
return offset
#标记锚框的类和偏移量
def multibox_target(anchors, labels):
"""使用真实边界框标记锚框。"""
batch_size, anchors = labels.shape[0], anchors.squeeze(0)
batch_offset, batch_mask, batch_class_labels = [], [], []
device, num_anchors = anchors.device, anchors.shape[0]
for i in range(batch_size):
label = labels[i, :, :]
anchors_bbox_map = assign_anchor_to_bbox(label[:, 1:], anchors,
device)
bbox_mask = ((anchors_bbox_map >= 0).float().unsqueeze(-1)).repeat(
1, 4)
class_labels = torch.zeros(num_anchors, dtype=torch.long,
device=device)
assigned_bb = torch.zeros((num_anchors, 4), dtype=torch.float32,
device=device)
indices_true = torch.nonzero(anchors_bbox_map >= 0)
bb_idx = anchors_bbox_map[indices_true]
class_labels[indices_true] = label[bb_idx, 0].long() + 1
assigned_bb[indices_true] = label[bb_idx, 1:]
offset = offset_boxes(anchors, assigned_bb) * bbox_mask
batch_offset.append(offset.reshape(-1))
batch_mask.append(bbox_mask.reshape(-1))
batch_class_labels.append(class_labels)
bbox_offset = torch.stack(batch_offset)
bbox_mask = torch.stack(batch_mask)
class_labels = torch.stack(batch_class_labels)
return (bbox_offset, bbox_mask, class_labels)
#在图像中绘制这些地面真相边界框和锚框
ground_truth = torch.tensor([[0, 0.1, 0.08, 0.52, 0.92],
[1, 0.55, 0.2, 0.9, 0.88]])
anchors = torch.tensor([[0, 0.1, 0.2, 0.3], [0.15, 0.2, 0.4, 0.4],
[0.63, 0.05, 0.88, 0.98], [0.66, 0.45, 0.8, 0.8],
[0.57, 0.3, 0.92, 0.9]])
fig = d2l.plt.imshow(img)
plt.show()
show_bboxes(fig.axes, ground_truth[:, 1:] * bbox_scale, ['dog', 'cat'], 'k')
show_bboxes(fig.axes, anchors * bbox_scale, ['0', '1', '2', '3', '4']);
#根据狗和猫的真实边界框,标注这些锚框的分类和偏移量
labels = multibox_target(anchors.unsqueeze(dim=0),
ground_truth.unsqueeze(dim=0))
print(labels[2])
print(labels[1])
print(labels[0])
#应用逆偏移变换来返回预测的边界框坐标
def offset_inverse(anchors, offset_preds):
"""根据带有预测偏移量的锚框来预测边界框。"""
anc = d2l.box_corner_to_center(anchors)
pred_bbox_xy = (offset_preds[:, :2] * anc[:, 2:] / 10) + anc[:, :2]
pred_bbox_wh = torch.exp(offset_preds[:, 2:] / 5) * anc[:, 2:]
pred_bbox = torch.cat((pred_bbox_xy, pred_bbox_wh), axis=1)
predicted_bbox = d2l.box_center_to_corner(pred_bbox)
return predicted_bbox
#以下 nms 函数按降序对置信度进行排序并返回其索引
def nms(boxes, scores, iou_threshold):
"""对预测边界框的置信度进行排序。"""
B = torch.argsort(scores, dim=-1, descending=True)
keep = []
while B.numel() > 0:
i = B[0]
keep.append(i)
if B.numel() == 1: break
iou = box_iou(boxes[i, :].reshape(-1, 4),
boxes[B[1:], :].reshape(-1, 4)).reshape(-1)
inds = torch.nonzero(iou <= iou_threshold).reshape(-1)
B = B[inds + 1]
return torch.tensor(keep, device=boxes.device)
#将非极大值抑制应用于预测边界框
def multibox_detection(cls_probs, offset_preds, anchors, nms_threshold=0.5,
pos_threshold=0.009999999):
"""使用非极大值抑制来预测边界框。"""
device, batch_size = cls_probs.device, cls_probs.shape[0]
anchors = anchors.squeeze(0)
num_classes, num_anchors = cls_probs.shape[1], cls_probs.shape[2]
out = []
for i in range(batch_size):
cls_prob, offset_pred = cls_probs[i], offset_preds[i].reshape(-1, 4)
conf, class_id = torch.max(cls_prob[1:], 0)
predicted_bb = offset_inverse(anchors, offset_pred)
keep = nms(predicted_bb, conf, nms_threshold)
all_idx = torch.arange(num_anchors, dtype=torch.long, device=device)
combined = torch.cat((keep, all_idx))
uniques, counts = combined.unique(return_counts=True)
non_keep = uniques[counts == 1]
all_id_sorted = torch.cat((keep, non_keep))
class_id[non_keep] = -1
class_id = class_id[all_id_sorted]
conf, predicted_bb = conf[all_id_sorted], predicted_bb[all_id_sorted]
below_min_idx = (conf < pos_threshold)
class_id[below_min_idx] = -1
conf[below_min_idx] = 1 - conf[below_min_idx]
pred_info = torch.cat(
(class_id.unsqueeze(1), conf.unsqueeze(1), predicted_bb), dim=1)
out.append(pred_info)
return torch.stack(out)
#将上述算法应用到一个带有四个锚框的具体示例中
anchors = torch.tensor([[0.1, 0.08, 0.52, 0.92], [0.08, 0.2, 0.56, 0.95],
[0.15, 0.3, 0.62, 0.91], [0.55, 0.2, 0.9, 0.88]])
offset_preds = torch.tensor([0] * anchors.numel())
cls_probs = torch.tensor([[0] * 4,
[0.9, 0.8, 0.7, 0.1],
[0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.9]])
#在图像上绘制这些预测边界框和置信度
fig = d2l.plt.imshow(img)
plt.show()
show_bboxes(fig.axes, anchors * bbox_scale,
['dog=0.9', 'dog=0.8', 'dog=0.7', 'cat=0.9'])
#返回结果的形状是(批量大小,锚框的数量,6)
output = multibox_detection(cls_probs.unsqueeze(dim=0),
offset_preds.unsqueeze(dim=0),
anchors.unsqueeze(dim=0), nms_threshold=0.5)
print(output)
#输出由非极大值抑制保存的最终预测边界框
fig = d2l.plt.imshow(img)
plt.show()
for i in output[0].detach().numpy():
if i[0] == -1:
continue
label = ('dog=', 'cat=')[int(i[0])] + str(i[1])
show_bboxes(fig.axes, [torch.tensor(i[2:]) * bbox_scale], label)