【模型部署】PaddleOCR模型openvino部署(一)
PaddleOCR:https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleOCR
PaddleOCR是一个非常好用的OCR工具,它有如下特性:
- PP-OCR系列高质量预训练模型,准确的识别效果
- 超轻量PP-OCRv2系列:检测(3.1M)+ 方向分类器(1.4M)+ 识别(8.5M)= 13.0M
- 超轻量PP-OCR mobile移动端系列:检测(3.0M)+方向分类器(1.4M)+ 识别(5.0M)= 9.4M
- 通用PP-OCR server系列:检测(47.1M)+方向分类器(1.4M)+ 识别(94.9M)= 143.4M
- 支持中英文数字组合识别、竖排文本识别、长文本识别
- 支持多语言识别:韩语、日语、德语、法语等约80种语言
- PP-Structure文档结构化系统
- 支持版面分析与表格识别(含Excel导出)
- 支持关键信息提取任务
- 支持DocVQA任务
- 丰富易用的OCR相关工具组件
- 半自动数据标注工具PPOCRLabel:支持快速高效的数据标注
- 数据合成工具Style-Text:批量合成大量与目标场景类似的图像
- 支持用户自定义训练,提供丰富的预测推理部署方案
- 支持PIP快速安装使用
- 可运行于Linux、Windows、MacOS等多种系统
本文将使用openvino部署PaddleOCR官方提供的检测模型,实现文本检测功能。其效果如下图。
原图:
检测结果:
目录
一、模型下载
1、下载推理模型
2、查看模型
二、Openvino部署
三、部署效果
一、模型下载
这里选择官方提供的中英文超轻量PP-OCRv2检测(DBNet)模型进行部署,DBNet是使用语义分割的方法来检测文本区域,其结构如下图:(论文传送门)
这里不多介绍原理,可自行阅读论文。
1、下载推理模型
PaddleOCR提供了很多预训练模型,本文选择【中英文超轻量PP-OCRv2模型】中的检测模型进行部署,首先下载模型:
!wget https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/PP-OCRv2/chinese/ch_PP-OCRv2_det_infer.tar解压压缩包,可以得到如下文件:
2、查看模型
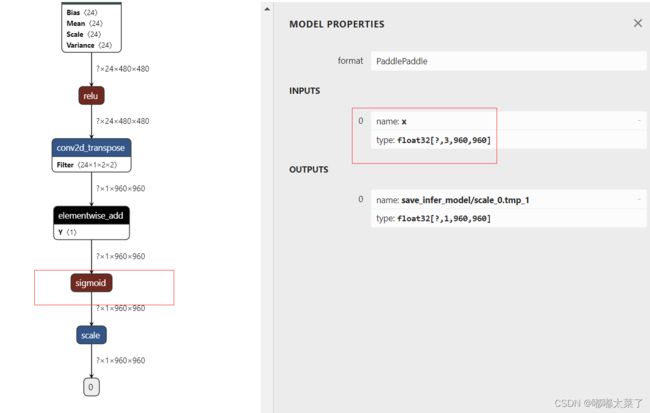
使用netron查看inference.pdmodel结构,如下图,主要关注2点:
(a)模型的输出(关系到后续的后处理);
(b)输入的维度(设计到后续的预处理);
二、Openvino部署
在模型部署阶段,我们只需要完成预处理和后处理的代码即可,预处理过程要和训练一致,查看PaddleOCR对应的配置文件(仅保留预处理和后处理部分):
PostProcess:
name: DBPostProcess
thresh: 0.3
box_thresh: 0.6
max_candidates: 1000
unclip_ratio: 1.5
Eval:
dataset:
name: SimpleDataSet
data_dir: ./train_data/icdar2015/text_localization/
label_file_list:
- ./train_data/icdar2015/text_localization/test_icdar2015_label.txt
transforms:
- DecodeImage: # load image
img_mode: BGR
channel_first: False
- DetLabelEncode: # Class handling label
- DetResizeForTest:
- NormalizeImage:
scale: 1./255.
mean: [0.485, 0.456, 0.406]
std: [0.229, 0.224, 0.225]
order: 'hwc'
- ToCHWImage:
- KeepKeys:
keep_keys: ['image', 'shape', 'polys', 'ignore_tags']这里需要关注的预处理部分的NormalizeImage 均值和标准差,此外上一步查看模型架构时发现模型的输入维度是[?, 3, 960, 960],需要在预处理添加resize操作。
后处理部分直接使用PaddleOCR提供的DBPostProcess类即可(需要稍作修改)。
下面给出具体代码及相关命令:
# 命令:python predict.py --model_path {上面导出的inference.pdmodel路径} --image_path {图片路径}
# 案例: python predict.py --model_path inference.pdmodel --image_path test.png
import cv2
import openvino
import argparse
import numpy as np
import pyclipper
from openvino.runtime import Core
from shapely.geometry import Polygon
def normalize(im, mean=[0.485, 0.456, 0.406], std=[0.229, 0.224, 0.225]):
im = im.astype(np.float32, copy=False) / 255.0
im -= mean
im /= std
return im
def resize(im, target_size=608, interp=cv2.INTER_LINEAR):
if isinstance(target_size, list) or isinstance(target_size, tuple):
w = target_size[0]
h = target_size[1]
else:
w = target_size
h = target_size
im = cv2.resize(im, (w, h), interpolation=interp)
return im
class DBPostProcess(object):
"""
The post process for Differentiable Binarization (DB).
"""
def __init__(self,
thresh=0.3,
box_thresh=0.7,
max_candidates=1000,
unclip_ratio=2.0,
use_dilation=False,
score_mode="fast",
**kwargs):
self.thresh = thresh
self.box_thresh = box_thresh
self.max_candidates = max_candidates
self.unclip_ratio = unclip_ratio
self.min_size = 3
self.score_mode = score_mode
assert score_mode in [
"slow", "fast"
], "Score mode must be in [slow, fast] but got: {}".format(score_mode)
self.dilation_kernel = None if not use_dilation else np.array(
[[1, 1], [1, 1]])
def boxes_from_bitmap(self, pred, _bitmap, dest_width, dest_height):
'''
_bitmap: single map with shape (1, H, W),
whose values are binarized as {0, 1}
'''
bitmap = _bitmap
height, width = bitmap.shape
outs = cv2.findContours((bitmap * 255).astype(np.uint8), cv2.RETR_LIST,
cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
if len(outs) == 3:
img, contours, _ = outs[0], outs[1], outs[2]
elif len(outs) == 2:
contours, _ = outs[0], outs[1]
num_contours = min(len(contours), self.max_candidates)
boxes = []
scores = []
for index in range(num_contours):
contour = contours[index]
points, sside = self.get_mini_boxes(contour)
if sside < self.min_size:
continue
points = np.array(points)
if self.score_mode == "fast":
score = self.box_score_fast(pred, points.reshape(-1, 2))
else:
score = self.box_score_slow(pred, contour)
if self.box_thresh > score:
continue
box = self.unclip(points).reshape(-1, 1, 2)
box, sside = self.get_mini_boxes(box)
if sside < self.min_size + 2:
continue
box = np.array(box)
box[:, 0] = np.clip(
np.round(box[:, 0] / width * dest_width), 0, dest_width)
box[:, 1] = np.clip(
np.round(box[:, 1] / height * dest_height), 0, dest_height)
boxes.append(box.astype(np.int16))
scores.append(score)
return np.array(boxes, dtype=np.int16), scores
def unclip(self, box):
unclip_ratio = self.unclip_ratio
poly = Polygon(box)
distance = poly.area * unclip_ratio / poly.length
offset = pyclipper.PyclipperOffset()
offset.AddPath(box, pyclipper.JT_ROUND, pyclipper.ET_CLOSEDPOLYGON)
expanded = np.array(offset.Execute(distance))
return expanded
def get_mini_boxes(self, contour):
bounding_box = cv2.minAreaRect(contour)
points = sorted(list(cv2.boxPoints(bounding_box)), key=lambda x: x[0])
index_1, index_2, index_3, index_4 = 0, 1, 2, 3
if points[1][1] > points[0][1]:
index_1 = 0
index_4 = 1
else:
index_1 = 1
index_4 = 0
if points[3][1] > points[2][1]:
index_2 = 2
index_3 = 3
else:
index_2 = 3
index_3 = 2
box = [
points[index_1], points[index_2], points[index_3], points[index_4]
]
return box, min(bounding_box[1])
def box_score_fast(self, bitmap, _box):
'''
box_score_fast: use bbox mean score as the mean score
'''
h, w = bitmap.shape[:2]
box = _box.copy()
xmin = np.clip(np.floor(box[:, 0].min()).astype(np.int), 0, w - 1)
xmax = np.clip(np.ceil(box[:, 0].max()).astype(np.int), 0, w - 1)
ymin = np.clip(np.floor(box[:, 1].min()).astype(np.int), 0, h - 1)
ymax = np.clip(np.ceil(box[:, 1].max()).astype(np.int), 0, h - 1)
mask = np.zeros((ymax - ymin + 1, xmax - xmin + 1), dtype=np.uint8)
box[:, 0] = box[:, 0] - xmin
box[:, 1] = box[:, 1] - ymin
cv2.fillPoly(mask, box.reshape(1, -1, 2).astype(np.int32), 1)
return cv2.mean(bitmap[ymin:ymax + 1, xmin:xmax + 1], mask)[0]
def box_score_slow(self, bitmap, contour):
'''
box_score_slow: use polyon mean score as the mean score
'''
h, w = bitmap.shape[:2]
contour = contour.copy()
contour = np.reshape(contour, (-1, 2))
xmin = np.clip(np.min(contour[:, 0]), 0, w - 1)
xmax = np.clip(np.max(contour[:, 0]), 0, w - 1)
ymin = np.clip(np.min(contour[:, 1]), 0, h - 1)
ymax = np.clip(np.max(contour[:, 1]), 0, h - 1)
mask = np.zeros((ymax - ymin + 1, xmax - xmin + 1), dtype=np.uint8)
contour[:, 0] = contour[:, 0] - xmin
contour[:, 1] = contour[:, 1] - ymin
cv2.fillPoly(mask, contour.reshape(1, -1, 2).astype(np.int32), 1)
return cv2.mean(bitmap[ymin:ymax + 1, xmin:xmax + 1], mask)[0]
def __call__(self, pred, shape_list):
pred = pred[:, 0, :, :]
segmentation = pred > self.thresh
boxes_batch = []
for batch_index in range(pred.shape[0]):
src_h, src_w, _, _ = shape_list[batch_index]
if self.dilation_kernel is not None:
mask = cv2.dilate(
np.array(segmentation[batch_index]).astype(np.uint8),
self.dilation_kernel)
else:
mask = segmentation[batch_index]
boxes, scores = self.boxes_from_bitmap(pred[batch_index], mask,
src_w, src_h)
boxes_batch.append({'points': boxes})
return boxes_batch
class Predictor:
def __init__(self, model_path, target_size=(960, 960), mean=[0.485, 0.456, 0.406], std=[0.229, 0.224, 0.225]):
self.target_size = target_size
self.mean = mean
self.std = std
self.model_path = model_path
self.post_process = DBPostProcess(thresh=0.3, box_thresh=0.6, max_candidates=1000, unclip_ratio=1.5, use_dilation=False, score_mode="fast") # 后处理流程参考PaddleOCR
def preprocess(self, image):
image = resize(image, target_size=self.target_size)
image = normalize(image, mean=self.mean, std=self.std)
return image
def draw_det(self, image, dt_boxes):
for box in dt_boxes:
box = box.astype(np.int32).reshape((-1, 1, 2))
cv2.polylines(image, [box], True, color=(255, 255, 0), thickness=2)
return image
def predict(self, image_path):
image = cv2.imread(image_path)
image_h, image_w, _ = image.shape
inputs = self.preprocess(image)
input_image = np.expand_dims(
inputs.transpose(2, 0, 1), 0
)
ie = Core()
model = ie.read_model(model=self.model_path)
compiled_model = ie.compile_model(model=model, device_name="CPU")
input_layer_ir = next(iter(compiled_model.inputs))
output_layer_ir = next(iter(compiled_model.outputs))
mask = compiled_model([input_image])[output_layer_ir]
shape_list = [[image_h, image_w, None, None]] # 对上batch size, batch size为1,所以这里套一个列表
boxes_batch = self.post_process(mask, shape_list) # DBPostProcess, 后处理流程参考PaddleOCR
image = self.draw_det(image, boxes_batch[0]['points']) # 绘制box
return image
def parse_args():
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description='Model export.')
# params of training
parser.add_argument(
'--model_path',
dest='model_path',
help='The path of pdmodel for export',
type=str,
default=None)
parser.add_argument(
'--image_path',
dest='image_path',
help='The path of image to predict.',
type=str,
default=None)
return parser.parse_args()
if __name__ == "__main__":
args = parse_args()
model_path = args.model_path
image_path = args.image_path
predictor = Predictor(model_path, target_size=(960, 960), mean=[0.485, 0.456, 0.406], std=[0.229, 0.224, 0.225])
image = predictor.predict(image_path)
cv2.imwrite("result.png", image)三、部署效果
原图:
预测结果: