【MATLAB】模拟退火算法(SA)求解TSP问题
目录
-
- 1. SA概述
-
- 1.1 SA介绍
- 1.2 SA核心
-
- 1.2.1 三个函数
- 1.2.2 两个准则
- 1.3 SA优缺点
-
- 1.3.1 优点
- 1.3.2 缺点
- 2. 基于SA解决TSP问题
-
- 2.1 tsp.m
- 2.2 CalDist.m
- 2.3 drawTSP.m
- 2.4 simulated_annealing.m
- 2.5 结果
1. SA概述
1.1 SA介绍
SA的提出:模拟退火算法最早的思想由Metropolies等(1953)提出,1983年Kirkpatrick等将其应用于组合优化。
SA的目的:
∙ \bullet ∙ 解决NP复杂性问题;
∙ \bullet ∙ 克服优化过程陷入局部最优;
∙ \bullet ∙ 克服初值依赖性。
SA的思路:
模拟自然界退火现象,从某一温度开始,伴随温度的不断下降,结合概率突跳特性在解空间中随机寻找全局最优解。
1.2 SA核心
1.2.1 三个函数
∙ \bullet ∙ 生成新状态 s j = G e n e t e ( s ) s_{j}=Genete(s) sj=Genete(s)
∙ \bullet ∙ 当前状态不符合,但是在一定概率内可以接受 i f m i n { 1 , e − C ( s j ) − C ( s ) t k } ≥ r a n d r o m [ 0 , 1 ] , s = s j if \ min \left \{ 1,e^{\frac{-C(s_{j})-C(s)}{t_{k}}} \right \}≥randrom[0,1],s=s_{j} if min{1,etk−C(sj)−C(s)}≥randrom[0,1],s=sj
∙ \bullet ∙ 更新温度 t k + 1 = u p d a t e ( t k ) t_{k+1}=update(t_{k}) tk+1=update(tk)
1.2.2 两个准则
∙ \bullet ∙ 抽样稳定准则(内循环终止准则):
∙ \bullet ∙ 检验目标函数的均值是否稳定
∙ \bullet ∙ 连续若干步的目标值变化较小
∙ \bullet ∙ 按一定的步数抽样
∙ \bullet ∙ 算法终止准则(外循环终止准则):
∙ \bullet ∙ 零度法:由于模拟退火算法最终温度为零,因此,可以给定一个较小的正数,当温度小于这个数时,算法停止。
∙ \bullet ∙ 循环总数控制法:总的下降次数为一定值K,当温度迭代次数达到K值时,停止运算。
∙ \bullet ∙ 基于不改进规则的控制法:在一个温度和给定的迭代次数内没有改进当前的局部最优解,则停止运算。
∙ \bullet ∙ 接受概率控制法:给定一个数 P > 0 P>0 P>0是一个比较小的数。除当前局部最优解以外,其他状态的接受概率都小于P时,停止计算。
1.3 SA优缺点
1.3.1 优点
∙ \bullet ∙ 质量高
∙ \bullet ∙ 初值鲁棒性强
∙ \bullet ∙ 简单、通用、易实现
1.3.2 缺点
由于算法要求较高的初始温度、较慢的降温速率、较低的终止温度、以及各温度下足够多次的抽样,因此优化过程较长。
2. 基于SA解决TSP问题
2.1 tsp.m
生成城市坐标与距离矩阵。这里我们写好了10、30、48、50、75个城市个数的坐标,调用的时候直接计算距离就好了。
注意当城市个数多的话最好不要随机生成坐标,那样的话会使城市分布很均匀,很难进行优化。而且可能会产生重复的坐标点。
function [DLn,cityn]=tsp(n)
%输入参数n为城市个数,返回参数DLn为n×n的距离矩阵,cityn为n×2的城市坐标矩阵
if n==10
city10=[0.4 0.4439;0.2439 0.1463;0.1707 0.2293;0.2293 0.761;0.5171 0.9414;
0.8732 0.6536;0.6878 0.5219;0.8488 0.3609;0.6683 0.2536;0.6195 0.2634];%10 cities d'=2.691
for i=1:10
for j=1:10
DL10(i,j)=((city10(i,1)-city10(j,1))^2+(city10(i,2)-city10(j,2))^2)^0.5;
end
end
DLn=DL10;
cityn=city10;
end
if n==30
city30=[41 94;37 84;54 67;25 62;7 64;2 99;68 58;71 44;54 62;83 69;64 60;18 54;22 60;
83 46;91 38;25 38;24 42;58 69;71 71;74 78;87 76;18 40;13 40;82 7;62 32;58 35;45 21;41 26;44 35;4 50];%30 cities d'=423.741 by D B Fogel
for i=1:30
for j=1:30
DL30(i,j)=((city30(i,1)-city30(j,1))^2+(city30(i,2)-city30(j,2))^2)^0.5;
end
end
DLn=DL30;
cityn=city30;
end
if n==48
city48=[6734 1453;2233 10;5530 1424;401 841;3082 1644;7608 4458;7573 3716;7265 1268;6898 1885;
1112 2049;5468 2606;5989 2873;4706 2674;4612 2035;6347 2683;6107 669;7611 5184;7462 3590;7732 4723;
5900 3561;4483 3369;6101 1110;5199 2182;1633 2809;4307 2322;675 6;7555 4819;7541 3981;3177 756;7352 4506;
7545 2801;3245 3305;6426 3173;4608 1198;23 2216;7248 3779;7762 4595;7392 2244;3484 2829;6271 2135;4985 140;
1916 1569;7280 4899;7509 3239;10 2676;6807 2993;5185 3258;3023 1942;];%48cities d'= by att48
for i=1:48
for j=1:48
DL48(i,j)=((city48(i,1)-city48(j,1))^2+(city48(i,2)-city48(j,2))^2)^0.5;
end
end
DLn=DL48;
cityn=city48;
end
if n==50
city50=[31 32;32 39;40 30;37 69;27 68;37 52;38 46;31 62;30 48;21 47;25 55;16 57;
17 63;42 41;17 33;25 32;5 64;8 52;12 42;7 38;5 25; 10 77;45 35;42 57;32 22;
27 23;56 37;52 41;49 49;58 48;57 58;39 10;46 10;59 15;51 21;48 28;52 33;
58 27;61 33;62 63;20 26;5 6;13 13;21 10;30 15;36 16;62 42;63 69;52 64;43 67];%50 cities d'=427.855 by D B Fogel
for i=1:50
for j=1:50
DL50(i,j)=((city50(i,1)-city50(j,1))^2+(city50(i,2)-city50(j,2))^2)^0.5;
end
end
DLn=DL50;
cityn=city50;
end
if n==75
city75=[48 21;52 26;55 50;50 50;41 46;51 42;55 45;38 33;33 34;45 35;40 37;50 30;
55 34;54 38;26 13;15 5;21 48;29 39;33 44;15 19;16 19;12 17;50 40;22 53;21 36;
20 30;26 29;40 20;36 26;62 48;67 41;62 35;65 27;62 24;55 20;35 51;30 50;
45 42;21 45;36 6;6 25;11 28;26 59;30 60;22 22;27 24;30 20;35 16;54 10;50 15;
44 13;35 60;40 60;40 66;31 76;47 66;50 70;57 72;55 65;2 38;7 43;9 56;15 56;
10 70;17 64;55 57;62 57;70 64;64 4;59 5;50 4;60 15;66 14;66 8;43 26];%75 cities d'=549.18 by D B Fogel
for i=1:75
for j=1:75
DL75(i,j)=((city75(i,1)-city75(j,1))^2+(city75(i,2)-city75(j,2))^2)^0.5;
end
end
DLn=DL75;
cityn=city75;
end
2.2 CalDist.m
计算该种排序情况下的距离总长度
function F=CalDist(dislist,s)
%计算总长度,dislist为距离矩阵,s为城市排序序列,F为距离总长度
DistanV=0;
n=size(s,2);
for i=1:(n-1)
DistanV=DistanV+dislist(s(i),s(i+1));
end
DistanV=DistanV+dislist(s(n),s(1));
F=DistanV;
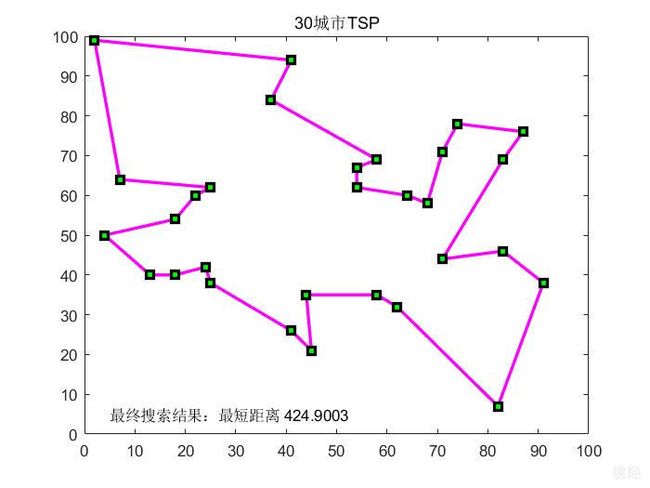
2.3 drawTSP.m
绘制行走路线
function m=drawTSP(Clist,BSF,bsf,p,f)
%Clist为n个城市坐标,BSF为n个城市序列,bsf为总距离,p用来记录第几步搜索
CityNum=size(Clist,1);
for i=1:CityNum-1
plot([Clist(BSF(i),1),Clist(BSF(i+1),1)],[Clist(BSF(i),2),Clist(BSF(i+1),2)],'ms-','LineWidth',2,'MarkerEdgeColor','k','MarkerFaceColor','g');
hold on;
end
plot([Clist(BSF(CityNum),1),Clist(BSF(1),1)],[Clist(BSF(CityNum),2),Clist(BSF(1),2)],'ms-','LineWidth',2,'MarkerEdgeColor','k','MarkerFaceColor','g');
title([num2str(CityNum),'城市TSP']);
if f==0
text(5,5,['第 ',int2str(p),' 步',' 最短距离为 ',num2str(bsf)]);
else
text(5,5,['最终搜索结果:最短距离 ',num2str(bsf)]);
end
hold off;
pause(0.05);
2.4 simulated_annealing.m
主函数
function sa
clear
CityNum=30;
[dislist,Clist]=tsp(CityNum);
%t0,tf是初始和最终温度;alpha是控制温度系数
tf=0.01;
alpha=0.80;
L=100*CityNum; %马尔可夫链的长度
for i=1:100
route=randperm(CityNum); %打乱整数序列随机排序
fval0(i)=CalDist(dislist,route); %计算每个序列的总长度
end
t0=-(max(fval0)-min(fval0))/log(0.9);
fval=fval0(100);
route_best=route;
fval_best=fval;
t=t0;
ii=0;
%外部循环条件,温度大于指定温度
while t>tf
for i=1:L
%exchange函数随机交换两个城市的顺序
[fval_after,route_after]=exchange(route,dislist);
if fval_after<fval
route=route_after;
fval=fval_after;
%满足一定条件可以保留该数据
elseif exp((fval-fval_after)/t)>rand
route=route_after;
fval=fval_after;
end
end
ii=ii+1;
drawTSP(Clist,route,fval,ii,0);
if fval<fval_best
route_best=route;
fval_best=fval;
end
t=alpha*t;
fval_sequence(ii)=fval;
end
drawTSP(Clist,route_best,fval_best,ii,1);
figure(2);
plot(1:ii,fval_sequence);%plot the convergence figure
title('搜索过程');
end
%----------------------------------------------------------------
function [fval_after,route_after]=exchange(route,d)
%通过颠倒两个选定地点之间的顺序来改变旅行路线
n=length(d);
location1=ceil(n*rand);
location2=location1;
while location2==location1
location2=ceil(n*rand);%两个交换号码的位置
end
loc1=min(location1,location2);loc2=max(location1,location2);
middle_route=fliplr(route(loc1:loc2));%交换的部分路线
route_after=[route(1:loc1-1) middle_route route(loc2+1:n)];%之后旅行路线
fval_after=CalDist(d,route_after);
end
%----------------------------------------------------------------
2.5 结果