卷积神经网络学习日记(VGG)学习日记
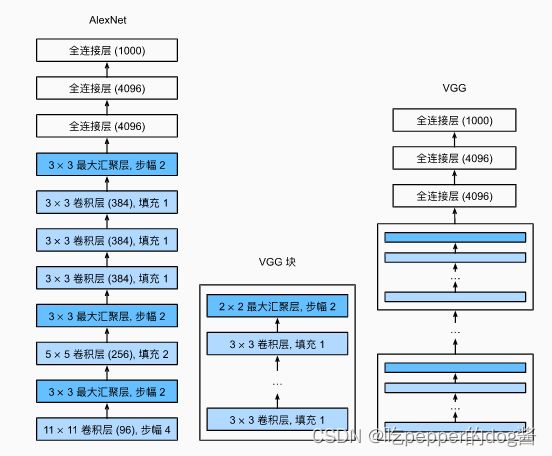
VGG与AlexNet网络结构差异图示(来自李沫《动手学深度学习》)
一个VGG块由一系列卷积层组成,在最后连接一个最大汇聚层
VGG块代码如下所示:
该函数有三个参数,分别对应于卷积层的数量num_convs、输入通道的数量in_channels 和输出通道的数量out_channels
import torch
from torch import nn
from d2l import torch as d2l
def vgg_block(num_convs, in_channels, out_channels):
layers = []
for _ in range(num_convs):
layers.append(nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels,
kernel_size=3, padding=1))
layers.append(nn.ReLU())
in_channels = out_channels
layers.append(nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2,stride=2))
return nn.Sequential(*layers)VGG网络实现代码:
def vgg(conv_arch):
conv_blks = []
in_channels = 1
# 卷积层部分
for (num_convs, out_channels) in conv_arch:
conv_blks.append(vgg_block(num_convs, in_channels, out_channels))
in_channels = out_channels
return nn.Sequential(
*conv_blks, nn.Flatten(),
# 全连接层部分
nn.Linear(out_channels * 7 * 7, 4096), nn.ReLU(), nn.Dropout(0.5),
nn.Linear(4096, 4096), nn.ReLU(), nn.Dropout(0.5),
nn.Linear(4096, 10))
网络结构:
其中sequential层为自定义的VGG层
Sequential output shape: torch.Size([1, 64, 112, 112])
Sequential output shape: torch.Size([1, 128, 56, 56])
Sequential output shape: torch.Size([1, 256, 28, 28])
Sequential output shape: torch.Size([1, 512, 14, 14])
Sequential output shape: torch.Size([1, 512, 7, 7])
Flatten output shape: torch.Size([1, 25088])
Linear output shape: torch.Size([1, 4096])
ReLU output shape: torch.Size([1, 4096])
Dropout output shape: torch.Size([1, 4096])
Linear output shape: torch.Size([1, 4096])
ReLU output shape: torch.Size([1, 4096])
Dropout output shape: torch.Size([1, 4096])
Linear output shape: torch.Size([1, 10])小结:VGG网络使用可复用的卷积块(VGG块)构造网络,使用块定义的网络十分简洁,避免了逐行逐句编写网络结构,使用块可高效构建层次深的网络结构。