基于C#的机器人仿真平台和机器人运动学算法实现
一、平台搭建
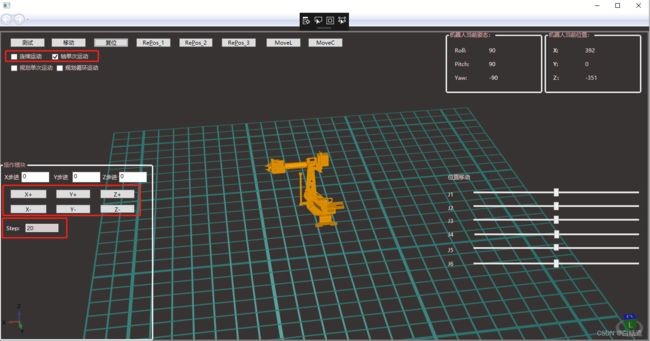
1.利用wpf自带的库进行机器人各关节导入
相关代码段:
private const string MODEL_PATH1 = "Base.stl";
private const string MODEL_PATH2 = "Asse1.stl";
private const string MODEL_PATH3 = "Asse2.stl";
private const string MODEL_PATH4 = "Asse3.stl";
private const string MODEL_PATH5 = "Asse4.stl";
private const string MODEL_PATH6 = "Asse5.stl";
private const string MODEL_PATH7 = "Asse6.stl";
private const string MODEL_PATH8 = "Leva.stl";
private const string MODEL_PATH9 = "Asta.stl";导入效果如图:
效果视频:
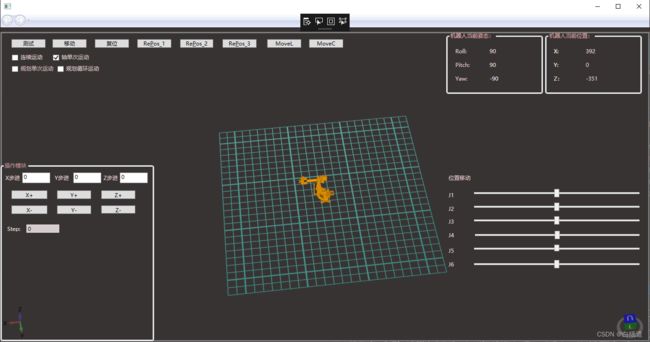
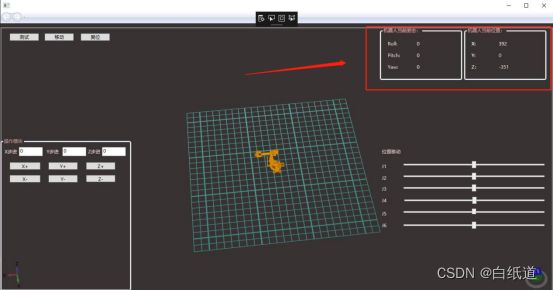
2.通过正运动学显示机器人当前位置信息
拖动机器人并且实时改变其位置信息:
xaml代码部分:
算法部分:
//第一种DH建模的方式
public static void Q2T(double ai,double di,double θi, double αi, ref double[,] T)
//正运动学方程模型矩阵
public static void Q2T2(double ai, double di, double θi, double αi, ref double[,] T)
public void diretta(double q1, double q2, double q3,
double q4, double q5, double q6, ref double[] C,ref double[,] resR)
{
Q2T2(a0, d1, q1, 0,ref T01);
Q2T2(a1, d2, q2, -90, ref T12);
Q2T2(a2, d3, q3, 0, ref T23);
Q2T2(a3, d4, q4, -90, ref T34);
Q2T2(a4, d5, q5, 90, ref T45);
Q2T2(a5, d6, q6, -90, ref T56);
T02 = math_matrix.MatrixMult(T01,T12);
T03 = math_matrix.MatrixMult(T02, T23);
T04 = math_matrix.MatrixMult(T03, T34);
T05 = math_matrix.MatrixMult(T04, T45);
T06 = math_matrix.MatrixMult(T05, T56);
T35 = math_matrix.MatrixMult(T34, T45);
T36 = math_matrix.MatrixMult(T35, T56);//T36 = t36
double[,] inv03 = math_matrix.MatInverse(T03);
double[,] t36 = math_matrix.MatrixMult(inv03,T06);//T36 = t36
//求得机器人末端相对于机器人基坐标系的位置关系(x,y,z)
C[0] = T06[0, 3];
C[1] = T06[1, 3];
C[2] = T06[2, 3];
initC[0] = T06[0, 3];
initC[1] = T06[1, 3];
initC[2] = T06[2, 3];
R36[0, 0] = T36[0, 0];
R36[0, 1] = T36[0, 1];
R36[0, 2] = T36[0, 2];
R36[1, 0] = T36[1, 0];
R36[1, 1] = T36[1, 1];
R36[1, 2] = T36[1, 2];
R36[2, 0] = T36[2, 0];
R36[2, 1] = T36[2, 1];
R36[2, 2] = T36[2, 2];
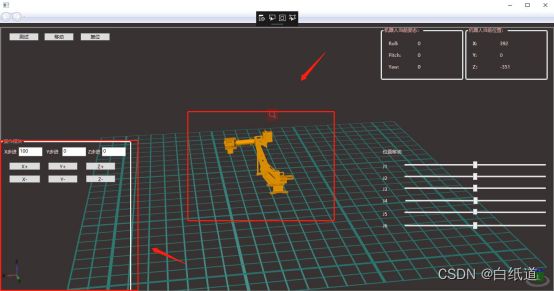
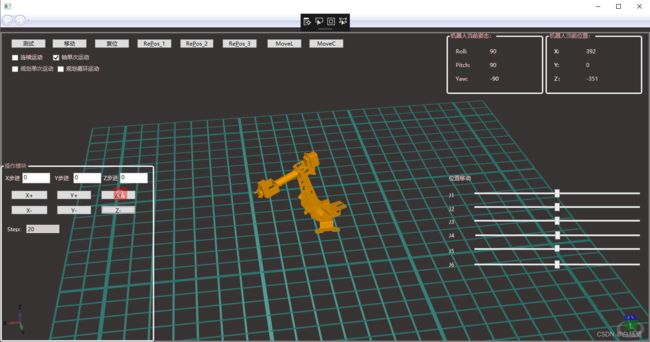
}3.功能实现(在X/Y/Z轴上设置一个移动距离,然后机器人自动移动该距离)
效果如图:
附上运动学算法代码:
public void Rob_Ik(double[] qc, double[] q)
{
}
//我们以RPY作为机器人的旋转方式
public void RPY2R(double[] rpy,ref double[,] R)
{
double cos_roll = Math.Cos(rpy[0]);
double cos_pitch = Math.Cos(rpy[1]);
double cos_yaw = Math.Cos(rpy[2]);
double sin_roll = Math.Sin(rpy[0]);
double sin_pitch = Math.Sin(rpy[1]);
double sin_yaw = Math.Sin(rpy[2]);
R[0, 0] = cos_roll * cos_pitch;
R[0, 1] = (cos_roll * sin_pitch * sin_pitch) - (sin_roll*cos_yaw);
R[0, 2] = (cos_roll * sin_pitch * cos_yaw) - (sin_roll * sin_yaw);
R[1, 0] = sin_roll * cos_pitch;
R[1, 1] = (sin_roll * sin_pitch * sin_yaw) - (cos_roll * cos_yaw);
R[1, 2] = (sin_roll * sin_pitch * cos_yaw) - (cos_roll * sin_yaw);
R[2, 0] = -sin_pitch;
R[2, 1] = cos_pitch * sin_yaw;
R[2, 2] = cos_pitch * cos_yaw;
}
public void R2PRY(double[,] R,ref double[] rpy)
{
rpy[0] = Math.Atan2(R[1,0],R[0,0]);
rpy[1] = Math.Atan2(-R[2, 1], (R[0, 0] * Math.Cos(rpy[0]) + R[1, 0] * Math.Sin(rpy[0])));
rpy[2] = Math.Atan2((-R[1,2]*Math.Cos(rpy[0])+R[0,2]*Math.Sin(rpy[0])),(R[1,1]*Math.Cos(rpy[0])-R[0,1]*Math.Sin(rpy[0])));
}
public void T2E(double[,] R,ref double[] Euler)
{
Euler[0] = Math.Atan2(Math.Sqrt(Math.Pow(R[2,0], 2) +Math. Pow(R[2,1], 2)), R[2,2]);
Euler[1] = Math.Atan2(R[1,2] /Math.Sin(Euler[0]), R[0,2] / Math.Sin(Euler[0]));
Euler[2] = Math.Atan2(R[2,1] /Math.Sin(Euler[0]), -R[2,0] /Math.Sin(Euler[0]));
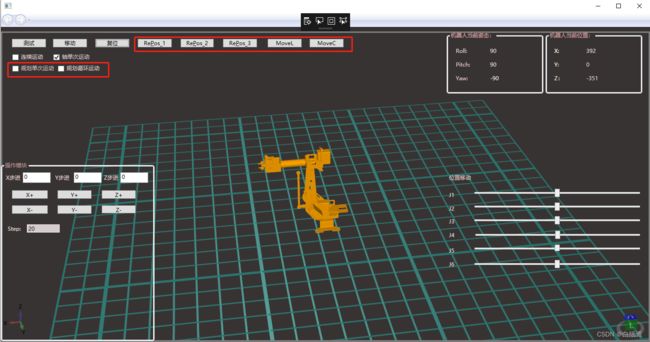
}4.通过选定运动方式和步进参数,单步移动各轴(各轴联合运动)
移动后效果图:
效果视频:
代码:
private void Button_Click_4(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e)
{
if (Continuity_Motion.IsChecked == true)
{
minus_x.Clear();
for (int i = 0; i < Convert.ToInt32(text_x.Text); i = i + 1)
{
minus_x.Add(i);
}
for (int j = 0; j < minus_x.Count; j++)
{
double[] qcii = new double[6];
qcii[0] = inverse.initC[0];//移动z
qcii[1] = inverse.initC[1];//移动y
qcii[2] = inverse.initC[2] - minus_x[j];//移动x
qcii[3] = inverse.euler[0];
qcii[4] = inverse.euler[1];
qcii[5] = inverse.euler[2];
double[] q = new double[6];
m_inverse.Rob_Ik(qcii, q);
refresh(inverse.g1, inverse.g2, inverse.g3, inverse.g4 - 90, inverse.g5 - 90, inverse.g6 + 90);
Delay(5);
}
}
else if(Once_Motion.IsChecked == true)
{
qci[0] = inverse.initC[0] + record_z_increase - record_z_reduce;//移动z
qci[1] = inverse.initC[1] + record_y_increase - record_y_reduce;//移动y
oadd_x = oadd_x + Convert.ToDouble(text_step.Text);
qci[2] = inverse.initC[2]+oadd_x-record_x_reduce;//移动x
qci[3] = inverse.euler[0];
qci[4] = inverse.euler[1];
qci[5] = inverse.euler[2];
double[] q = new double[6];
m_inverse.Rob_Ik(qci, q);
refresh(inverse.g1, inverse.g2, inverse.g3, inverse.g4 - 90, inverse.g5 - 90, inverse.g6 + 90);
Delay(5);
}
else
{
MessageBox.Show("请选择移动模式!");
}
}5.基于直线轨迹规划的机器人移动(规划算法加逆解算法)
效果视频:
代码部分:
public void Plan_path(double xs, double ys, double zs, double xe, double ye, double ze, double speed)
private void Button_Click_9(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e)
{
pos[0] = qci[0];
pos[1] = qci[1];
pos[2] = qci[2];
pos[3] = inverse.g4;
pos[4] = inverse.g5;
pos[5] = inverse.g6;
plp1[0] = pos[0];
plp1[1] = pos[1];
plp1[2] = pos[2];
MessageBox.Show("位置一已记录!");
}
private void Button_Click_10(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e)
{
pos_1[0] = qci[0];
pos_1[1] = qci[1];
pos_1[2] = qci[2];
pos_1[3] = inverse.g4;
pos_1[4] = inverse.g5;
pos_1[5] = inverse.g6;
plp2[0] = pos_1[0];
plp2[1] = pos_1[1];
plp2[2] = pos_1[2];
MessageBox.Show("位置二已记录!");
}
public void LinePath()
{
linerPath.Plan_path(pos[2],pos[1],pos[0],pos_1[2],pos_1[1],pos_1[0],5);
if (loop_sport.IsChecked == true)
{
loop = true;
while (loop)
{
for (int i = 0; i < linerPath.x_start.Count; i++)
{
double[] linepos = new double[6];
linepos[2] = linerPath.x_start[i];
linepos[1] = linerPath.y_start[i];
linepos[0] = linerPath.z_start[i];
linepos[3] = inverse.euler[0];
linepos[4] = inverse.euler[1];
linepos[5] = inverse.euler[2];
double[] q = new double[6];
m_inverse.Rob_Ik(linepos, q);
refresh(inverse.g1, inverse.g2, inverse.g3, inverse.g4 - 90, inverse.g5 - 90, inverse.g6 + 90);
Delay(20);
}
}
}Xaml代码:
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
xmlns:d="http://schemas.microsoft.com/expression/blend/2008"
xmlns:mc="http://schemas.openxmlformats.org/markup-compatibility/2006"
xmlns:local="clr-namespace:WpfApp3"
xmlns:helix ="http://helix-toolkit.org/wpf"
mc:Ignorable="d"
d:DesignHeight="300" d:DesignWidth="800" Background="#FF383333">
欢迎添加qq:675260963进行技术交流!