若依缓存使用浅析
配置
这块主要涉及两个类
- FastJson2JsonRedisSerializer : 继承 RedisSerializer 接口自定义使用 fastjson 进行序列化和反序列化
- RedisConfig:配置使用 StringRedisSerializer 来进行key的序列化与反序列,使用刚才我们 FastJson2JsonRedisSerializer 来进行 value 的序列化与反序列
下面贴下相关代码
@Configuration
@EnableCaching
public class RedisConfig extends CachingConfigurerSupport
{
@Bean
@SuppressWarnings(value = { "unchecked", "rawtypes" })
public RedisTemplate<Object, Object> redisTemplate(RedisConnectionFactory connectionFactory)
{
RedisTemplate<Object, Object> template = new RedisTemplate<>();
template.setConnectionFactory(connectionFactory);
FastJson2JsonRedisSerializer serializer = new FastJson2JsonRedisSerializer(Object.class);
ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper();
mapper.setVisibility(PropertyAccessor.ALL, JsonAutoDetect.Visibility.ANY);
mapper.activateDefaultTyping(LaissezFaireSubTypeValidator.instance, ObjectMapper.DefaultTyping.NON_FINAL, JsonTypeInfo.As.PROPERTY);
serializer.setObjectMapper(mapper);
template.setValueSerializer(serializer);
// 使用StringRedisSerializer来序列化和反序列化redis的key值
template.setKeySerializer(new StringRedisSerializer());
template.afterPropertiesSet();
return template;
}
}
public class FastJson2JsonRedisSerializer<T> implements RedisSerializer<T>
{
@SuppressWarnings("unused")
private ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();
public static final Charset DEFAULT_CHARSET = Charset.forName("UTF-8");
private Class<T> clazz;
static
{
ParserConfig.getGlobalInstance().setAutoTypeSupport(true);
}
public FastJson2JsonRedisSerializer(Class<T> clazz)
{
super();
this.clazz = clazz;
}
@Override
public byte[] serialize(T t) throws SerializationException
{
if (t == null)
{
return new byte[0];
}
return JSON.toJSONString(t, SerializerFeature.WriteClassName).getBytes(DEFAULT_CHARSET);
}
@Override
public T deserialize(byte[] bytes) throws SerializationException
{
if (bytes == null || bytes.length <= 0)
{
return null;
}
String str = new String(bytes, DEFAULT_CHARSET);
return JSON.parseObject(str, clazz);
}
public void setObjectMapper(ObjectMapper objectMapper)
{
Assert.notNull(objectMapper, "'objectMapper' must not be null");
this.objectMapper = objectMapper;
}
protected JavaType getJavaType(Class<?> clazz)
{
return TypeFactory.defaultInstance().constructType(clazz);
}
}
简单提一嘴 ruoyi 的模块拆分,common 与 framework 的拆分思想很值得学习,之前我自己拆分的时候没有拆出 framework 这一层,就导致很多与具体业务模块无关的内容与业务模块代码耦合过于严重
这两个配置类放在了 framework 模块中,然后所有对 redistemplate 的操作封装在了 common 的工具类 RedisCache
应用场景浅析
我们通过全局搜索 RedisCache,可以很方便的找到 redis 在项目中的使用,下面我们一个一个走一遍
登录验证码与登录token存储鉴权
这几个比较类型放在一起说
验证码这块,在获取验证码的时候会把 生成的验证码放到 redis 缓存,并设置 过期时间
redisCache.setCacheObject(verifyKey, code, Constants.CAPTCHA_EXPIRATION, TimeUnit.MINUTES);
简单提一下验证码工具,调用验证码工具类会生成一个图片和一个对应的code,我们在生成个uuid标识这次的结果,和短信登录意思差不多,只不过把手机号变成了 uuid,后面校验登录时传来的 uuid 和 code 是否匹配
后面看login这块,就是 token 存储的使用了
/**
* 登录验证
*
* @param username 用户名
* @param password 密码
* @param code 验证码
* @param uuid 唯一标识
* @return 结果
*/
public String login(String username, String password, String code, String uuid)
{
// <1> 根据 uuid 和 code 去 redis 中找,并且删除掉这个验证码的code
String verifyKey = Constants.CAPTCHA_CODE_KEY + uuid;
String captcha = redisCache.getCacheObject(verifyKey);
redisCache.deleteObject(verifyKey);
if (captcha == null)
{
AsyncManager.me().execute(AsyncFactory.recordLogininfor(username, Constants.LOGIN_FAIL, MessageUtils.message("user.jcaptcha.expire")));
throw new CaptchaExpireException();
}
if (!code.equalsIgnoreCase(captcha))
{
AsyncManager.me().execute(AsyncFactory.recordLogininfor(username, Constants.LOGIN_FAIL, MessageUtils.message("user.jcaptcha.error")));
throw new CaptchaException();
}
// 用户验证
Authentication authentication = null;
try
{
//<2> 该方法会去调用UserDetailsServiceImpl.loadUserByUsername
authentication = authenticationManager
.authenticate(new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(username, password));
}
catch (Exception e)
{
if (e instanceof BadCredentialsException)
{
AsyncManager.me().execute(AsyncFactory.recordLogininfor(username, Constants.LOGIN_FAIL, MessageUtils.message("user.password.not.match")));
throw new UserPasswordNotMatchException();
}
else
{
AsyncManager.me().execute(AsyncFactory.recordLogininfor(username, Constants.LOGIN_FAIL, e.getMessage()));
throw new CustomException(e.getMessage());
}
}
AsyncManager.me().execute(AsyncFactory.recordLogininfor(username, Constants.LOGIN_SUCCESS, MessageUtils.message("user.login.success")));
// <3> 拿到刚才的 LoginUser(UserDetail实现类)
LoginUser loginUser = (LoginUser) authentication.getPrincipal();
// <4> 生成token
return tokenService.createToken(loginUser);
}
<1> 处看下注释即可
<2> 这块调用 UserDetailsServiceImpl.loadUserByUsername,调用自定义的函数,判断账号密码是否匹配,匹配后返回 UserDetails 的自定义实现类,这步还可以一起返回该用户所有权限
<3> <4> 调用 createToken方法在 redis 中记录 token(基于用户信息用 jwt 生成,但是也是基于持久化存储的,这种实现是最灵活且安全的)
springsecurity 不清楚的可以看这篇文章 芋道 Spring Boot 安全框架 Spring Security 入门 | 芋道源码 —— 纯源码解析博客 (iocoder.cn)
接着看后面这块实现 TokenService
/**
* 创建令牌
*
* @param loginUser 用户信息
* @return 令牌
*/
public String createToken(LoginUser loginUser)
{
// <1> 用 uuid 作为key,这个token只是叫 token ,但其实是 key
String token = IdUtils.fastUUID();
loginUser.setToken(token);
setUserAgent(loginUser);
// <2> 把loginUser缓存到 redis
refreshToken(loginUser);
// <3> 生成 jwt 的 token
Map<String, Object> claims = new HashMap<>();
claims.put(Constants.LOGIN_USER_KEY, token);
return createToken(claims);
}
/**
* 刷新令牌有效期
*
* @param loginUser 登录信息
*/
public void refreshToken(LoginUser loginUser)
{
loginUser.setLoginTime(System.currentTimeMillis());
loginUser.setExpireTime(loginUser.getLoginTime() + expireTime * MILLIS_MINUTE);
// 根据uuid将loginUser缓存
String userKey = getTokenKey(loginUser.getToken());
redisCache.setCacheObject(userKey, loginUser, expireTime, TimeUnit.MINUTES);
}
/**
* 从数据声明生成令牌
*
* @param claims 数据声明
* @return 令牌
*/
private String createToken(Map<String, Object> claims)
{
String token = Jwts.builder()
.setClaims(claims)
.signWith(SignatureAlgorithm.HS512, secret).compact();
return token;
}
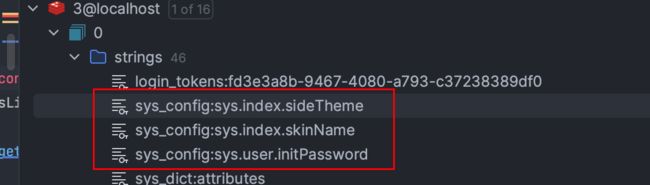
查看redis 可以看到我们序列化的信息
debug下,看到我们把生成的uuid再使用jwt加密返回,然后 uuid 关联用户信息的json序列化后存储到 redis

还是要debug啊
然后把生成的token返回给前端,后面的请求前端会带上这个 token
下面来讲下token是如何被解析的,也就是debug需要校验是否登录的接口,这块是JwtAuthenticationTokenFilter中实现的
@Override
protected void doFilterInternal(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, FilterChain chain)
throws ServletException, IOException
{
// <1>
LoginUser loginUser = tokenService.getLoginUser(request);
if (StringUtils.isNotNull(loginUser) && StringUtils.isNull(SecurityUtils.getAuthentication()))
{
// <2>
tokenService.verifyToken(loginUser);
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken authenticationToken = new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(loginUser, null, loginUser.getAuthorities());
authenticationToken.setDetails(new WebAuthenticationDetailsSource().buildDetails(request));
SecurityContextHolder.getContext().setAuthentication(authenticationToken);
}
chain.doFilter(request, response);
}
// tokenService
/**
* 获取用户身份信息
*
* @return 用户信息
*/
public LoginUser getLoginUser(HttpServletRequest request)
{
// 获取请求携带的令牌
String token = getToken(request);
if (StringUtils.isNotEmpty(token))
{
Claims claims = parseToken(token);
// 解析对应的权限以及用户信息
String uuid = (String) claims.get(Constants.LOGIN_USER_KEY);
String userKey = getTokenKey(uuid);
LoginUser user = redisCache.getCacheObject(userKey);
return user;
}
return null;
}
/**
* 验证令牌有效期,相差不足20分钟,自动刷新缓存
*
* @param loginUser
* @return 令牌
*/
public void verifyToken(LoginUser loginUser)
{
long expireTime = loginUser.getExpireTime();
long currentTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
if (expireTime - currentTime <= MILLIS_MINUTE_TEN)
{
refreshToken(loginUser);
}
}
<1> 从 header 中取出 token,用 jwt 解密出来 uuid,看下这个uuid是否在redis中存在
<2> 判断 token 时效性,刷新 token
在线用户统计与签退
下面来看在线用户的实现
@PreAuthorize("@ss.hasPermi('monitor:online:list')")
@GetMapping("/list")
public TableDataInfo list(String ipaddr, String userName)
{
Collection<String> keys = redisCache.keys(Constants.LOGIN_TOKEN_KEY + "*");
List<SysUserOnline> userOnlineList = new ArrayList<SysUserOnline>();
for (String key : keys)
{
LoginUser user = redisCache.getCacheObject(key);
if (StringUtils.isNotEmpty(ipaddr) && StringUtils.isNotEmpty(userName))
{
if (StringUtils.equals(ipaddr, user.getIpaddr()) && StringUtils.equals(userName, user.getUsername()))
{
userOnlineList.add(userOnlineService.selectOnlineByInfo(ipaddr, userName, user));
}
}
else if (StringUtils.isNotEmpty(ipaddr))
{
if (StringUtils.equals(ipaddr, user.getIpaddr()))
{
userOnlineList.add(userOnlineService.selectOnlineByIpaddr(ipaddr, user));
}
}
else if (StringUtils.isNotEmpty(userName) && StringUtils.isNotNull(user.getUser()))
{
if (StringUtils.equals(userName, user.getUsername()))
{
userOnlineList.add(userOnlineService.selectOnlineByUserName(userName, user));
}
}
else
{
userOnlineList.add(userOnlineService.loginUserToUserOnline(user));
}
}
Collections.reverse(userOnlineList);
userOnlineList.removeAll(Collections.singleton(null));
return getDataTable(userOnlineList);
}
就是拿到所有在线用户的key,模糊查询,然后取set
强退用户
/**
* 强退用户
*/
@PreAuthorize("@ss.hasPermi('monitor:online:forceLogout')")
@Log(title = "在线用户", businessType = BusinessType.FORCE)
@DeleteMapping("/{tokenId}")
public AjaxResult forceLogout(@PathVariable String tokenId)
{
redisCache.deleteObject(Constants.LOGIN_TOKEN_KEY + tokenId);
return AjaxResult.success();
}
在 redis 里面把这条登录的记录删除掉
系统设置的缓存
这块在用的时候最直观的就是项目启动时会发现有很多查询sys_config的sql的debug信息,其中第一条就是加载系统配置啦,下面的就是加载数据字典,放在后面说
/**
* 项目启动时,初始化参数到缓存
*/
@PostConstruct
public void init()
{
List<SysConfig> configsList = configMapper.selectConfigList(new SysConfig());
for (SysConfig config : configsList)
{
redisCache.setCacheObject(getCacheKey(config.getConfigKey()), config.getConfigValue());
}
}
SysConfigServiceImpl 中配置了这个,会在项目启动时初始化,拿到所有 sys_config,加载到redis
看下查询配置的实现
/**
* 根据键名查询参数配置信息
*
* @param configKey 参数key
* @return 参数键值
*/
@Override
public String selectConfigByKey(String configKey)
{
// <1> 首先从缓存中取,存在返回缓存中的
String configValue = Convert.toStr(redisCache.getCacheObject(getCacheKey(configKey)));
if (StringUtils.isNotEmpty(configValue))
{
return configValue;
}
// <2> 不存在的话,查数据库,数据库中存在,写缓存并返回
SysConfig config = new SysConfig();
config.setConfigKey(configKey);
SysConfig retConfig = configMapper.selectConfig(config);
if (StringUtils.isNotNull(retConfig))
{
redisCache.setCacheObject(getCacheKey(configKey), retConfig.getConfigValue());
return retConfig.getConfigValue();
}
return StringUtils.EMPTY;
}
新增,修改与删除,看下是否存在缓存与db不一致的情况
/**
* 新增参数配置
*
* @param config 参数配置信息
* @return 结果
*/
@Override
public int insertConfig(SysConfig config)
{
int row = configMapper.insertConfig(config);
if (row > 0)
{
redisCache.setCacheObject(getCacheKey(config.getConfigKey()), config.getConfigValue());
}
return row;
}
/**
* 修改参数配置
*
* @param config 参数配置信息
* @return 结果
*/
@Override
public int updateConfig(SysConfig config)
{
int row = configMapper.updateConfig(config);
if (row > 0)
{
redisCache.setCacheObject(getCacheKey(config.getConfigKey()), config.getConfigValue());
}
return row;
}
/**
* 批量删除参数信息
*
* @param configIds 需要删除的参数ID
* @return 结果
*/
@Override
public int deleteConfigByIds(Long[] configIds)
{
for (Long configId : configIds)
{
SysConfig config = selectConfigById(configId);
if (StringUtils.equals(UserConstants.YES, config.getConfigType()))
{
throw new CustomException(String.format("内置参数【%1$s】不能删除 ", config.getConfigKey()));
}
}
int count = configMapper.deleteConfigByIds(configIds);
if (count > 0)
{
Collection<String> keys = redisCache.keys(Constants.SYS_CONFIG_KEY + "*");
redisCache.deleteObject(keys);
}
return count;
}
新增与修改,删除,先写数据库再写redis,如果写表成功,写redis,都是基于这个原则,可以思考下为什么不能先写 redis(缓存不一致问题)
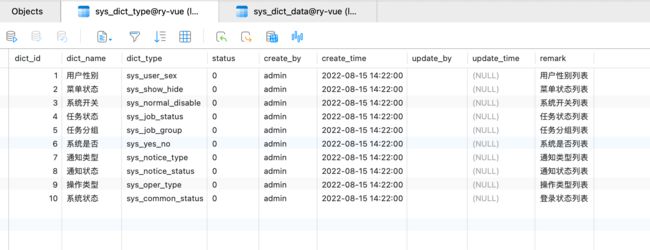
数据字典
数据字典的键和值是分开存储的
根据 dict_code 关联存储
还是看下初始化代码
/**
* 项目启动时,初始化字典到缓存
*/
@PostConstruct
public void init()
{
List<SysDictType> dictTypeList = dictTypeMapper.selectDictTypeAll();
for (SysDictType dictType : dictTypeList)
{
List<SysDictData> dictDatas = dictDataMapper.selectDictDataByType(dictType.getDictType());
DictUtils.setDictCache(dictType.getDictType(), dictDatas);
}
}
// DictUtils
/**
* 设置字典缓存
*
* @param key 参数键
* @param dictDatas 字典数据列表
*/
public static void setDictCache(String key, List<SysDictData> dictDatas)
{
SpringUtils.getBean(RedisCache.class).setCacheObject(getCacheKey(key), dictDatas);
}
先查主表,然后关联查询子表
子表的数据集合整个序列化成一个json,举一个dict为例看下存储在 redis 里面的 value(加 @ 是防止关键字冲突?)

[{"@type":"com.ruoyi.common.core.domain.entity.SysDictData","createBy":"admin","createTime":1658803658000,"default":false,"dictCode":147,"dictLabel":"工业","dictSort":1,"dictType":"attributes","dictValue":"1","isDefault":"N","params":{"@type":"java.util.HashMap"},"status":"0"},{"@type":"com.ruoyi.common.core.domain.entity.SysDictData","createBy":"admin","createTime":1658803659000,"default":false,"dictCode":148,"dictLabel":"商业","dictSort":2,"dictType":"attributes","dictValue":"2","isDefault":"N","params":{"@type":"java.util.HashMap"},"status":"0"}]
后面的分析比较类似,大家有兴趣自己 debug 把(其实是因为懒,哈哈)
后记
其实写这个系列完全是兴趣,因为 redis 的一些东西看了好多,但是不知道具体是怎么用的, 索性就拿若依来看看吧
后面想到啥了再补充把,先写到这里