Mybatis基础学习之缓存原理浅析和自定义缓存Ehcache的简单使用
前言:
小伙伴们,大家好,我是狂奔の蜗牛rz,当然你们可以叫我蜗牛君,我是一个学习Java半年多时间的小菜鸟,同时还有一个伟大的梦想,那就是有朝一日,成为一个优秀的Java架构师。
这个Mybatis基础学习系列是用来记录我学习Mybatis框架基础知识的全过程 (这个系列是参照B站狂神的Mybatis最新教程来写的,由于是之前整理的,但当时没有发布出来,所以有些地方可能有错误,希望大家能够及时指正!)
之后我将尽量以两天一更的速度更新这个系列,还没有学习Mybatis3框架的小伙伴可以参照我的博客学习一下;当然学习过的小伙伴,也可以顺便跟我一起复习一下基础。最后,希望能够和大家一同进步吧!加油吧!少年们!
特别提醒:如果对Mybatis基础学习系列感兴趣,可以阅读本系列往期博客:
第一篇:Mybatis基础学习之初识Mybatis
第二篇:Mybatis基础学习之第一个Mybatis程序
第三篇:Mybatis基础学习之CRUD增删改查
第四篇:Mybatis基础学习之万能的Map和模糊查询
第五篇: Mybatis基础学习之配置解析(上篇)
第六篇: Mybatis基础学习之配置解析(下篇)
第七篇: Mybatis基础学习之使用ResultMap解决字段名不一致
第八篇: Mybatis基础学习之日志工厂的简单使用
第九篇: Mybatis基础学习之数据分页的简单使用
第十篇: Mybatis基础学习之使用注解开发
第十一篇: Mybatis基础学习之Lombok的简单使用
第十二篇: Mybatis基础学习之多对一关系处理
第十三篇: Mybatis基础学习之一对多关系处理
第十四篇: Mybatis基础学习之动态SQL的简单使用
第十五篇: Mybatis基础学习之一级缓存和二级缓存的简单使用
今天我们来到了Mybatis基础学习的第十五站:缓存原理浅析和自定义缓存Ehcache的简单使用。废话不多说,让我们开始今天的学习内容吧。
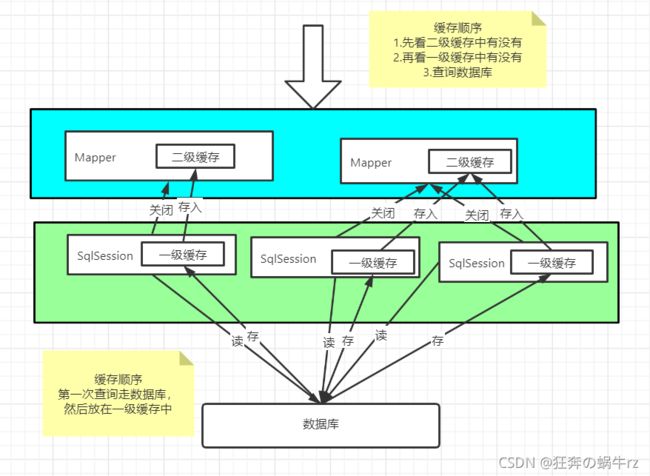
15.1 缓存原理浅析
大致思路:第一查询走数据库,然后放在一级缓存中,一次会话关闭后,一级缓存将数据存入二级缓存
15.1.1 缓存执行顺序
- 先看二级缓存中有没有
- 再看一级缓存中有没有
- 最后查询数据库
15.1.2 缓存执行顺序图解
15.1.3 缓存执行顺序测试
1.创建项目和导入资源依赖
- 创建一个Maven项目,在pom.xml文件中导入资源依赖jar包
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombokgroupId>
<artifactId>lombokartifactId>
<version>1.18.10version>
dependency>
dependencies>
2.编写核心配置文件
1-1 编写db.properties配置文件
driver=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis?useSSL=true&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8
username=root
pwd=123456
1-2 编写mybatis-config.xml配置文件
DOCTYPE configuration
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<configuration>
<properties resource="db.properties">properties>
<settings>
<setting name="logImpl" value="STDOUT_LOGGING"/>
settings>
<typeAliases>
<package name="com.kuang.pojo"/>
typeAliases>
<environments default="development">
<environment id="development">
<transactionManager type="JDBC"/>
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="${driver}"/>
<property name="url" value="${url}"/>
<property name="username" value="${username}"/>
<property name="password" value="${pwd}"/>
dataSource>
environment>
environments>
<mappers>
<mapper class="com.kuang.dao.UserMapper"/>
mappers>
configuration>
3.编写实体类和工具类
3-1 编写User实体类
package com.kuang.pojo;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
@Data // 使用@Data注解, 引入无参构造, get和set方法以及toString方法
@AllArgsConstructor // 引入有参构造方法
@NoArgsConstructor // 引入无参构造方法
public class User {
private int id; // 用户编号
private String name; // 用户名
private String pwd; // 密码
}
3-2 编写MybatisUtils工具类
package com.kuang.utils;
/**
* SqlSessionFactoryBuilder -- 建造工厂
* --> sqlSessionFactory -- 生产sqlSession
* --> sqlSession
*/
public class MybatisUtils {
// 获取SqlSessionFactory
private static SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory;
// 静态方法体
static {
try {
// 读取配置文件
String resource = "mybatis-config.xml";
// 解析配置文件流
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
// 获取工厂
sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* SqlSession提供了在数据库执行SQL命令所需的所有方法
*/
public static SqlSession getSqlSession() {
// 设置参数为true,实现自动提交
return sqlSessionFactory.openSession(true);
}
}
4.编写Mapper接口及映射文件
4-1 编写Mapper接口
package com.kuang.dao;
public interface UserMapper {
// 根据id查询指定用户
User queryUserById(@Param("id") int id);
// 更新用户信息
int updateUser(User user);
}
4-2 编写UserMapper.xml
DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.kuang.dao.UserMapper">
<select id="queryUserById" resultType="user">
Select * from user where id = #{id}
select>
<update id="updateUser" parameterType="User">
Update mybatis.user set name = #{name}, pwd = #{pwd} where id = #{id}
update>
mapper>
5.编写测试类和查看测试结果
5-1 编写MyTest测试类
package com.kuang.dao;
public class MyTest {
// 通过id查询指定的用户信息
@Test
public void queryUserById2() {
// 分别获取两个sqlSession对象
SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtils.getSqlSession();
SqlSession sqlSession2 = MybatisUtils.getSqlSession();
// 获取第一个Mapper接口对象
UserMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
// 调用queryUserById方法,查询id为1的用户信息
User user = mapper.queryUserById(1);
// 打印用户信息
System.out.println(user);
// 关闭第一个sqlSession对象
sqlSession.close();
// 没有特别含义, 仅用于分隔上下内容
System.out.println("======================");
// 获取第二个Mapper接口对象
UserMapper mapper2 = sqlSession2.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
// 调用queryUserById方法,再次查询id为1的用户信息
User user2 = mapper2.queryUserById(1);
// 打印用户信息
System.out.println(user2);
// 调用queryUserById方法,查询id为2的用户信息
User user3 = mapper2.queryUserById(2);
// 分别打印id为1和2的用户信息
System.out.println(user2);
System.out.println(user3);
// 调用queryUserById方法,再次查询id为2的用户信息
User user4 = mapper2.queryUserById(2);
// 打印用户信息
System.out.println(user4);
// 关闭第二个sqlSession对象
sqlSession2.close();
}
}
5-2 测试结果及分析
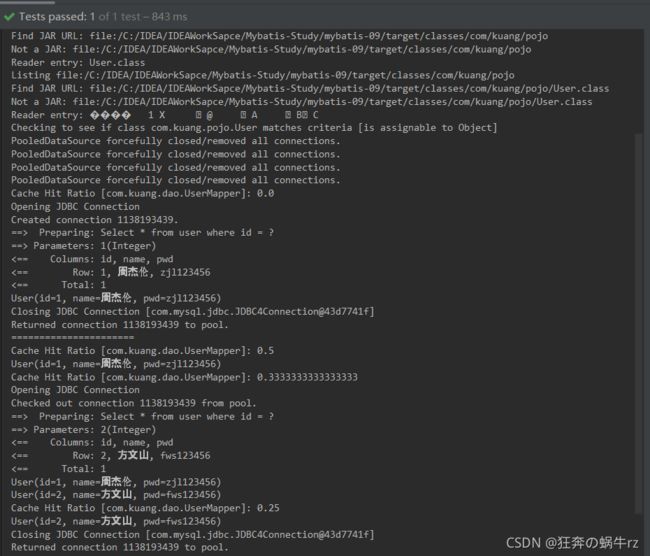
结果:都先后成功查询到了id为1和id为2的用户信息!
分析:
-
第一次查询id为1的用户时,执行一次预编译SQL去查询数据库,然后将数据存入一级缓存
-
第一次查询结束后,关闭sqlSession会话时,一级缓存又将数据存入二级缓存中,因此,当第二次查询id为1的用户时,就直接查询二级缓存,不需要再次访问数据库了
-
同理,第一次查询id为2的用户时,由于第一次查询,即不存在二级缓存,也不存在一级缓存,因此执行一次预编译SQL,去查询数据库,然后将数据存入一级缓存中
-
当关闭本次会话后,一级缓存又把数据存入二级缓存,当第二次查询id为2时,便直接查询二级缓存,也不需要再次访问数据库了
15.1.4 开启关闭使用缓存和刷新缓存
1.开启与关闭使用缓存
- 在使用二级缓存的Mapper.xml映射文件中设置useCache的值即可,一般用于查询数据信息
DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.kuang.dao.UserMapper">
<cache/>
<select id="queryUserById" resultType="user" useCache="true">
Select * from user where id = #{id}
select>
mapper>
2.开启与关闭刷新缓存
- 在使用二级缓存的Mapper.xml映射文件中设置 flushCache的值即可,一般在修改数据时使用
DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.kuang.dao.UserMapper">
<cache/>
<update id="updateUser" parameterType="user" flushCache="false">
Update mybatis.user set name = #{name}, pwd = #{pwd} where id = #{id}
update>
mapper>
15.2 自定义缓存-Ehcache的简单使用
15.2.1 什么是Ehcache?
- Ehcache是一个纯Java的进程内缓存框架,具有快速、精干的特点,是==Hibernate中默认的CacheProvider==
- Ehcache是一种广泛使用的开源Java分布式缓存
- 主要面向通用缓存、JavaEE和轻量级容器
- 它具有内存和磁盘存储、缓存加载器、缓存拓展、缓存异常处理程序、一个gzip缓存servlet过滤器、支持REST和SOAP API等特点
15.2.2 Ehcache主要特点
- 快速、简单,具有多种缓存策略
- 缓存数据有两级:内存和磁盘,因此无需担心容量问题
- 缓存数据会在虚拟机重启的过程中写入磁盘
- 可以通过RMI、可插入API等方式进行分布式缓存
- 具有缓存和缓存管理器的监听接口
- 支持多级缓存管理器实例,以及一个实例的多个缓存区域
- 提供Hibernate的缓存实现
15.2.3 Ehcache的简单使用
1.导入相关的资源依赖jar包
- 在项目的pom.xml文件中导入mybatis-ehcache资源依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.cachesgroupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-ehcacheartifactId>
<<font color='red'>versiondependency>1.1.0version>
dependency>
2.编写ehcache缓存的配置文件
- 在resources文件夹下创建ehcache.xml文件,然后编写具体的配置信息
<ehcache xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:noNamespaceSchemaLocation="http://ehcache.org/ehcache.xsd"
updateCheck="false">
<diskStore path="./tmpdir/Tmp_EhCache"/>
<defaultCache
eternal="false"
maxElementsInMemory="10000"
overflowToDisk="false"
diskPersistent="false"
timeToIdleSeconds="1800"
timeToLiveSeconds="259200"
memoryStoreEvictionPolicy="LRU"/>
<cache
name="cloud_user"
eternal="false"
maxElementsInMemory="5000"
overflowToDisk="false"
diskPersistent="false"
timeToIdleSeconds="1800"
timeToLiveSeconds="1800"
memoryStoreEvictionPolicy="LRU"/>
ehcache>
名词解释:
-
name:缓存名称
-
maxElementsInMemory:缓存最大数目
-
maxElementsOnDisk:硬盘最大缓存个数
-
eternal:对象是否永久有效,一旦设置,timeout将不起作用
-
overflowToDisk:是否保存到硬盘,当系统宕机时
-
timeToIdleSeconds:设置对象在失效前的允许闲置时间(单位:秒),仅eternal="false"对象不是永久有效时使用,可选属性,默认值是0,也就是可闲置的时间无穷大
-
timeToLiveSecond: 设置对象在失效前允许存活时间(单位:秒),最大时间介于创建时间和失效时间之间,仅当eternal="false"对选不是永久有效时使用,默认是0,也就是对象存活时间无穷大
-
diskPersistent:是否缓存虚拟机重启数据
-
diskSpoolBufferSizeMB: 这个参数设置DiskStore(磁盘缓存)的缓存区大小;默认是300MB,每个Cache都应该有自己的一个缓冲区
-
diskExpiryThreadIntervalSeconds:磁盘失效线程运行时间间隔,默认是120秒 ==
-
memoryStoreEvictionPolicy: 当达到maxElementsInMemory限制时,Ehcache将会根据指定的策略去清理内存,默认策略是LRU(最近最少使用)
-
memoryStoreEvictionPolicy可选策略:LRU(最近最少使用,默认策略)、FIFO(先进先出)、LFU(最少访问次数)
-
FIFO:英文全称为First In First Out,即先进先出
-
LFU:英文全称为Less Frequently Used,简单来说,就是一直以来最少被使用的
-
LRU:英文全称为Least Recently Used,即最近最少使用的。缓存的元素有一个时间戳,当缓存容量容量满了,而又需要腾出地方来缓存新的元素的时候,那么现有缓存元素中时间戳离当前时间最远的元素出缓存
3.在Mapper配置文件中指定ehcache
- 在要使用ehcache缓存的UserMapper.xml配置文件中指定使用
DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.kuang.dao.UserMapper">
<cache type="org.mybatis.caches.ehcache.EhcacheCache"/>
<select id="queryUserById" resultType="user" useCache="true">
Select * from user where id = #{id}
select>
mapper>
- 也可以自定义实现Cache接口的MyCache工具类,但是个人感觉没有必要
package com.kuang.utils;
import org.apache.ibatis.cache.Cache;
// 定义实现Cache接口的MyCache工具类,就可以使用ehcache的缓存策略了
public class MyCache implements Cache {
public String getId() {
return null;
}
public void putObject(Object key, Object value) {
}
public Object getObject(Object key) {
return null;
}
public Object removeObject(Object key) {
return null;
}
public void clear() {
}
public int getSize() {
return 0;
}
}
4.编写MyTest测试类和查看测试结果
4-1 编写MyTest测试类
package com.kuang.dao;
public class MyTest {
// 通过id查询指定的用户信息
@Test
public void queryUserById2() {
// 分别获取两个sqlSession对象
SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtils.getSqlSession();
SqlSession sqlSession2 = MybatisUtils.getSqlSession();
// 获取第一个Mapper接口对象
UserMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
// 调用queryUserById方法,查询id为1的用户信息
User user = mapper.queryUserById(1);
// 打印用户信息
System.out.println(user);
// 关闭第一个sqlSession对象
sqlSession.close();
// 没有特别含义, 仅用于分隔上下内容
System.out.println("======================");
// 获取第二个Mapper接口对象
UserMapper mapper2 = sqlSession2.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
// 调用queryUserById方法,再次查询id为1的用户信息
User user2 = mapper2.queryUserById(1);
// 打印用户信息
System.out.println(user2);
// 调用queryUserById方法,查询id为2的用户信息
User user3 = mapper2.queryUserById(2);
// 打印用户信息
System.out.println(user2);
System.out.println(user3);
// 调用queryUserById方法,再次查询id为2的用户信息
User user4 = mapper2.queryUserById(2);
// 打印用户信息
System.out.println(user4);
// 关闭第二个sqlSession对象
sqlSession2.close();
}
}
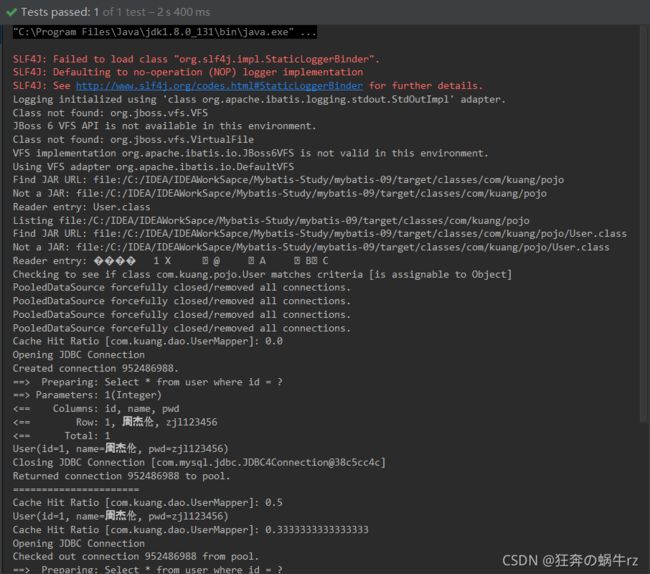
4-2 查看测试结果
结果:与14.5.3的缓存执行顺序测试结果基本相同!
5.缓存知识扩展
- 实际开发中,一般都会会用Redis数据库来做缓存:即K-V键值对
- Redis是NOSQL型 (即非关系型) 数据库的一种,非关系型数据库通常指数据以对象的形式存储在数据库中,而 对象之间的关系通过每个对象自身的属性来决定
好了,今天的有关 缓存原理浅析和自定义缓存Ehcache的简单使用 的学习就到此结束啦。欢迎小伙伴们积极学习和讨论,喜欢的可以给蜗牛君点个关注,顺便来个一键三连。我们下期见,拜拜啦!
参考视频链接:【狂神说Java】Mybatis最新完整教程IDEA版通俗易懂