namespace System {
public delegate void Action<T>(T obj);
public delegate bool Predicate<T>(T obj);
public delegate U Converter<T,U>(T from);
public delegate int Comparison<T>(T x, T y);
}
public class List<T> : … {
public int FindIndex(Predicate<T> match);
public int FindIndex(int index, Predicate<T> match);
public int FindIndex(int index, int count, Predicate<T> match);
public int FindLastIndex(Predicate<T> match);
public int FindLastIndex(int index, Predicate<T> match);
public int FindLastIndex(int index, int count, Predicate<T> match);
public List<T> FindAll(Predicate<T> match);
public T Find(Predicate<T> match);
public T FindLast(Predicate match);
public bool Exists(Predicate<T> match);
public bool TrueForAll(Predicate<T> match);
public int RemoveAll(Predicate<T> match);
public void ForEach(Action<T> action);
public void Sort(Comparison<T> comparison);
public List<U> ConvertAll<U>(Converter<T,U> converter);
}
Finding Even Integers in List<T>
List<int> integers = new List<int>();
For(int i=1; i<=10; i++) integers.Add(i);
List<int> even = integers.FindAll(delegate(int i){
return i%2==0;
});
public class Order {
public Order(int number, string item) { … }
public int Number { get { return number; } }
public string Item { get { return item; } }
…
}
List<Order> orders = new List<Order>();
int orderNumber = 10;
Order order = orders.Find(delegate(Order o){
return o.Number==orderNumber;
});
List<int> integers = new List<int>();
for(int i=1; i<=10; i++) integers.Add(i);
int sum;
integers.ForEach(delegate(int i){ sum+=i; });
List<Order> orders = new List<Order>();
orders.Add(new Order(10,”Milk”));
orders.Add(new Order(5,”Cheese”));
orders.Sort(delegate(Order x, Order y){
return Comparer<int>.Default.Compare(x.Number,y.Number);
});
List<Order> orders = new List<Order>();
orders.Add(new Order(10,”Milk”));
orders.Add(new Order(5,”Cheese”));
List<int> numbers = orders.ConvertAll(delegate(Order x){
return o.Number;
});
转自:http://www.dotblogs.com.tw/puma/archive/2009/05/28/asp.net-generic-list-sort-find-findall-exsit.aspx#12190
最近寫案子常常用到List<T>,這個東西還真好用
因為它有下列東西:
List<T>.Sort() → 排序T
List<T>.Find() → 找出一個T
List<T>.FindAll() →找出多個T
List<T>.Exist() →判斷T是否存在
小弟就寫個範例介紹這些東西吧..
GenericList.aspx
01 |
<%@ Page Language="C#" AutoEventWireup="true" CodeFile="GenericList.aspx.cs" Inherits="GenericList" %> |
07 |
<title>GenericList</title> |
10 |
<form id="form1" runat="server"> |
13 |
<asp:GridView ID="GridView1" runat="server"> |
GenericList.aspx.cs
002 |
using System.Collections.Generic; |
005 |
using System.Web.UI.WebControls; |
007 |
public partial class GenericList : System.Web.UI.Page |
010 |
protected void Page_Load(object sender, EventArgs e) |
012 |
List<Person> lstPerson = new List<Person>(); |
013 |
lstPerson.Add(new Person(1, "puma", 10)); |
014 |
lstPerson.Add(new Person(2, "F6 Team", 20)); |
015 |
lstPerson.Add(new Person(3, "ASP.NET", 30)); |
016 |
lstPerson.Add(new Person(4, "Dotblogs", 40)); |
019 |
this.GridView1.DataSource = lstPerson; |
020 |
this.GridView1.DataBind(); |
026 |
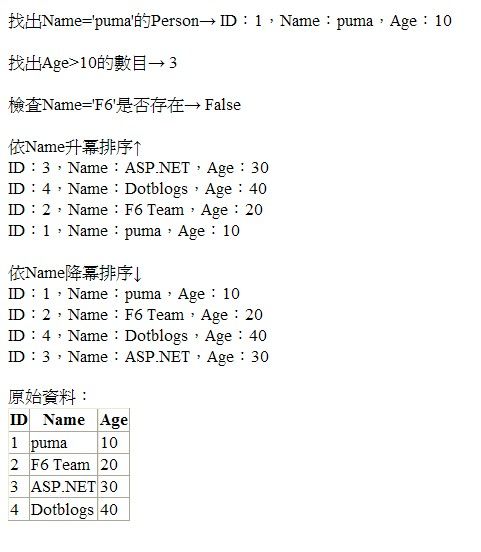
Response.Write("找出Name='puma'的Person→ "); |
027 |
Response.Write(lstPerson.Find(delegate(Person p) { return p.Name == "puma"; }).ToString() + "<p>"); |
033 |
Response.Write("找出Age>10的數目→ "); |
034 |
Response.Write(lstPerson.FindAll(delegate(Person p) { return p.Age > 10; }).Count.ToString() + "<p>"); |
040 |
Response.Write("檢查Name='F6'是否存在→ "); |
041 |
Response.Write(lstPerson.Exists(delegate(Person p) { return p.Name == "F6"; }).ToString() + "<p>"); |
047 |
Response.Write("<p>依Name升冪排序↑<br/>"); |
048 |
lstPerson.Sort(delegate(Person p1, Person p2) { return Comparer<string>.Default.Compare(p1.Name, p2.Name); }); |
049 |
foreach (Person p in lstPerson) |
051 |
Response.Write(p.ToString() + "<br/>"); |
058 |
Response.Write("<p>依Name降冪排序↓<br/>"); |
059 |
lstPerson.Sort(delegate(Person p1, Person p2) { return Comparer<string>.Default.Compare(p2.Name, p1.Name); }); |
060 |
foreach (Person p in lstPerson) |
062 |
Response.Write(p.ToString() + "<br/>"); |
070 |
private string _Name; |
073 |
public Person(int ID, string Name, int Age) |
088 |
set { _Name = value; } |
089 |
get { return _Name; } |
094 |
set { _Age = value; } |
098 |
public override string ToString() |
100 |
return string.Format("ID:{0},Name:{1},Age:{2}", _ID, _Name, _Age); |
執行結果:
转自微软官方:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Xml.Linq;
namespace Find
{
class Program
{
private static string IDtoFind = "bk109";
private static List<Book> Books = new List<Book>();
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
FillList();
// Find a book by its ID.
Book result = Books.Find(
delegate(Book bk)
{
return bk.ID == IDtoFind;
}
);
if (result != null)
{
DisplayResult(result, "Find by ID: " + IDtoFind);
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("\nNot found: {0}", IDtoFind);
}
// Find last book in collection published before 2001.
result = Books.FindLast(
delegate(Book bk)
{
DateTime year2001 = new DateTime(2001, 01, 01);
return bk.Publish_date < year2001;
});
if (result != null)
{
DisplayResult(result, "Last book in collection published before 2001:");
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("\nNot found: {0}", IDtoFind);
}
// Find all computer books.
List<Book> results = Books.FindAll(FindComputer);
if (results != null)
{
DisplayResults(results, "All computer:");
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("\nNo books found.");
}
// Find all books under $10.00.
results = Books.FindAll(
delegate(Book bk)
{
return bk.Price < 10.00;
}
);
if (results != null)
{
DisplayResults(results, "Books under $10:");
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("\nNo books found.");
}
// Find index values.
Console.WriteLine();
int ndx = Books.FindIndex(FindComputer);
Console.WriteLine("Index of first computer book: {0}", ndx);
ndx = Books.FindLastIndex(FindComputer);
Console.WriteLine("Index of last computer book: {0}", ndx);
int mid = Books.Count / 2;
ndx = Books.FindIndex(mid, mid, FindComputer);
Console.WriteLine("Index of first computer book in the second half of the collection: {0}", ndx);
ndx = Books.FindLastIndex(Books.Count - 1, mid, FindComputer);
Console.WriteLine("Index of last computer book in the second half of the collection: {0}", ndx);
}
// Populates the list with sample data.
private static void FillList()
{
// Create XML elements from a source file.
XElement xTree = XElement.Load(@"c:\temp\books.xml");
// Create an enumerable collection of the elements.
IEnumerable<XElement> elements = xTree.Elements();
// Evaluate each element and set set values in the book object.
foreach (XElement el in elements)
{
Book book = new Book();
book.ID = el.Attribute("id").Value;
IEnumerable<XElement> props = el.Elements();
foreach (XElement p in props)
{
if (p.Name.ToString().ToLower() == "author")
{
book.Author = p.Value;
}
else if (p.Name.ToString().ToLower() == "title")
{
book.Title = p.Value;
}
else if (p.Name.ToString().ToLower() == "genre")
{
book.Genre = p.Value;
}
else if (p.Name.ToString().ToLower() == "price")
{
book.Price = Convert.ToDouble(p.Value);
}
else if (p.Name.ToString().ToLower() == "publish_date")
{
book.Publish_date = Convert.ToDateTime(p.Value);
}
else if (p.Name.ToString().ToLower() == "description")
{
book.Description = p.Value;
}
}
Books.Add(book);
}
DisplayResults(Books, "All books:");
}
// Explicit predicate delegate.
private static bool FindComputer(Book bk)
{
if (bk.Genre == "Computer")
{
return true;
}
{
return false;
}
}
private static void DisplayResult(Book result, string title)
{
Console.WriteLine();
Console.WriteLine(title);
Console.WriteLine("\n{0}\t{1}\t{2}\t{3}\t{4}\t{5}", result.ID,
result.Author, result.Title, result.Genre, result.Price,
result.Publish_date.ToShortDateString());
Console.WriteLine();
}
private static void DisplayResults(List<Book> results, string title)
{
Console.WriteLine();
Console.WriteLine(title);
foreach (Book b in results)
{
Console.Write("\n{0}\t{1}\t{2}\t{3}\t{4}\t{5}", b.ID,
b.Author, b.Title, b.Genre, b.Price,
b.Publish_date.ToShortDateString());
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
}
public class Book
{
public string ID { get; set; }
public string Author { get; set; }
public string Title { get; set; }
public string Genre { get; set; }
public double Price { get; set; }
public DateTime Publish_date { get; set; }
public string Description { get; set; }
}
}
