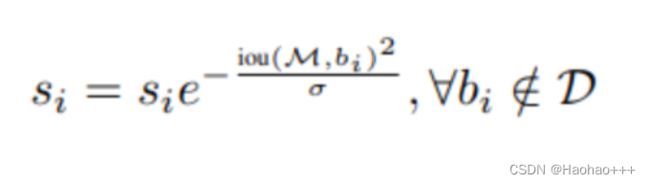NMS与Soft NMS算法解析以及numpy实现
1. NMS算法
1.1 什么是NMS算法
NMS全称为Non Maximum Suppression,中文意思是非极大值抑制,字面意思就是不是极大值的元素被抑制掉,其实就是筛选出局部最大值得到最优解。NMS算法被广泛运用于目标检测算法处理网络输出的边界框。
1.2 为什么在目标检测中要使用NMS算法
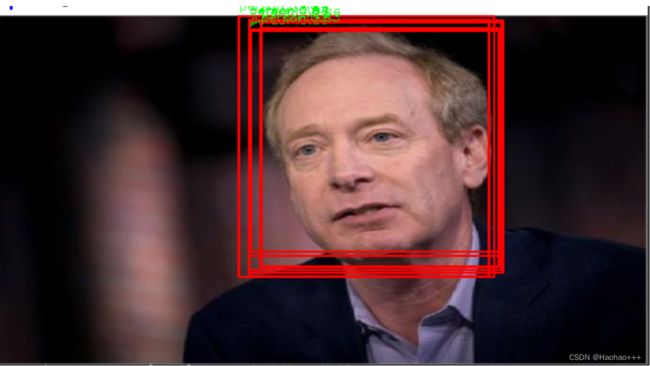
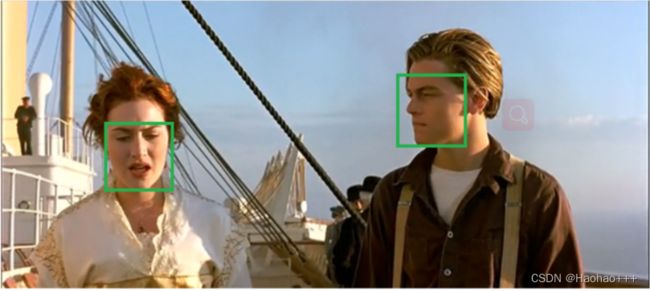
在目标检测中如果不是用NMS算法,则网络的输出结果就会向如下图所示,许多预测框都框住了目标,但是这些框并不是我们都想要的,我们想要的是其中框出来最好的那一个预测框。此时,我们就需要利用NMS算法去筛选出最适合的预测框。
1.3 在目标检测中怎么样使用NMS算法
我们以检测人脸为例,在目标检测中使用NMS算法的流程:
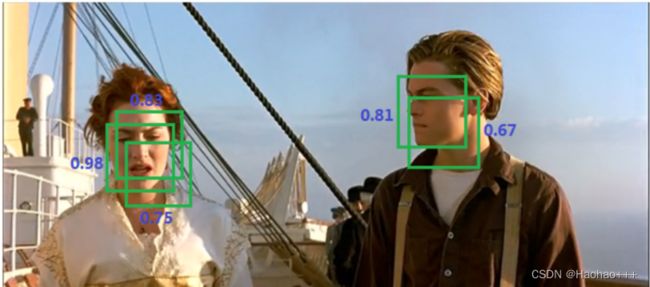
- 首先,需要通过置信度阈值消除小于阈值的预测框,比如阈值为0.5,如图下图所示,得到过滤后的预测框。
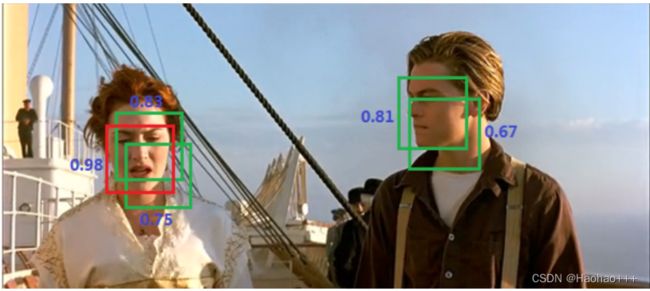
- 将所有的预测框的置信度降序排列,得到置信度最大的预测框,如下图红色框:
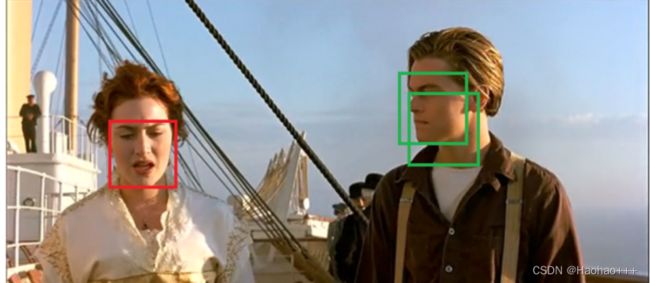
- 再设置一个IOU阈值,所谓IOU就是两个框面积的交并比,遍历其余的框,如果和当前最高分框的IOU大于一定阈值,我们就将框删除,如下图所示。
- 再重复1、2、3步骤,得到最终的结果。
Python代码如下:
代码来自:https://github.com/rbgirshick/fast-rcnn/blob/master/lib/utils/nms.py
import numpy as np
def nms(dets, thresh):
# ------------------------------------ #
# 获取所有预测框的左上角x1, y1、右上角x2, y2以及置信度scores
# ------------------------------------ #
x1 = dets[:, 0]
y1 = dets[:, 1]
x2 = dets[:, 2]
y2 = dets[:, 3]
scores = dets[:, 4]
# ------------------------------------ #
# 获取所有预测框的面积
# ------------------------------------ #
areas = (x2 - x1 + 1) * (y2 - y1 + 1)
# ------------------------------------ #
# 所有预测框降序排列(保存的是下标)
# ------------------------------------ #
order = scores.argsort()[::-1]
# ------------------------------------ #
# keep为最后计算保留下来预测框的下标
# ------------------------------------ #
keep = []
while order.size > 0:
# ------------------------------------ #
# 取出置信度值最大的下标
# ------------------------------------ #
i = order[0]
keep.append(i)
# ------------------------------------ #
# 计算IOU
# ------------------------------------ #
xx1 = np.maximum(x1[i], x1[order[1:]])
yy1 = np.maximum(y1[i], y1[order[1:]])
xx2 = np.minimum(x2[i], x2[order[1:]])
yy2 = np.minimum(y2[i], y2[order[1:]])
w = np.maximum(0.0, xx2 - xx1 + 1)
h = np.maximum(0.0, yy2 - yy1 + 1)
inter = w * h
ovr = inter / (areas[i] + areas[order[1:]] - inter)
# ------------------------------------ #
# 过滤小于IOU阈值的边界框
# ------------------------------------ #
inds = np.where(ovr <= thresh)[0]
# ------------------------------------ #
# ovr 数组的长度比 order 数组少一个,这里将所有下标后移一位
# ------------------------------------ #
order = order[inds + 1]
return keep
2. Soft NMS算法
2.1 什么是Soft NMS算法
Soft NMS是对NMS的优化算法,它在不增加额外参数的情况下且只需要对NMS算法进行简单的改动就能提高AP。该Soft-NMS算法在标准数据集PASCAL VOC2007(较R-FCN和Faster-RCNN提升1.7%)和MS-COCO(较R-FCN提升1.3%,较Faster-RCNN提升1.1%)上均有提升。
Soft NMS的主要思想
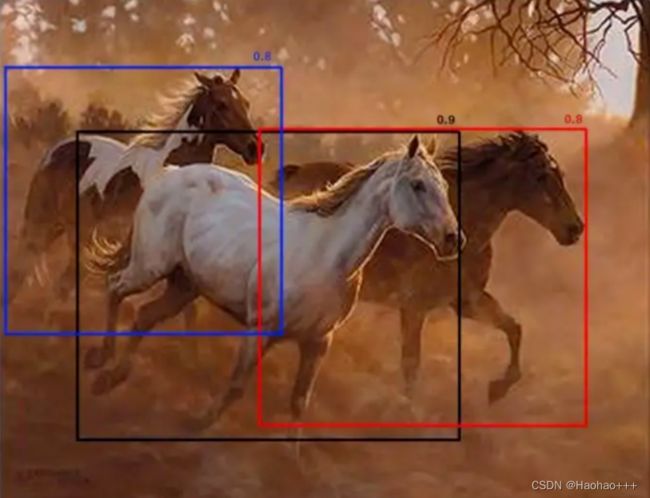
如下图所示,假设重叠的阈值为 0.5,图 中当黑框与红框比较时,两者之间的IoU为0.51,则红框将被删除,即使置信度高于许多其他 IoU 较小的框。因此,如果有两个并排的对象,则其中一个将被消除,这会降低模型的精度。
NMS与Soft NMS都有一个共同点,都是从置信度最大的框开始逐渐迭代的。
因此,Soft NMS则不再是直接将大于重叠的阈值的框删除,而是根据重叠程度衰减框的置信度得分,再根据设定的置信度阈值,去除小于置信度阈值的框。
改变置信度的方法有两种:
- 线性法
如下公式:
其中, i o u ( M , b i ) iou(M, b_i) iou(M,bi)代表最大置信度得分的框 M M M与第 i i i个框 b i b_i bi的IOU, N t N_t Nt代表重叠的阈值, s i s_i si代表第 i i i个框的置信度得分 s i s_i si
通过分析可以得出,当重叠的IOU增大时,置信度得分确实得到线性的下降。
- 高斯法
如下公式:
其中: i o u ( M , b i ) iou(M, b_i) iou(M,bi)代表最大置信度得分的框 M M M与第 i i i个框 b i b_i bi的IOU, σ \sigma σ为一个可设定的常数, s i s_i si代表第 i i i个框的置信度得分 s i s_i si。
通过分析可以得出,当重叠的IOU增大时,置信度得分确实下降了。
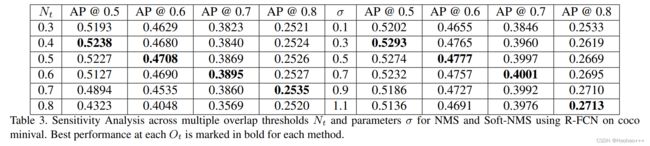
如下图是原论文中Soft NMS在R-FCN中 N t N_t Nt与 σ \sigma σ的变化对AP的影响。
2.2 代码实现:
参考代码:https://github.com/DocF/Soft-NMS/blob/master/soft_nms.py
import numpy as np
def py_cpu_softnms(dets, sc, Nt=0.3, sigma=0.5, thresh=0.001, method=2):
"""
py_cpu_softnms
:param dets: boexs 坐标矩阵 format [y1, x1, y2, x2]
:param sc: 每个 boxes 对应的分数
:param Nt: iou 交叠门限
:param sigma: 使用 gaussian 函数的方差,根据需要设置
:param thresh: 最后的分数门限
:param method: 使用的方法
:return: 留下的 boxes 的 index
"""
# indexes concatenate boxes with the last column
N = dets.shape[0]
indexes = np.array([np.arange(N)])
dets = np.concatenate((dets, indexes.T), axis=1)
# the order of boxes coordinate is [y1,x1,y2,x2]
y1 = dets[:, 0]
x1 = dets[:, 1]
y2 = dets[:, 2]
x2 = dets[:, 3]
scores = sc
areas = (x2 - x1 + 1) * (y2 - y1 + 1)
for i in range(N):
# intermediate parameters for later parameters exchange
tBD = dets[i, :].copy()
tscore = scores[i].copy()
tarea = areas[i].copy()
pos = i + 1
#
if i != N-1:
maxscore = np.max(scores[pos:], axis=0)
maxpos = np.argmax(scores[pos:], axis=0)
else:
maxscore = scores[-1]
maxpos = 0
if tscore < maxscore:
dets[i, :] = dets[maxpos + i + 1, :]
dets[maxpos + i + 1, :] = tBD
tBD = dets[i, :]
scores[i] = scores[maxpos + i + 1]
scores[maxpos + i + 1] = tscore
tscore = scores[i]
areas[i] = areas[maxpos + i + 1]
areas[maxpos + i + 1] = tarea
tarea = areas[i]
# IoU calculate
xx1 = np.maximum(dets[i, 1], dets[pos:, 1])
yy1 = np.maximum(dets[i, 0], dets[pos:, 0])
xx2 = np.minimum(dets[i, 3], dets[pos:, 3])
yy2 = np.minimum(dets[i, 2], dets[pos:, 2])
w = np.maximum(0.0, xx2 - xx1 + 1)
h = np.maximum(0.0, yy2 - yy1 + 1)
inter = w * h
ovr = inter / (areas[i] + areas[pos:] - inter)
# Three methods: 1.linear 2.gaussian 3.original NMS
if method == 1: # linear
weight = np.ones(ovr.shape)
weight[ovr > Nt] = weight[ovr > Nt] - ovr[ovr > Nt]
elif method == 2: # gaussian
weight = np.exp(-(ovr * ovr) / sigma)
else: # original NMS
weight = np.ones(ovr.shape)
weight[ovr > Nt] = 0
scores[pos:] = weight * scores[pos:]
# select the boxes and keep the corresponding indexes
inds = dets[:, 4][scores > thresh]
keep = inds.astype(int)
return keep