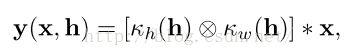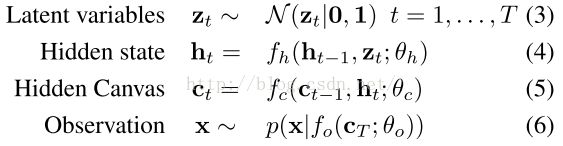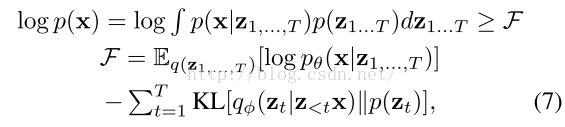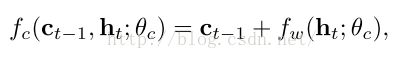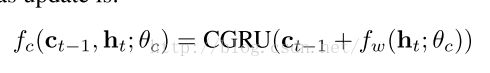DeepMind one shot learning 论文批注 One-Shot Generalization in Deep Generative Models
One-Shot Generalization in Deep Generative Models
Danilo J. RezendeShakir Mohamed Ivo Danihelka Karol Gregor Daan Wierstra
Google DeepMind,London
2. Varieties of Attention
Spatially-transformed attention
A more powerful approach is to use amechanism that provides invariance to shape and size of objects in the images (generalaffine transformations).
Spatial transformers (ST) process an inputimage x, using parameters h, and generate anoutput y(x,h):
where κh and κw are 1-dimensional kernels, ⊗ indicates the tensor outer-product of the two kernels and ∗ indicates a convolution.
Inference,readingattention: spatial transformers allow the model toobserve the input image in a canonical form, providing the desired invariance
生成,writing attention:handle position, scale and rotation of parts of the generated image
3. Iterative and Attentive Generative Models
3.1. Latent Variable Models and Variational Inference
带潜变量的生成模型通过一个观察样本描述概率的产生。
最简单的公式:使用高斯潜变量z的PCA和因子分析
Generativemodels with latent variables:
DeepGenerative Models:A hierarchyof L layers of latent variables, where each layerdepends on the layer above in a non-linear way
使用深度神经网络表示非线性依赖。
We specifythisnon-linear dependency using deep neural netWorks.
To compute the marginal probability of the data, we must integrate over anyunobserved variables:
Deep latent Gaussian models深度潜在高斯模型
——prior distributionp(z)先验概率(关于潜变量z),高斯分布(分布已知,非线性组合)
Likelihoodfunction似然函数p(x|z),appropriate for the observed data, suchas a Gaussian, Bernoulli, categorical or other distribution, and that isdependent in a nonlinear way on the latent variables.
潜变量z,数据点data points x
积分难求,变分:
Variational inference: Transforms the difficult integration into an optimization problemthat is typically more scalable and easier to solve.
使用下界近似边缘似然Approximate the marginal likelihood by a lower bound
Negative free energy负自由能
折中——
第一项:重构能力
第二项:后验分布复杂性
通过已知的带有变分参数φ的后验概率posteriorsqφ(z|x)近似真正的后验分布
Optimization parameters θ和φ:
amortizedinference approach 平摊推理方法
Represent the distribution q(z|x) as a recognition or inferencemodel
平摊后验推断posterior inference的开销
Generativemodel:A decoder of the latent variables
Inference network: data —(encoder)—> latent description
Combination :
deep latent variable model (typically latent Gaussian)
with variational inferencethat is implemented using an inference network is referred to as avariational auto-encoder (VAE).
3.2. Sequential Generative Models
目前提出的生成模型:刻画单步模型single step:
通过使用非线性前馈转换为潜变量,估计i.i.d(独立同分布)数据的似然函数。
Asequential generative model:
使用VAE(变分自编码)的潜变量模型的扩展。
Combine:stochastic & deterministic computation
Toform a multi-step generative process uses recursive transformations of thelatent variables.
结合随机和确定计算,使用潜变量的递归变换形成一个多步生成过程。
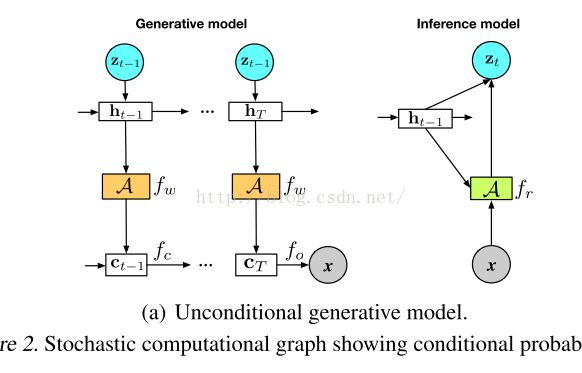
3.2.1. GENERATIVE MODEL
Describe the observed data over T timesteps using a set of latent variables zt at each step.
使用一系列潜变量z,在T个时间步长上描述观测数据
Each step:
1. Generate an independent set of K-dimensionallatent variables Zt (Stochasitc随机产生)
2. 函数Fh联系了相邻潜变量的依赖关系(类似LSTM)Deterministic
Fh transition function : LSTM network
3. hidden canvas 隐画布:输入:LSTMfcallows for many different transformations, and it is here where generative(writing) attention is used.生成了(写)注意力
4. Condition使用observationfunction fo(c; θo)计算
All parameters of this generative model asθ = {θh, θc, θo}.
3.2.2. Free Energy Objective
Objective function for inference andparameter learning
Optimize this objective function for the variationalparameters φ and the modelparameters θ, by stochastic gradientdescent using a mini-batch of data.
As with other VAEs, we use a single sampleof the latent variables generated from qφ(z|x)when computing the Monte Carlogradient.
当计算蒙特卡洛梯度时,使用单个从qφ(z|x)分布生成的浅变量。
3.2.3. HIDDEN CANVAS FUNCTIONS
Canvas transition function fc(ct−1,ht;θc)更新hiddencanvas状态:
使用非线性变换fw转换当前隐状态ht,然后和已存在的canvas Ct-1融合。
Hidden canvas:隐画布,与原始图像拥有同样 ,多个通道。
更新hidden canvas的两种方法
1. Additive Canvas
在原画布上添加hidden state的转换fw(Ct-1,ht; θc)
2. Gated Recurrent Canvas
使用Convolutional gatedrecurrent unit(CGRU)卷积门循环单元,提供非线性递归更新机制,类似于convolutional LSTMSs
Functionfw(ht; θw) is a writing function that is used by the canvas function to transformthe LSTM hidden state into the coordinate system of the hidden canvas.
LSTM隐层状态——>隐画布的坐标系。
这个映射可以使全部/部分连接,本文使用writing or generative attentionfunction
Final phase of the generative processtransforms
Hidden canvas CT—fo(c; θo)—>似然函数的参数
output function fo(c; θo) : 1*1卷积实现,当隐画布hidden canvas有不同尺寸时,使用CNN.
Transform the LSTM hidden state into the coordinatesystem of the hidden canvas.
3.2.4. DEPENDENT POSTERIOR INFERENCE 依赖后验推断
使用拥有自回归形式结构化的后验近似,i.e.q(zt|z
Inference network实现这个分布。
Each step:
1. 使用非线性变换fr生成一个关于输入图像和隐状态t-1的低维表示rt。
Reading function(与writing attention function配对)。
Reading function:Input image to be transformed into a new coordinate space that allows for easierinference computations.
Be implemented as a fully- orlocally-connected network,
Better inferenceis obtained using a reading or recognitionattention.
进一步使用非线性函数将Fr的结果与先前状态ht-1融合生成K维对角高斯分布的均值μ和方差σ。
Inference模型的所有参数![]()
3.2.5. MODEL PROPERTIES AND COMPLEXITY
模型特点:
(1)隐画布函数的选择:在hidden space产生pre-image,最后反向转换到图像空间。
One of the largest deviations is the introduction of the hidden canvas into the generativemodel that provides an important richness to the model, since it allows apre-image to be constructed in a hidden space before a finalcorrective transformation, using the function fo,is used.
Inference network
shareparameters of the LSTM from the prior—the removal of this additional recursivefunction has no effect on performance.
4. Image Generation and Analysis
数据 Data: Binary images
像素概率模型 Modelthe probability of the pixels : Bernoullilikelihood 伯努利分布
神经元单元 Units: 400 LSTMhidden units
空间变换 Spatial transformer : 12x12 kernels, used for recognition orgenerative attention
潜变量 Latent variable Zt: 4-D Gaussian distributions
时间步长 Timestep: 20-80
隐画布 Hiddencanvas: size of Image with4 channels
训练迭代 Approximativelyiterations: 800K
批量 mini-batches 24
训练集似然边界 likelihood bounds: 训练的最后1K次迭代的平均值
测试集似然边界 likelihood bounds: 24000个随机样本bound边界均值
4.1. MNIST and Multi-MNIST
Data Set
1. The binarized MNIST data set of Salakhutdinov &Murray (2008)
28X28 binary imageswith 50,000 training and 10,000test images.
2. Multi-MNIST data set
3. 64x64 images,two MNIST digits placed at random
Importance of each step
These results alsoindicate that longer sequences can lead to better performance。
The latent variableszt have diminishing contribution to the model as the number of steps grow.
Efficiently allocateand decide on the number of latent variables to use
4.2. Omniglot
The omniglot data set
105 X105 binaryimages across ;
1628 classes withjust 20 images per class.
4.3. Multi-PIE
Multi-PIE dataset:
48X48 RGB faceimages from various viewpoints
convertedto grayscale
Trainedour model on a subset comprising of all 15-viewpoints but only 3 out of the 19illumination conditions.
93,130training samples and 10, 000 test samples
5. One-Shot Generalization
Three tasks toevaluate one-shot generalization
(1) unconditional(free) generation,
(2) generation ofnovel variations of a given exemplar,
(3) generation ofrepresentative samples from a novel alphabet
Weak and one-shotgeneralization tests:
模型可以使用字母表中相近的字符训练,被期待将这种知识迁移到弱生成任务中。
Training data consists of all available alphabets,3character types from each
alphabet were removedto form test set.
Strong one-shot generalization test
使用30中字母表中字符训练,剩余20个字母表作为测试。