python——数学模块(math模块)
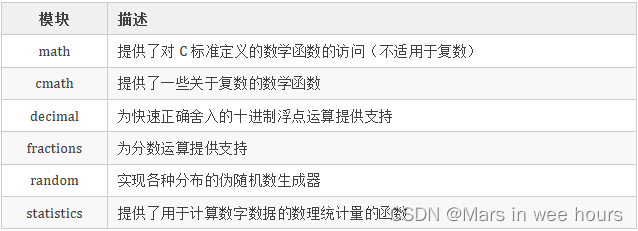
我们来看一下 Python 中数学相关模块,如下所示:
本文具体介绍一下相对比较常用的模块:math、decimal 和 random。
math 模块
先来看一下 math 模块中包含内容,如下所示:
>>> import math
>>> dir(math)
['__doc__', '__loader__', '__name__', '__package__', '__spec__', 'acos', 'acosh', 'asin', 'asinh', 'atan', 'atan2', 'atanh', 'ceil', 'copysign', 'cos', 'cosh', 'degrees', 'e', 'erf', 'erfc', 'exp', 'expm1', 'fabs', 'factorial', 'floor', 'fmod', 'frexp', 'fsum', 'gamma', 'gcd', 'hypot', 'inf', 'isclose', 'isfinite', 'isinf', 'isnan', 'ldexp', 'lgamma', 'log', 'log10', 'log1p', 'log2', 'modf', 'nan', 'pi', 'pow', 'radians', 'sin', 'sinh', 'sqrt', 'tan', 'tanh', 'tau', 'trunc']接下来具体看一下该模块的常用函数和常量。
ceil(x)
返回 x 的上限,即大于或者等于 x 的最小整数。看下示例:
import math
x = -1.5
print(math.ceil(x))floor(x)
返回 x 的向下取整,小于或等于 x 的最大整数。看下示例:
import math
x = -1.5
print(math.floor(x))fabs(x)
返回 x 的绝对值。看下示例:
import math
x = -1.5
print(math.fabs(x))fmod(x, y)
返回 x/y 的余数,值为浮点数。看下示例:
import math
x = 3
y = 2
print(math.fmod(x, y))factorial(x)
返回 x 的阶乘,如果 x 不是整数或为负数时则将引发 ValueError。看下示例:
import math
x = 3
print(math.factorial(3))pow(x, y)
返回 x 的 y 次幂。看下示例:
import math
x = 3
y = 2
print(math.pow(x, y))fsum(iterable)
返回迭代器中所有元素的和。看下示例:
import math
print(math.fsum((1, 2, 3, 4, 5)))gcd(x, y)
返回整数 x 和 y 的最大公约数。看下示例:
import math
x = 9
y = 6
print(math.gcd(x, y))sqrt(x)
返回 x 的平方根。看下示例:
import math
x = 9
print(math.sqrt(x))trunc(x)
返回 x 的整数部分。看下示例:
import math
x = 1.1415926
print(math.trunc(x))exp(x)
返回 e 的 x 次幂。看下示例:
import math
x = 2
print(math.exp(2))log(x[, base])
返回 x 的对数,底数默认为 e。看下示例:
import math
x = 10
y = 10
# 不指定底数
print(math.log(x))
# 指定底数
print(math.log(x, y))常量
import math
# 常量 e
print(math.e)
# 常量 π
print(math.pi)tan(x)
返回 x 弧度的正切值。看下示例:
import math
print(math.tan(math.pi / 3))atan(x)
返回 x 的反正切值。看下示例:
import math
print(math.atan(1))sin(x)
返回 x 弧度的正弦值。看下示例:
import math
print(math.sin(math.pi / 3))asin(x)
返回 x 的反正弦值。看下示例:
import math
print(math.asin(1))cos(x)
返回 x 弧度的余弦值。看下示例:import math
print(math.cos(math.pi / 3))acos(x)
返回 x 的反余弦值。看下示例:
import math
print(math.acos(1))