pytorch 二分类 生物数据预测
写在前面
这几天做了一些简单的对比实验,使用数据为长度39(处理后)的字母串形式的多肽链样本。本文将使用的函数打包记录。
模型架构
反卷积 nn.ConvTranspose2d和BCEloss nn.BCELoss()
将字母串编码成整数后用embedding层嵌入到向量空间中。
嵌入后需要用unsqueeze手动添加一层维度即一维通道,同卷积核的输入维度匹配。
由于嵌入后的样本特征维度为39*39较小,调用cv模型前先经过一层反卷积,能够放大特征维度。
torch.nn.ConvTranspose2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride=1, padding=0, output_padding=0, groups=1, bias=True, dilation=1, padding_mode='zeros', device=None, dtype=None)
训练时用到的也是二分类最典型的Loss Function:Binary Cross Entropy:
B C E L o s s = − y t r u e log ( p ( x ) ) + ( 1 − y t r u e ) log ( 1 − p ( x ) ) , y t r u e ∈ { 0 , 1 } BCELoss = -y_{true} \log(p(x)) + (1-y_{true})\log(1-p(x)),y_{true} \in \{0,1\} BCELoss=−ytruelog(p(x))+(1−ytrue)log(1−p(x)),ytrue∈{0,1}
p ( x ) p(x) p(x)为对样本 x x x的预测概率。
nn.BCELoss()的输入为一维向量,数值为 ( 0 , 1 ) (0,1) (0,1)内的概率,所以需要经过sigmoid函数,并用torch.squeeze将size为1的维度消去。
class network(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, net, em_dim=39, win_size=39):
super().__init__()
self.win_size = win_size
self.em_dim = em_dim
self.kernal = int((self.win_size-1)/2)
self.embedding = nn.Embedding(22, em_dim)
self.conv = nn.ConvTranspose2d(1, 3, 19, 2)#反卷积
self.net = net
self.classifier = nn.Linear(2, 1)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.embedding(x)
x = torch.unsqueeze(x, dim=1)
#(batchsize,seq_length,em_dim) -> (batchsize,input_tunnel,seq_length,em_dim)
x = self.conv(x)
x = self.net(x)
x = self.classifier(x)
x = torch.sigmoid(x)
x = torch.squeeze(x, dim=-1)
#注意这里的squeeze:(batchsize,1)->batchsize
return x
resnet18
模型架构调用timm即可
import timm
resnet = timm.create_model('resnet18', pretrained=False, num_classes=2)
model = network(resnet)
定义一个简单的train函数:
def train(model, num_epoch, train_loader, criterion, optimizer, device):
total_step = len(train_loader)
for epoch in range(num_epoch):
for i, (images, labels) in enumerate(train_loader):
images = images.to(device)
labels = labels.to(device)
# Forward pass
outputs = model(images)
loss = criterion(outputs, labels.float())
# Backward and optimize
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
if (i+1) % 100 == 0:
print('Epoch [{}/{}], Step [{}/{}], Loss: {:.4f}'
.format(epoch+1, num_epoch, i+1, total_step, loss.item()))
AlexNet
class AlexNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, num_classes: int = 2, dropout: float = 0.5) -> None:
super().__init__()
self.features = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(3, 64, kernel_size=11, stride=4, padding=2),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2),
nn.Conv2d(64, 192, kernel_size=5, padding=2),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2),
nn.Conv2d(192, 384, kernel_size=3, padding=1),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(384, 256, kernel_size=3, padding=1),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(256, 256, kernel_size=3, padding=1),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2),
)
self.avgpool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d((6, 6))
self.classifier = nn.Sequential(
nn.Dropout(p=dropout),
nn.Linear(256 * 6 * 6, 4096),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Dropout(p=dropout),
nn.Linear(4096, 4096),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Linear(4096, num_classes),
)
def forward(self, x: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
x = self.features(x)
x = self.avgpool(x)
x = torch.flatten(x, 1)
x = self.classifier(x)
return x
model = network(AlexNet())
LSTM
LSTM模型是自己搭的
class Lstm(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, em_dim=39, num_layers=1, num_classes=2):
super(Lstm, self).__init__()
self.num_layers = num_layers
self.embedding = nn.Embedding(22, em_dim)
self.lstm1 = nn.LSTM(em_dim, 64,
self.num_layers, batch_first=True, bidirectional=False)
self.fc_task = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(64, 32),
nn.Dropout(0.5),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(32, 2),
)
self.classifier = nn.Linear(2, 1)
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(0.5)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.embedding(x)
batch_size, features, seq_len = x.size()
out, (h_n, _) = self.lstm1(x)
h_n = h_n.view(batch_size, out.size()[-1])
out = self.fc_task(h_n)
out = self.classifier(out)
x = torch.sigmoid(out)
x = torch.squeeze(x)
return x
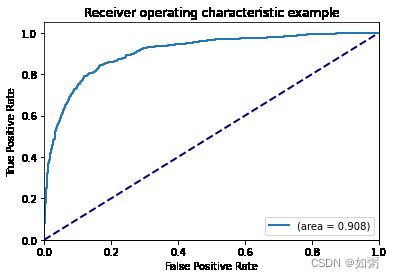
模型评估:ROC和PR曲线
测试的时候,绘制一条ROC曲线和PR曲线
def compute_metrics(prob, ytest):
## INPUT:prob:全部测试集的预测概率;ytest:测试集真实标签
## OUTPUT: False Positive Rate,True Positive Rate,auc
fpr, tpr, _ = roc_curve(ytest, prob)
auc_ = sklearn.metrics.auc(fpr, tpr)
return fpr, tpr, auc_
def draw_once_roc(prob, ytest):
plt.figure()
plt.plot([0, 1], [0, 1], color='navy', lw=2, linestyle='--')
fpr, tpr, auc = compute_metrics(prob, ytest)
lw = 2
plt.plot(fpr, tpr,
lw=lw, label='(area = %0.3f)' % auc)
plt.xlim([0.0, 1.0])
plt.ylim([0.0, 1.05])
plt.xlabel('False Positive Rate')
plt.ylabel('True Positive Rate')
plt.title('ROC curve')
plt.legend(loc="lower right")
plt.show()
def draw_once_pr(prob,ytest):
# models: a dictionary model_name:prob
plt.figure()
precision, recall, _ = precision_recall_curve(ytest, prob)
auc_precision_recall = sklearn.metrics.auc(recall, precision)
lw = 2
plt.plot(recall, precision,
lw=lw, label=model_name+'(area = %0.3f)' % auc_precision_recall)
plt.xlim([0.0, 1.0])
plt.ylim([0.0, 1.05])
plt.xlabel('Recall')
plt.ylabel('Precision')
plt.title('Precision/Recall Curve')
plt.legend(loc="lower right")
plt.show()
def draw_ROC(models):
# models: a dictionary (model_name:prob)
plt.figure()
plt.plot([0, 1], [0, 1], color='navy', lw=2, linestyle='--')
for i, model_name in enumerate(models):
prob = models[model_name]
fpr, tpr, auc = compute_metrics(prob)
lw = 2
plt.plot(fpr, tpr,
lw=lw, label=model_name+'(area = %0.3f)' % auc)
plt.xlim([0.0, 1.0])
plt.ylim([0.0, 1.05])
plt.xlabel('False Positive Rate')
plt.ylabel('True Positive Rate')
plt.title('ROC curve')
plt.legend(loc="lower right")
plt.show()
def draw_PR(models):
# models: a dictionary model_name:prob
plt.figure()
for i, model_name in enumerate(models):
prob = models[model_name]
precision, recall, _ = precision_recall_curve(ytest, prob)
auc_precision_recall = sklearn.metrics.auc(recall, precision)
lw = 2
plt.plot(recall, precision,
lw=lw, label=model_name+'(area = %0.3f)' % auc_precision_recall)
plt.xlim([0.0, 1.0])
plt.ylim([0.0, 1.05])
plt.xlabel('Recall')
plt.ylabel('Precision')
plt.title('Precision/Recall Curve')
plt.legend(loc="lower right")
plt.show()